I HAVE A SEXUAL REPRODUCTION TEST MON AND I DIDN'T STUDY
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Points I took straight from my reproduction handout for bio class
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
what is pregnancy
The development of a zygote into an embryo to a fetus in preparation of child birth
Define the stage of infancy
A ‘Baby” is the earliest part of childhood and is from child birth to the age of three.
A Humans Childhood will be between which ages?
4 to 8
At what ages will puberty start?
At ages nine to 13
At which growing stage will puberty start?
Adolescence is the stage where physical and hormonal changes occur, leading to sexual maturity, typically starting between ages nine to thirteen.
At what ages will older adolescence take place ?
14 to 18
Define the stage of adulthood
This stage comes after adolescence starting at the age of nineteen and going on until the person dies
3 names are given to the last stage of human reproduction, they are
Old age, elderly, Seniors
At what age does the last stage of human reproduction take place
51
The general name given to sex cells of both genders
gametes
The name of the female sex cell is called an…
Ovum
What is Fertilization?
The process where a male sperm cell and a female ovum combine to form a zygote, initiating the development of a new organism.
Explain how a zygote forms into a baby.
After fertilization, the zygote undergoes several rounds of cell division, to develop into an embryo and eventually a fetus, growing into a baby over a nine-month gestation period.
Explain how Sex cells contribute to the embryo having characteristics from both
Each Gametes will contain half the amount of chromosomes found in a cell body, in both of their nucleus so that when the two sex cells fuse during fertilization the number of chromosomes to be restored.
An Embryo will get nutrients from the mother through a structure called the…
Placenta
This is the process where the Penis enters the female during intercorse
internal fertilization
Name two structures apart of the female reproductive system that gives nutrients to a ‘baby’
Internally: The placenta Externally: Mammary glands
The testes glands produce which hormone into the body ?
testosterone
List four secondary sexual characteristics a male human during adolescence will undergo due to hormonal changes.
Facial hair
Pubic hair
A deep voice
muscles
Which Hormone is produced by the ovaries when I see a tatted black nerd ?
Oestrogen
List 3 secondary sexual characteristics that ruined my life at the ages 9-thirteen
Broad hips
development of breasts
pubic hair
This Hormone A will have the following effects.
Thickening of the uterus lining
Menstruation
ovulation
Thickening of the uterus lining
Menstruation
ovulation Hormone Oestrogen
Explain the function of progesterone
This is secreted to maintain the thickness of the uterus lining after ovulation
This hormone stimulates the growth of mammary glands in the breasts
Identify the difference between Progesterone and Oestrogen
Both Hormones serve similar but different functions.
Oestrogen serves to develop the thickening of the uterus lining while progesterone helps to maintain that thickened uterus after OVULATION.
Progesterone helps stimulate the development of mammary glands within the breasts while Oestrogen controls menstruation.
Which Hormone in the female body is responsible for developing secondary sexual characteristics?
Oestrogen
During the ages of A to B both girls on average will become SEXUALLY mature.
11 to 15
In Males Puberty begins between the ages
12 and 14
This secondary sexual characteristic due to testosterone results in the voice deepening from the
Voice box becoming enlarged
The name given to the sweat glands that become more active during puberty in both males and females.
Sebaceous glands
List three changes that result from puberty in males that do not fall under the main secondary sexual characteristics
Developing fat above the Abdomen
The development and enlargement of the male testes
They undergo “mood swings” and emotional changes
In females on average puberty begins at the ages
11 to 13
In the male reproductive system sperm is produced by this organ
The testes
The Male organ responsible for producing sperm is contained in a sac called a…
Scrotum
How much sperm is produced by a male till death daily ?
Over 100 million
Where is the male sex cell stored after being produced by the the A male organ
The Epididymis
What is the function of the Urethra In the male reproductive system?
To expel urine and sperm from the Epididymis
label the male reproduction system
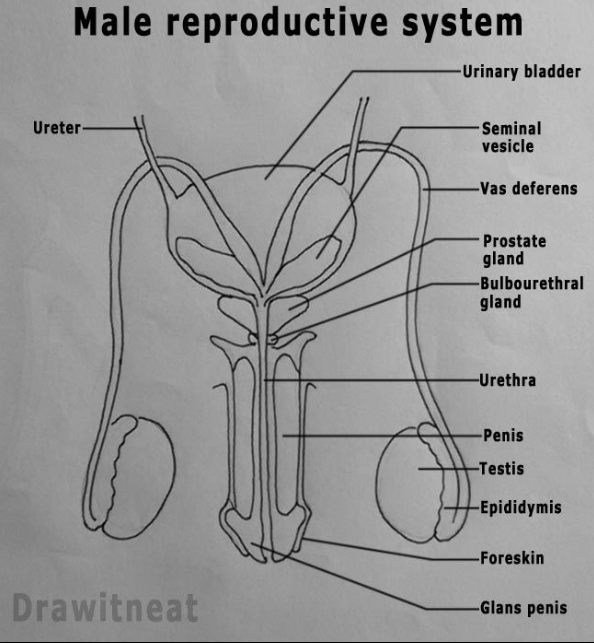
This temperature is optimal for sperm production
35c degrees C
match the function with the structure part one
Structure: Testes
Function: Produces the male sex cell (Gametes) called sperm for it to be stored by the epididymis
Match the function with the structure, Part two
Structure: Epididymis
Function: Keeps Sperm cells protected inside the testes
Match the function with the structure part 3
Structure: Scrotum
Function one: Suspends the sperm cells outside of the body at a temperature they are able to survive in.
Function Two: contains and protects the testes
Match the function with the structure Part four
Structure: Vas deferens /sperm duct
Function: Transports sperm cells from the epididymis to the urethra
Match the function with the structure part five
Structure: Cowpers gland
Function: Creates seminal fluid rich in nutrients and enzymes that activate the sperm
Match the function with the structure part six
structure: Prostate gland
Function: This creates seminal fluid rich in nutrients and enzymes which activate the sperm cells
Match the function with the structure part seven
structure: Seminal Vesicle
Function:This creates seminal fluid rich in nutrients and enzymes which activate the sperm cells
Match the function with the structure part eight
Structure: Urethra
Function: Transports both urine and sperm out of the body
Match the function with the structure part nine
Structure: Vagina
Function one: Expels blood from the body during menstruation
Function two: Accepts sperm during copulation
Function three: Serves as a pathway for child birth
Match the function with the structure part Ten
Structure: Ovaries
Function: produce ova/eggs
Match the function with the structure part 11
Structure: Uterus
Function: protects the fertilized egg and supplies egg with nutrients
Match the function with the structure part twelve
Structure: Fallopian Tube
Function: Transports egg/ova to the upper part of the uterus
Match the function with the structure part 13b
Structure: Oviduct Funnel
Function: collects ova
Inside these two structures, Cilia/ fluid will move the ova down into the uterus
The Ovi duct and Fallopian tube
Where are ovaries found?
In the abdominal Cavity
Ovaries are held by….
Ligaments
Approximately how many eggs are produced between puberty and menopause ?
lps 450
At which age does menopause begin?
At 45 yearsnold
In which structure does fertilization take place?
The Oviduct
What is the purpose of the corpus luteum?
Produces Progesterone witch helps thicken the lining of the uterus
Explain the process of implantation
The sperm and the Ova egg fuses during fertilization. turning into a zygote this divides into cells which IMPLANT into the thick lining of the uterus
The name given to my first menstrual cycle also when my life ended
A menarche