Tissue types - Intro to integument - Layers of the skin
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
get ready to memorize a bunch of random shit!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
epithelial tissue
general meaning
large sheets of cells that cover interior and exterior surfaces
interior: blood vessels, external surfaces of internal organs
external: skin, respiratory tract, digestive tract, urinary system, reproductive system
epithelial tissue > internal surfaces
never gonna encounter something outside the body
blood vessels, external surfaces of internal organs
epithelial tissue > external surfaces
skin, respiratory tract (cilia), digestive tract, urinary system, reproductive system
epithelial tissue function
provide protection from wear and tear (e.g., skin, serous membranes)
protection from external threats (e.g., respiratory epithelium)
control of materials across barriers (e.g., absorption in digestive tract, alveolar tissue absorbs O2)
secretion of chemical compounds (e.g., digestive enzymes - acidic breaks things down)
simple squamous epithelium location and function
air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
THIN = Allow materials to pass thru by diffution and iltration, and secretes lubricating substance
simple cuboidal epithelium location and function
in ducts and secretory portions of small glands and in kidney tubules
secretes and absorbs
simple columnar epithelium location and function
ciliated tissues are in larger bronchioles, uterine tubes, and uterus;
smooth (non ciliated) are in the digestive tract, bladder
absorbs; it also secretes mucus and enzymes
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium location and function
ciliated tissue lines the bronchi, trachea, and much of the upper respiratory tract
secretes mucus; ciliated tissue moves mucus
stratified squamous epithelium location and function
lines the esophagus, mouth, and vagina
protects against abrasion 😏😏
stratified cuboidal epithelium location and function
sweat glands, salivary glands, and the mammary glands
protective tissue
stratified columnar epithelium location and function
the male & female urethra and the ducts of some glands
secretes and protects
transitional epithelium location and function
lines the bladder, urethra, and the ureters
allows the urinary organs to expands and stretch
what are glands
structure made of one or more cells that synthesize and secrete chemical substances
endocrine
secretes directly into surrounding tissues/fluids, picked up by whatever is nearby, usually blood
NO ducts
exocrine
secretes to the external environment via ducts (indirectly or directly)
merocrine secretion
apocrine secretion
holocrine secretion
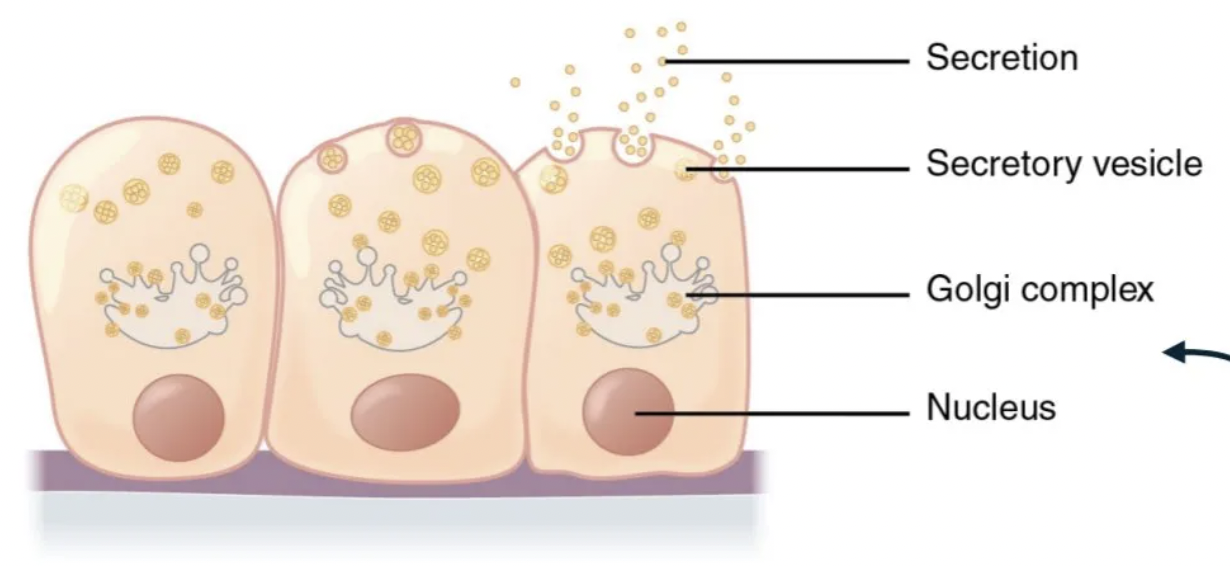
merocrine secretion
secretions are enclosed in vesicles that move to the apical surface of the cell where the contents are released by exocytosis.
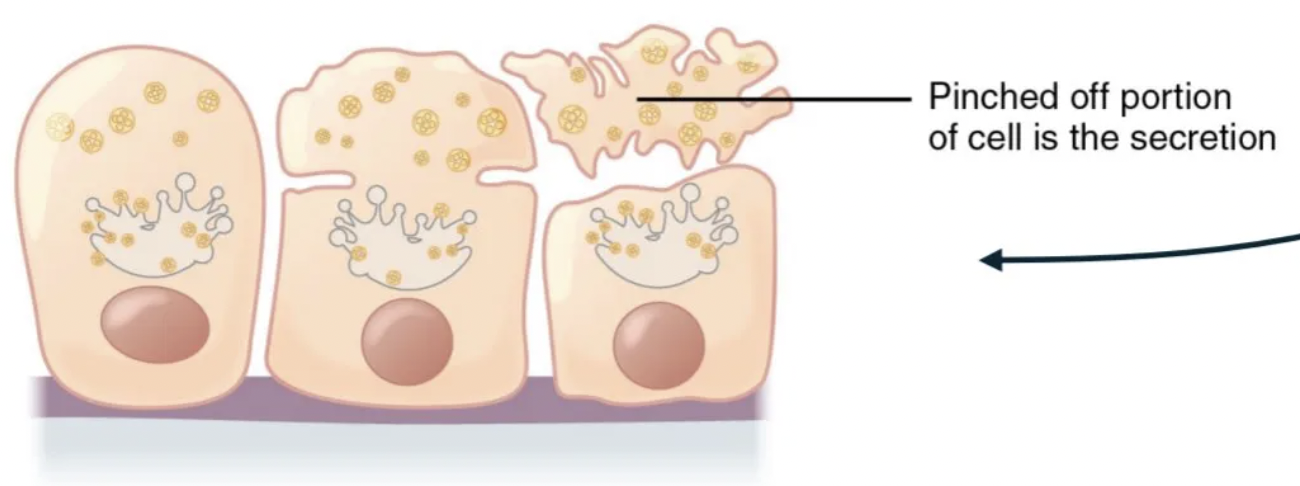
apocrine secretion
portion of the cell and its secretory contents pinch off from the cell and are released.
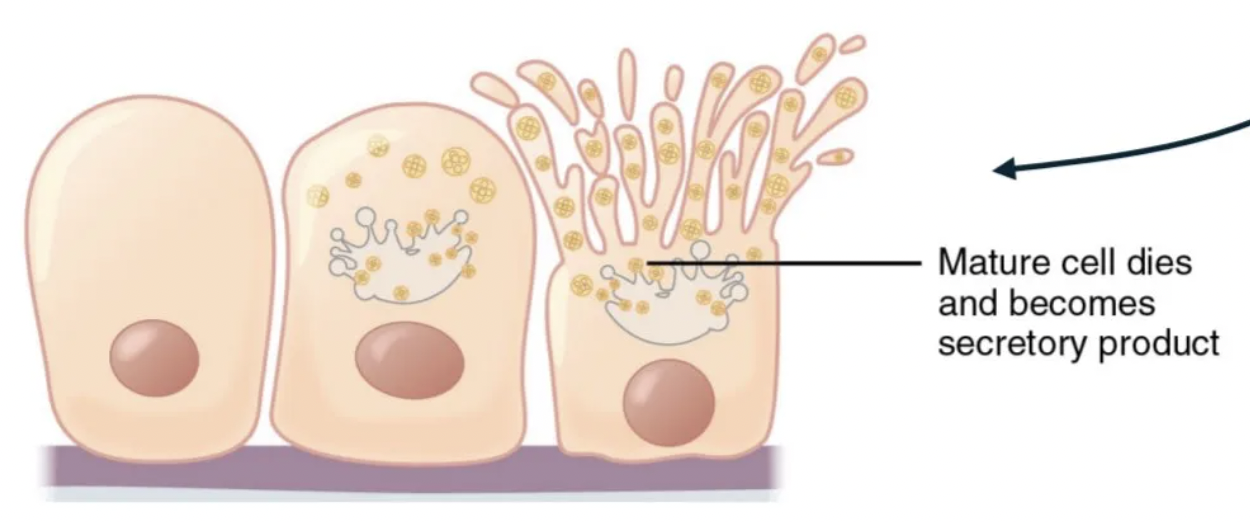
holocrine secretion
cell does not regrow (a new cell grows in its place)
faster release
connective tissue function
support and connect other tissues (bones, tendons)
protection (fibrous capsules around more delicate structures)
transport of materials (blood, lymph)
storage of energy (fat cells)
all connective tissues are ____ dispersed in ____
cells dispersed in a extracellular matrix
extracellular matrix is made of…
ground substance - major component, can be fluid or solid
protein fibers - rigid proteins that contribute structural strength to the tissue
ground substance
stuff in the ECM that is not protein fibers
rigid ground substance in bones
protein fibers
rigid proteins that contribute structural strength to the tissue
wtf is connective tissue proper
support, attachment and protection of structures; immune functions.
common cells:
fibroblasts - most common, produce the EC matrix
adipocytes - fatass cells for energy storage (store lipids)
macrophages - immune cells, help destroy infectious agents “big eater”
2 subtypes": loose and dense connective tissue
fibroblasts
fibroblasts - most common, produce the EC matrix
connective tissue proper → loose connective tissue
commonly found btwn organs,
absorb shock and bind tissues together
adipose tissue
reticular tissue
areolar tissue
loose connective tissue→adipose tissue
fatass storage cells, very little ECM
loose connective tissue→reticular tissue
mesh like framework for soft organs
(lymphatic tissue, spleen, liver)
require having stuff moved thru them.
supports developing blood cells
loose connective tissue→areolar tissue
broad group of tissues underlying most epithelia
between muscle fibers, surrounds blood and lymph vessels,
glue that holds epithelium to the organs
dense connective tissue
higher abundance of collagen fibers in the matrix than loose connective tissue. greater resistance to stretching
ex: ligaments and tendons - connections btwn structures that experience extreme strain
supportive connective tissue
maintains body posture/position, protects internal organs
2 types! cartilage and bone
cartilage
chondrocytes within matrix. they produce cartilage within lacunae.
cartilage matrix is avascular - nutrients must diffuse through matrix to reach chondrocytes = heal very slowly
types of cartilage:
hyaline - strong and flexible; most common (rib cage, nose, joints between bones)
fibrocartilage – strongest (meniscus in the knee, intervetrbral discs)
elastic – most flexible (ear)
hyaline cartilage
hyaline - strong and flexible; most common (rib cage, nose, joints between bones)
fibrocartilage
strongest (meniscus in the knee, intervetrbral discs)
elastic cartilage
most flexible (ear)
bone
osteocytes – bone cells within lacunae
bone matrix is vascular – blood carries nutrients to osteocytes – bone heals quickly
ridgid ECM contains collagen fibers (protein fibers for flexibility) within hydroxyapatite (ground substance for rigidity)
bone matrix has……
collagen fibers (protein fibers for flexibility)
within
hydroxyapatite (ground substance for rigidity)
fluid connective tissue
carry materials throughout the body
blood and lymph
blood contains…
erythrocytes - red blood cells, carry oxygen and carbon dioxide
leukocytes - white blood cells, immune response
muscle tissue
allows mobility of body parts.
excitation of myocytes (muscle cells) cause muscles to
contract or relax!
skeletal – voluntary movement, most common
cardiac – involuntary, forms the heart
smooth – involuntary movements of internal organs
three types of muscle tissue
skeletal – voluntary movement, most common
cardiac – involuntary, forms the heart
smooth – involuntary movements of internal organs
nervous tissue
allows transmission and processing of information about the internal and external environments AKA sends signals thruout the body
cell types: neurons and neuroglia
neurons
have 3 major components:
cell body – contains most organelles
dendrite(s) – receives signals from other cells
axon – sends signals to other cells
(in some neurons the dendrite and neuron have the same structure)
synapse
junction btwn 2 neurons
functions of the integumentary system
protection
sensation
thermoregulation
vitamin D synthesis
merkel cells
sensory touch sensor in the stratum basale of the epidermis.
only sensory cell in the epidermis
How does skin protecc
protect against:
physical damage
corrosive chemicals
UV radiation
How is vitamin D synth good
crucial to the formation of many types of white blood cells + essential for absorption of calcium and phosphorous
what is rickets
misshapen bones in children due to lack of calcium resulting from insufficient vitamin D
true skin is made of
epidermis + dermis
hypodermis
aka subcutaneous tissue
aka superficial fascia
thick skin layers and location
has five epidermal layers, only on palms of hands and soles of feet
thin skin layers and location
has four epidermal layers, everywhere else in the body
layers of the epidermis from top to bottom
Stratum corneum
lucidum !!
granulosum
spinosum
basale
(come lets get sun burned)
layers of the epidermis from top to bottom (minimal)
corneum
lucidum !!
granulosum
spinosum
basale
keratin
intracellular fibrous proteins that give structures hardness and water resistance
keratinocytes
cells that produce keratin