patho exam 1
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
Hypermagnesemia causes
-Renal insufficiency or failure
-Excessive intake of magnesium-containing antacids
-Adrenal insufficiency
pathophysiology
the study of the disorder or breakdown of the human body's function
disease occurs when
there is a disruption of homeostasis
homeostasis
relatively constant internal physical and chemical conditions that organisms maintain; self regulating
etiology
study of causes or reasons for phenomena
idiopathic
unknown cause
iatrogenic
produced by a physician (the unexpected results from a treatment prescribed by a physician)
risk factor
A factor that when present increases the likelihood of disease
pathogenesis
development of disease
signs
observed manifestations
symptoms
subjective feeling of abnormality of the body
syndrome
etiology of signs and symptoms has not yet been determined (cold)
fever is objective
101.5
latent period
Time between exposure to first sign or symptoms
(incubation period)
CAN ALSO BE REFFERED TO WHEN SYMPTOMS BECOME MILD OR DISAPPEAR
proximal period
time between first symptom and full blown disease
acute period
the disease is at its height
subclinical stage
patient functions normally
acute clinical course
short-lived; may have severe manifestation
chronic clinical course
may last months to years, sometimes following an acute course
exacerbation
sudden increase in the severity of a disease or its symptoms
remission
decrease in severity; may indicate cure
convalescence
stage of recovery after a disease, injury, or surgical operation
sequela
subsequent pathologic condition resulting from an acute illness
(pnumonia is sequela of flu)
statistical normality
estimate of diseases in a normal population, based on a bell-shaped curve
reliability
test's ability to give same results in repeated measurements
validity
degree to which measurement reflects true value of what it intends to measure
predictive value
extent to which a test can differentiate between presence or absence of a person's condition
sensitivity
probability that a test will be positive when applied to a person with a particular condition
specificity
probability that a test will be negative when applied to a person without a particular condition
individual factors
culture, age, gender
epidemiology
study of patterns of disease involving populations and examining the occurrence, incidents, prevalence, transmission, and distribution of disease in large groups of population
endemic disease
localized to specific area
primary prevention
altering susceptibility or reducing exposure for susceptible persons
secondary prevention
early detection, screening, and management of disease
tertiary prevention
rehab, supportive care, reducing disability and restoring effective functioning
cell membrane
semipermeable
contains receptors
involved in electric conduction
regulates cell growth and proliferation
lipid bilayer
cell membrane proteins
major histocompatibility complex proteins (MHC)
cell membrane receptors
open and close ion channels, activate G protein linked signal, activate enzyme linked cell function
passive cell transport
Cell doesn't use energy to transport materials
osmosis
diffusion of water
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
pinocytosis
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
Cell drinking
phagocytosis
Cell eating
exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
most diseases start with
cell injury, which is reversible, and in normal states is balanced with cell renewal
physiologic cell death
Death of a cell at the end of its normal lifespan
apoptosis (immune, protection)
programmed cell death
normal process of cell replacement and development; balance between death and regeneration
cell injury physical agents
mechanical, temperature, electrical
cell injury radiation agents
ionizing, ultraviolet, non-ionizing
cell injury chemical agents
poison, drugs
cell injury biological agents
nutritional imbalances
ischemia
not enough oxygen in blood
necrosis
tissue death
mechanisms of injury
ischemia, necrosis, free radicals
free radicals
chemical particles with an odd number of electrons
failure to prevent/repair contributes to cancer, aging, and degenerative diseases
antioxidants
can prevent and repair damage from free radicals
necrotic cell death (coagulate)
gelatinous protein; firm and opaque
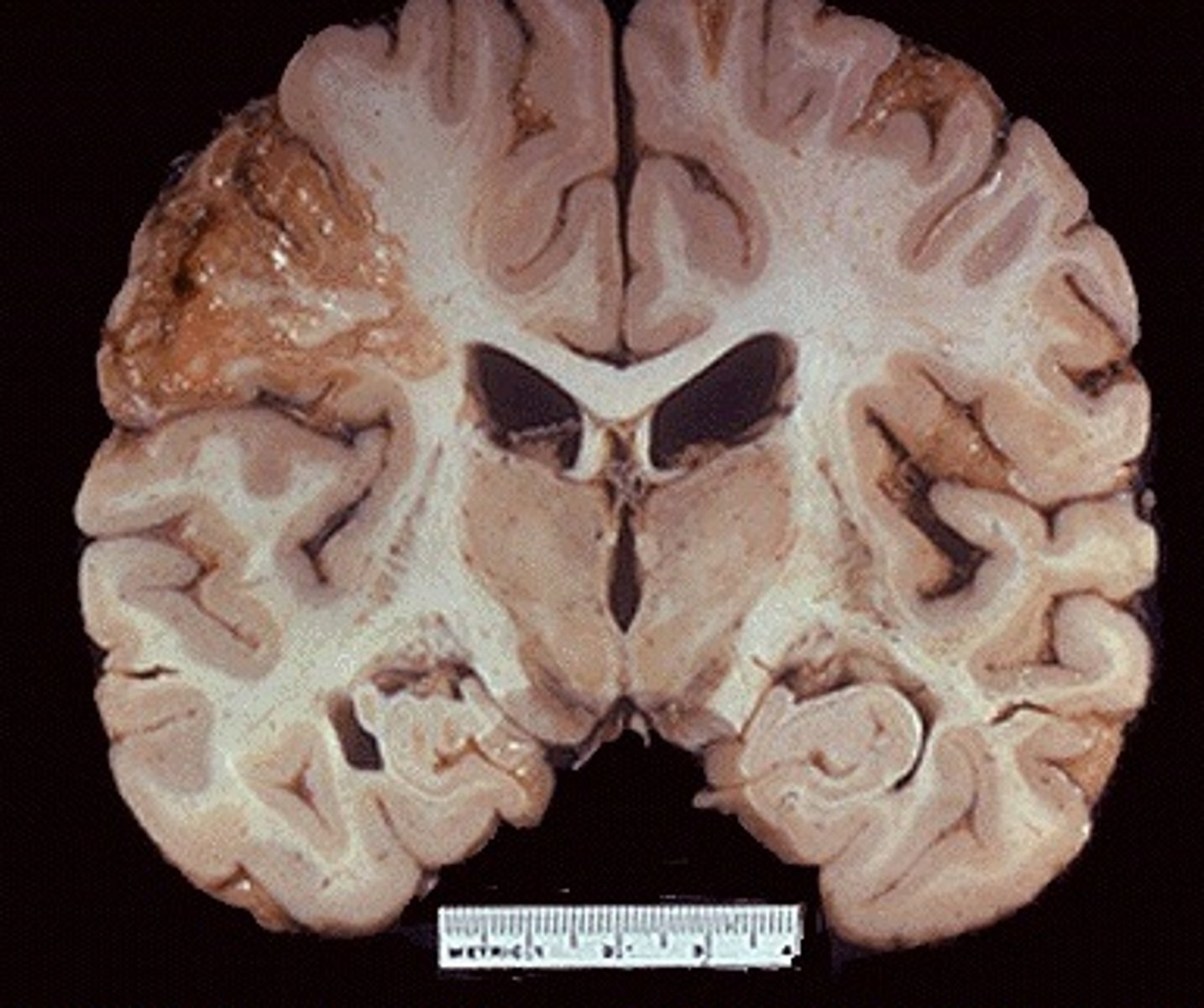
necrotic cell death (liquefactive)
-brain & neurons
-walled-off liquid goo
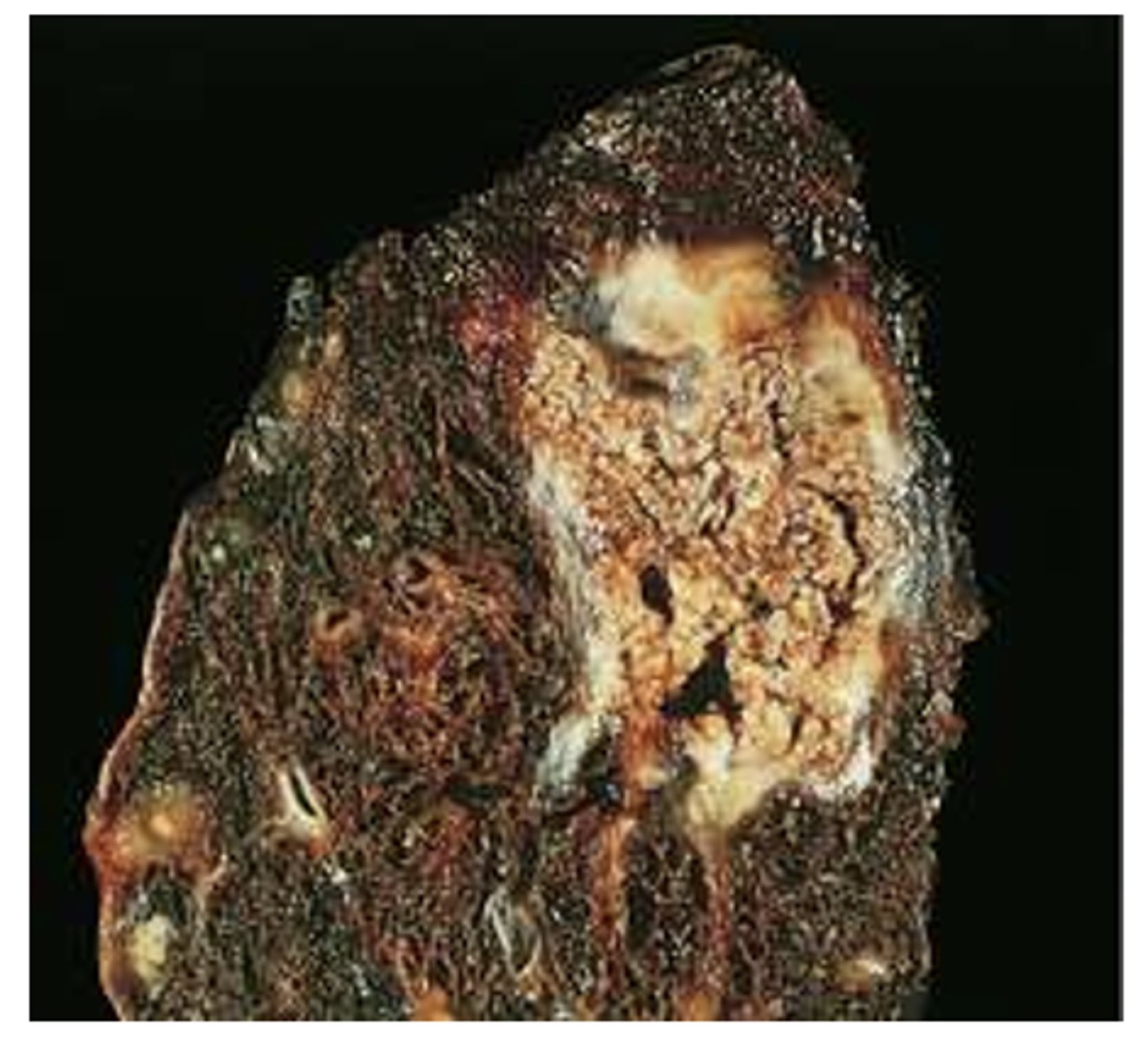
necrotic cell death (caseous)
mycobacterium
cased off, encased globules
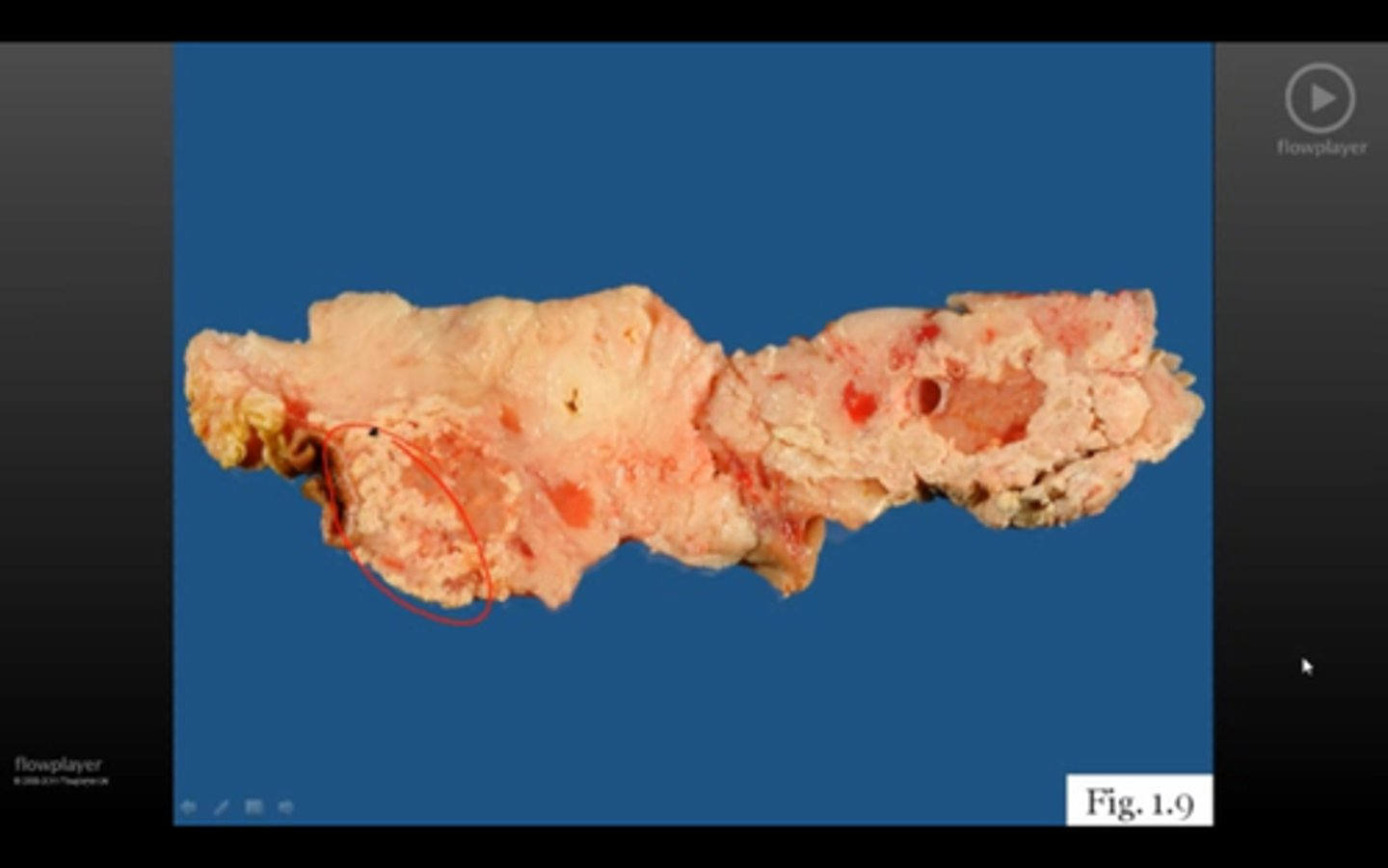
necrotic cell death (fatty)
breast, pancreas, glandular tissue
opaque, chalky soap
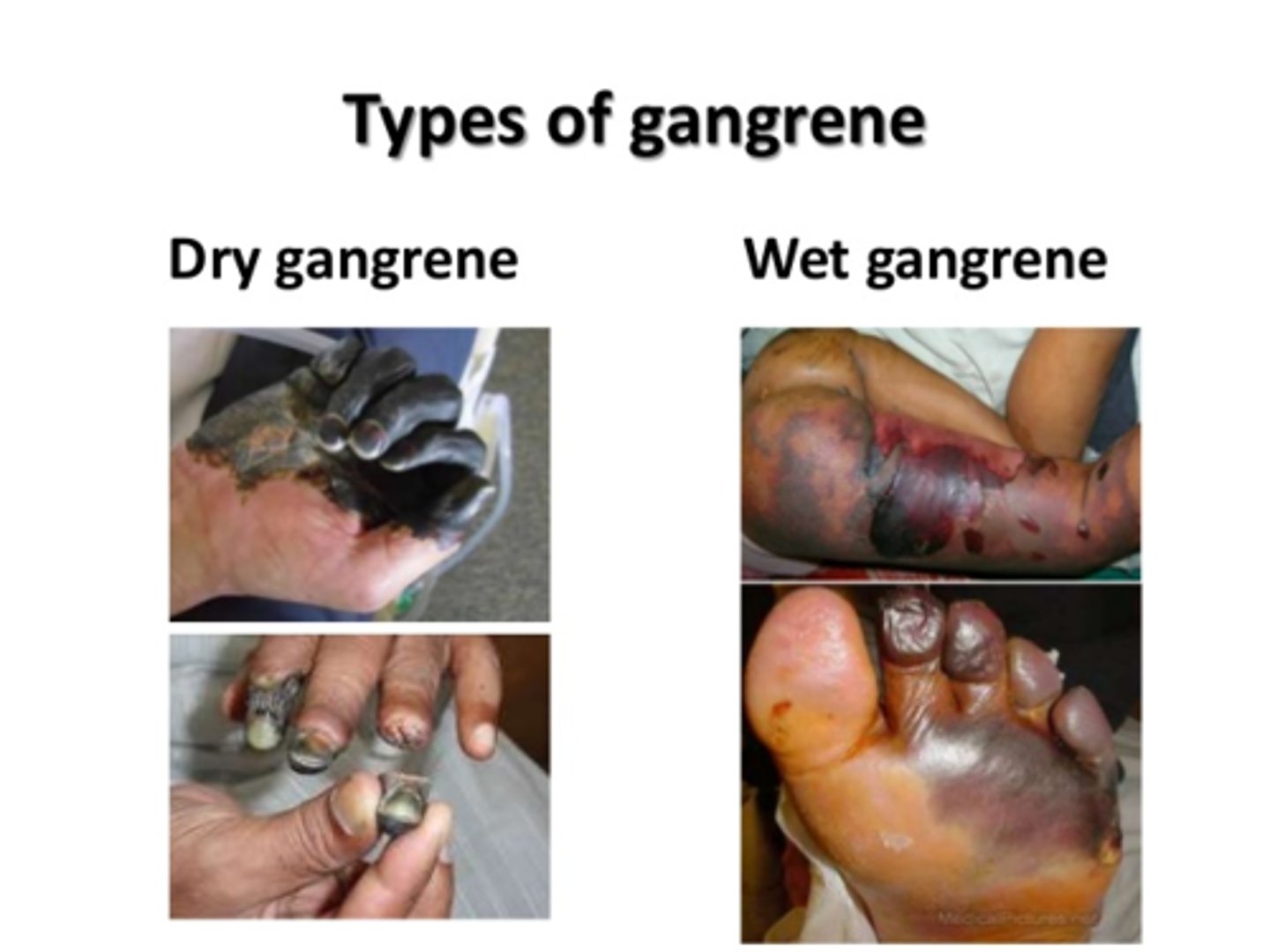
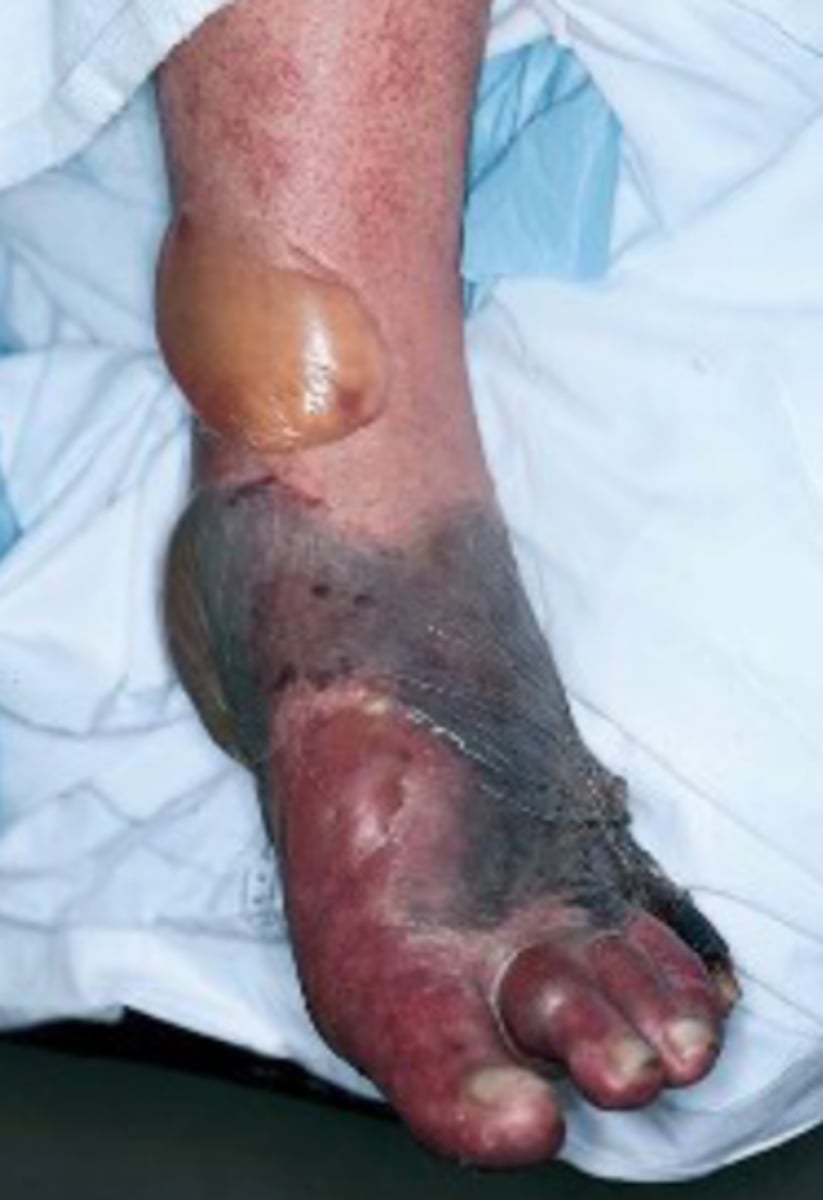
gangrene
caused by hypoxia injury
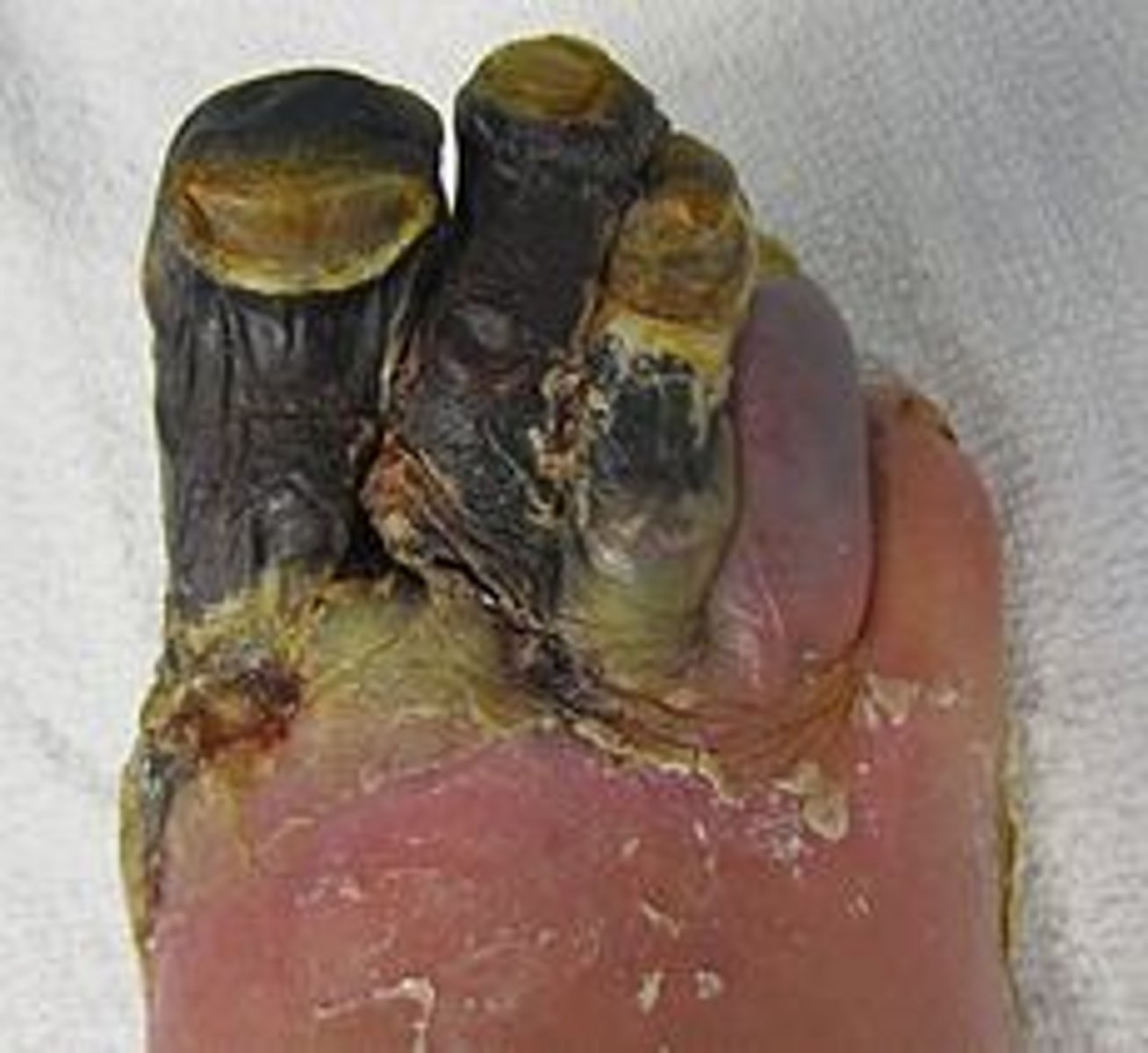
dry gangrene
Coagulative
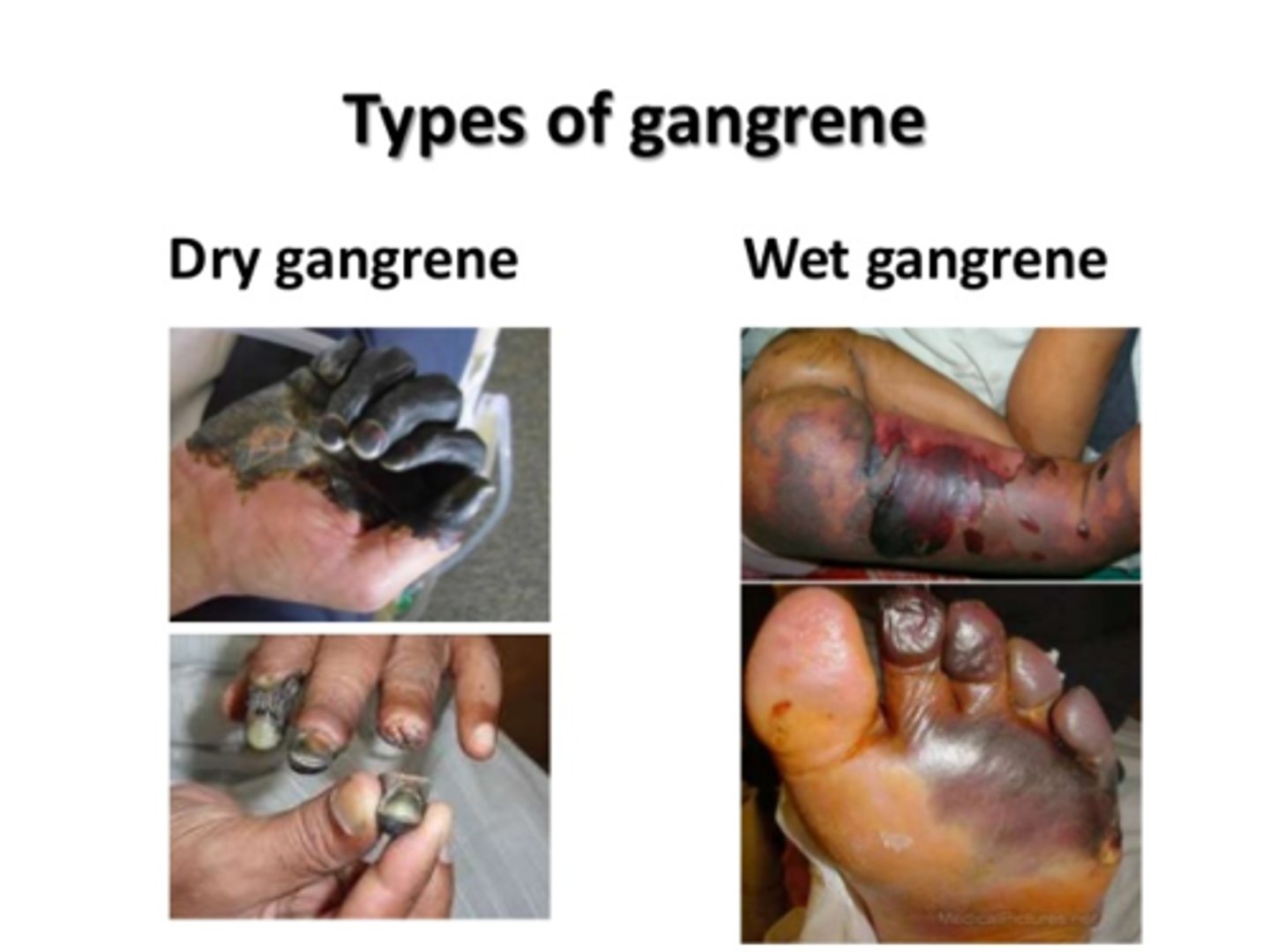
wet gangrene
liquefactive
gas gangrene
clostridium (tissues not just cells; release gas into tissues)
somatic death
death of the entire organism
absence of respirations and heartbeat
rigor mortis within 6 hours
tissue deterioration and postmortem autolysis within 24-48 hours
postmortem autolysis
Breaks down muscle and other tissues
allostasis
-overall process of adaptive changes necessary to maintain survival and well being
-helps body achieve homeostasis
-may involve altering multiple physiological variables to match the resources of the body to environmental demands
stress
anything that disrupts homeostasis
physical state of tension
can be pos or neg
hans 3 stages
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)- alarm, resistance, exhaustion
hans seyle
observed bodily changes produced by stress
influenced by: natural reserve, time, genetics, age, gender, health issues, nutrition, sleep, hardiness, physiological factors
alarm stage
fight or flight
hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis (HPA)
resistance stage
-second stage of the stress response; body attempts to return to homeostasis
-allostatic state
exhaustion state
-point where body is no longer able to return to homeostasis
-allostatic overload
Catecholamines
(norepinephrine and epinephrine) play a role in Allostasis, sympathetico adrenal system response mediates fight or flight
immune cytokins
Secreted by macrophages during stress --response. Enhance immune system response.
Prolonged stress can suppress immune functioning
adrenocortical steroids
cortisol and aldosterone
Critical to maintenance of homeostasis
May synergize or antagonize effects of catecholamines
sex hormones
dehydroepiadosterone, estrogen, and testosterone
effect stress response influencing allostasis
may help explain gender responses during stress
endorphins and enkephalins
natural painkillers
endogenous opioids
raise pain threshold
produce sedation and euphoria
growth hormone and oxytocin
can increase during stress to enhance immune function
prolactin
similar to structure of growth hormone
role in immune response
oxytocin
produced during childbirth lactation
associated with bonding
thought to mod stress response (calming)
coping
ability to deal with stressor
physical activity, sleep, diet, relaxation, distraction and biofeedback all play roles
maladaptive coping
Smoking, substance abuse, and overeating
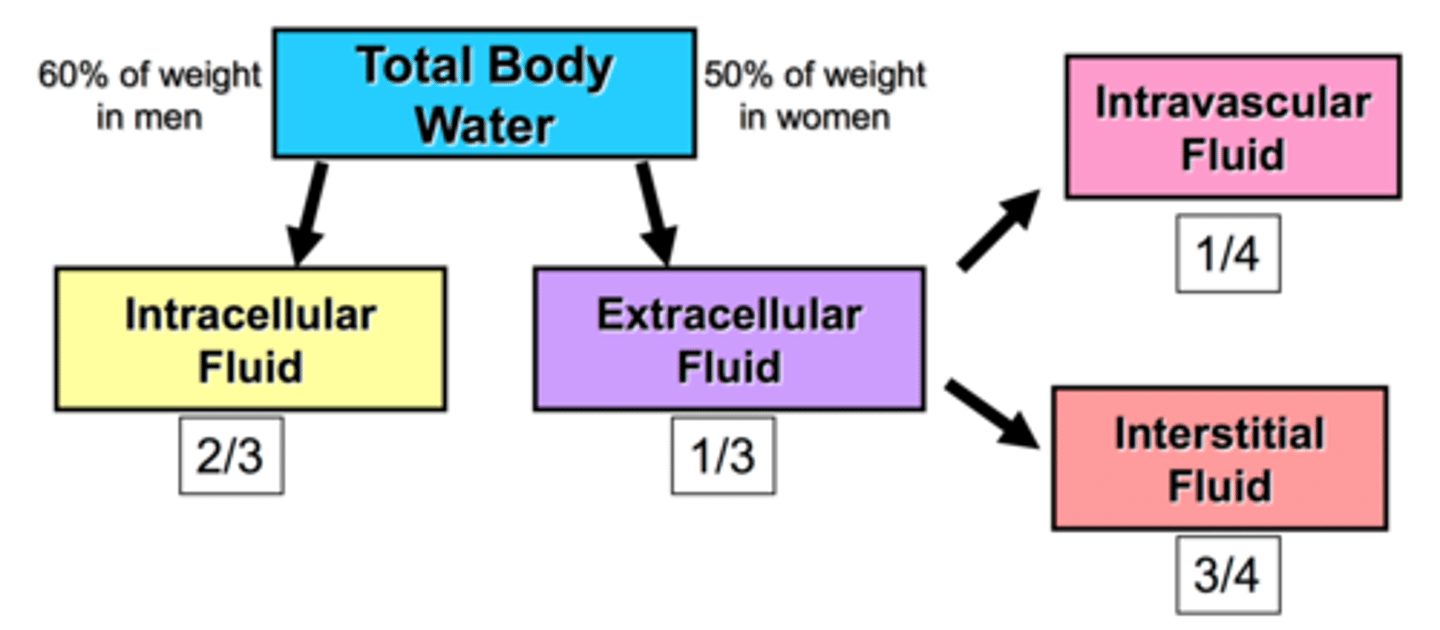
body fluid
water within the body and the particles dissolved in it (intra and extra cellular)
total body water
maintained via fluid intake (oral and IV) fluid absorption, fluid distrtibution and fluid excretion
intravenous solutions
isotonic (.9% saline and lactated ringers), hypotonic (.45% saline), hypertonic (5% sugar, in .9% saline)
sources of fluid loss
urine, feces, emesis, wound drainage, blood loss, hemorrhage
insensible loss
sweat and water vapor in breath
extracellular fluid volume
Volume deficit or excess in the extracellular fluid compartment
body fluid concentration
The thirst center is stimulated when this is increased (hypo/hypernatremia)
interstitial fluid volume imbalance
edema
electrolyte abnormalities
imbalance in sodium, chloride and water balance
isotonic fluid loss; bleeding
isotonic fluid excess; IV fluid
isotonic alterations
total body water change with proportional electrolyte and water change; no change in concentration
normal: 135-145 mEq/L
hypernatremia causes
serum sodium is greater than or = 145 mEq/L
related to sodium gain or water loss
water movement from ICF to ECF (intracellular dehydration)
hypernatremia manifestations
Clinical: secretions of ADH from pituitary gland
weight gain, bounding pulse, increased blood pressure)
CNS: muscle twitching and hyperflexia, hyperactive reflexes, confusion, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage and coma)
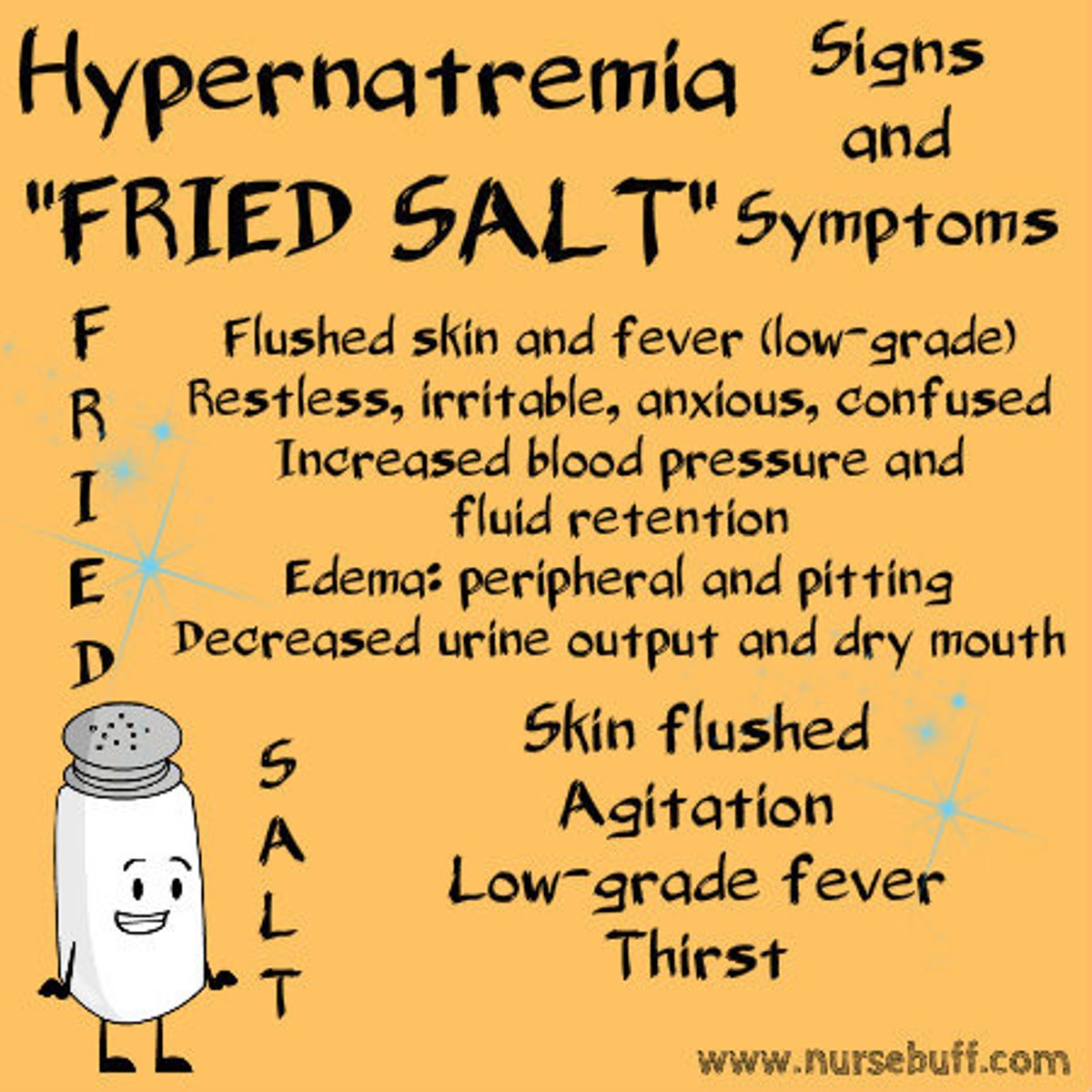
hypernatremia fried salt
FRIED
F - Fever (low), flushed skin
R - Restless (irritable)
I - Increased fluid retention & increased BP
E - Edema (peripheral and pitting)
D - Decreased urinary output, dry mouth
SALT
S - Skin flushed
A - Agitation
L - Low-grade fever
T - Thirst
CAUSE: MODEL
Medications, meals
Osmotic diuretics
Diabetes insipidus
Excessive water loss
Low water intake