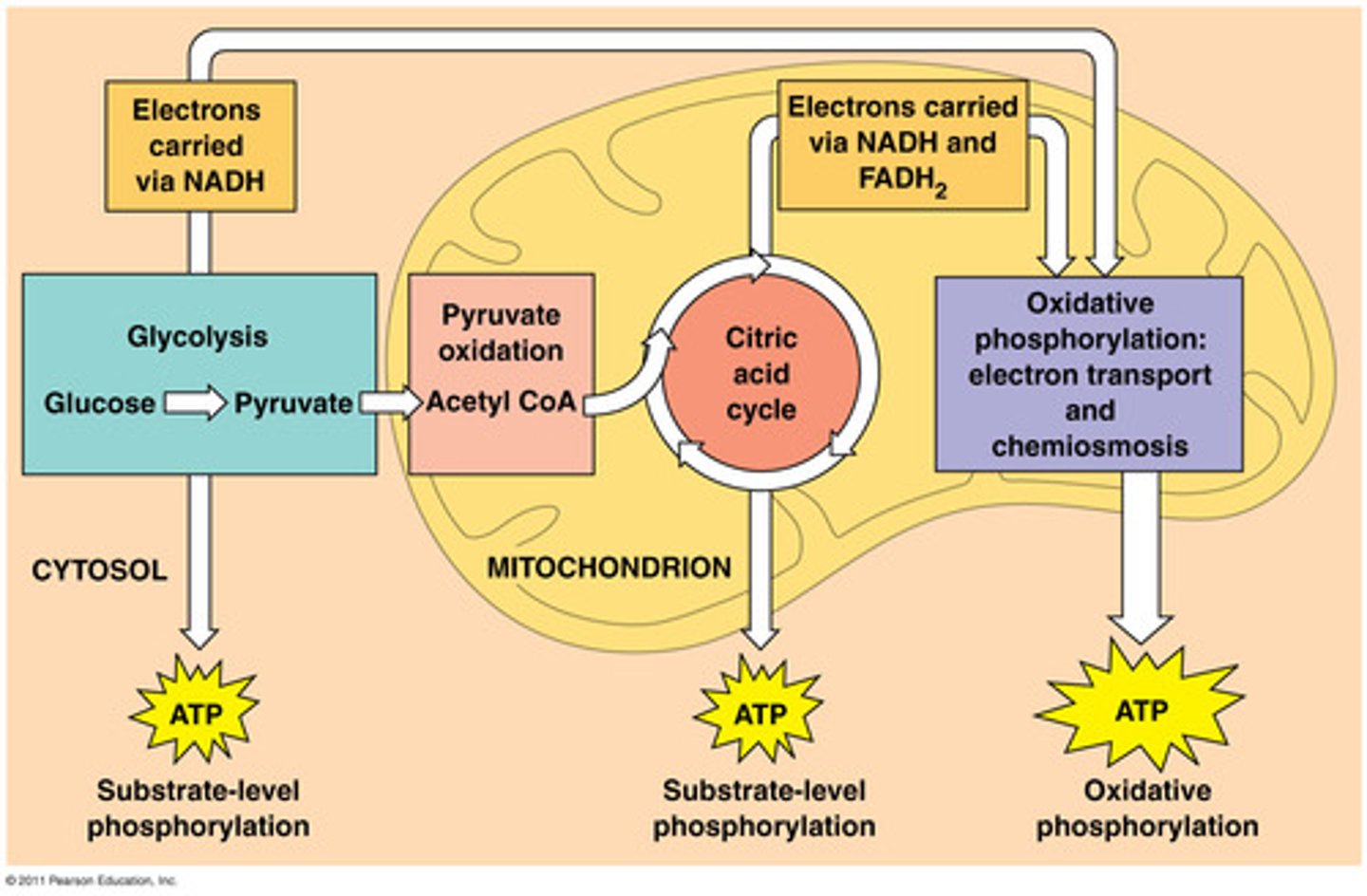
energy processing: CR and photosynthesis
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
there are ____ major bio molecules that living things can create to ____ ____ or break down to ____ ____.
what r they + where do they come from?
3; store energy; obtain energy
- carbs (sugar/starch), proteins, lipids; food
catabolism is ______ LBMs to ____ for an organism.
ex. _____, _____
anabolism is _____ LBMs to ____ for an organism
ex. ____, ____
breaking down; release energy
ex. CR, fermentation
creating; store energy
ex. photosynthesis, fat storage
which LBMs give u energy?
all
what is a bond + what is released when its broken?
energy + electrons
cells cannot use ____ directly in energy metabolism to perform cellular process and need to ____ this energy to ____
LBMs; convert; ATP
cells can use energy from ______ reactions to do what?
catabolic; phosphorylate ADP into ATP (add P)
______/breaking the ______ in ATP can ____ energy for cellular processes.
catabolizing; last phosphate bond; release
ATP to ADP is _____.
ADP to ATP is _____.
why?
catabolism; anabolism
- ATP has more bonds + energy
to get max energy possible out of ____, ____ needs to be present in ___
glucose; oxygen; aerobic CR
oxygen acts as an ____ ___, which is important for and _____ the last step of CR, _____
electron acceptor; powers; oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport chain)
why is O2 an electron acceptor, and what is O2 necessary for?
wants electrons to fill its shell; aerobic CR
glucose (______) is the molecule ____ by autotrophs or ____ by heterotrophs to ____ ___
C6H12O6; produced; eaten; recharge ATP
NAD and FAD can be REDUCED to _____ and ___, and are important in ____
NADH; FADH2; oxidative phosphorylation
CO2 is the ____ ____ during CR
waste product
ATP is the _____ of CR, and cells use it to ____/____ ____
end goal; store/release; energy
CR's first step in using chemical bonds in ____ is called ____.
what happens?
glucose; glycolysis
- glucose split using enzyme (hexokinase) to release energy + intermediate molecules
what are the reactants and products of glycolysis?
R: glucose
P: 2 pyruvate, 4 ATP (NET 2), 2 NADH
glycolysis location + does it require O2?
cytoplasm; no
what is the energy input used to activate glycolysis? where does this take place
2 ATP (net is also 2 ATP); cytoplasm
in step 2 of CR (______), _____ from ____ enters the _______ and is enzymatically converted to ______
pyruvate decarboxylation; pyruvate; glycolysis; mitochondrial matrix (liquid phase); Acetyl Co-A
_____ from pyruvate decarboxylation enters the citric acid/krebs cycle
2 Acetyl Co-A
reactants + products of pyruvate decarboxylation
R: pyruvate
P: 2 acetyl co-a, 2 NADH, 2 CO2
pyruvate decarboxylation location + does it require O2?
mitochondria; yes
step 3 of CR (______) enzymatically converts ______ from the ____ into what? (3)
citric acid/krebs cycle; acetyl co-a; mitochondrial matrix (liquid phase)
1. FADH
2. NADH2
3. ATP
reactants + products of citric acid/krebs cycle
R: acetyl co-a
P: 2-4 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 4 CO2
krebs cycle location + does it require O2?
mitochondrial matrix; yes
reactants + products of ETC
R: 10 NADH, 2 FADH2
P: 34-36 ATP (grand total is 38 tho)
ETC location + does it require O2?
mitochondrial inner membrane; yes
what happens in the krebs cycle pic? idk
theres a substrate and enzyme that converts things many times (ex. NADH > NADH + H) bc ur trying to get ATP out of it
NADH and FADH2 are ____ molecules that carry ____ to ____ ___ in the ___ __
reduced; electrons; membrane proteins; mitochondrial cristae
LEO says GER + examples
Loss of Electrons = Oxidation
NADH to NAD / FADH2 to FAD
Gain of Electrons = Reduction
NAD to NADH / FAD TO FADH2
what makes something reduced or oxidized?
reduction: product has more bonds/electrons/energy
what oxidation/reduction reactions happen in the krebs cycle?
reduction of NAD and FAD to NADH and FADH2
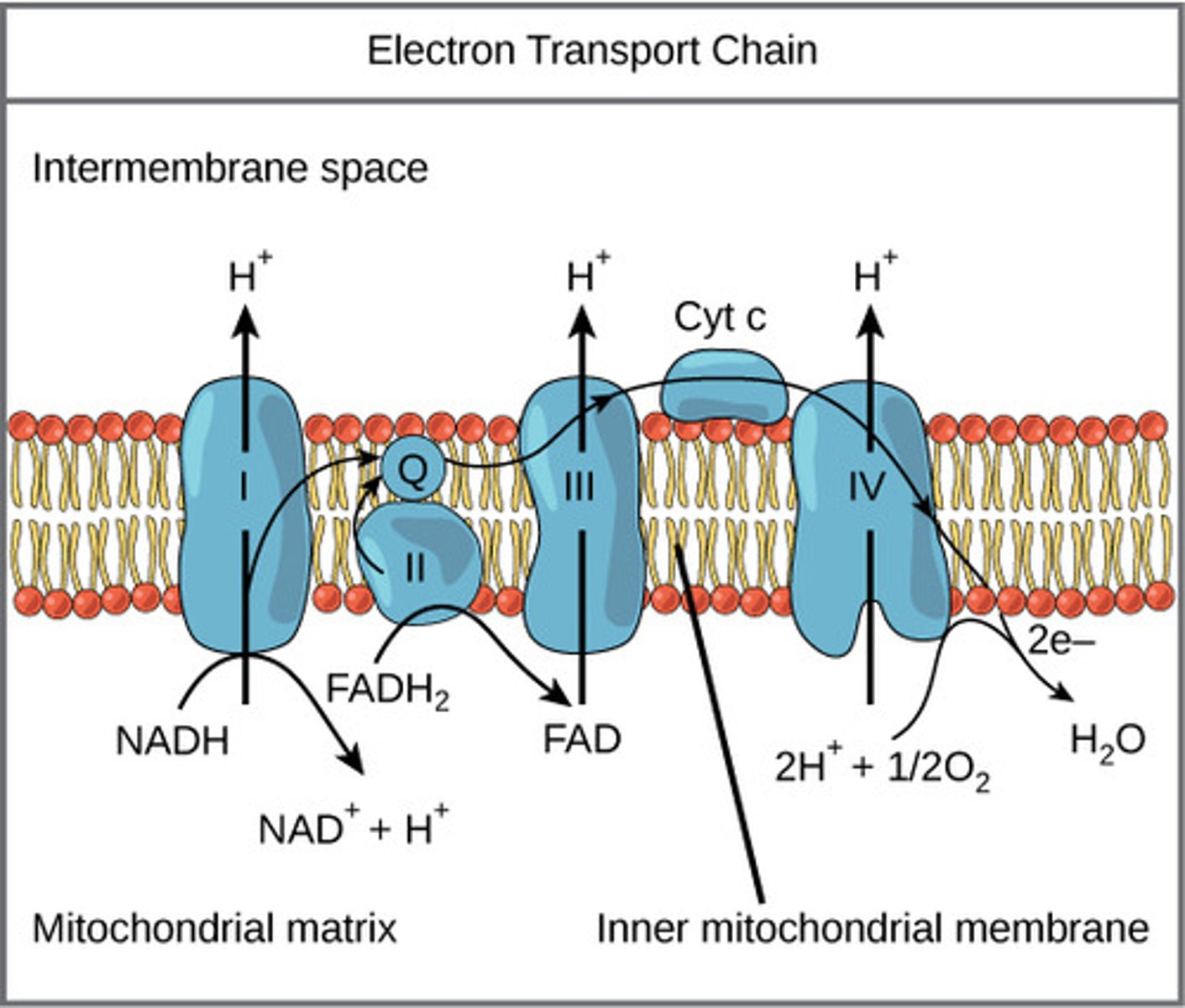
step 4 of CR (_____) takes place via ____. the main purpose of this process is to:
oxidative phosphorylation; Electron Transport Chain (ETC); create a proton gradient
proteins that allow for the transfer of electrons occur where?
on the cristae of the mitochondria
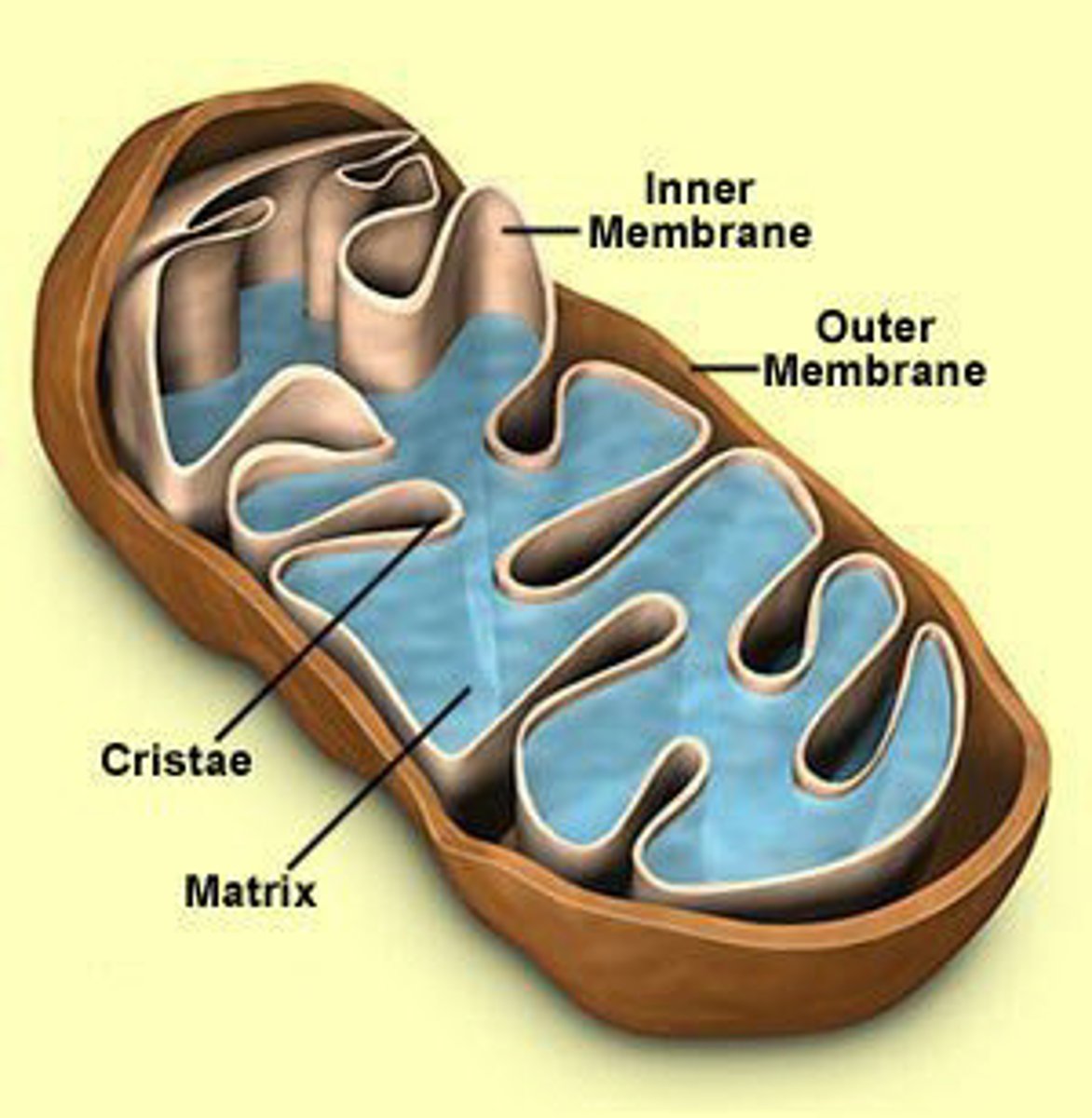
cristae proteins use ___ (____) stored in ___ and ___ to pump ___ into the ____
energy (electrons); NADH; FADH2; H ions; intermembrane space
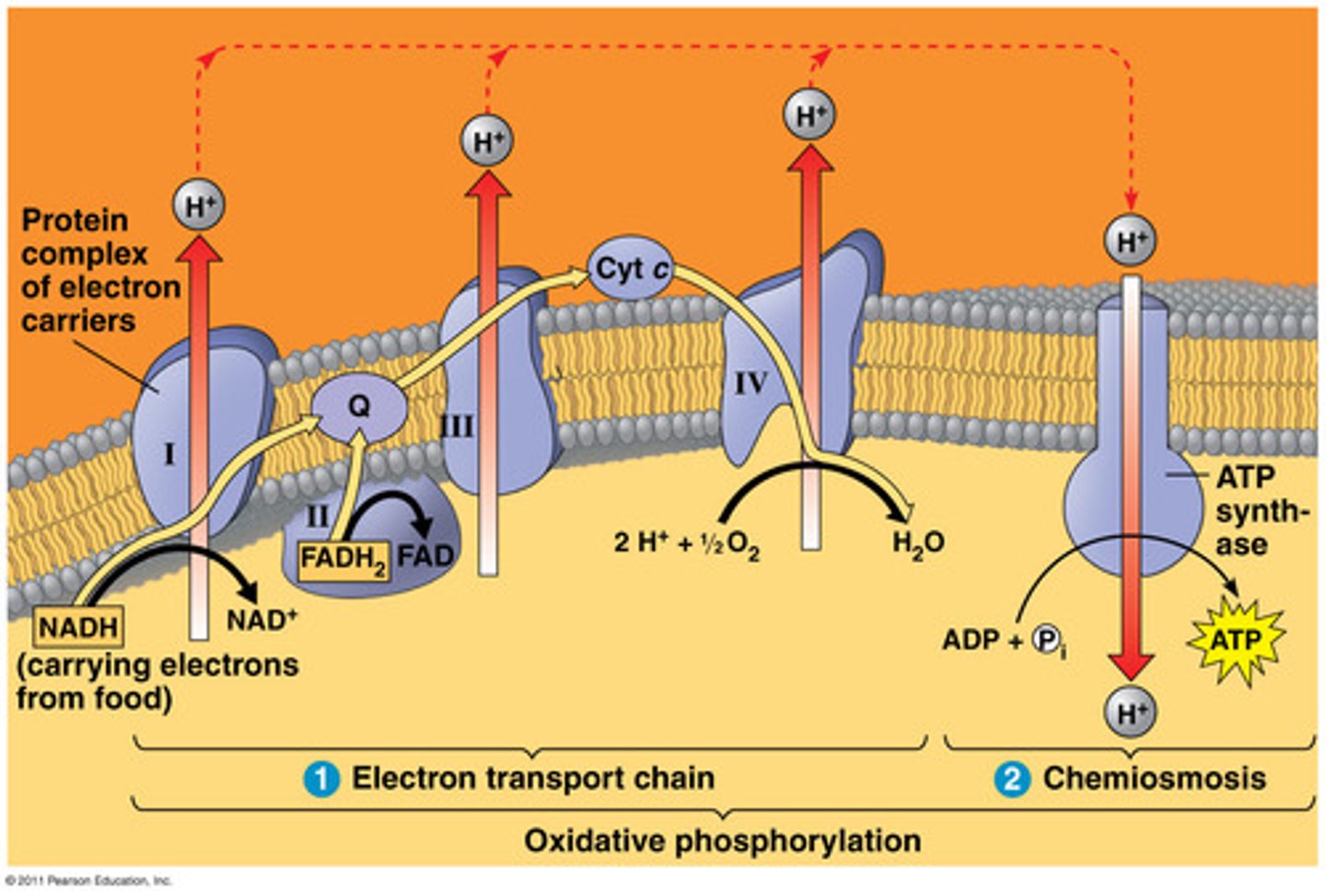
explain the electron transport chain
1. proteins I, III, IV are energized by NADH/FADH2 to pump out H+
2. outside is pos charge, inside is neg, so H tries to go inside
3. H builds up outside mitochondria then goes thru ATP synthase to enter
4. ATP synthase makes ADP + P = ATP
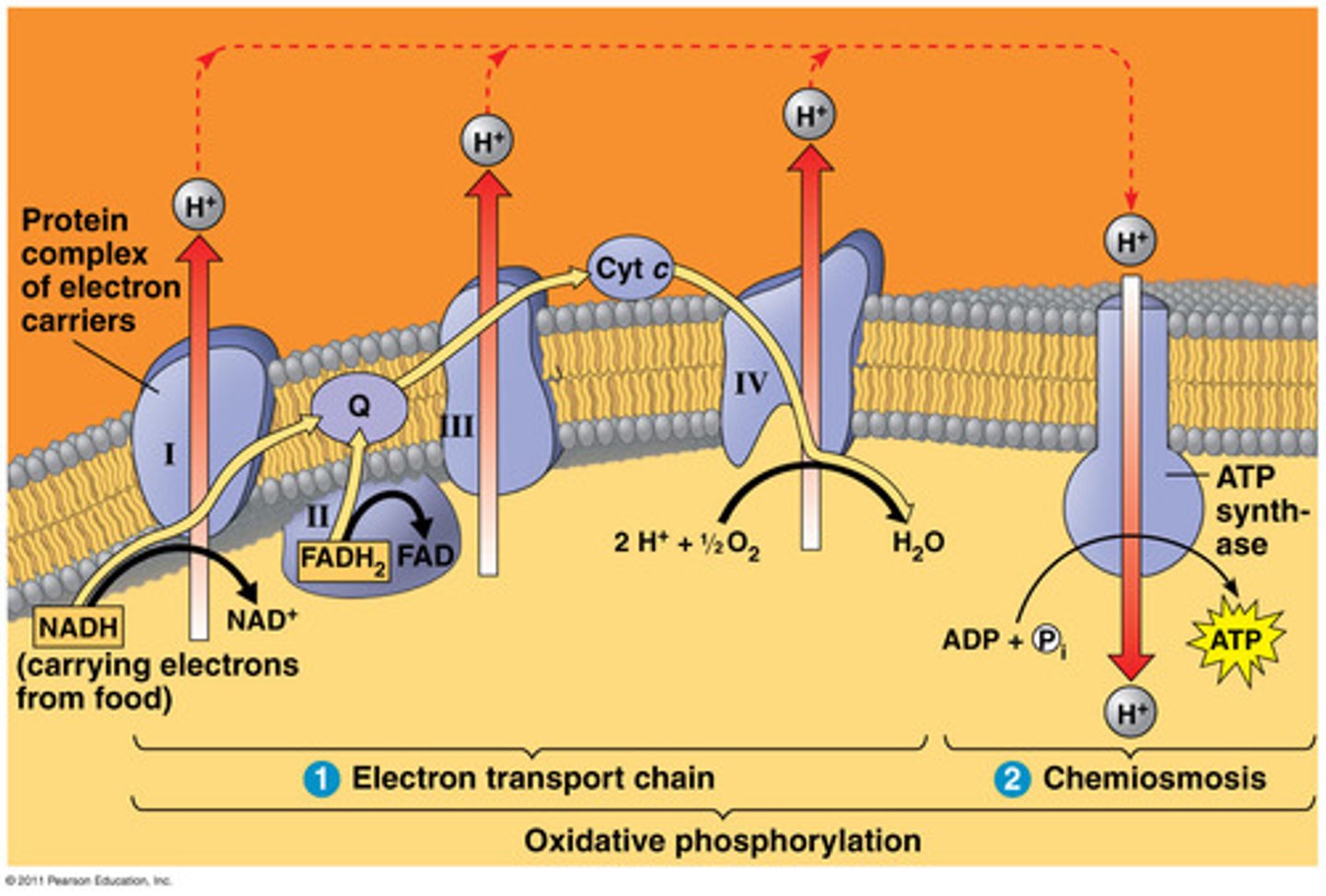
increased number of ___ ions outside the membrane result in an ____ ___.
these protons are forced back into intermembrane space through _____ via ____ and ___
H; electrical gradient
ATP synthase; diffusion; repulsion
reentering H ions into the intermembrane space powers the crank of ____ and forces ____ and ___ together to form ____
ATP synthase; ADP; P; ATP
how do NADH and FADH affect the ETC? idk
- protein I: NADH split to NAD + H, energy is released to pump out H
- protein III: freed electrons go here and FADH2 split to FAD, energy released to pump out H
- protein IV: freed electrons pump out another H
- extra electrons contribute to H2O
action + products in glycolysis (step 1) and pyruvate decarboxylation (step 2)
A: split sugar to make 2 pyruvate
P: 2 ATP, 2 NADH
A: make 2 acetyl co-A
P: 2 NADH, 2 CO2
action + products in kreb's cycle (step 3) and ETC (step 4)
A: acetyl co-a enters kreb's cycle
P: 6 NADH, 2 FADH, 2 ATP
A: NADH2 + FADH enter ETC + are converted to ATP
P: 34 ATP
ETC makes ____ ATP, so how much does CR make altogether from 1 glucose molecule?
34; 38
NADH is produced by what processes?
the only process that produces FADH is?
glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation, krebs cycle
krebs cycle
3 different categories of o2 requirement for cells + examples
obligate aerobes: need O2 to survive
- brain cells
facultative aerobes: can survive with or without O2
- muscle cells
obligate anaerobes: cannot survive in O2
- tetanus
facultative anaerobes (/aerobes ??) can switch strategies depending on:
if O2 is present: cellular respiration
no O2: fermentation
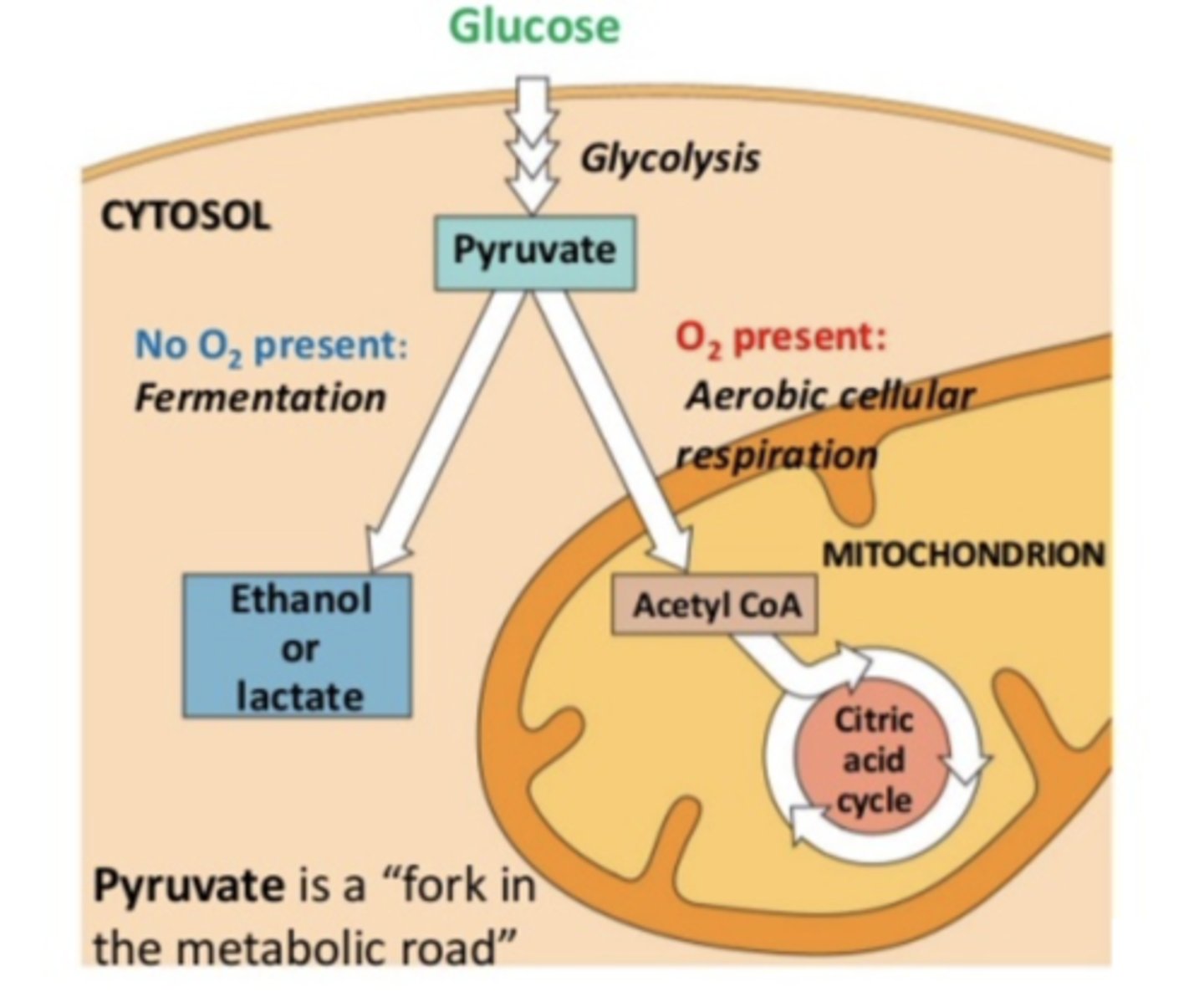
cells that want to metabolize glucose without O2 are at a disadvantage because:
O2 is needed to accept electrons
of the 4 stages of CR, only ____ can proceed w/o oxygen.
glycolysis
fermentation allows cells to produce ATP without ___, whereas cellular respiration requires ___ to produce ATP
O2
how does anaerobic/aerobic conditions affect glycolysis?
glycolysis can produce ATP with OR without O2
- BUT, without O2, you have net 2 ATP TOTAL bc no 3 steps
fermentation consists of ____ and reactions that regenerate ____, which can be reused by ____
glycolysis; NAD
in alcohol fermentation, ____ is converted to ____ in 2 steps, with the first releasing ____.
alcohol fermentation by ____ is used in brewing, baking, winemaking
pyruvate; ethanol; CO2
yeast
alcohol vs lactic acid fermentation idk ask
alcohol: makes 2 ethanol, releases CO2
lactic acid: makes 2 lactate, no CO2
both: make 2 ATP
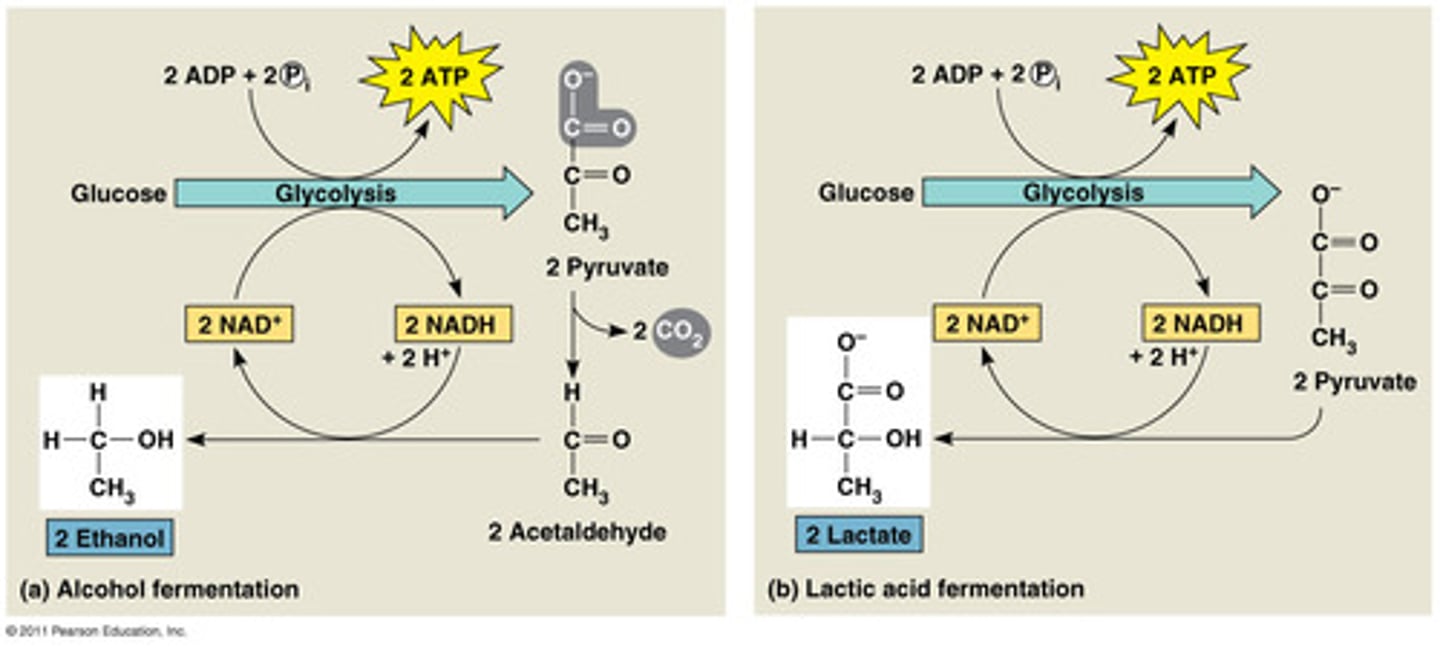
how do u make ethanol from yeast?
yeast + carb + NO O2 = ethanol
- ethanol is yeast's metabolic waste product
in lactic acid fermentation, ____ is reduced to ___, forming ____ as an end product with no release of _____
pyruvate; NADH; lactate; CO2
lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make:
cheese + yogurt
_____ use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when ___ is scarce.
why do ur muscles burn when u exercise?
muscle cells; O2
- lactic acid buildup bc ^^^^^
fermentation vs cellular respiration
FERMENTATION:
- organic molecule (pyruvate) as final electron acceptor
- produces less ATP
CR:
- O2 as final electron acceptor
- produces MUCH more ATP
BOTH:
- use glycolysis to oxidize glucose + other organic fuels to pyruvate
yeast and bacteria are ______, meaning that they can survive using either ____ or ___.
facultative anaerobes; fermentation; CR
how can facultative anaerobes live?
how is pyruvate affecting it?
prefer to live w/o O2, but can survive in its presence
- pyruvate is fork in metabolic road that leads to 2 diff catabolic routes (fermentation, CR)
3 diff btwn cell respiration + fermentation (slide in class)
CR:
38 ATP
aerobic (O2 required except in glycolysis)
waste - CO2, water
FERM:
2 ATP
anaerobic (O2 not required
waste - CO2, lactic acid, ethanol
photosynthesis is the process of harnessing ___ ___ and forming:
organic molecules (_____) and ____
from:
____ and ____
glucose; O2
CO2; water
what is the photosynthesis equation?
what is it in reverse?
6CO2 + 6H2O -sunlight-> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Cellular Respiration:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ---> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
photosynthesis energy is stored in the bonds of _____ (4) and can be used by ____ and ___ organisms for life processes
CO2, O2, water, glucose
autotrophic; heterotrophic
how do plants absorb the materials they need to make glucose and other macros? (2)
leaves - absorb CO2 + sunlight
roots - absorb water + electrolytes
the energy in sunlight gives a plant the energy to rearrange and form ____ to make molecules like ____ (_______)
bonds; glucose; light dependent reactions
leaves are like solar panels + lungs. why?
1. solar panels that absorb light
2. lungs that convert O2 to CO2
what goes into light dependent vs light independent/calvin reactions and what comes out?
light dependent:
water + sunlight = O2
light independent/calvin
CO2 -> sugar
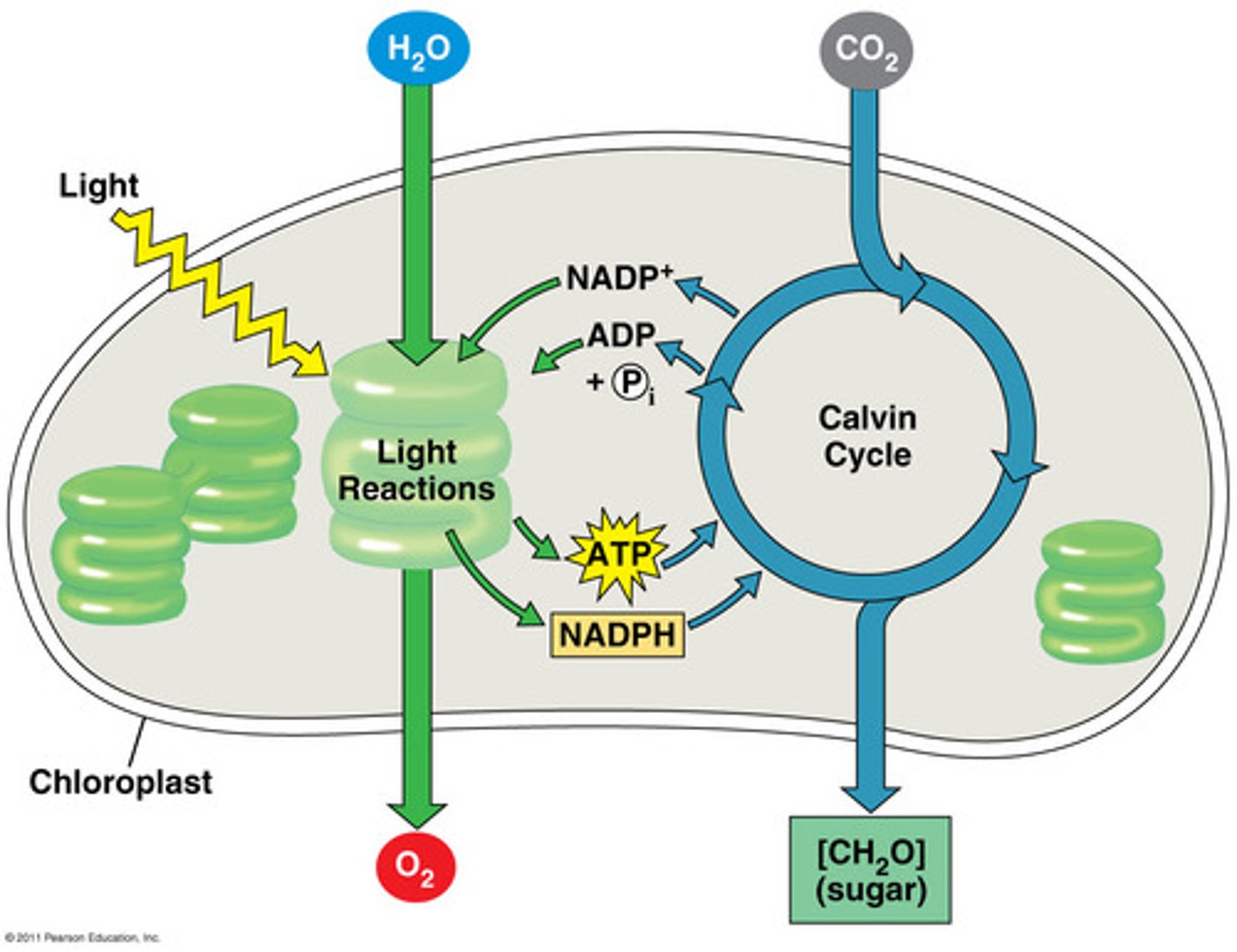
what energy molecules come from light dependent vs light independent /calvin reactions?
INDEPENDENT/CALVIN gives uncharged ADP and NADP+ to dependent
DEPENDENT sends charged ATP and NADPH back
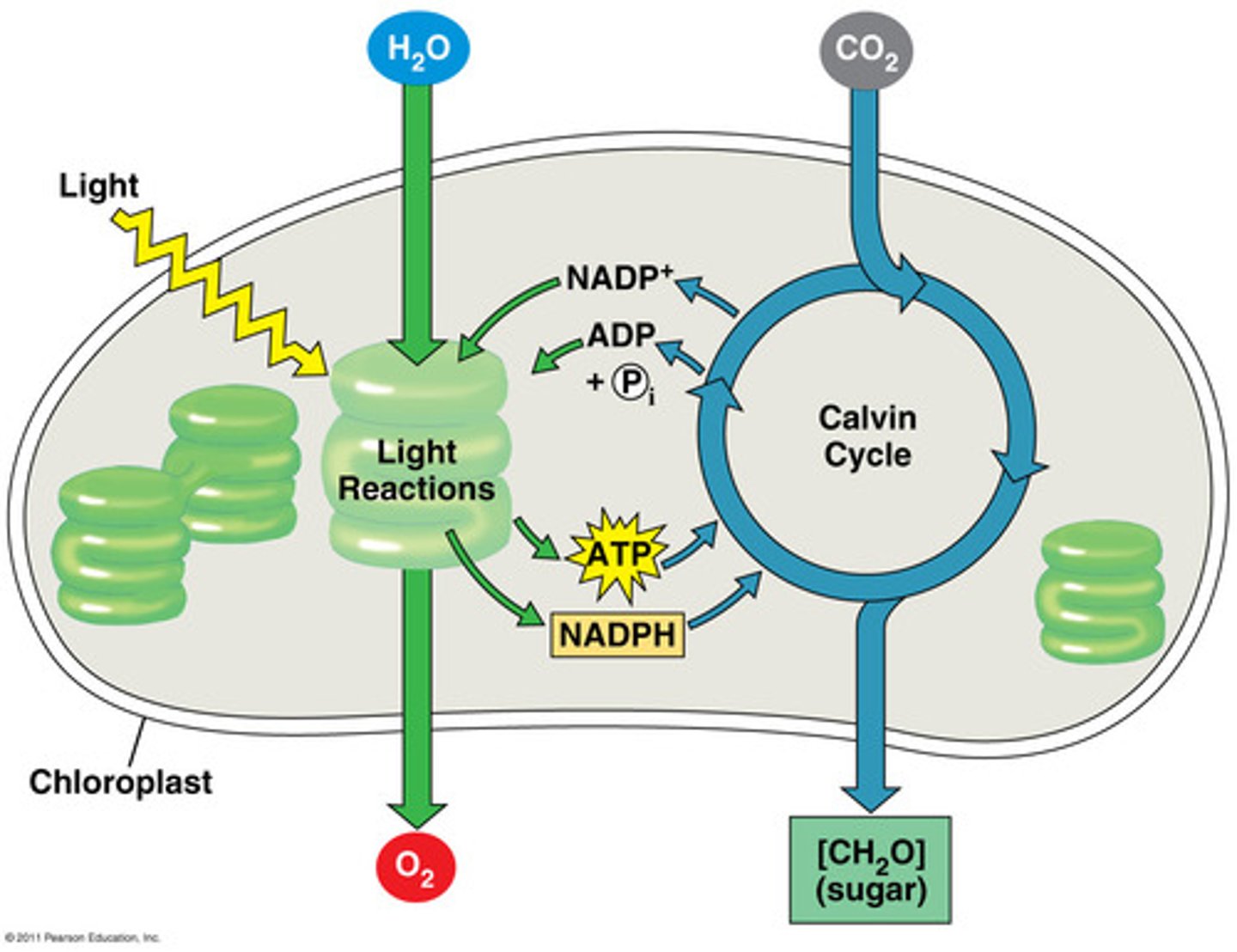
when do the light-dependent and light-independent/calvin reactions take place?
DEPENDENT: day
INDEPENDENT/calvin: day AND night
2 things plants use sugar for
its own energy + structure
why does sunlight reduce molecules (ATP, NADPH) during photosynthesis?
to carry energy into light independent/calvin
_____ are the start of photosynthesis, taking place in ____
light DEPENDENT reactions; chloroplasts
granum, a stack of ____, in chloroplasts contain _____, the ___ pigment that absorbs ____ ___
thylakoids; chlorophyll; green; light energy
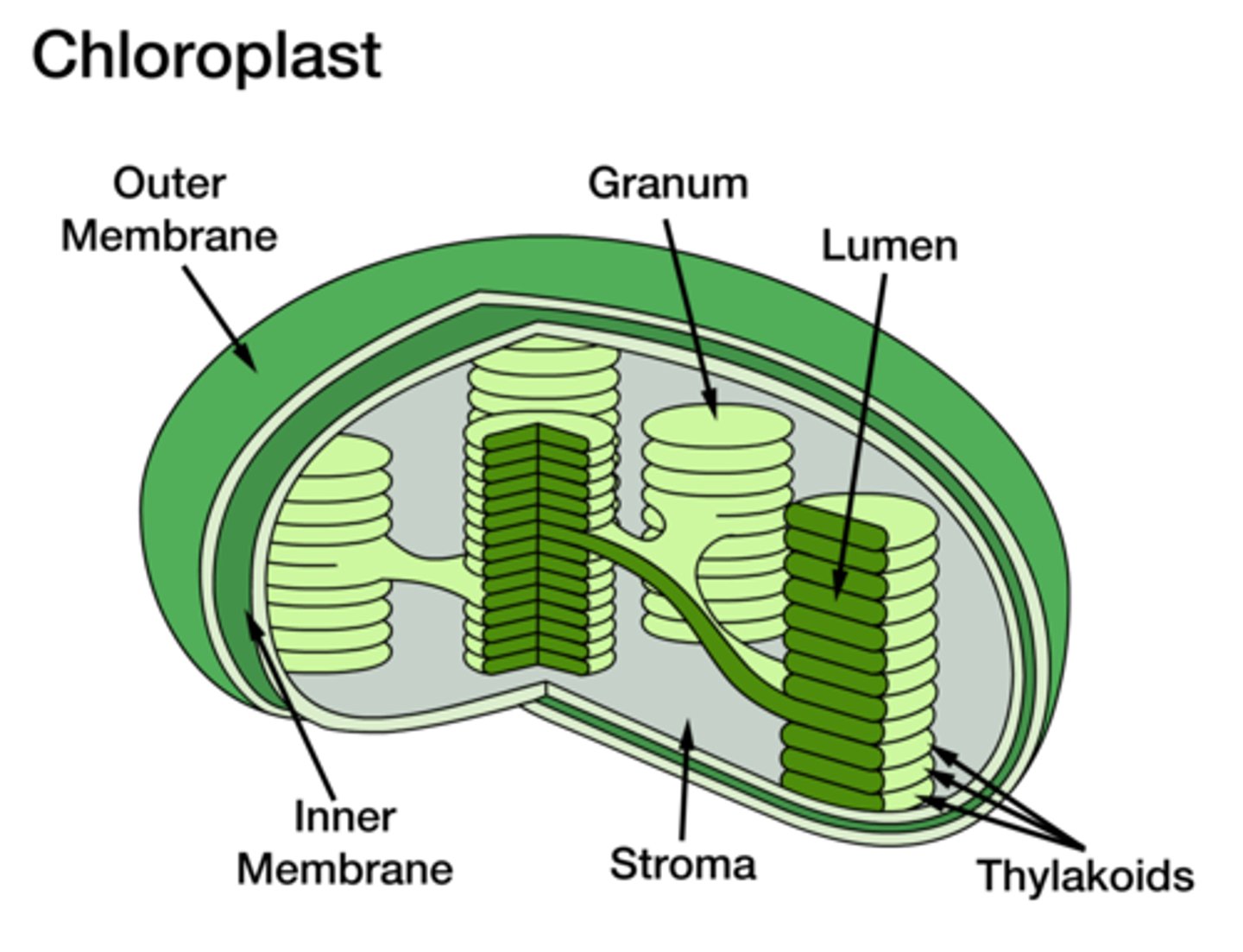
thylakoids and the liquid ____ is where _____ happen in the chloroplast
stroma; light-reactions
the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a suggests that ____ and ___ light work best for photosynthesis
violet-blue; red
longest vs shortest color wavelength
highest vs lowest energy color
ROYGBIV
longest: red
highest energy: violet
what does chlorophyll's absorption spectra show?
why is this?
HIGH absorption: violet-blue + red
LOW absorption: green-yellow
- plants r mostly green bc of chlorophyll, which reflects away green-yellow light
what was Engelmann's action spectrum of photosynthesis experiment?
- exposed sections of algae filament to diff light wavelengths
- sections receiving wavelengths good for photosynthesis produced high O2
- O2 production measured by growth of aerobic bacteria; thicker bacteria = more O2
-- rate of photosynthesis highest in violet-blue, lowest in green-yellow
when a pigment absorbs light, it goes from a ___ state to a ___, ___ state.
if illuminated, chlorophyll will ____, giving off ___ and heat
ground; unstable; excited
fluoresce, light
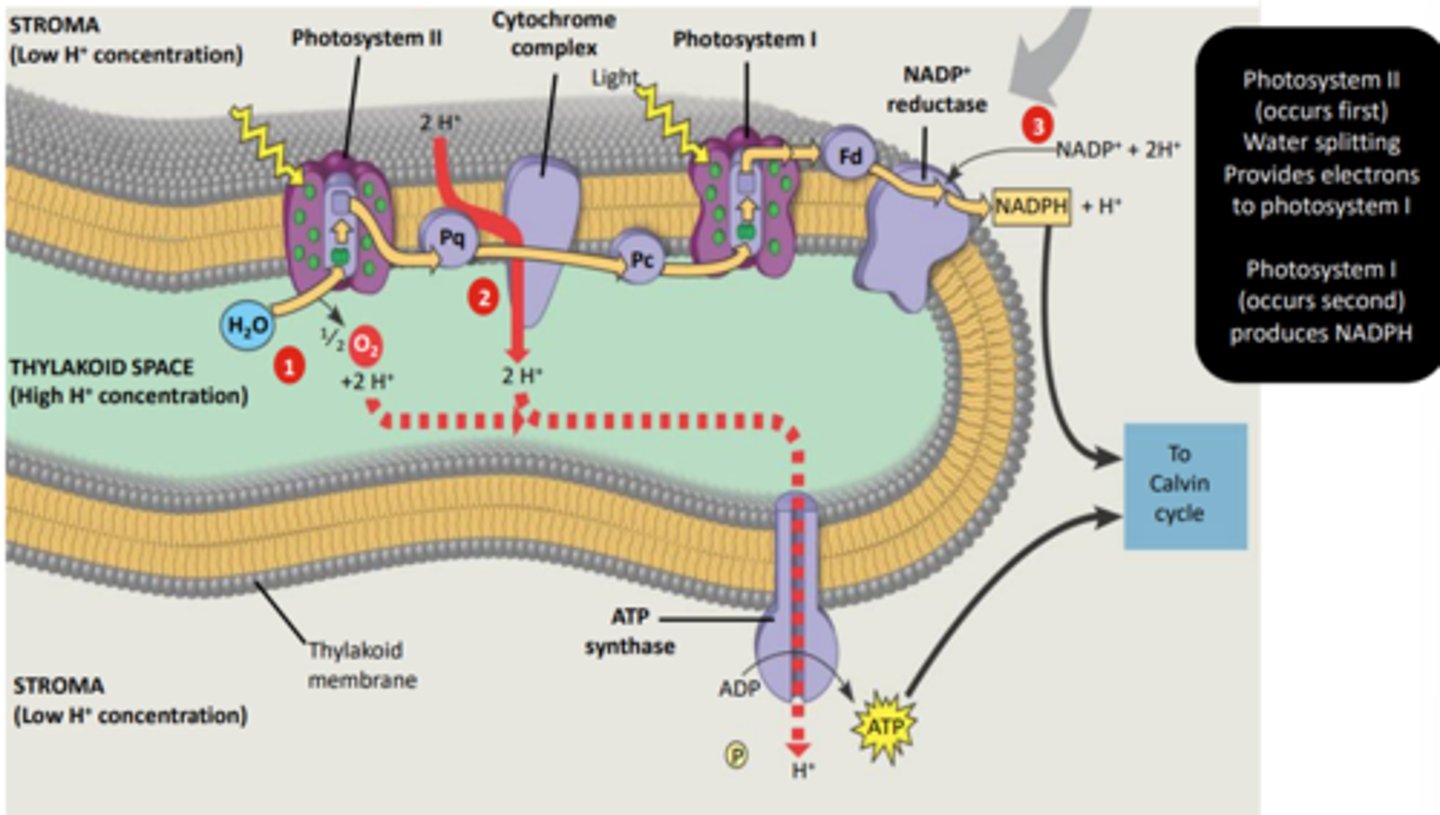
light DEPENDENT reactions' 2 photosystems + what happens
photosystem II (FIRST)
- light absorbed by chlorophyll splits water to free O2, electrons, and H
- free O2 leaves the leaves
photosystem I (LAST)
- light + electrons from PSII reduce NADP to NADPH
plants try to make ___ ___, because their movement powers ATP synthase to make ____
H ions; ATP
how do PSII and PSI work together to make ATP?
1. light comes in
2. PSII splits water into H + O2 + electrons
3. electrons energizes PQ to pull in H
4. PSI uses electrons + light to turn NAD into NADPH
5. many Hs make pos charge inside and neg outside
6. Hs leave thru ATP synthase and make ADP into ATP
- makes O2, NADPH, and ATP
in light INDEPENDENT reactions (______) ____ is absorbed by the leaves
(calvin cycle); CO2
in light INDEPENDENT reactions/calvin cycle, CO2 is converted into _____ using what?
glucose; ATP + NADPH from light DEPENDENT
the light dependent and light independent/calvin reactions are ____, and NADP and ADP go back to be ____ in the light reactions
re-energized
the energy in ATP/NADPH from LD reactions drives:
light independent/calvin reactions