BUSINESS PROCESSES (TRANSACTION CYCLES)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
These are the means through which an accounting system process transactions of related activities such as:
sale of goods to customers;
acquisition of merchandise and payment to vendors;
production of finished products for sale;
and payment to employees for services they processes are also referred to as "transaction cycles".
Business Processes
Two Categories of Business Processes
Operating Business Processes
Administrative Business Processes
It is an agreement between two entities to exchange goods or services or any other event that can be measured in economic terms by an organization.
Transaction
These processes relate to the core business activities that help the entity in achieving its primary objectives. These processes generally produce voluminous transactions that are occurring in a recurring intervals.
Operating Business Processes
Types of Operating Business Processes
Order to Cash (Revenue and Receipt)
Purchase to Pay (Expenditure and Disbursement)
Hire to Retire (Human Resources and Payroll)
Acquire to Retire (Fixed Asset/PPE)
Plan to Inventory (Conversion)
It includes the following:
receives order from the customer
examines the order for creditworthiness
ships goods or provides services to customer
issues an invoice
collects payment
Order to Cash
It includes the following:
issues a purchase order to a supplier
receives the goods or services
records the related liability
pays the supplier
Purchase to Pay
It includes the following:
acquires services from employees
monitors and records the time of its employees
verifies hours and overtime worked
calculates gross pay, deductions, and net pay
pays the employees
Hire to Retire
It includes the following:
obtains board approval for the purchase of capital assets
issues a purchase order to a vendor
receives the fixed assets
records the related liability
accounts for depreciation, gains or losses from disposal, and impairment of fixed assets
Acquire to Retire
It includes the following:
monitors and records the production of the entity’s product for sale
Plan to Inventory
These processes relate to transactions that are specifically approved by senior management. It also includes processes that generate relevant information for use of management in performing their administrative duties. These processes are also referred to as “management and support business processes”
Administrative Business Processes
Type of Administrative Business Processes
Financial Planning and Analysis
Financial Process
Investing Process
Record to Report
It includes the following:
planning and budgeting
integrated financial planning
management and performance reporting
forecasting and modeling
It enhances the finance department’s ability to manage performance by linking corporate strategy to execution
Financial Planning and Analysis
It deals with the entity’s activities to raise the required capital funds to purchase capital assets, and to properly account the capital raised. Capital funds are typically sourced from long-term borrowings or equity
Financing Process
It delas with the entity’s activities to invest excess capital funds to other profitable activities, and to properly account for these investments
Investing Process
It captures all financial transactions arising from other business processes within an entity. This process enables the accounting cycle by recording, classifying, and summarizing financial information into useful reports. Specific activities in this process include:
Posting of transactional data to the general ledger
Preparation of the trial balance
Determination and posting of adjusting entries
Preparation and presentation of financial statements
Recording and posting of closing entries
Record to report
Entity’s Responsibility
A key role of the entity, through its management and those charged with governance, is to design and implement an appropriate set of policies, procedures, forms, and integrated controls for each of these business processes to minimize the opportunities for fraudulent activities and ensure that transactions are processed in as reliable and consistent manner as possible.
Auditor’s Objective
The auditor should consider and obtain an understanding of these business processes sufficient to plan the audit and develop an effective and efficient audit approach. Moreover, the auditor will emphasize the following objectives.
To determine the reliability of financial reporting of the different functions affected by each transaction cycle.
To determine the fairness of presentation in accordance with applicable financial reporting framework of the account balances affected by each transaction cycle.
General Objectives of Business Processes:
To promote adequate segregation of incompatible duties
To provide safeguards to entity’s resources
Basic Concepts
Departments involved, including their functions, objective, and possible control that may be implemented
Forms or documents initiated and processed
Important concepts related to forms or document initiated and processed
The department that initiated the processing approves the form
The department that initiated the processing is accountable for unused forms. Also, access to those forms shall be limited to the said department.
The notification of forms does not necessarily mean a hard copy shall be forwarded. Notification can be done thru electronic mail.
The department that initiated, received, or processed a form shall retain a copy for filling (not necessarily a hard copy)
Major Assumptions
Entities are operating under normal operating cycle conditions. With this, we will only be accounting for sales and purchases on account
Entities are using imprest and voucher systems
Order to Cash
Business Functions | |
Accounts Affected | |
Departments Involved |
Business Functions | Two major business functions are
|
Accounts Affected | Accounts affected include the following:
|
Departments Involved | Significant departments affecting the cycle are: Sale
Cash Collection
|
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Contains the details of goods ordered (quantity, prices, and payment terms) | Sales Department |
|
Sales order (order slip; customer order)
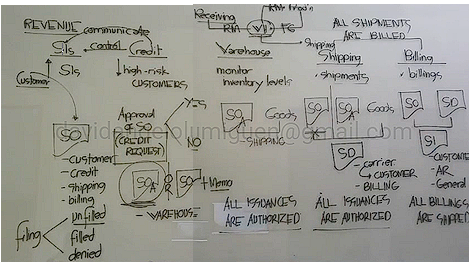
Main Objective of Credit Department
Minimize high risk customers by controlling the sales order (credit request) through approval. Control the Sales Department.
Whatever the result, they must communicate it with the Sales Department
Main Objective of Warehouse or Inventory Control
Monitor Inventory Levels
Audit Objective: All issuance of goods are authorized
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Describes the goods to be shipped and serves as a contract between the entity and carrier | Shipping Department |
|
Shipping Document (bill of lading or delivery receipt)
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Describes the goods sold, amount due, and the terms of payment | Billing Department |
|
Audit Objective:
Sales Invoice (billing statement or statement of account)
Audit Objective: All Billings Are Shipped (Mas mauunang gawing yung SO and SD kaysa sa SI)
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Intended to facilitate the accounting for cash collection | Billing department | Customers |
Remittance Advice
Departments that can be merged
Warehouse and Shipping
Billing to Accounting (except those who have control in A/R)
Receipts
Sales Returns
Uncollectible Accounts:
Basis: Past Due A/R —— A/R Department
Credit Dep’t will recommend the write-off
Write-off will be authorized by Sales Department (Selling) or Treasurer (General and Admin)
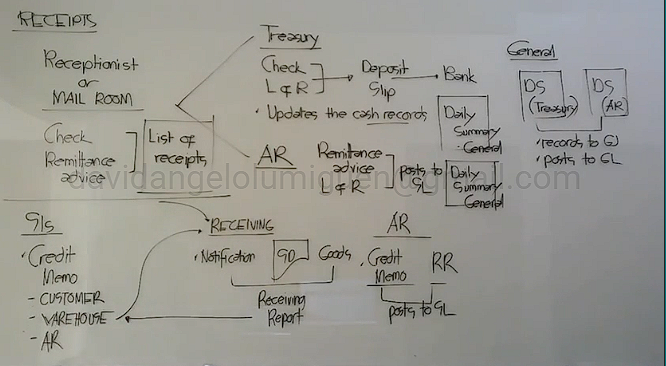
If the receptionist only see the check and not with remittance advice, what shall he do?
Fill-up Remittance Advice
If there is no credit department, whose department shall do its function?
Any department other than sales department
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Summarizes transactions recorded during the day by the different department | Receivable and Treasury (for sales and collection, respectively) Mail room (for mail received) |
|
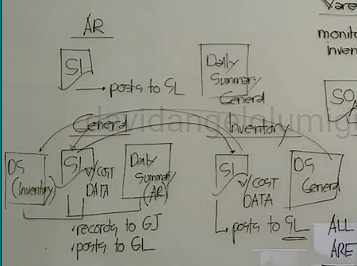
Daily Summaries
Purchase to Pay Process
Business Functions | |
Accounts Affected | |
Departments Involved |
Business Functions | Two major business functions are
|
Accounts Affected | Accounts affected include the following:
|
Departments Involved | Significant departments affecting the cycle are: Expenditure
Disbursement
|
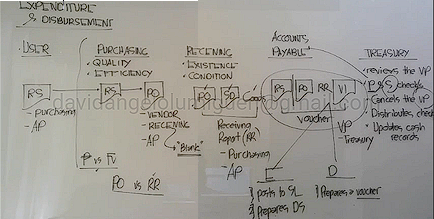
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Contains the details of the user department’s request | User Department | Purchasing |
Requisition Slip (Purchase Requisition)
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Describes the goods to be acquired (quantity and description) | Purchasing Department |
|
Purchase Order
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Describes the goods received (quantity, description, and condition) | Receiving department |
|
Receiving Report
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Describes the goods to be shipped and serves as a contract between the entity and carrier | Vendor (thru the carrier) | Receiving report |
Shipping document
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Describes the goods sold, amount due, and the terms of payment | Vendor | Account Payable |
Vendor’s Invoice
It summarizes the transactions recorded during the day by the different department (Purchase to Pay)
Accounts Payable (for purchases)
Treasury (for payment)
Hire to Retire Process
Business Functions | Two major business functions are
|
Accounts Affected | Accounts affected include, but not limited to the following:
|
Department Involved | Significant departments affecting the cycle are: Expenditure
Disbursement and Distribution
|
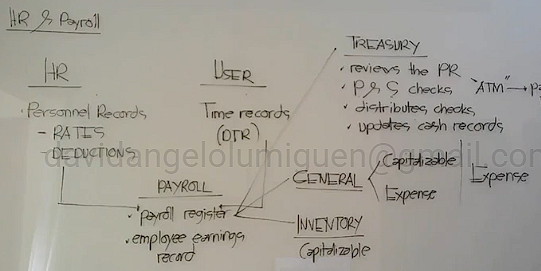
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
It contains all information related to entity’s employees from time they are hired up to their eventual termination It documents all actions taken by the employees or management on behalf of an employee Commonly, it also documents salary rates, deductions, and other payroll-related information | HR Department |
|
HR Records (Personnel Records or 201 files)
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Describes the number of hours worked by an employee during a particular day covered by a pay period | User Department | Payroll |
Daily Time Record (DTR)
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
It shows all related payroll information (gross pay, all deductions, and net pay) for each pay period | Payroll |
|
Payroll Register
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Shows payroll information that is capitalizable or can be attributed to a particular job or customer order | Payroll | Inventory Accounting |
Labor Cost Summary
Description | Initiated By | Distributed To: |
Shows the cumulative, year-to-date summary of earnings and deductions of every employee | Payroll | Accounts Payable |
Employee Earnings Record
It summarizes transactions recorded during the day by the different department (Hire to Retire Process)
Payroll (for liability recognition)
Inventory (for capitalizable labor costs)
Treasury (for payment)
Acquire to Retire
Duties and Responsibilities | Person/s Assigned to Perform the Function | Procedures Performed by the Auditor |
Custody | ||
Authorization | ||
Recording |
Duties and Responsibilities | Person/s Assigned to Perform the Function | Procedures Performed by the Auditor |
Custody | Physical controls in the user department where PPE is placed should be present to prevent loss or theft of assets | Auditor observes the physical count and inspection of PPE and reconciles the result of such inspection to the entity’s PPE subsidiary ledger |
Authorization | Purchase of high-value PPE items must be properly reviewed and approved by the appropriate level of management (e.g., BOD approval). As part of the review process, an investment analysis (e.g., analysis of quantitative and qualitative factors) and comparison with capital budget shall be made. Likewise, specific approval for PPE disposals should be obtained. The selected depreciation method, estimated useful lives, and residual values should be properly reviewed by management as well | The auditor inspects sample PPE acquisitions and disposals, and requests for supporting documents that serve as evidence of compliance with the internal process of purchasing PPE. For management estimates, the auditor considers the approval procedures of management and evaluates the methods, assumptions, and data on which the estimate is based. |
Recording | The PPE department shall regularly update the PPE subsidiary ledger for all acquisitions, disposals, and changes in the assets. Prenumbered PPE tags are also used to facilitate the recording and inspection of PPE. Furthermore, the depreciation schedule for all depreciable PPE shall be updated periodically based on the approved method. In the case of servicing or manufacturing companies, it shall also prepare an inventoriable depreciation report for the use of inventory accounting department. For disposals, the PPE department shall compute the resulting gain or loss on disposal | Auditor normally performs the following:
|
It covers the production of entity’s product for sale. It is where materials, labor, and overhead are converted into finished goods.
The primary objective of this process is the proper valuation of inventories and cost of goods sold. Such objective encompasses the proper allocation of costs to each run made by the production department. In order to attain this, the production department uses inputs from the purchase to pay process and provides resources and information to order to cash process.
Plan to Inventory Process (Production or Conversion Process)
Plan to Inventory Process
Duties and Responsibilities | Person/s Assigned to Perform the Function | Procedures Performed by the Auditor |
Custody | ||
Authorization | ||
Recording |
Duties and Responsibilities | Person/s Assigned to Perform the Function | Procedures Performed by the Auditor |
Custody | Physical custody of materials and labor documents is normally held by the production department. Since most of the assets here are highly susceptible to theft and misappropriation, adequate physical controls must be implemented. | Auditor observes the physical count and reconciles the result of such count to entity's records. If held by other parties, auditor may send confirmation requests to the custodian (e.g. third-party warehouses, consignees, agents, or branches) |
Authorization | The production department is authorized to make normal production runs. However, in case of special runs (to meet a special order), authorization must come from the board of directors or its authorized representative. | Auditor reviews production orders and related documents supporting production runs made by the department to determine whether it bears the necessary authorization. |
Recording | Transactions are recorded by the cost accounting. Daily summaries are then prepared and forwarded to general accounting for recording and posting in the general journal and ledger, respectively. | Auditor normally reviews the
|
Financing Process
Duties and Responsibilities | Person/s Assigned to Perform the Function | Procedures Performed by the Auditor |
Custody | ||
Authorization | ||
Recording |
Duties and Responsibilities | Person/s Assigned to Perform the Function | Procedures Performed by the Auditor |
Custody | Unissued equity and debt certificates must be kept by an appropriate internal official (e.g. Corporate Secretary) or independent external custodian | Auditor inquires directly to assigned custodian. If held internally, auditor observes the accounting of unissued certificates |
Authorization | As mentioned, transactions covered in this cycle involve large amounts of cash or other resources. With this, transactions shall be approved by the board of directors | Auditors reviews minutes of the BOD’s meetings |
Recording | Transactions are recorded in the general journal by personnel in general accounting | Auditor normally reviews the
|
Investing Process
Duties and Responsibilities | Person/s Assigned to Perform the Function | Procedures Performed by the Auditor |
Custody | ||
Authorization | ||
Recording |
Duties and Responsibilities | Person/s Assigned to Perform the Function | Procedures Performed by the Auditor |
Custody | Generally, investment certificates are kept as follows (Treasurer):
| Auditors inquires directly to assigned custodians thru sending confirmation requests. If held internally, the auditor observes the accounting for certificates held |
Authorization | Transactions covered in this cycle involve large amount of cash or other resources. With this, transactions shall be approved by the BOD or by an investment committee | Auditor reviews minutes of the board of directors’ meetings |
Recording | Transactions are recorded in the general journal by personnel in general accounting Moreover, most companies monitor transactions in the investment cycle through a subsidiary ledger/s maintained by the treasury department | Auditor normally reviews the
|
Tracing shipping documents to sales invoices provides evidence that
Shipments were billed
Tracing sales invoices to shipping documents provides evidence that
Goods billed were shipped