BIOL 300 Class 2.4: General Recombination
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the purpose of Homologous Recombination?
It increases diversity as well as repairs DNA damage and restart stalled replication forks.
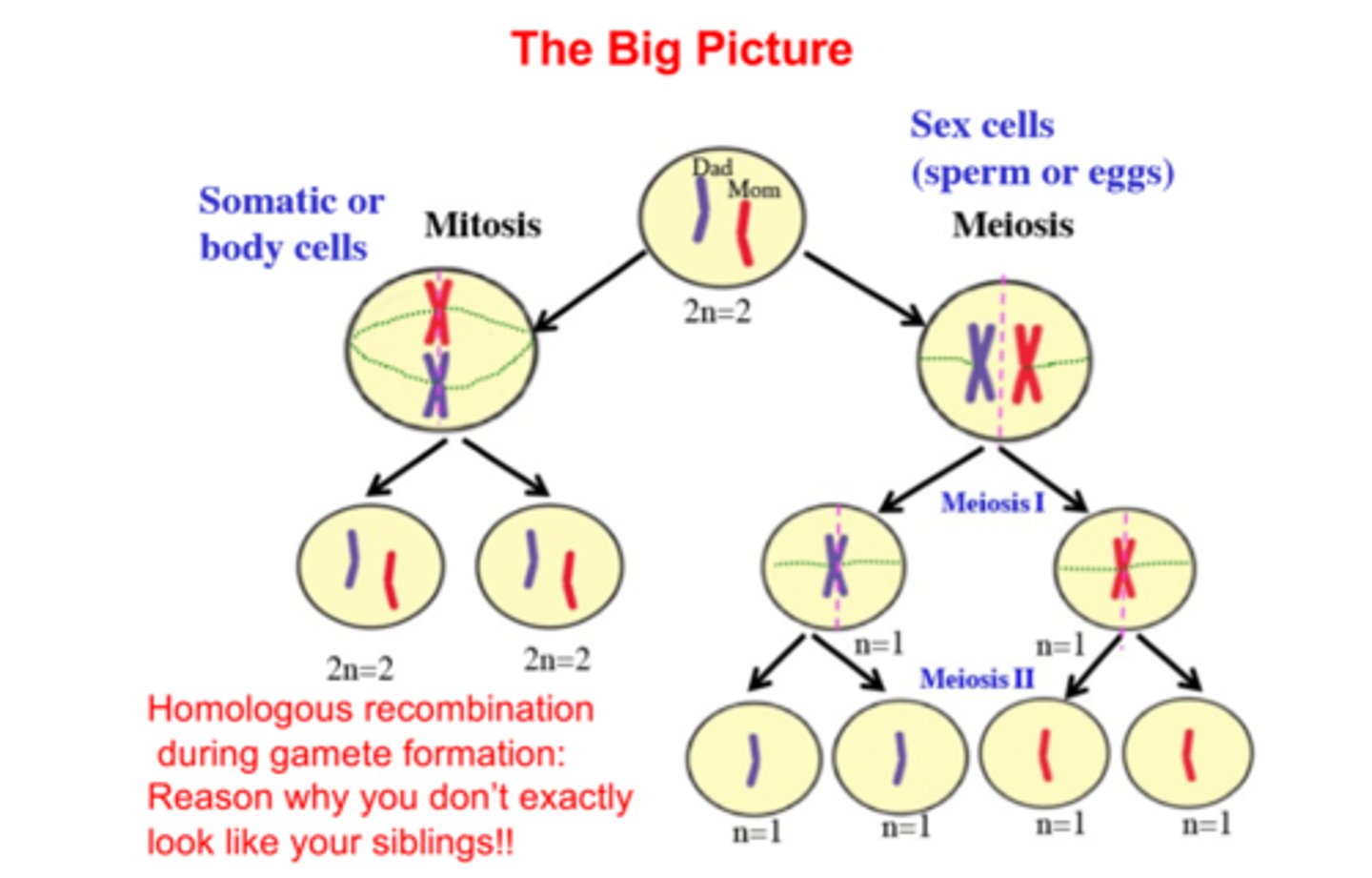
What is recombination in Meiosis? When does it occur?
It occurs as cross overs between two non-sister chromatids, it occurs during prophase 1. Each chromosome is then replicated.
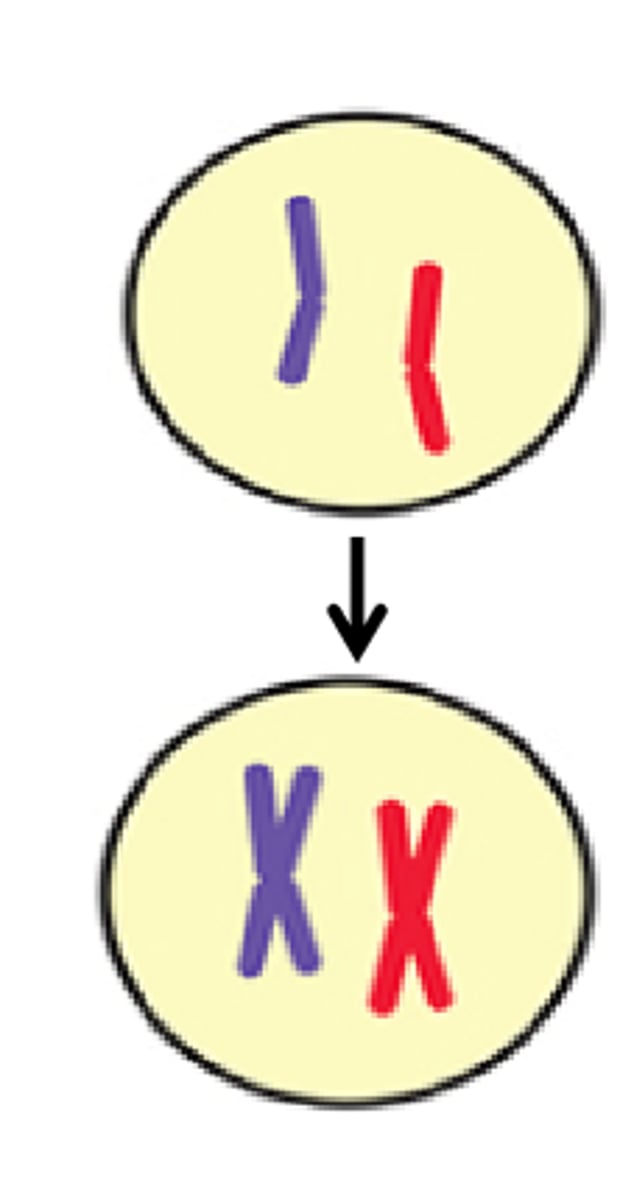
What is the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis?
Mitosis results in two daughter cells identical to the parent cell while meiosis results in 4 genetically diverse daughter cells.
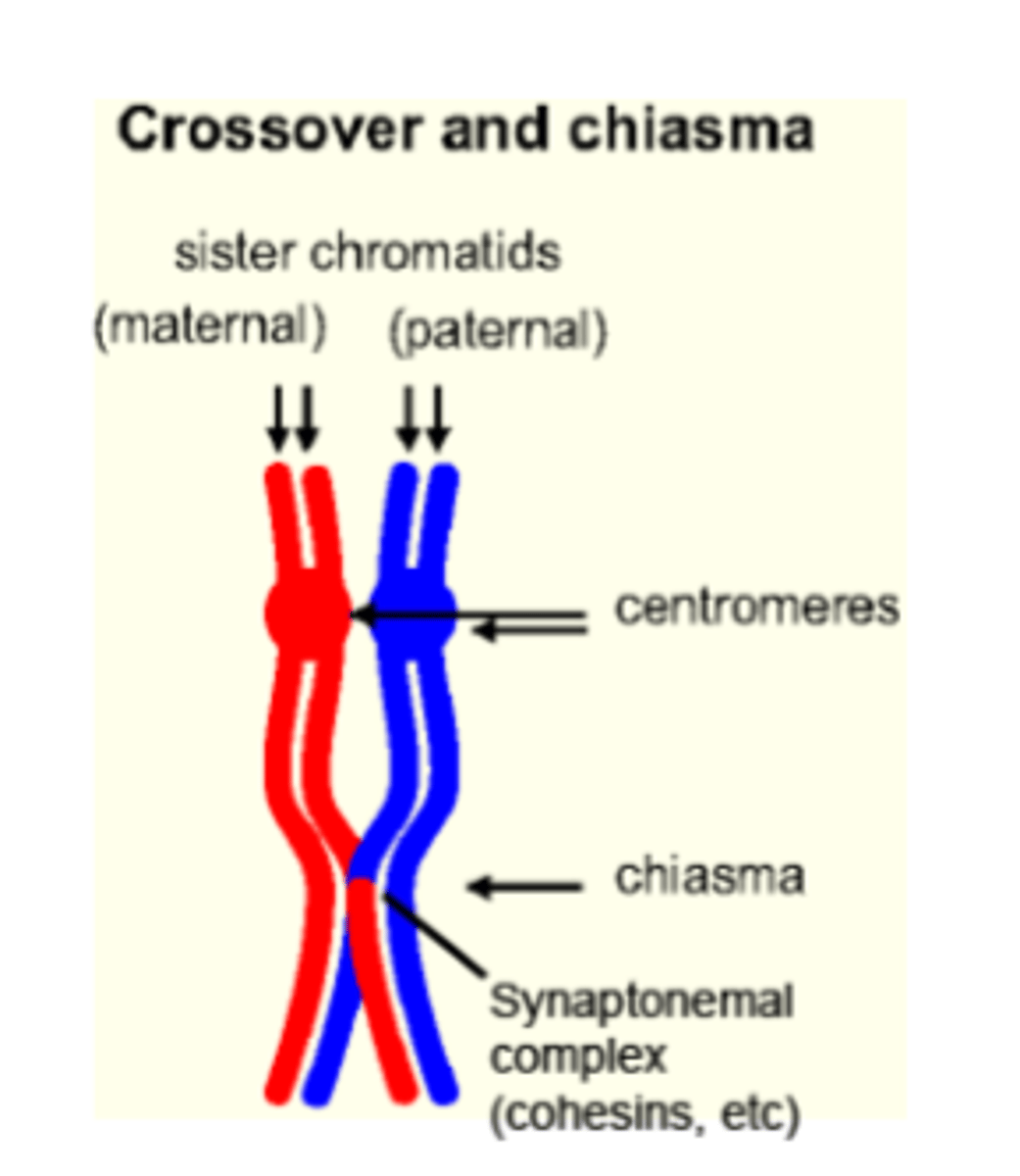
What is the Synaptonemal complex?
It is a complex of proteins that holds homologous chromosomes together; produced after recombination
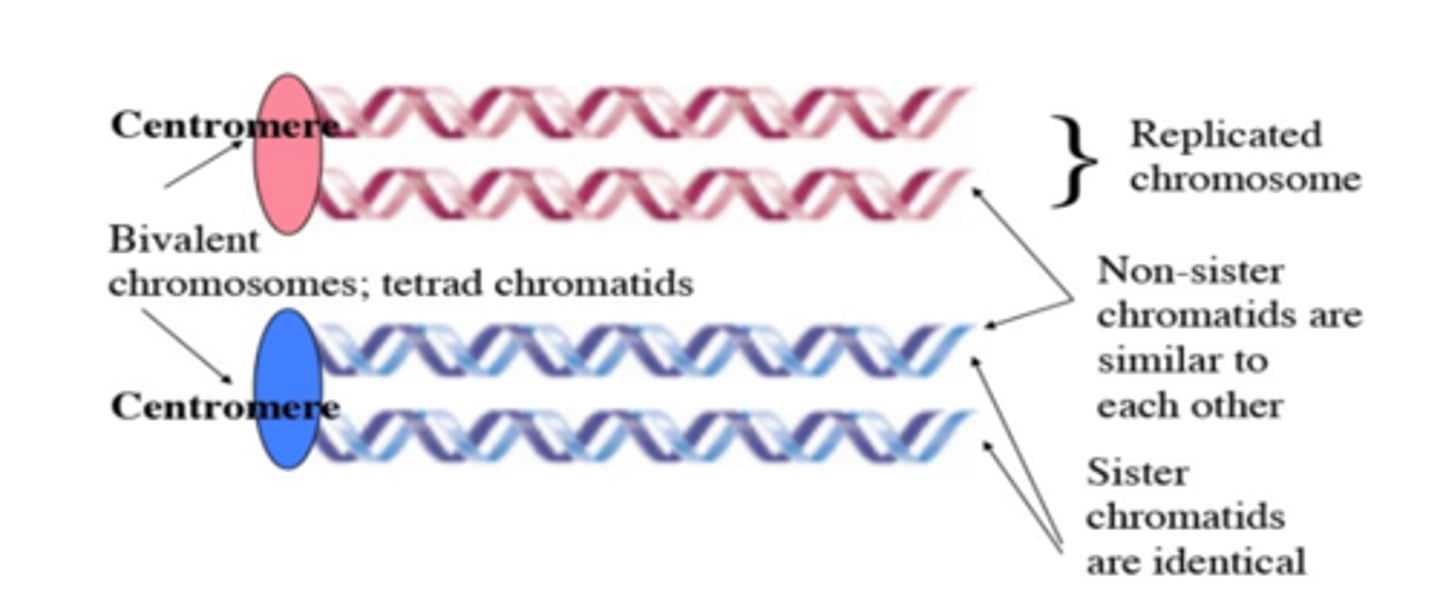
How big of a region is needed for Homologous recombination?
A region that is bigger than 75 base pairs of sequence homology is needed.
When does Homologous Chromosome occur during Meosis 1?
It occurs as stages within Prophase 1
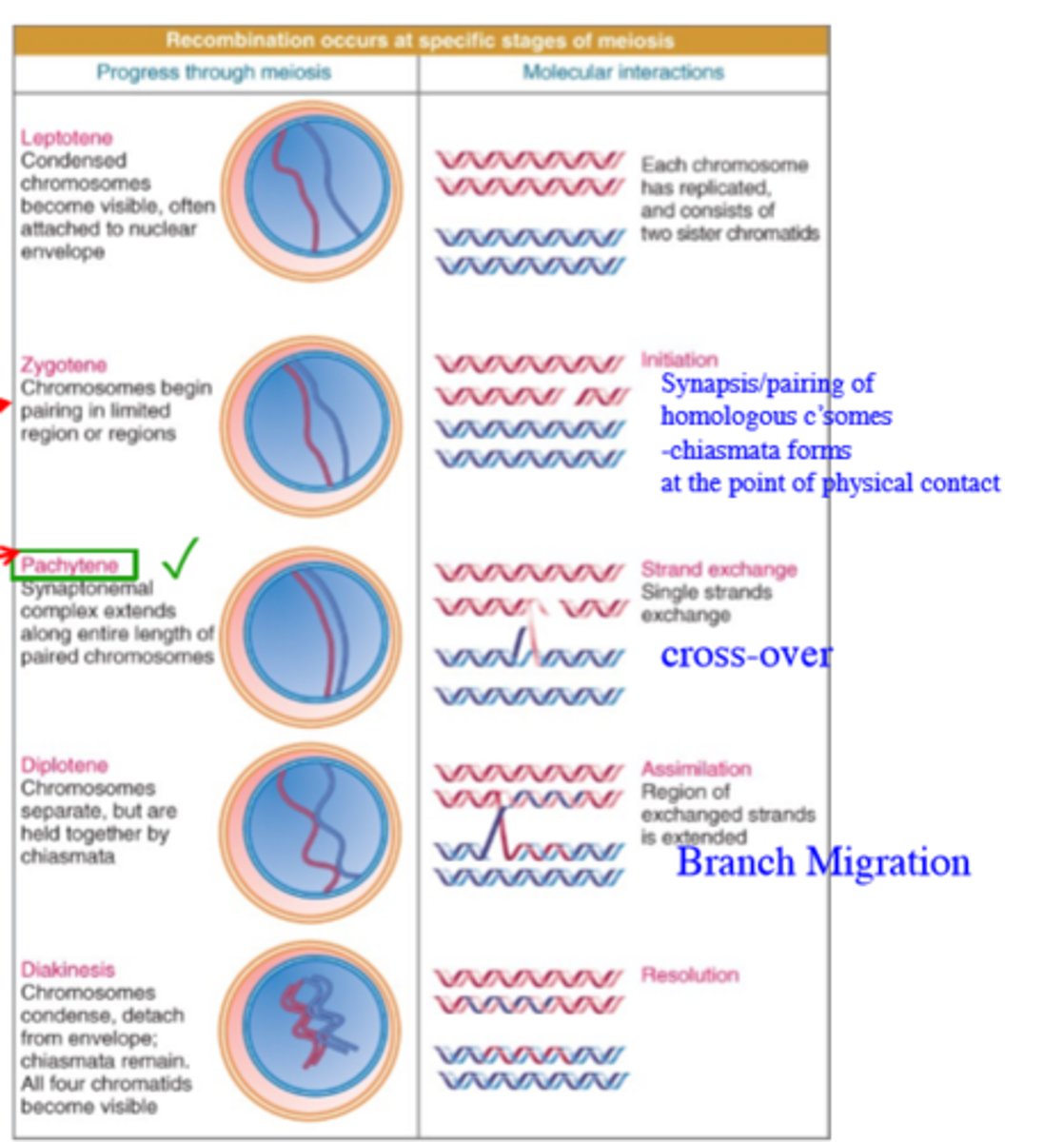
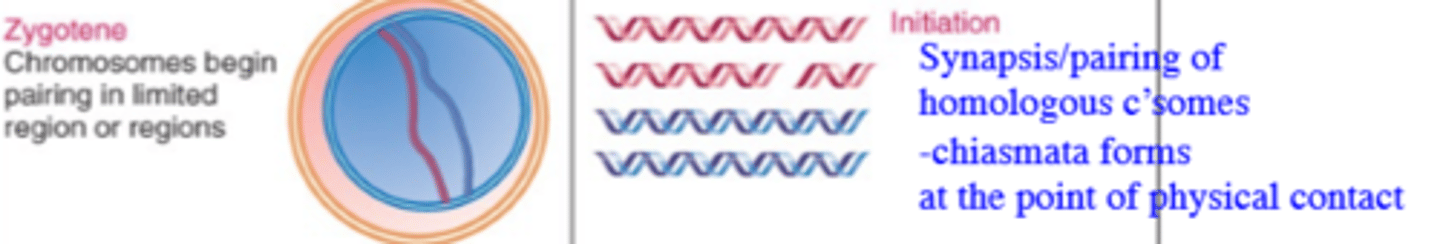
When does chromosomal synapsis/pairing and the formation of the chiasmata occur in prophase 1?
It occurs during Zygotene phase of Prophase 1
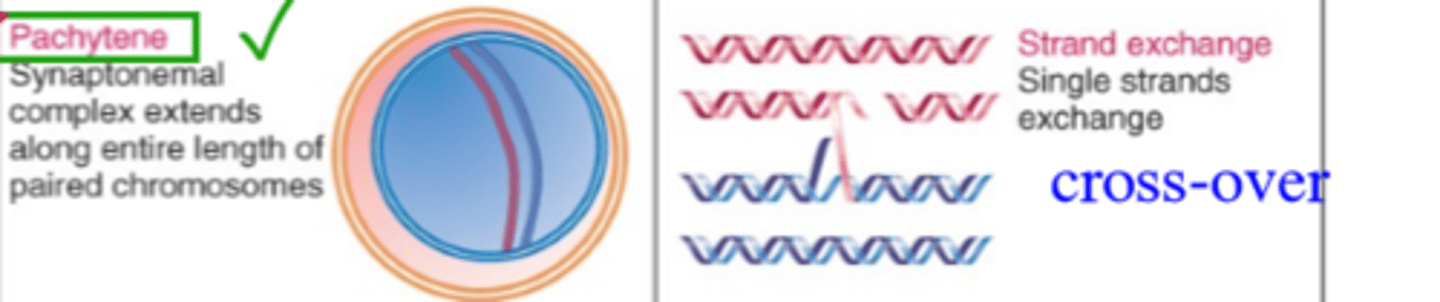
When does Crossing Over occur in prophase 1?
It occurs during the Pachytene phase of Prophase 1
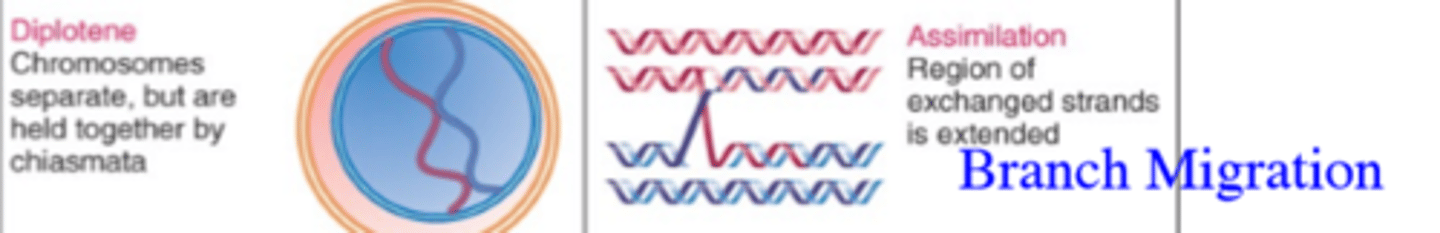
When does Branch Migration occur during prophase 1?
It occurs during the Diplotene phase of prophase 1.
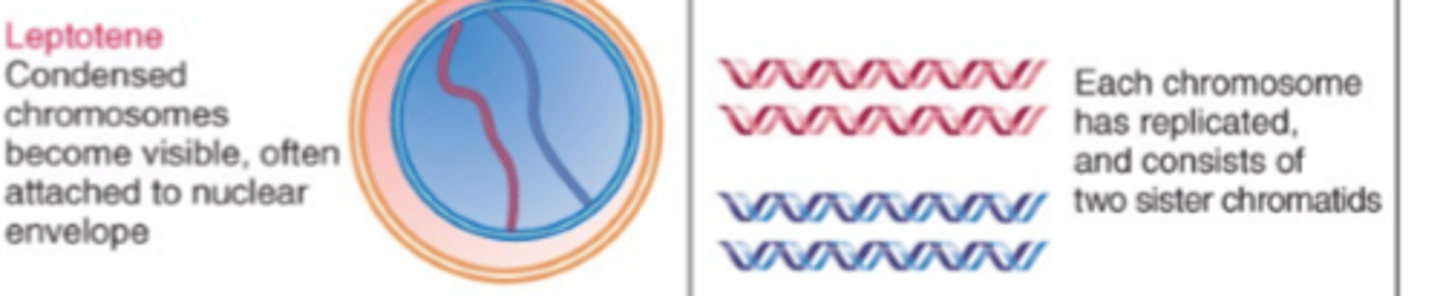
When do chromosomes become condensed and visible in prophase 1?
During the Leptotene phase of prophase 1.
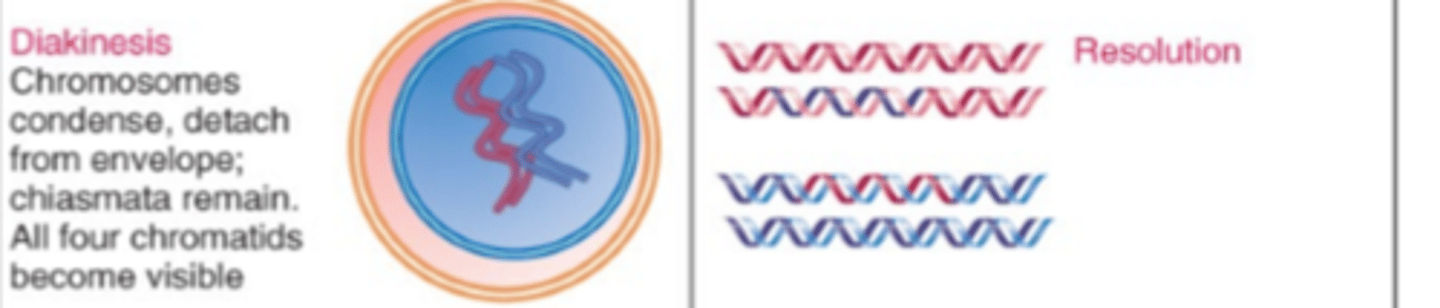
When does the resolution of recombination occur during prophase 1?
During the Diakinesis phase of prophase 1.
What are the three models of recombination?
1. Holliday Model
2. Double Stranded Break Model (DSB)
3. Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing Model (SDSA)
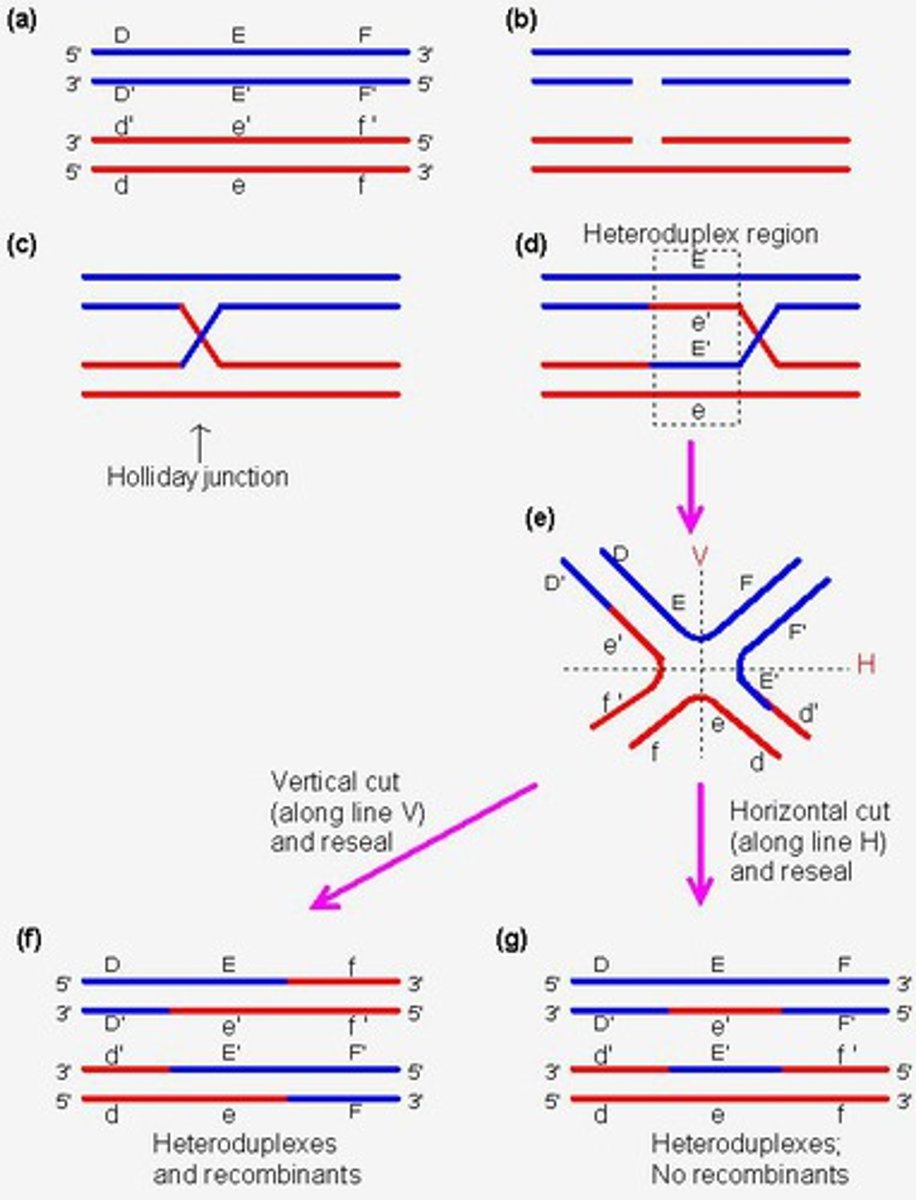
What is the Holliday Model?
It is an early model, it does not require new synthesis of DNA; its unique feature is it needs 2 single stranded breaks on each non-sister chromatid
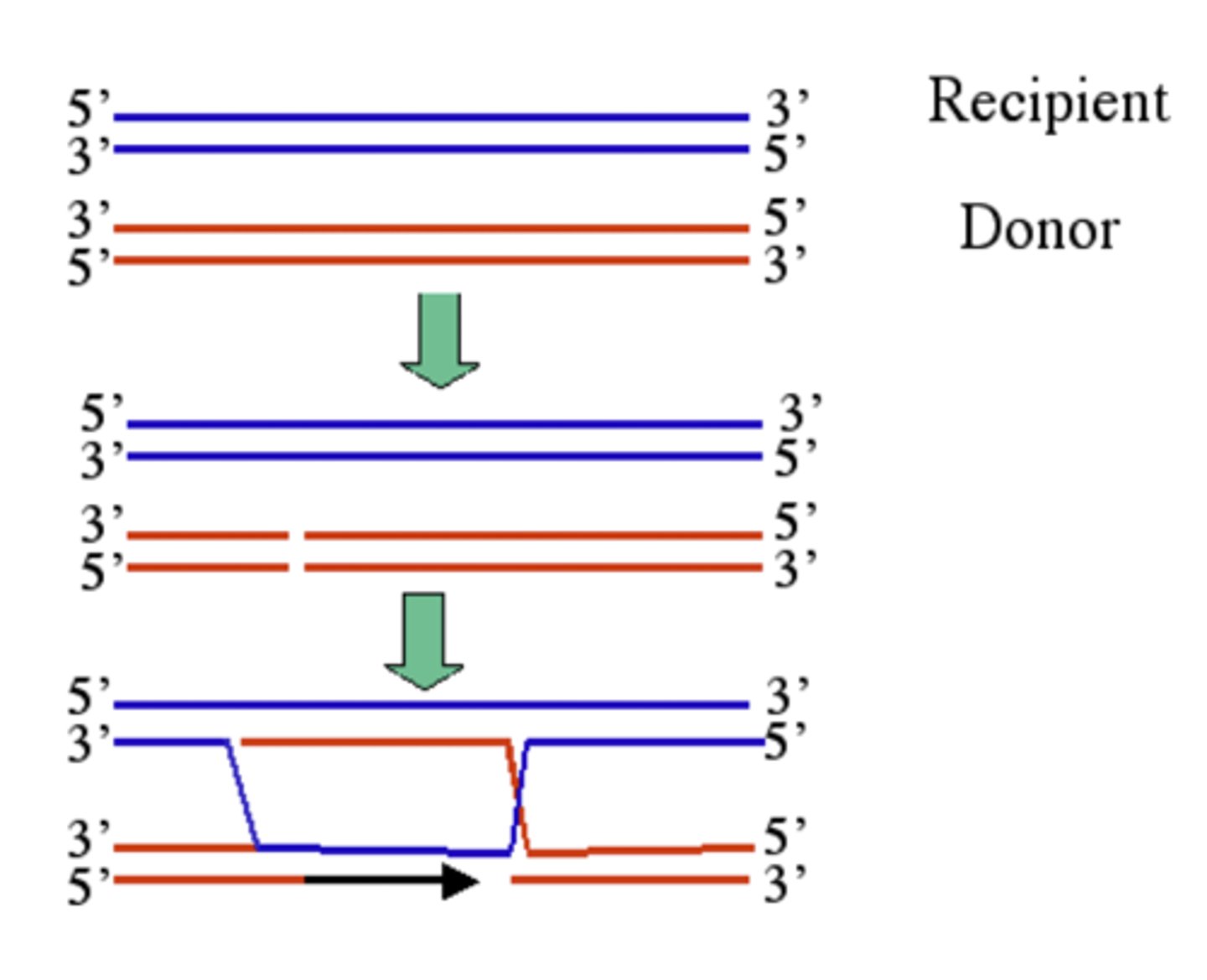
What is the Double Stranded Break Model?
This model requires the synthesis of new DNA, from a double stranded break in one of the sister chromatids; its unique feature is a second end capture = crossover or recombinants.
What is the Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing Model?
This model requires the synthesis of new DNA, from double stranded break in one of the non-sister chromatids; its unique feature is no second end capture = lack of recombinants.