SolidWorks Simulation Certification
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
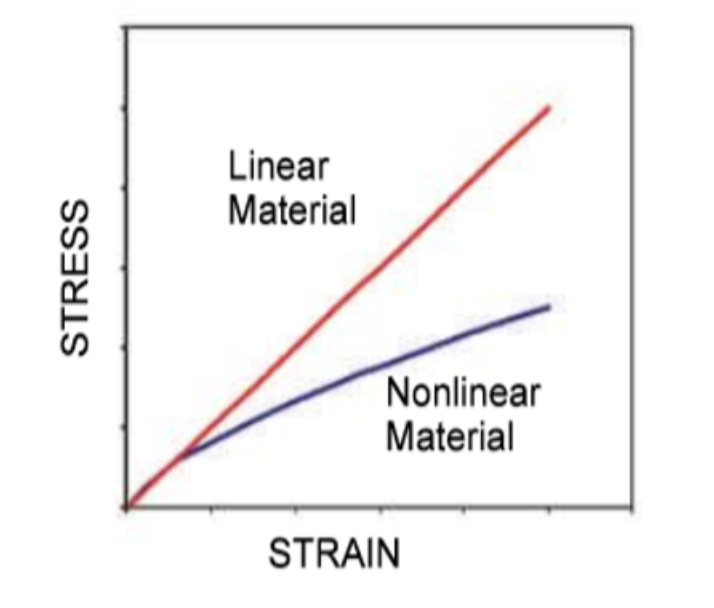
From the stress-strain curves depicted below, which kind of material can SW Simulation model?
A) Red Line B) Blue Line C) Both
A) Red Line (SW Simulation only models elastic stress-strain behavior, not plastic)
A force "F" applied in a static analysis produces a resultant displacement URES. If the force is now 2*F and the mesh is not changed, then URES will:
A) Double if there is no source of nonlinearity in the study (like contacts or large displacement option)
B) Be divided by 2 if contacts are specified
C) The analysis must be run again to find out
D) Double if there are no contacts specified and there are large displacements in the structure
A) Double if there is no source of nonlinearity in the study (like contacts or large displacement option)
...following Hooke's Law --> F= k.x
The primary unknown in FEA is (_______________). This quantity is therefore the most accurate.
A) Displacements
B) Strains
C) Stresses
D) Not listed
A) Displacements
Where do most errors in FEA modeling most likely come from?
A) Solid Model
B) Solver
C) Mesh
D) Boundary Conditions
D) Boundary Conditions
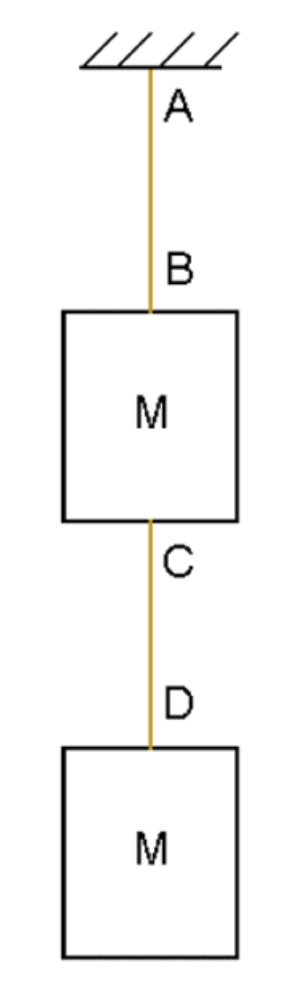
Two equal masses M=1000 kg are suspended on cables as shown opposite. What are the tensions in the cables AB and CD.
A) TAB = 19.62 N, TCD = 9.81 N
B) TAB = 9.81 kN, TCD = 19.62 kN
C) TAB = 19.62 kN, TCD = 9.81 kN
C) TAB = 19.62 kN, TCD = 9.81 kN
To prevent rigid body motion in FEA:
A) The displacement at a restraint must be constant
B) The displacement at a restraint must be zero
C) Elastic material properties must be fully defined
D) Applied loads must be counteracted by sufficient restraints
A) displacement at a restraint must be zero
Why do "sufficient restraints" counteracting an applied load NOT confirm that rigid body motion is prevented?
Parts can move due to applied loads without causing rigid body motion. you must know the displacement at a constraint to prevent the model drifting into space
St Venant's Principle States that:
A) The difference between the effects of different but statically equivalent loads become very small at sufficiently large distances from the load
B) if a part is separated or isolated from a body or surroundings, appropriate reactions and / or internal forces must be added
C) When an elastic body is acted upon by some external forces on various points, then the resultant effect on the body is the vector sum of the effects caused by each of the loads acting independently on the respective points of the body
D) A body has a definite shape and dimensions before loading
A) The difference between the effects of different but statically equivalent loads become very small at sufficiently large distances from the load
Two wires of equal diameter and length have an equal longitudinal force applied to them. One wire is made of steel, the other of aluminum. Given that steel has a Young's modulus (the ratio of stress to strain) which is 3 times as much as that of aluminum, the extension of the aluminum wire will be:
A) 9x as much as the steel wire
B) 3x as much as the steel wire
C) 1/9 as much as the steel wire
D) 1/3 as much as the steel wire
B) 3x as much as the steel wire
Which one of the following statements is true?
A) The node between truss elements is rigid
B) Beam elements have more nodes than truss elements
C) Truss elements are good for models involving bending
D) If used correctly, beam elements are more accurate than the truss elements
B) Beam elements have more nodes than truss elements
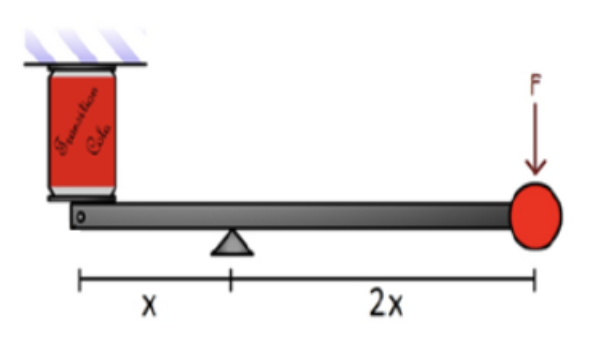
A diagram of a simple can crusher is shown. The downward force, labelled 'F' is:
A) 1/3 of that exerted on the can
B) 2x that exerted on the can
C) 1/2 of that exerted on the can
D) equal to that exerted on the can
C) 1/2 of that exerted on the can
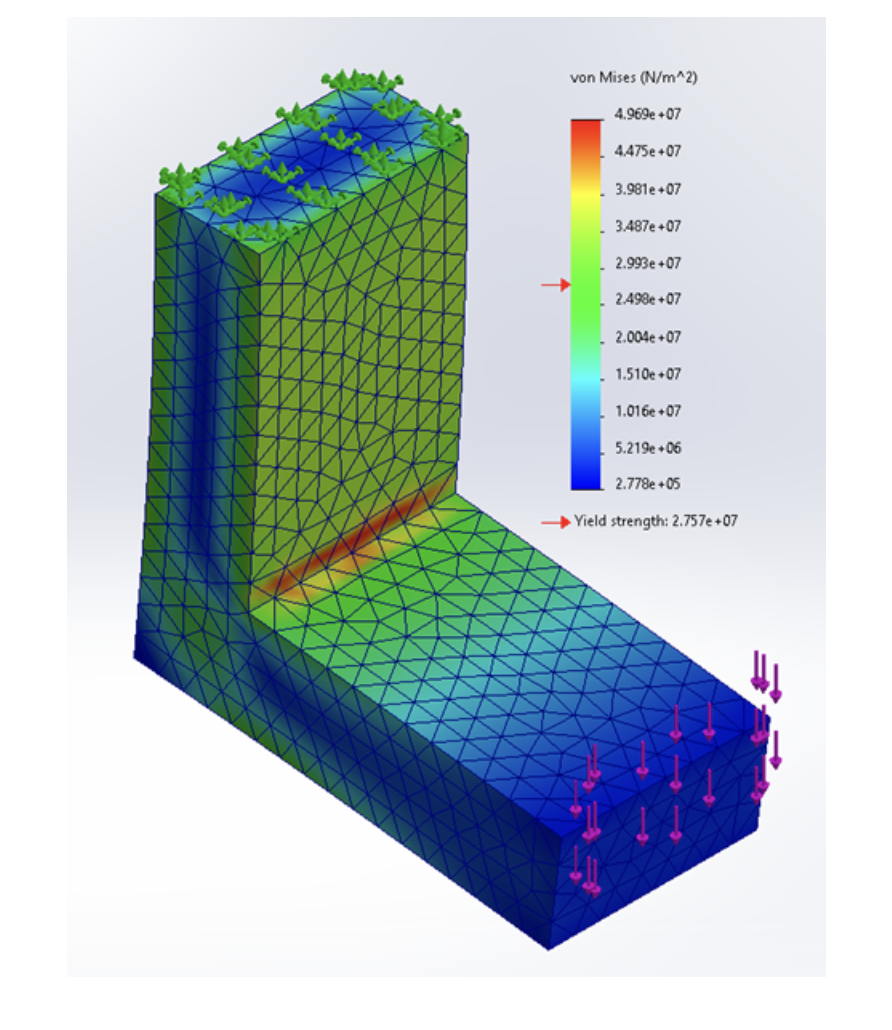
An "L" bracket is constrained a loaded with a 2000 N force with the resulting von Mises stress plot shown in the figure. part a - What is the most likely reason for the high stress area (Red) shown in the figure? part b - how could the high stressed be reduced to more realistic values in the model?
part a - Stress Singularity
part b - add a fillet
In a static analysis, at a given node, the principal stresses P1, P2 and P3 are all equal to 50psi. What is the von Mises stress at that node equal to?
A) 0
B) 50
C) 100
D) 150
A) 0
The equation for von Mises stress based on principle stresses is:
If all of the principle stresses are equal, then von Mises stress has to be ....
zero
SW simulation can use the p-adaptive type method. Which of the following is true?
A) The number of degrees of freedom does not change with the P-adaptive technique
B) P-adaptive technique increases the element density
C) P-adaptive technique increases the number of nodes in each element
D) The p-adaptive technique is more accurate than the h-adaptive technique
A) The number of degrees of freedom does not change with the P-adaptive technique
What does "convergence analysis" refer to?
A) It is a procedure for determining appropriate element size based on the tradeoff between accuracy and run time
B) It is a procedure whereby element sizes are progressively reduced
C) It describes the procedure whereby stress results are intially calculated at Gaussian points and then extrapolated to the rest of the element
D) It describes the problem of the averaged results calculated from Gaussian points varying depending on the size of the element
A) It is a procedure for determining appropriate element size based on the tradeoff between accuracy and run time
To compute thermal stresses on a model with a uniform temperature distribution, what type/types of study/studies are required?
A) Static only
B) Thermal Only
C) Both static and thermal
D) Correct answer not listed
A) Static only
Which of the following meshing scenarios will create the mesh the quickest?
A) Coarse Mesh
B) Coarse mesh with mesh refinement
C) Fine Mesh
D) All of the above take about the same amount of time
A) Coarse mesh
Adding fillets to sharp edges in a model will cause the stress to increase to infinity:
A) True
B) False
B) False
All metals expand on heating. If a sheet of metal with a hole in the centre is heated, how is the diameter of the hole affected by the increase in temperature?
A) It is the same as before
B) It is larger than before
C) It is smaller than before
B) It is larger than before
A heavy car is travelling at 30mph and a light car at 40mph, when they collide head on. The collision force...
A) on the lighter car is the same as the force on the heavier car
B) On the lighter car is less than the force on the heavier car
C) On the lighter car is greater than the force on the heavier car
A) On the lighter car is the same as the force on the heavier car
Newton's third law is...
every action has an equal and opposite reaction
Imagine you have a symmetrical model and you take advantage of it. If you must apply one of the following loads /boundary conditions to a face cut in half by the plane of symmetry, for which one(s) of them will you have to divide the value by 2? And which not?
- Convection coefficient
- Temperature
- Prescribed non-zero displacement
- Bolt pre-load
- Pressure
- Heat flux density
- Force
Yes : - Force and Bolt pre-load bc both force and load are divided by area
In FEA, loads are applied to...
nodes
Stress concentrations can be calculated with:
- Solid Elements
- Beam Elements
- Truss Elements
- All of the above
- None of the above
solid elements
- it was only when we used solid elements that we could see stress concentrations around the fillest
A complicated linear, elastic, static stress analysis uses a low cost 1018 steel with yield strength = 36,000 psi. The peak predicted stress is 52,000 psi. The material is changed to a more expensive AISI 4340 steel with yield strength = 80,000 psi. How would you expect the analysis results to change?
- Overall stress will remain the same
- Answer not listed
- Overall stress will decrease
- Overall stress will increase
overall stress will remain the same
A horse pulls forward on a carriage with a given force. By Newton's Third Law, the carriage must be pulling on the horse backward with an equal and opposite force. Given this, what explains why the horse and carriage can move forward?
- The forward and backward forces are equal, so it actually cannot move forward
- The cart is rolling on wheels, while the horses hooves have traction with the ground
- There is a brief moment where the horse pulls before the traction kicks in
The cart's force is only in reaction to the horse's forces, so it does not define direction of movement
- The forward force of the horse is just big enough to overcome the backward force of the cart and start the cart forward
- The cart is rolling on wheels, while the horses hooves have traction with the ground
How many degrees of freedom does each node of a beam element have?
6 - Displacement in X, Y and Z; Rotation around X, Y and Z
Which of the following is not true when discussing beam and truss elements?
- SW Simulation can plot the "Upper Bound Axial and Bending" stress This is the most suitable option for analyzing the stress in truss elements.
- Torque loads can be applied to beam element models, but not to truss element models.
- The node between two truss-elements rotates when loaded, but the node between two beam elements is rigid (constant angle under load).
- Beam elements can model flexure and bending in addition to axial stress, but truss elements can only model axial stress.
SW Simulation can plot the "Upper Bound Axial and Bending" stress This is the most suitable option for analyzing the stress in truss elements.
Which of the following is not true. The advantages of sub-modelling are:
- Helps transfer complex global loading from entire structure to local regions to obtain more accurate results
- Helps demonstrate the importance of mesh refinements
- Enables complex models to be broken down into simple two dimensional analyses ensuring faster, more accurate local solutions
- Enables experimentation of different designs in the area of interest
Enables complex models to be broken down into simple two dimensional analyses ensuring faster, more accurate local solutions
You are asked to create a finite element model of a tensile test piece. How many symmetry planes can you take advantage of?
3
The value of Poisson's ratio for any material is always:
<1
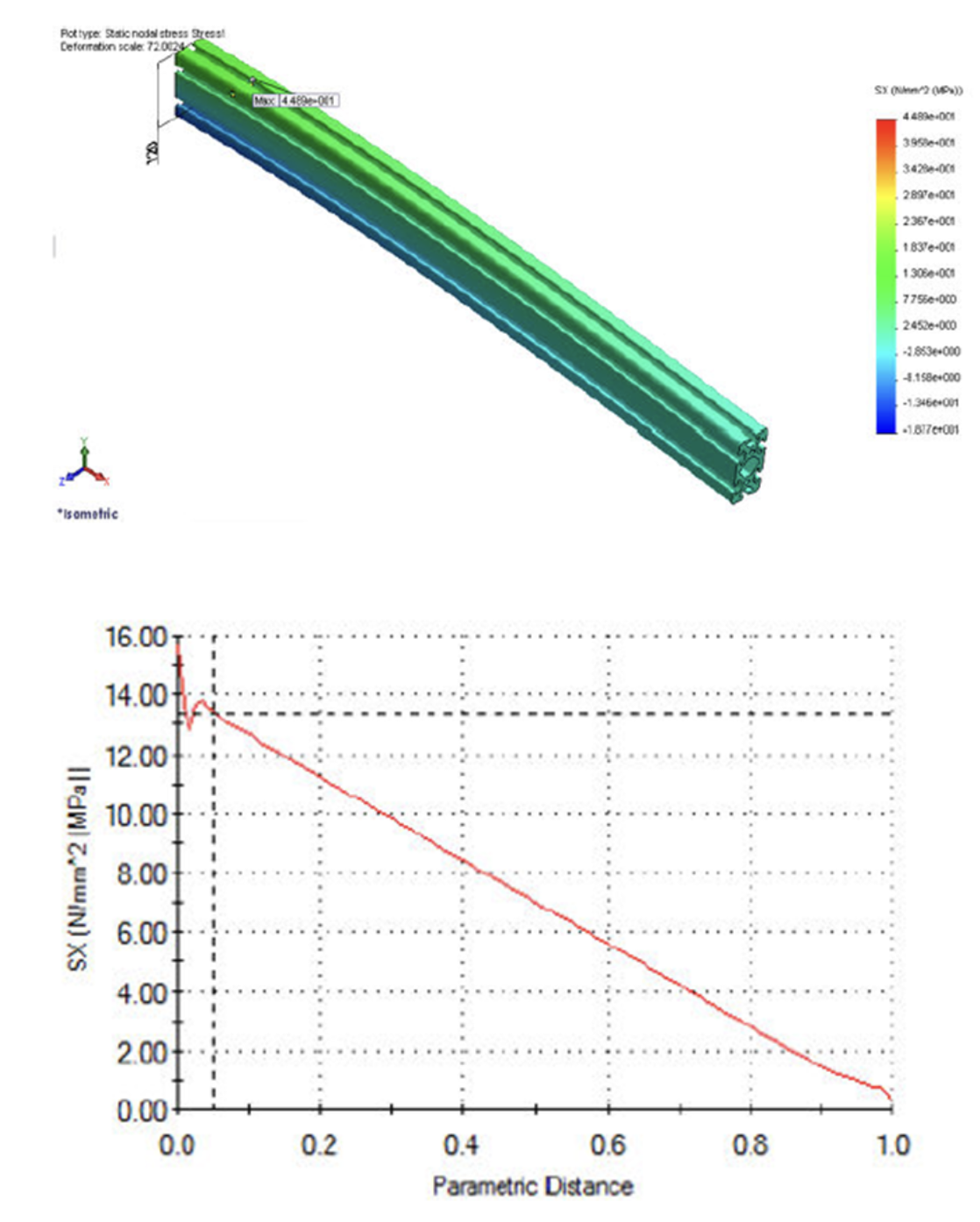
Early in this module we applied a load to the end of the 3D model of a beam shown below resulting in displacement in y, also shown below. This graph clearly shows:
St. Venants principle
what is Von Mises stress principal
Von Mises stress is a way to combine all the different stresses acting at a point into a single value that can be compared to the material's yield strength.
what is Tresca's criterion
way to predict when a material will start to yield under complex stress --> A material will yield when the maximum shear stress reaches a critical value—equal to the shear stress at yield in a simple tension test.
can truss elements calculate bending stress?
no
To calculate von Mises stress for a component in tensile or compressive loading scenario, which of the following stress results are required?
- Directional stresses only
- Principal stresses only
- Axial stresses only
- Shear stresses only
Principle Stresses only
If you use directional stresses, you also need
shear stresses
How is Tresca stress calculated?
from the difference between the maximum and minimum principal stress.
For brittle materials, which of the following is the most appropriate for calculating a factor of safety?
- Von Mises
- Not possible to calculate FoS for brittle materials, as they just break and have no yield point.
- Mohr-Coulomb
- Tresca
Mohr-Coulomb
If a metal bar fixed at both ends is cooled by reducing the temperature by 30°C, the nature of the stress developed in the bar will be
Tensile... The bar will contract, so will pull away from the fixed supports leaving it in tension.
In a bimetallic strip, when the temperature is changed, what type of stress develops at the interface between the two metals?
shear stress
Is it possible to predict shear stresses in truss elements?
no
What type of stress can you predict in truss elements
axial
Shear stresses can be predicted with the following element types:
- Solid, shell, beam and truss
- Just solid elements
- Solid, shell, and beam
- Solid and shell
Solid, shell, and beam
For modelling the interaction of a sliotar (ball) with a Hurley, what type of load should be applied?
static load
Regarding Large Displacement analyses, which of the following is incorrect?
- The large displacement option takes more time and resources than the small displacement solution but gives more accurate results for large displacement problems.
- The large displacement option is available in SW, but it is just a warning that there has been an error made when setting up the model, due to an incorrect or missing boundary condition.
- The large displacement option assumes that the normals to contact areas change direction during loading, so it applies the load in steps and updates the normals for each solution step.
- The large displacement option assumes that the stiffness changes during loading so it applies the load in steps and updates the stiffness for each solution step.
The large displacement option is available in SW, but it is just a warning that there has been an error made when setting up the model, due to an incorrect or missing boundary condition.
You are asked to find the stress at a point in a model represented by the coordinates in the form (5, 30°, 2). Which of the following coordinate systems is represented by these coordinates?
- Cylindrical coordinates system
- Cartesian coordinate system
- Spherical coordinate system
- Cuboid system
Cylindrical coordinates system
The stress plot ERR: Energy Norm Error provides an estimate of the stress field discontinuity from one element to another. Which of the following is true? ERR is only available for:
- Beam element studies
- All static studies
- Static and drop test studies
- Beam and truss element studies
Static and drop test studies
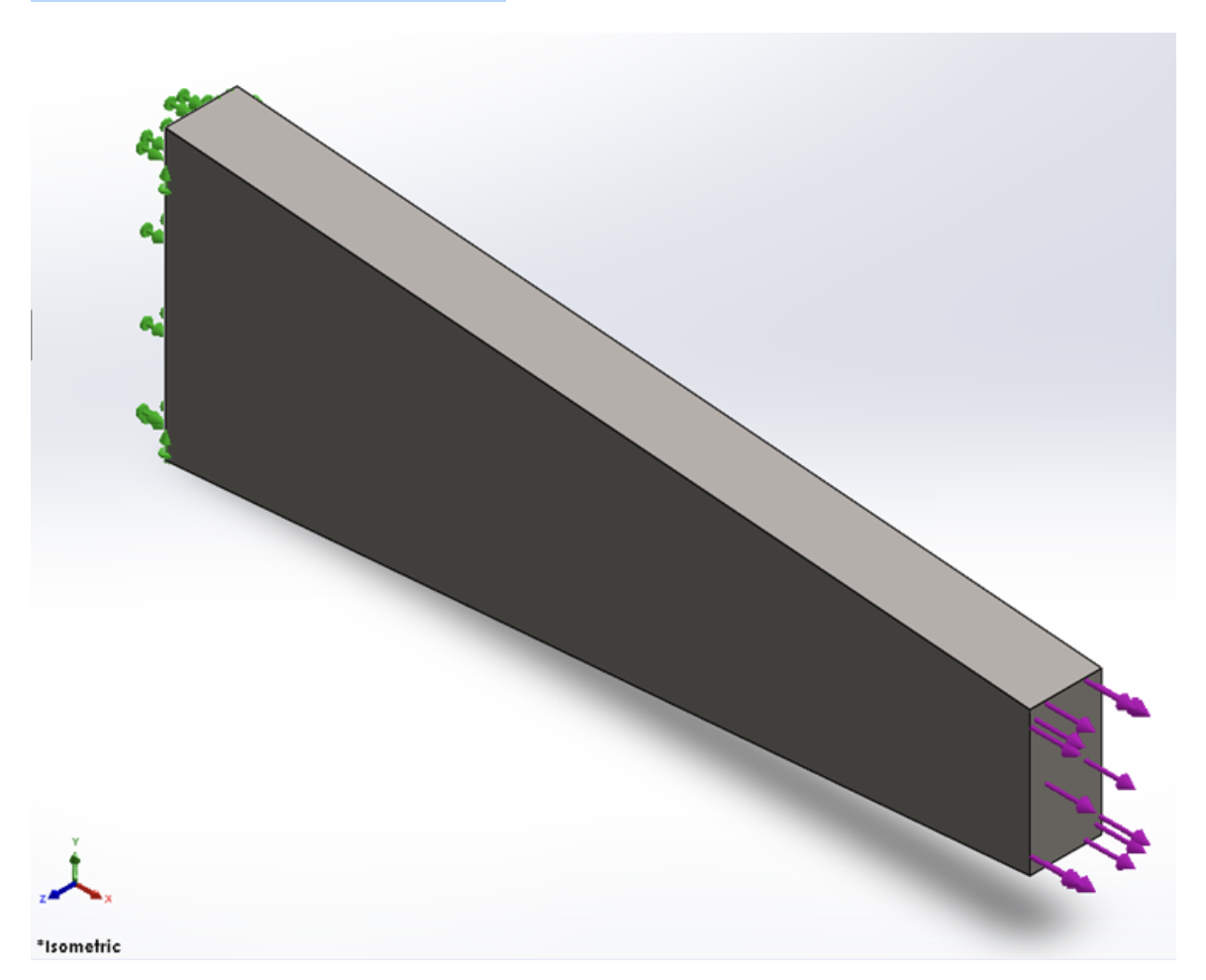
For the part shown (from week 3) with an axial load (x-direction), which symmetry model would be most appropriate?
- Symmetry model not possible
- One Half symmetry
- One Quarter symmetry
- One Eight symmetry
- One Quarter symmetry
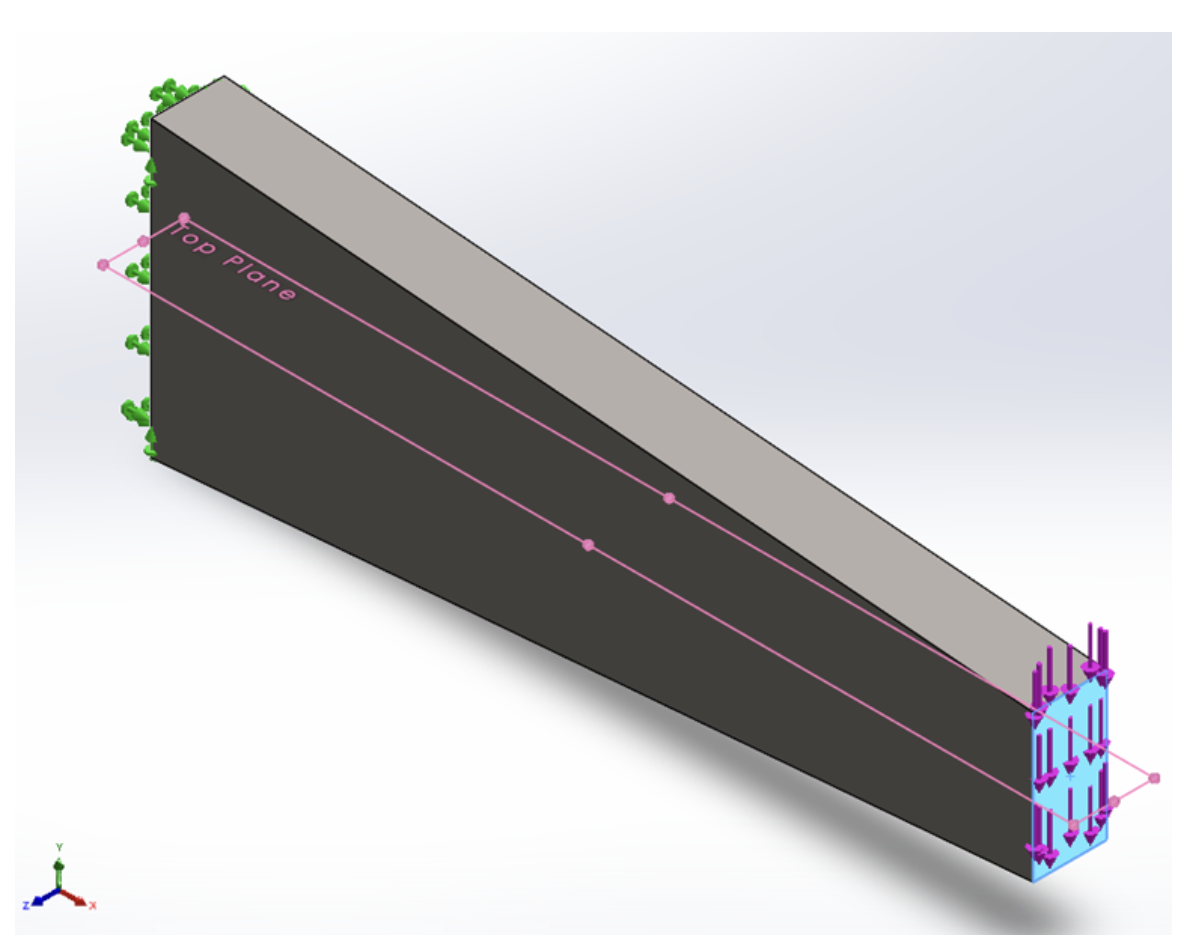
For the part shown (from week 3) with a vertical load (y-direction), which symmetry model would be most appropriate?
- Symmetry model not possible
- One Half symmetry
- One Quarter symmetry
- One Eight symmetry
- One Half symmetry
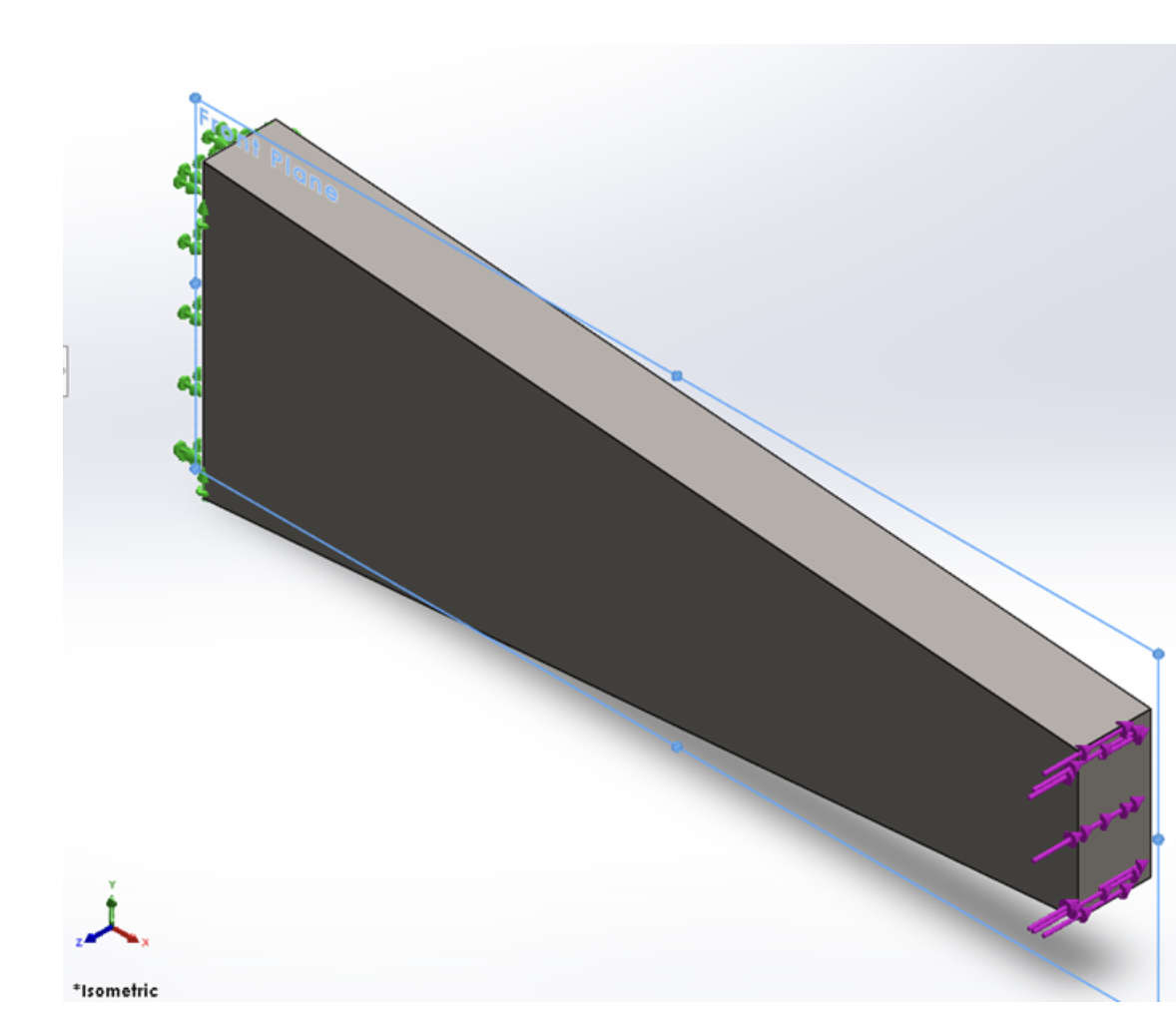
For the part shown in the last question with the load acting in the z-direction, which symmetry model would be most appropriate?
- Symmetry model not possible
- One Half symmetry
- One Quarter symmetry
- One Eight symmetry
- One Half symmetry
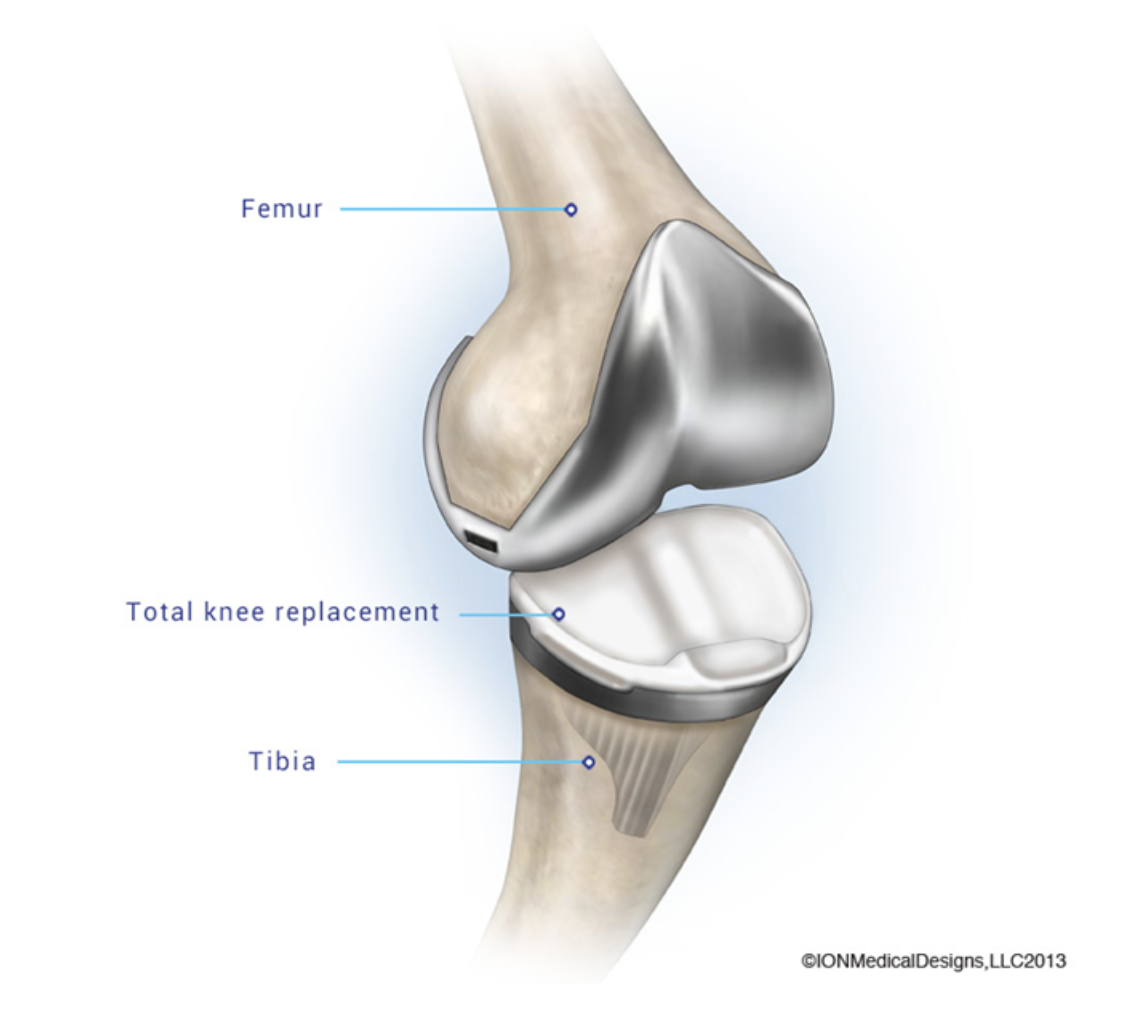
For a finite element analysis of a knee replacement, which symmetry model would be most appropriate?
- Symmetry model not possible
- One Half symmetry
- One Quarter symmetry
- One Eight symmetry
Symmetry model not possible
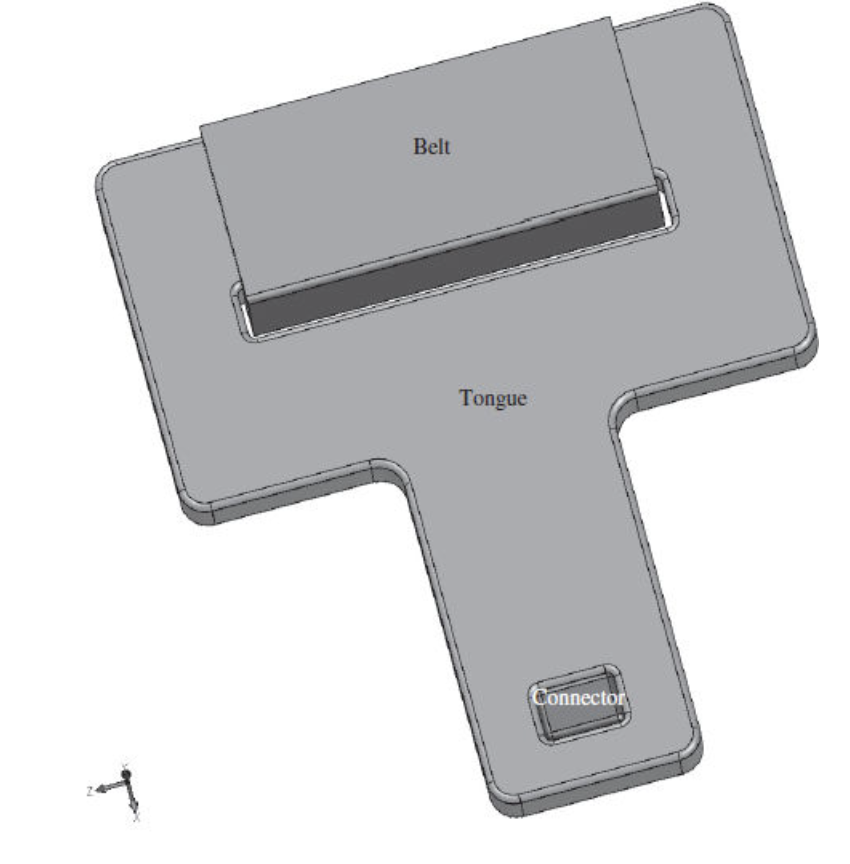
For the seat belt part that we analyzed in class, which symmetry model would be most appropriate?
- Symmetry model not possible
- One Half symmetry
- One Quarter symmetry
- One Eight symmetry
One Quarter Symmetry
Can you do symmetry with beams?
no
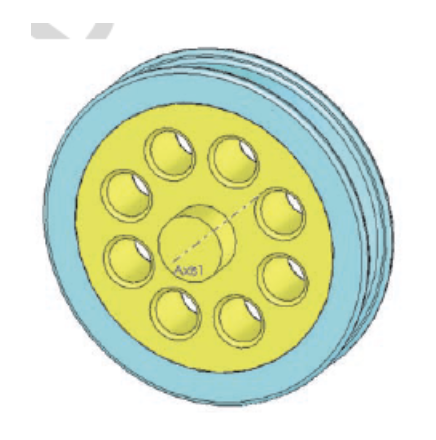
The image shows a wheel assembly, where the rim (blue) is shrunk fit onto the hub (yellow). Using cyclic symmetry only, which symmetry model would be most appropriate?
- Symmetry model not possible
- One Half symmetry
- One Quarter symmetry
- One Eight symmetry
One Eight symmetry