Ascending/Descending Pathways (B)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Lateral Pathways
Control voluntary movement + stimulate flexor muscles
(class of pathways)
Medial Pathways
Control posture and balance + stimulate axial extensor muscles
(class of pathways)
lateral corticospinal tract, rubrospinal tract
Lateral pathways - (2)
ventral corticospinal tract, vestibulospinal tract, reticulospinal tract, tectospinal tract
Medial pathways - (4)
Corticospinal pathways
Function of pathway is primarily synapse onto inhibitory interneurons
Corticospinal Tracts
Run from motor cortex
Cross at Medullary Pyramids
Up lateral or ventral divisions of pathway
Anterior horn of spinal cord
Descending pathway
Motor, brainstem, never, bi, uni, contra
Corticobulbar pathway DESCENDING PATHWAY
Location - Originates in __ cortex; descends to the __
Corticobulbar tract __ (usually/never) enters spinal cord
Most synapses are __lateral
Some synapses are __lateral on the __lateral side from origin (i.e. lower division of facial nerve)
Corticobulbar pathway
Synapses on cranial motor neurons and interneurons that control muscles of head and neck
Uni, corticobulbar, both
In patients who experience a stroke, why is lower portion of the face more susceptible to paralysis than upper portion of the face?
Lower portion of face is innervated __laterally by the __ pathway
Unlike most head/neck muscles controlled by __ hemisphere(s) of motor cortex
Extrapyramidal, red, inter, cerebral, cerebellum
Rubrospinal pathway
Is an __ pathway
Location - Originates in __ nucleus of midbrain
Synapses on __neurons that communicate with alpha motor neurons
Modulated by input from - __ cortex and __
Rubrospinal pathway
Extrapyramidal pathway that is major system of voluntary/fine motor control AND excites flexors
Extrapyramidal, vestibular, cerebellum, NOT
Vestibulospinal pathway
Is an __ pathway
Receives input from __ organ and __
__ (does/not) receive input from cerebral cortex
Vestibulospinal pathway
Extrapyramidal pathway that regulates balance and posture AND excites extensors in trunk and proximal limbs
Extrapyramidal, posture, tone, intrafusal
Reticulospinal pathway
Is an __ pathway
Composed of 2 antagonistic pathways regulating fine control of __ and muscle __
Influence muscle spindles via communication with __ fibers
Reticulospinal pathway
Extrapyramidal pathway that ONLY modulates activity of extensor muscles
Tectospinal pathway
Extrapyramidal pathway that modulates head and eye movement in response to auditory and visual cues
Corticospinal, vestibulospinal, rubrospinal
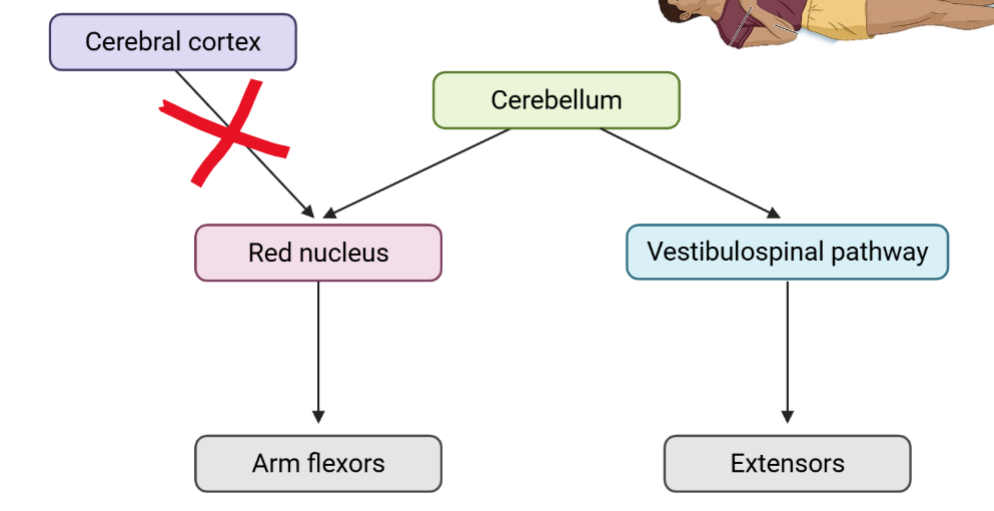
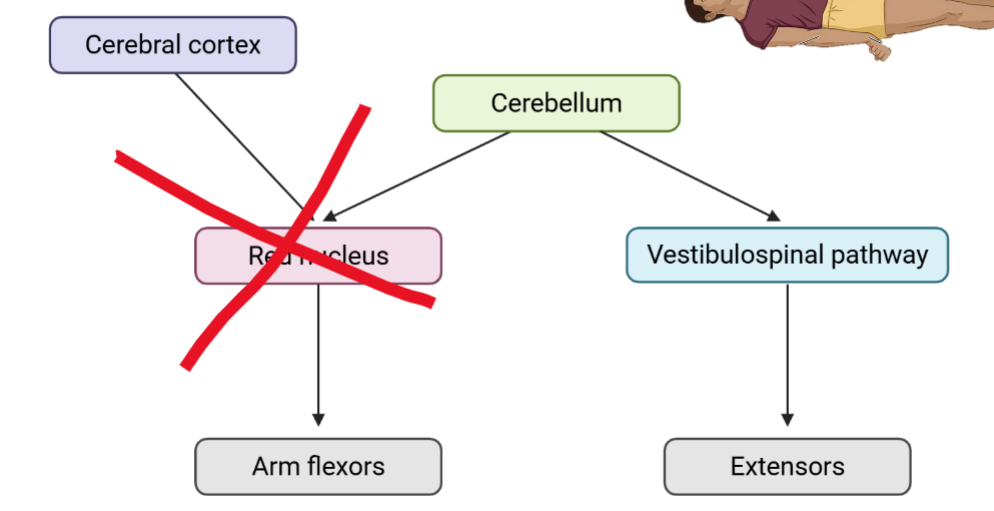
Communication disruption between cerebral cortex and brainstem associated with “posturing” leads to:
*Losing function of __ pathways
*__ pathway remains intact
__ pathway may or may not be disrupted
Decorticate, decerebrate
__ Posturing = Upper limb flexion, arms folded in
__ Posturing = Upper limb extension, arms parallel
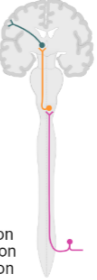
Dorsal column pathway
Pathway
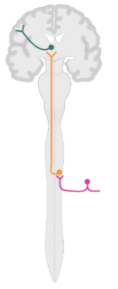
Spinothalamic pathway
Pathway
Fine touch, vibration, proprioception, ascending
Dorsal Column Pathway Senses + ascending or descending
Ipsilateral, contralateral (ipsi, contra)
Dorsal column pathway injury
Sx from spinal cord lesion below medulla will be loss of __ sensation
Sx from spinal cord lesion at/above medulla will be loss of __ sensation
Ipsilateral, white, medulla, thalamus, somatosensory
Dorsal Column Pathway - Crosses over!
First Order neuron
Sensory neuron with cell body in dorsal root
Axon ascends via __ (ipsilateral/contralateral) dorsal column __ (grey/white) matter to medulla
Second Order neuron
Originates and immediately decussates in __
Ascends via medial lemniscus tract to __
Third Order neuron
Originates in thalamus and ascends to __ cortex
Crude touch, pain, temperature, ascending
Spinothalamic Pathway Senses + ascending or descending
2, tract of lissauer, ipsilateral, grey, immediately, thalamus, somatosensory
Spinothalamic Pathway - Crosses over!
First Order neuron
Sensory neuron with cell body in dorsal root
Ascends about _ spinal segments in the __ __ __
Terminates in __ (ipsilateral/contralateral) dorsal horn __ (grey/white) matter
Second Order neuron
Originates in dorsal horn gray matter and __ (immediately/later) decussates
Ascends via anterolateral spinothalamic tract to __
Third Order neuron
Originates in thalamus and ascends to __ cortex
above, contra, below
Spinothalamic pathway
Site of decussation is 2 spinal segments __ (above/below) level where sensory afferent neurons enter spinal cord
Damage to second order neuron results in __lateral sensation loss beginning about 2 spinal segments __ site of lesion
Brown Sequard Syndrome
Unilateral spinal cord hemisection
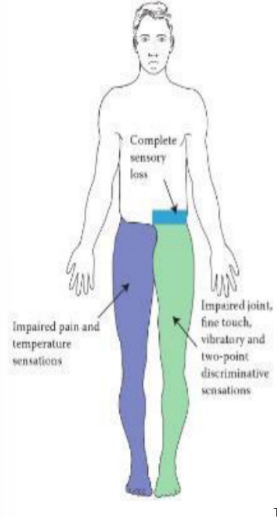
Spinothalamic, 2, below, spinothalamic, at, ipsi, corticospinal, at, ipsi, dorsal column, at
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
Contralateral loss of pain and temp sensation from __ tract, _ levels __ site of injury and all dermatomes distally
Ipsilateral loss of pain and temp sensation from __ tract, __ level of injury and 2 distal dermatomes
__lateral loss of motor control from __ tract, __ level of injury and all distal dermatomes
__lateral loss of vibration and fine touch from __ __ tract, __ level of injury and all distal dermatomes
(contra/ipsi AND — pathway AND at/below)
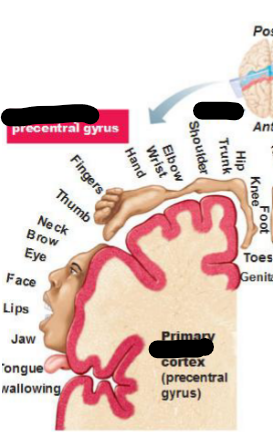
Precentral Gyrus
Controls motor output in motor cortex
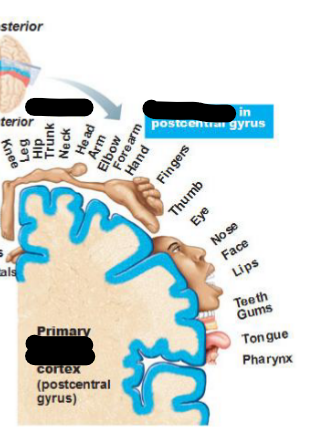
Postcentral Gyrus
Receives sensory input in somatosensory cortex
Disc herniation
Spinal discs push outward and infringe on spinal nerve root(s) // Always an ipsilateral effect!
Motor homunculus
Sensory homunculus
Deceberate, rubrospinal disrupted, vestibulospinal intact
Posturing and pathway effects

Decerebrate posturing
Decorticate posturing