THEME 3
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
formula for total revenue
price x quantity sold
2
New cards
what is marginal revenue
extra revenue a firm earns from the sale of one extra unit
3
New cards
what is average revenue
the average receipt per unit, calculated by total revenue divided by quantity sold
4
New cards
what is the AR curve
the firms demand curve as it is the price of the good
5
New cards
when is the AR curve horizontal
in markets where firms are price takers - perfectly elastic demand for the goods
6
New cards
when is the AR curve downward sloping
when firms are price setters
7
New cards
total cost
how much it costs to produce a given level of output
FC + VC = TC
FC + VC = TC
8
New cards
fixed costs
indirect costs that do not vary with output and firms always have to pay.
e.g rent
e.g rent
9
New cards
variable costs
direct costs that change with output e.g costs of raw materials increases as output increases
10
New cards
average total cost formula
TC/ quantity produced
ATC= AVC+AFC
ATC= AVC+AFC
11
New cards
average fixed costs formula
FC/quantity
12
New cards
average variable costs formula
VC/quantity
13
New cards
marginal cost
how much it costs to produce one extra unit of output
change in TC/ change in quantity
change in TC/ change in quantity
14
New cards
internal economies of scale
occur when a firm becomes larger
15
New cards
examples of internal economies of scale
Really Fun Mums Try Making Pies
Really Fun Mums Try Making Pies
risk bearing
financial
managerial
technoligcal/ production
marketing
purchasing
financial
managerial
technoligcal/ production
marketing
purchasing
16
New cards
marginal cost
cost of making the next one
17
New cards
marginal revenue
revenue from selling the next one
18
New cards
what does each example of internal EOS mean
risk bearing- 7/10 work
financial - negotiate low interest loans
marketing- promote the brand name
technological/ production - best machinery
managerial- best staff
purchasing - discount (buying in bulk)
financial - negotiate low interest loans
marketing- promote the brand name
technological/ production - best machinery
managerial- best staff
purchasing - discount (buying in bulk)
19
New cards
external economies of scale
occur within an industry when it gets larger
20
New cards
examples of external EOS
* better universities
* road infrastructure
* communication networks
* highly skilled population
\
* road infrastructure
* communication networks
* highly skilled population
\
21
New cards
diseconomies of scale
when average costs rise
22
New cards
examples of diseconomies of scale
* control - can’t monitor how productive workforce is
* coordination and communication reducing
* overused machinery
* no value workers/ poor staff morale
* coordination and communication reducing
* overused machinery
* no value workers/ poor staff morale
23
New cards
profit
difference between total revenue and total cost
24
New cards
profit maximisation
occurs when marginal cost = marginal revenue
each extra unit produced gives no extra loss or revenue
each extra unit produced gives no extra loss or revenue
25
New cards
normal profit
The minimum profit required to keep factors of production in the long run
when TR-TC
when TR-TC
26
New cards
supernormal profit
the profit above normal profit
when TR > TC.
\
when TR > TC.
\
27
New cards
losses
a firm makes a loss when they fail to cover their total costs
28
New cards
market structures
identifies how a market is
29
New cards
concentration ratio
the percentage of market share taken up by the largest firms
30
New cards
sub-normal profit
profit which is less than normal
31
New cards
perfect competition
market structure where many firms offer a homogeneous product
32
New cards
###
33
New cards
features of perfect competition
* many firms
* freedom of entry and exit
* all firms produce an identical product
* all firms are price takers so demand curve is elastic
* perfect information
* freedom of entry and exit
* all firms produce an identical product
* all firms are price takers so demand curve is elastic
* perfect information
34
New cards
why do firms want to grow
* experience economies of scale
* more revenue
* larger profit
* more market share
* monopsony power
* build up assets and cash
* more revenue
* larger profit
* more market share
* monopsony power
* build up assets and cash
35
New cards
why do some firms stay small
* constraints on growth
* size of market
* access to finance
* owner regulation
* size of market
* access to finance
* owner regulation
36
New cards
what is the principal agent problem
separation of ownership and control in larger firms and this can cause issues as they have differing aims
37
New cards
what is the aim of a business owner
short run profit maximise
38
New cards
what are managers aims
maximise their own benefits
39
New cards
what are the two types of business growth
organic growth and integration
40
New cards
what is organic growth
firms grow by increasing output. e.g increased investment or longer working hours
41
New cards
what is vertical integration of firms
integration of firms in the same industry but at different stages in the production process
42
New cards
what is backwards integration
when the merger takes the firm back towards the supplier of a good
43
New cards
what is forward integration
when the firm is moving towards the eventual consumer of a good
44
New cards
what is horizontal intergration
where firms in the same industry at the same stage of production integrate.
45
New cards
what is profit maximisation
goal to make the most profit possible in the short run - can generate funds for investment and survive a slowdown
46
New cards
in order to profit maximise where do firms produce
where MC=MR
47
New cards
wha is revenue maximisation
producing the most of revenue - looks better for managers
48
New cards
what is sales maximisation
aim to maximise growth of company, gets the company well known and increases market share
49
New cards
short run
where at least one factor of production is fixed
50
New cards
long run
when all factors of production become variable
51
New cards
### **diminishing marginal productivity**
if a variable factor is increased when another factor is fixed, there will come a point when each extra unit of the variable factor will produce less extra output than the previous unit.
e.g costs fall initially as machinery is efficient but as production continues, efficiently falls as machinery is overused.
e.g costs fall initially as machinery is efficient but as production continues, efficiently falls as machinery is overused.
52
New cards
allocative efficiency
more concerned with the distribution and allocation of resources in society and achieved when resources and used to produce goods and services which consumers want.
occurs where price = marginal cost (MC)
occurs where price = marginal cost (MC)
53
New cards
productive efficiency
producing goods and services for the lowest cost so fewest resources are used to produce each product.
MC=AC
MC=AC
54
New cards
dynamic efficiency
achieved when resources are allocated efficiently over time - concerned with investment
55
New cards
what is perfect competition
when there is a high degree of competition - few industries fit this type of market structure e.g agriculture
56
New cards
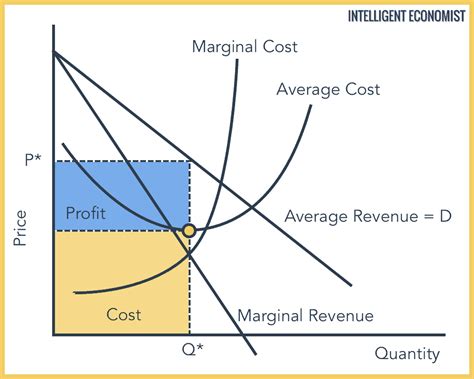
long term perfect competition diagram
because there is freedom to entry this allows for more firms to enter, this causes supply to increase and therefore it will return to equilibrium over time
57
New cards
what shape is the demand curve for perfect competition and why
horizontal as they are price takers, this is also D=MR=AR
58
New cards
what shape is the demand curve for monopoly and why
There are 2 curves which are diagonally going downwards. One is the demand curve and the other is MR as they are price setters so they can reduce the MR for every extra unit.
59
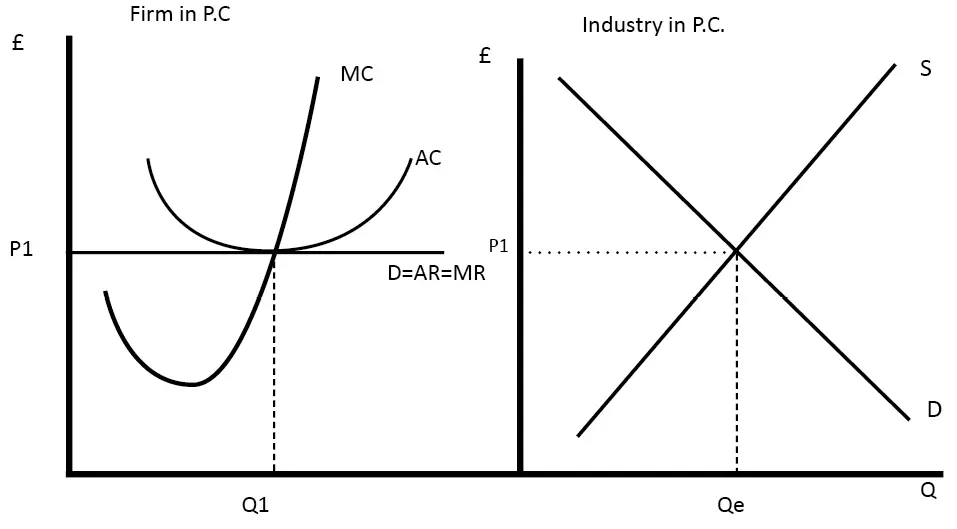
New cards
short run profit minimisation for perfect competition (losses) diagram
operates where MC=MR
60
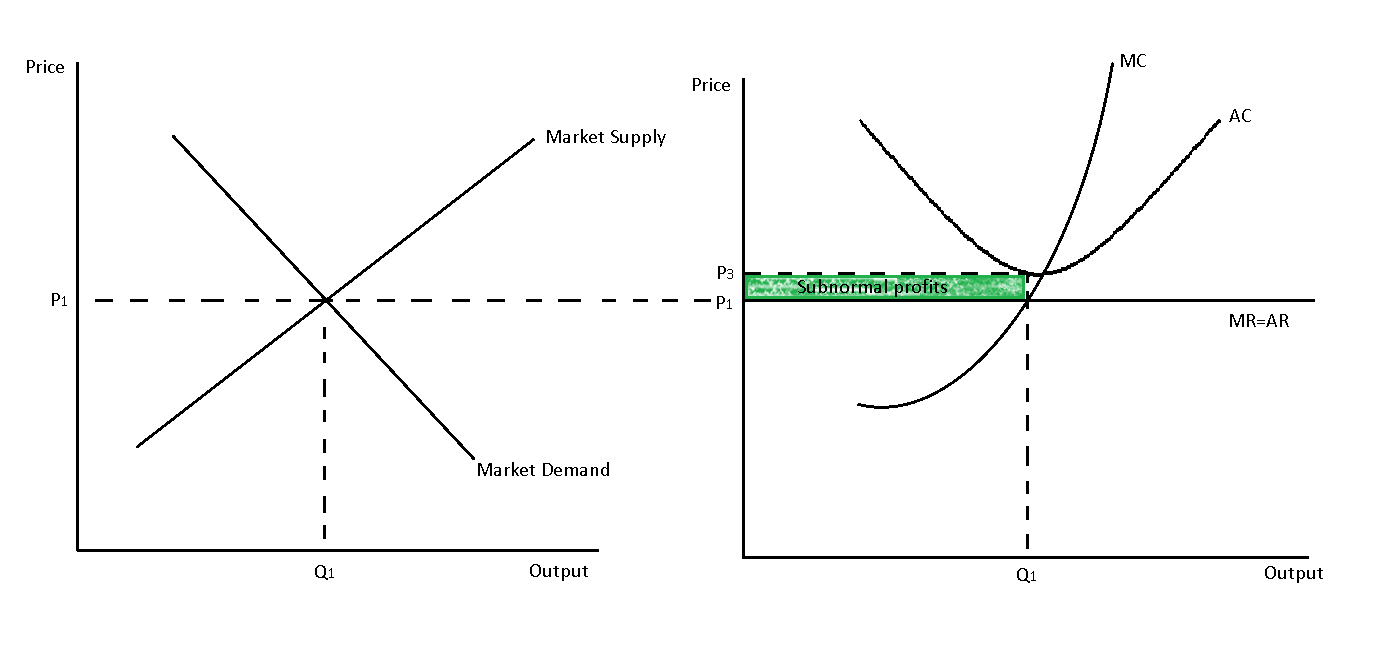
New cards
short run profit maximisation for perfect competition (supernormal profits)
operates where MC=MR
61
New cards
what is the outcome of perfect competition
* Firms are price-takers
* Firms will make normal profits which means consumers are getting the lowest place leading to greater equality in society (where AR=AC). If firms made supernormal profits – more firms would enter causing prices to fall
* Firms will make normal profits which means consumers are getting the lowest place leading to greater equality in society (where AR=AC). If firms made supernormal profits – more firms would enter causing prices to fall
62
New cards
X efficiency
Competition between firms will act as a spur to increase efficiency. In perfect competition, this is likely to occur.
63
New cards
what are the problems of perfect competition
* no dynamic efficiency as no supernormal profit is made in the LT so R and D is unlikely.
* no economies of scale
* with perfect knowledge there is no incentive to develop new tech as it’ll be shared with other firms
* products can get boring and not varied
* no economies of scale
* with perfect knowledge there is no incentive to develop new tech as it’ll be shared with other firms
* products can get boring and not varied
64
New cards
monopolistic competition
market structure which combines elements of monopoly and competitive markets
65
New cards
pure monopoly
where only one produces exists in the industry - rarely exists
66
New cards
characteristics of a pure monopoly
* lots of buyers, one seller
* total control over prices
* barriers to entry
* higher prices
* price setters
* poor quality/lower output
* homogenous products
* total control over prices
* barriers to entry
* higher prices
* price setters
* poor quality/lower output
* homogenous products
67
New cards
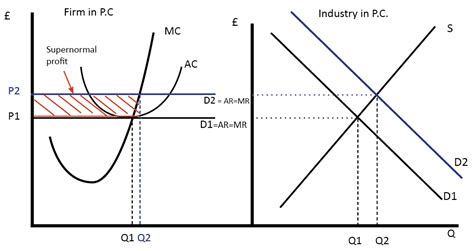
monopoly short and long run profit maximisation
as there is barriers to entry, it is the same for both short and long term.