Untitled
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:05 AM on 9/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
ecosystem
a community of different species interacting together and with the chemical and physical factors making up its non-living environment
2
New cards
biosphere
part of Earth in which life exists including land, water, and air or atmosphere
3
New cards
species
groups of organisms that can mate and produce fertile offspring
4
New cards
community
the population of all species living and interacting in an area
5
New cards
habitat
the place where an organism or a population lives
6
New cards
niche
the total way of life or role of a species in an ecosystem
7
New cards
ecotone
A transitional zone where ecosystems meet.
8
New cards
common
usual; shared by all
9
New cards
productivity
the rate of production of energy from a source
10
New cards
autotrophs/producers
base level of the pyramid; organisms that create their own food
11
New cards
organic
Contains carbon; living matter
12
New cards
inorganic
Does not contain carbon; non living
13
New cards
heterotrophs/consumers
organisms that consume other organisms
14
New cards
10% rule
transfer of energy from one trophic level to the next
15
New cards
photosynthesis
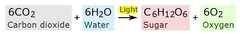
16
New cards
climate
Overall weather in an area over a long period of time
17
New cards
primary succession
follows a disturbance so severe that no vegetation or soil life remains; no soil, slow
18
New cards
secondary succession
follows a disturbance that alters an existing community but does not destroy all living things or living things in soil; faster process, begins with natural disaster
19
New cards
aquatic succession
when a body of water is taken over by vegetation; water becomes shallow, less water volume, more fertile
20
New cards
invasive species
species that can live and/or thrive outside of their normal habitat
21
New cards
climax community
a community that remains in place with little modifications until another disturbance restarts succession
22
New cards
food pyramid
a hierarchy of food chains with the principle predator at the top
23
New cards
decomposer
consume all trophic levels; fungi and bacteria; break down material into simpler elements that can be recycled back into the ecosystem
24
New cards
trophic level
producers/autotrophs, consumers
25
New cards
biome
contains characteristic communities of plants and animals that result from, and are adapted to, its climate
26
New cards
indicator species
a plant or animal that, by its presence, abundance, scarcity, or chemical composition, demonstrates that some distinctive aspect of the character or quality of an ecosystem is present
27
New cards
keystone species
a species whose activities have a particularly significant role in determining community structure
28
New cards
umbrella species
species selected for making conservation-related decisions, typically because protecting these species indirectly protects the many other species that make up the ecological community of its habitat
29
New cards
commensalism
one organism benefits, the other one is not helped no harmed
30
New cards
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
31
New cards
population density
number of individuals in a population per unit area
32
New cards
energy
flows in one direction through ecosystems
33
New cards
exponential growth
when a population increases by a fixed percentage each year
34
New cards
nitrification
ammonia (NH3) is converted to nitrate ions (NO3)
35
New cards
denitrification
Conversion of nitrates into nitrogen gas
36
New cards
ammonification
decomposers convert organic waste into ammonia
37
New cards
resource partitioning
using the resources in different ways, places, or at different times; can reduce the negative impact of competition on survival
38
New cards
interspecific competition
competition between members of different species
39
New cards
intraspecific competition
competition between members of the same species
40
New cards
detritus
Dead organic matter
41
New cards
limiting factors
determine the carrying capacity of a population
42
New cards
euphotic zone
the upper layers of water where photosynthesis is largely confined because sunlight can penetrate
43
New cards
eutrophication
occurs when a body of water is enriched in nutrients which causes algal bloom; this leads to a decrease in oxygen which kills all organisms
44
New cards
thermal stratification
temperature changes sharply with depth
45
New cards
groundwater
the water that is beneath Earth's surface
46
New cards
surface water
water that collects on the surface of the ground.
47
New cards
oligotrophic
Describes a lake with a low level of productivity
48
New cards
transpiration
water enters the atmosphere by the release of water vapor by plants through their leaves
49
New cards
evapotranspiration
Evaporation of water from soil plus transpiration from plants
50
New cards
infiltration/run off
water returns to earth through streams, rivers, lakes, etc.; some precipitation and surface water soaks down through soil
51
New cards
turbidity
increased sediment in waterways can reduce light infiltration, which can affect primary producers and visual predators
52
New cards
abiotic
Non-living things
53
New cards
biotic
living things
54
New cards
zooplankton
small free-floating animals that form part of plankton
55
New cards
phytoplankton
photosynthetic algae found near the surface of the ocean
56
New cards
mutualism
both organisms benefit from the relationship
57
New cards
parasitism
one organism benefits, the other is harmed
58
New cards
pioneer species
First species to populate an area during primary succession
59
New cards
reservoir
reserves, large supply
60
New cards
watershed
An ecosystem where all water runoff drains into a single body of water
61
New cards
riparian
Having to do with the banks of a body of water
62
New cards
net primary productivity
biomass created from photosynthesis

63
New cards
gross primary productivity
all the energy plants take in from the sun for photosynthesis
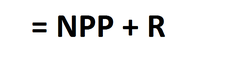
64
New cards
flood plains
a plain built up by stream deposition
65
New cards
wetlands
a lowland area, such as a marsh or swamp, that is saturated with moisture, especially when regarded as the natural habitat of wildlife.
66
New cards
micronutrients
vitamins and minerals
67
New cards
macronutrients
carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
68
New cards
cellular respiration
the process by which cells use oxygen to produce energy from food
69
New cards
detritivore
organism that feeds on plant and animal remains and other dead matter
70
New cards
energy flow
The passage of energy through the components of an ecosystem
71
New cards
density-dependent factors
limiting factors are influenced by the population density
72
New cards
density-independent factors
limiting factors are not influenced by population density