RP 4: Determination of the Young modulus by a simple method.
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is the method used to determine the Young modulus of a wire? (9)
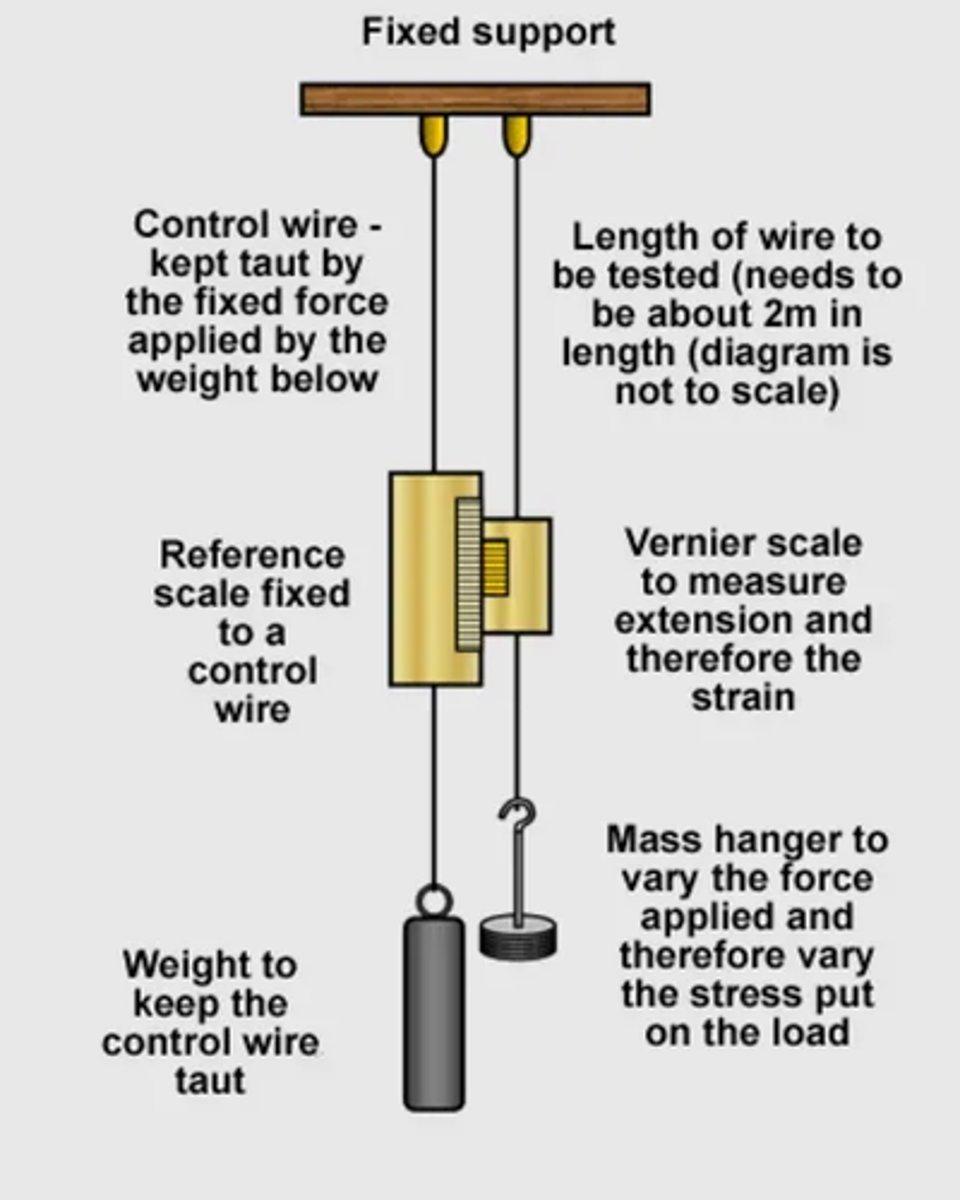
- Secure a long steel test wire at one end to a rigid support such as a ceiling or a clamp stand bolted to a wall bracket.
- Attach a scale to the wire and place a vernier scale alongside it, ensuring it can move freely as the wire stretches.
- Measure the original length of the test wire between the fixed point and the marker (usually the vernier scale or pointer) using a metre ruler.
- Add a mass hanger with 1 kg of slotted masses to the test wire to ensure it is taut and remove any initial kinks. Record the initial scale reading.
- Add additional 1 kg masses incrementally, each time recording the new scale reading and calculating the extension by subtracting the initial reading.
- Repeat the process up to around 8 kg, recording the extension for each mass added.
- Repeat the experiment at least twice more for improved accuracy and calculate the mean extension for each load.
- Measure the diameter of the wire at multiple points along its length using a micrometer and calculate the average diameter.
- Use the data to calculate the Young modulus from the gradient of a graph of force against extension.
What equipment is needed to determine the Young modulus of a wire? (9)
- Steel test wire (approximately 1.5 m).
- Comparison wire (same length and material as test wire).
- Beam or clamp stand fixed securely to a wall or ceiling.
- Slotted masses (1 kg) and mass holders.
- Main scale and vernier scale.
- Metre ruler.
- Micrometer.
- Safety goggles.
- Sand tray or cushioning tray (for catching falling masses).
What does the setup used to determine the Young modulus of a wire look like? (3)
What is the independent variable in the Young modulus experiment? (1)
The independent variable is the load or force applied to the wire.
What is the dependent variable in the Young modulus experiment? (1)
The dependent variable is the extension of the wire.
What are the controlled variables in the Young modulus experiment? (4)
- Controlled variables include the wire's material.
- Another controlled variable is the wire's diameter.
- Another variable is the wire's initial length.
- The final controlled variable is the ambient temperature.
How is the cross-sectional area of the wire calculated? (1)
First calculate the cross-sectional area (A) of the wire using A = (pi × d²)/4, where d is the average diameter.
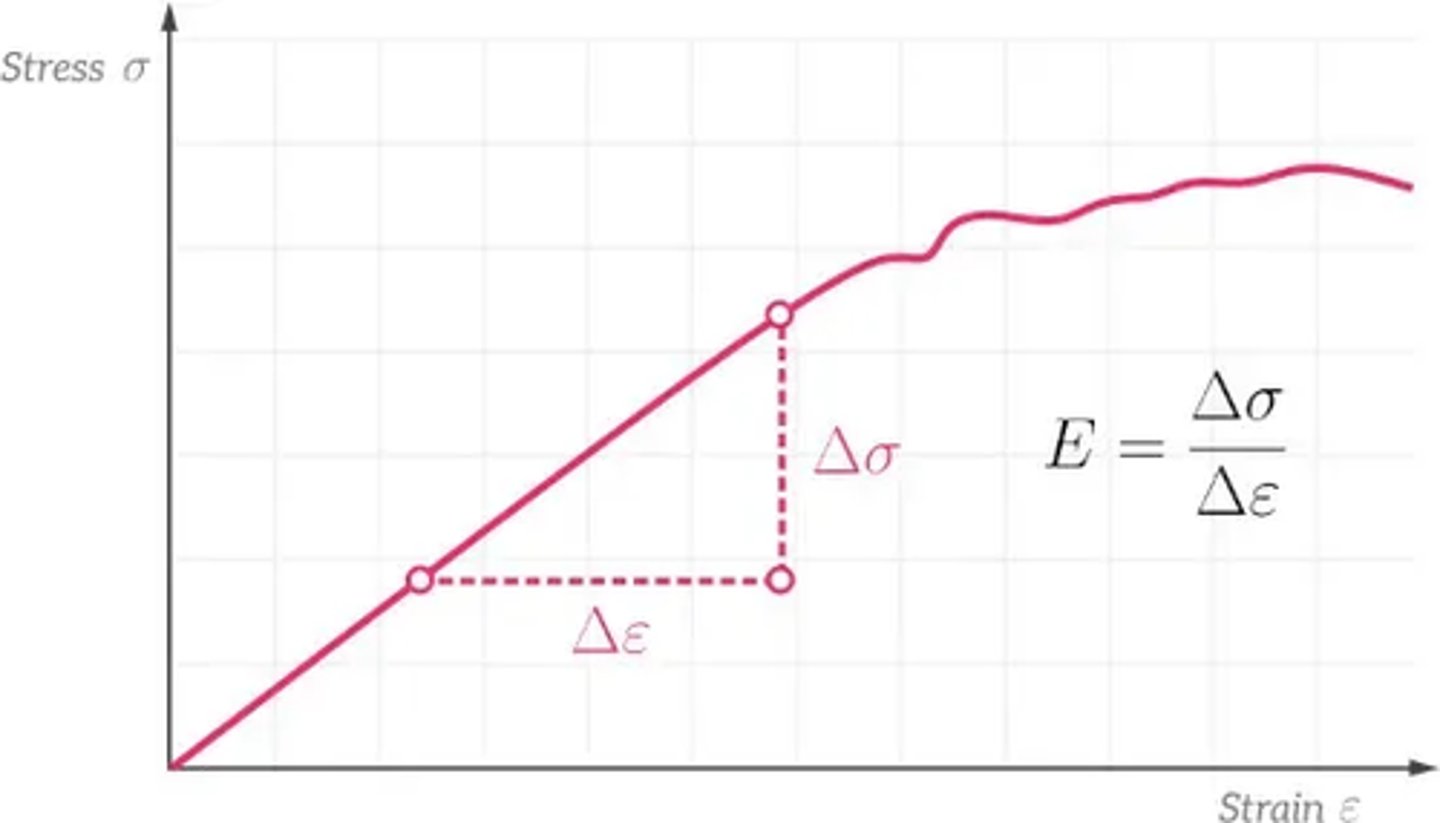
What graph is plotted in the Young modulus experiment and how is the gradient found? (1)
Plot a graph of force (F) against extension (e) and find the gradient (G) of the best-fit line.
What does the graph plotted in the Young modulus experiment look like? (3)
What formula is used to calculate the Young modulus from experimental measurements? (2)
- The formula is
E = (l × G) / A.
- Where E is the Young modulus, l is the original length of the wire, G is the gradient of the graph plotted, and A is its cross-sectional area.
How is the Young modulus formula derived from stress and strain? (1)
E = stress/strain = (Force/Area)/(extension/original length) = (Force × original length)/(Area × extension) = (original length × gradient)/Area.
How is the energy per unit volume calculated in this experiment? (1)
The energy per unit volume is calculated by the area under the graph as it equals 0.5 × stress × strain.
What is one safety precaution in the Young modulus experiment? (2)
- Safety goggles must be worn because the wire is stretched under high tension and could snap suddenly.
- This could potentially cause injury from recoiling wire or falling weights.
How does using a comparison wire improve the Young modulus experiment? (1)
Use a comparison wire to account for sagging or thermal expansion of the support structure.
How can the experiment be made safer if the wire breaks? (1)
Place a sand tray or soft pad below the weights to cushion any falling masses if the wire breaks.
How can the accuracy of extension measurements be improved? (1)
Use a long wire to reduce percentage uncertainty in the measurement of extension.