Gas exchange ppq
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Describe and explain one feature of the alveolar epithelium that makes the epithelium well
adapted as a surface for gas exchange. Do not refer to surface area or moisture in your
answer.
1. Flattened cells
OR
Single layer of cells;
Reject thin cell wall/membrane
Accept thin cells
Accept ‘one cell thick’
2. Reduces diffusion distance/pathway;
3. Permeable;
4. Allows diffusion of oxygen/carbon dioxide;
Ignore gas exchange
Tidal volume is the volume of air inhaled and exhaled during a single breath when a person
is resting. The tidal volume in a person with emphysema is reduced compared with the tidal
volume in a healthy person.
Suggest and explain how a reduced tidal volume affects the exchange of carbon dioxide
between the blood and the alveoli.
1. Less carbon dioxide exhaled/moves out (of lung)
OR
More carbon dioxide remains (in lung);
2. (So) reduced diffusion/concentration gradient (between blood and alveoli);
3. Less/slower movement of carbon dioxide out of blood
OR
More carbon dioxide stays in blood;
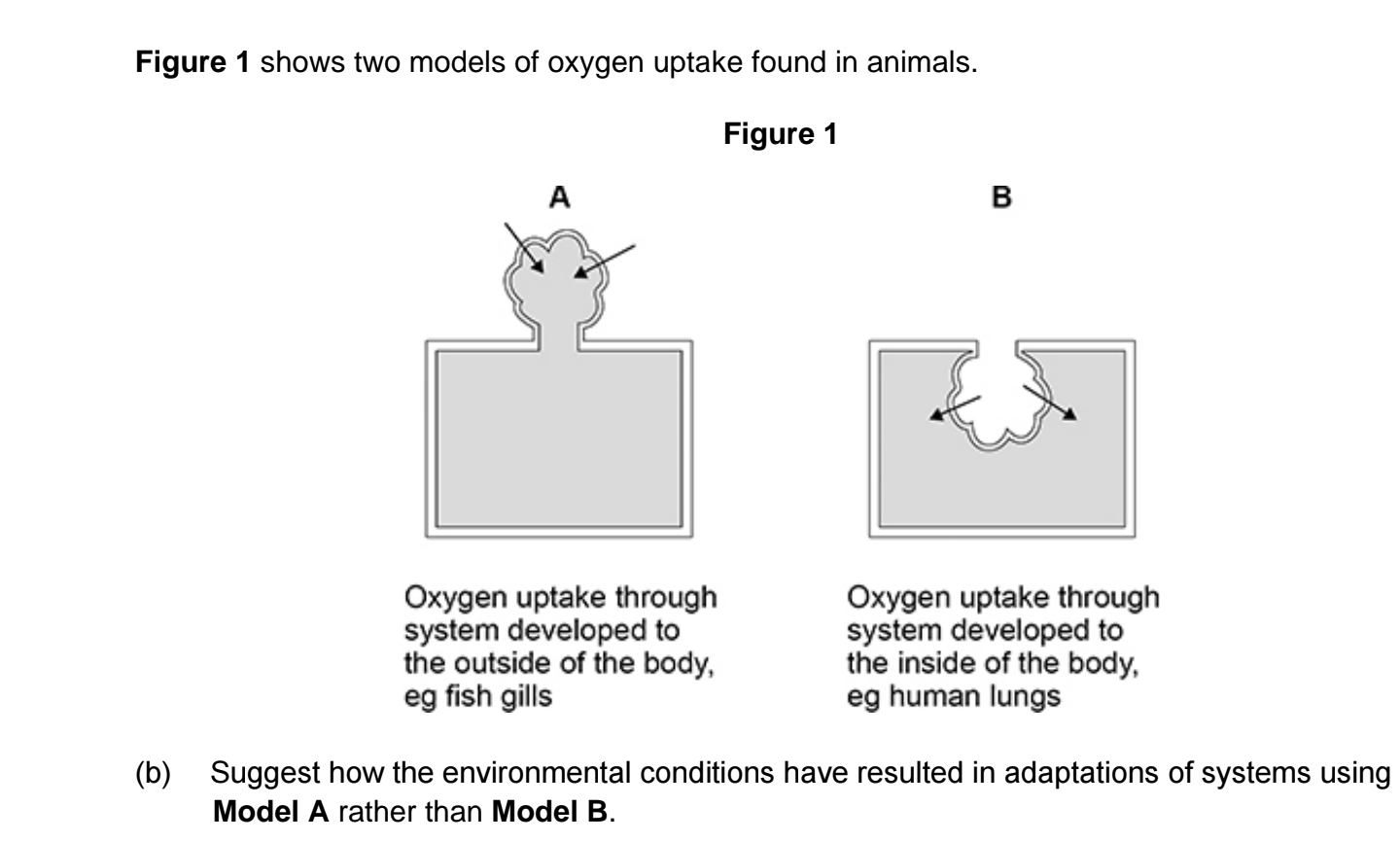
1. Water has low(er) oxygen partial pressure/concentration (than air);
2. So (system on outside) gives large surface area (in contact with water)
OR
So (system on outside) reduces diffusion distance (between water and
blood);
3. Water is dense(r) (than air);
4. (So) water supports the systems/gills;
Explain how the counter cirrent principle allows efficient oxygen uptake in fish gas exchange system
1. Blood and water flow in opposite directions;
2. Diffusion/concentration gradient (maintained) along (length of)
lamella/filament;
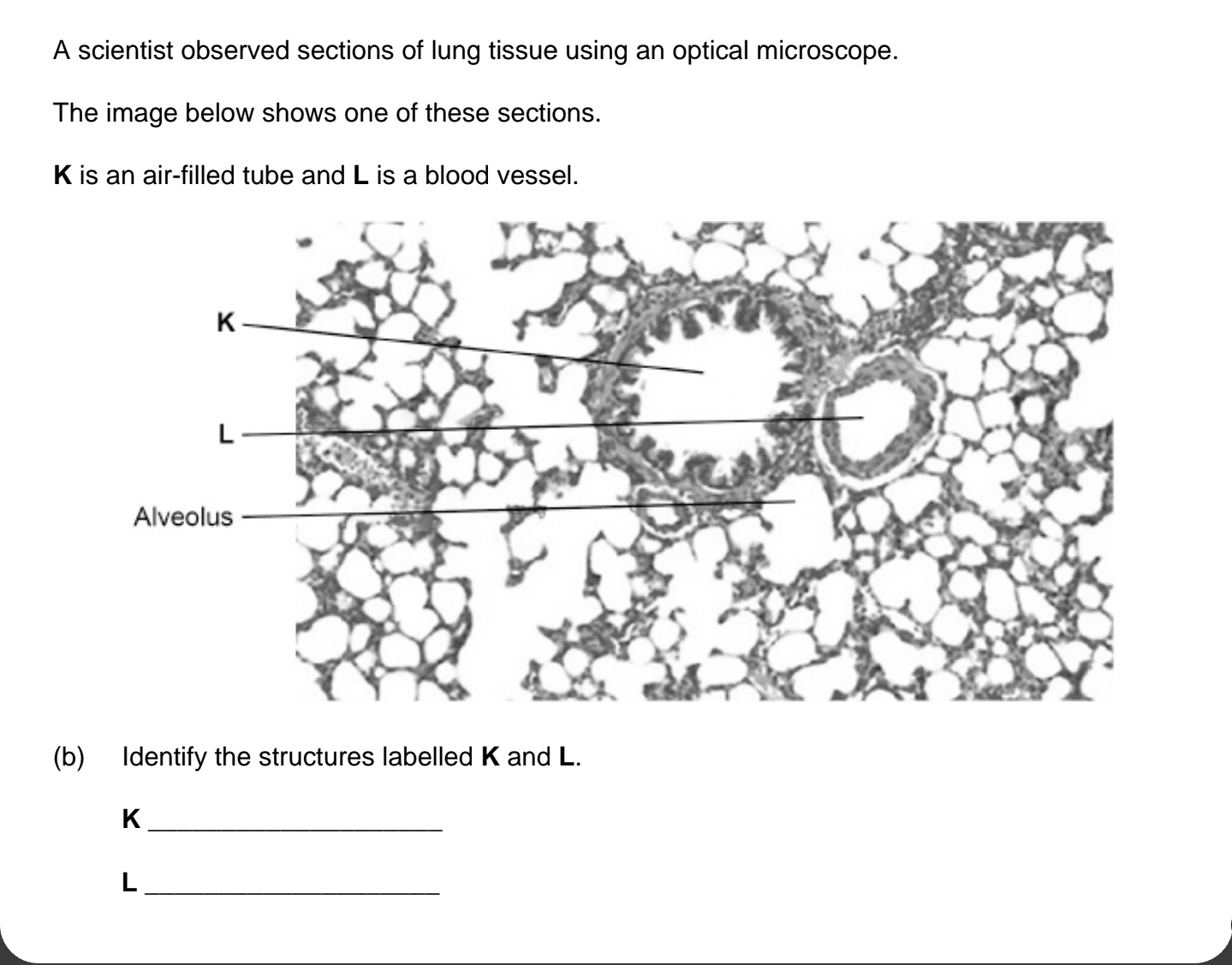
) K = Bronchiole and
L = artery/arteriole/vein/venule;
Two solutions often used to stain tissues are haematoxylin solution and iodine solution.
• Haematoxylin solution stains DNA a blue colour.
• Iodine solution stains starch a blue-black colour.
The scientist used haematoxylin solution and not iodine solution to stain the lung tissue.
Suggest why.
1. This/animal/lung tissue does not contain starch;
Accept cell(s) for ‘tissue’
2. (Makes) nucleus visible;
OR
Nucleus contains DNA;

A student who looked at these results concluded that all three risk factors are linked with
asthma. Evaluate this conclusion.
(d) In support
1. (Link/risk with asthma and) living with cat or dog is (statistically) significant;
2. (Link with) obesity is most/highly significant;
Reject ‘results are significant’
Not supported
3. (Link/risk with asthma and) burned wood (indoors) is not (statistically) significant;
Accept ‘due to chance’ for ‘not significant’ and converse
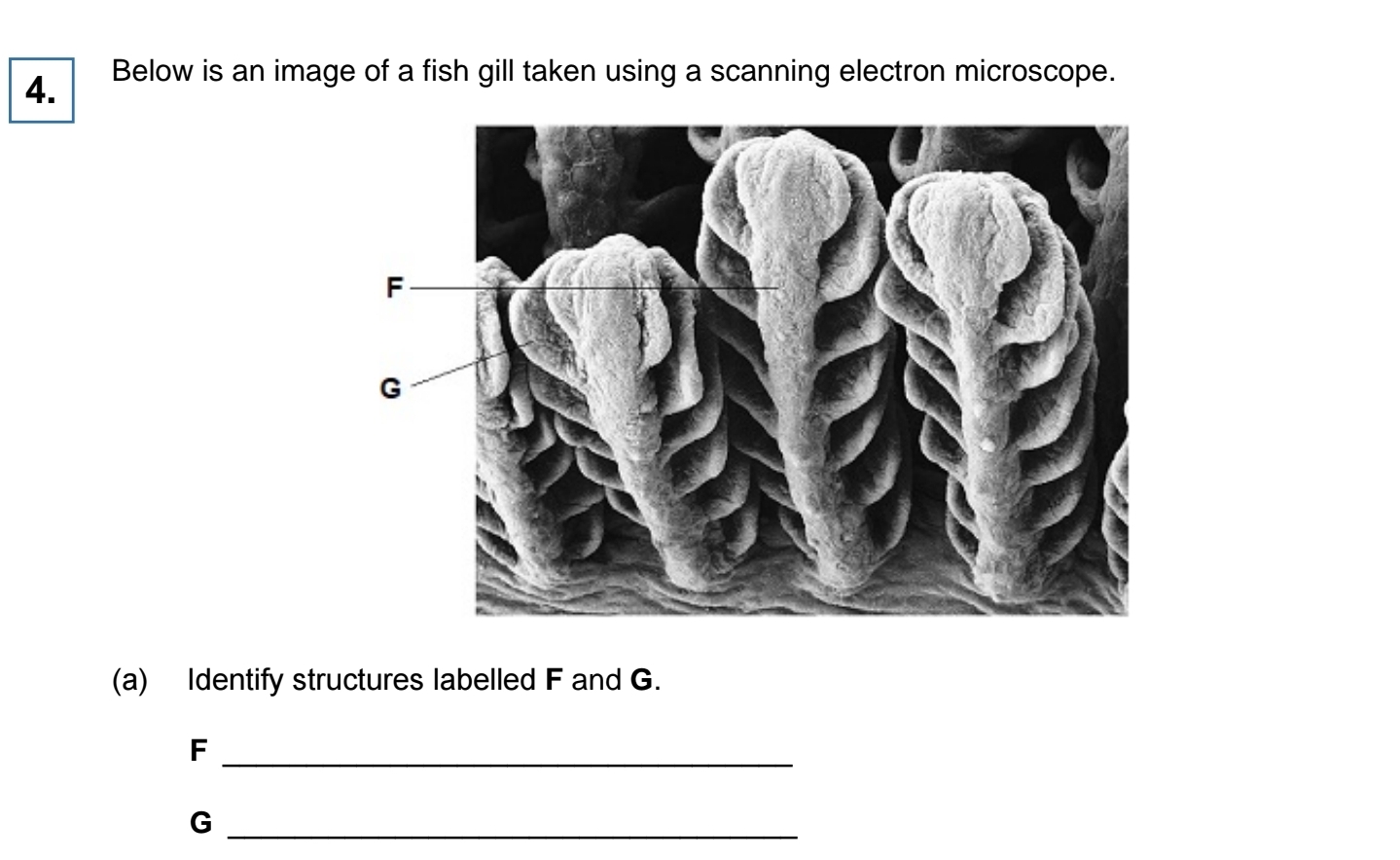
F = Filament and
G = (Secondary) lamella(e) / (gill) plate;
Reject gill arch
Accept primary lamella(e) for F
(b) Describe and explain the advantage of the counter-current principle in gas exchange
across a fish gill.
(b) 1. Water and blood flow in opposite directions;
2. Maintains diffusion/concentration gradient of oxygen
Accept: converse for carbon dioxide
Accept: equilibrium not reached
OR
Oxygen concentration always higher (in water);
3. (Diffusion) along length of lamellae/filament/gill/capillary;
Accept: all/whole of lamellae/filament//gill/capillary
Describe the pathway taken by an oxygen molecule from an alveolus to the blood.
(Across) alveolar epithelium;
2. Endothelium / epithelium of capillary;
Incorrect sequence = maximum of 1 mark
Breathing out as hard as you can is called forced expiration.
(a) Describe and explain the mechanism that causes forced expiration.
(a) 1. Contraction of internal intercostal muscles;
2. Relaxation of diaphragm muscles / of external intercostal muscles;
3. Causes decrease in volume of chest / thoracic cavity;
4. Air pushed down pressure gradient.
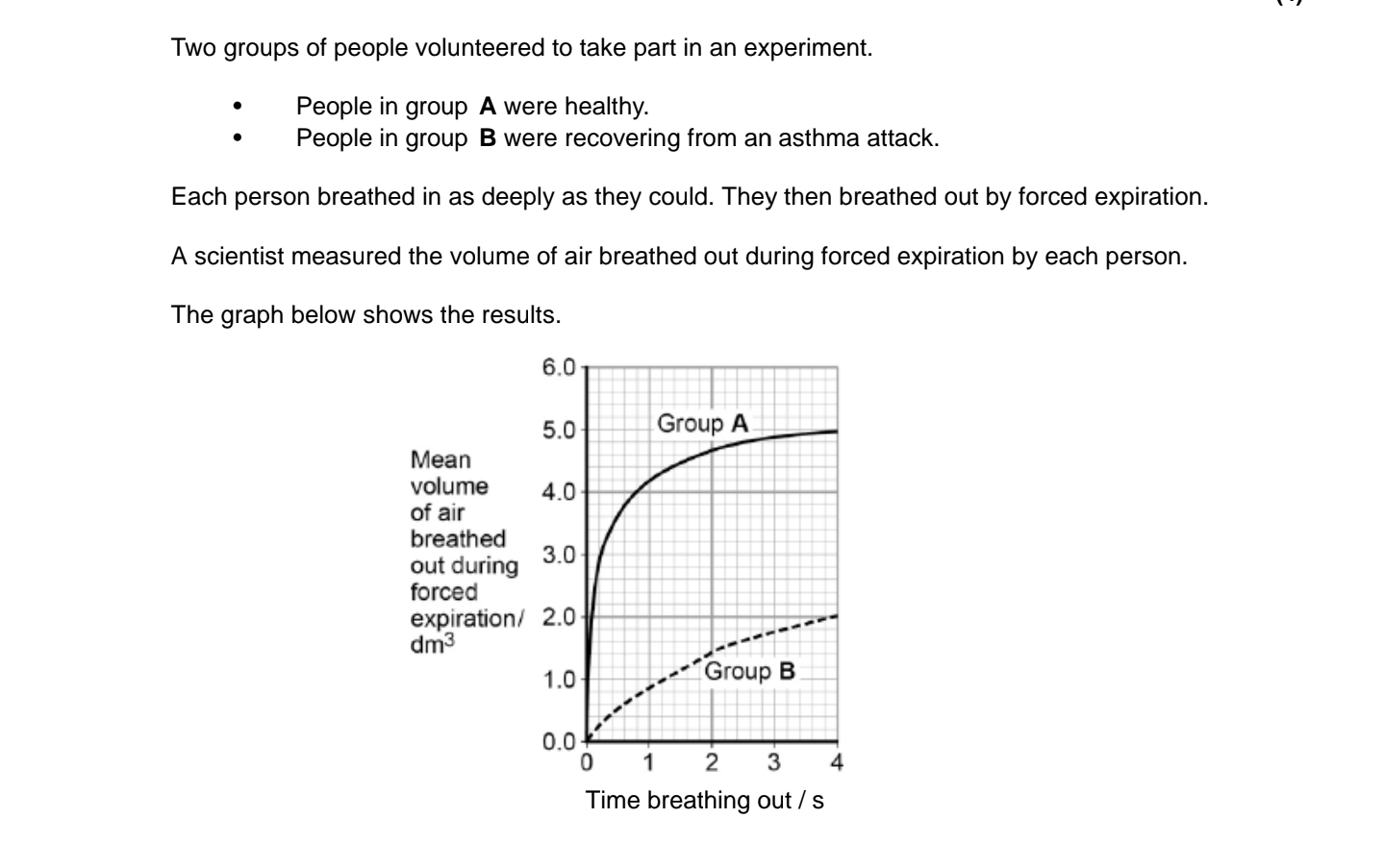
(c) The people in group B were recovering from an asthma attack.
Explain how an asthma attack caused the drop in the mean FEV shown in the figure above.
(c) 1. Muscle walls of bronchi / bronchioles contract;
2. Walls of bronchi / bronchioles secrete more mucus;
3. Diameter of airways reduced;
4. (Therefore) flow of air reduced.