Comprehensive Human Anatomy and Physiology: Structural Organization, Body Regions, and Imaging Techniques
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Gross anatomy
the study of larger body structures without magnification
Microscopic anatomy
study of microscopic body structures
Regional anatomy
study of the relationships of all structures in a specific area
Systematic anatomy
study of structures that make up a discrete system
Physiology
study of chemistry/physics of body structures and how they work together to perform bodily functions
Organization
maintains distinct compartments, acts as a barrier
Metabolism
consume energy from food and convert it into fuel for structure, movement, and function
Anabolism
combines small molecules into larger ones
Catabolism
complex substances broken down for energy
Responsiveness
ability to adjust to environmental changes
Movement
actions of organs and body overall
Development
changes to the body throughout life
Growth
increase in body size
Reproduction
formation of a new organism
Oxygen
key component of chemical reactions
Nutrients
food/substances essential for survival
Water
chemicals dissolved, chemical reactions, cell component
Energy-yielding
provides energy for bodily functions
Micronutrients
vitamins and minerals essential for survival
Homeostasis
physiological value around which normal range fluctuates
Negative Feedback
mechanism that prevents a response from going beyond the normal range by reversing the action
Positive Feedback
intensifies a change in body's condition
Prone
facedown position
Supine
faceup position
Anterior/ventral
front of the body
Superior/cranial
position above another part of the body
Inferior/caudal
position below another part of the body
Lateral
towards the outer body
Medial
towards the middle of the body
Proximal
near point of attachment or trunk
Distal
far from point of attachment or trunk
Superficial
closer to surface
Deep
farther from surface
Plane
imaginary 2-D surface passing through the body
Sagittal
divides body into right and left sides
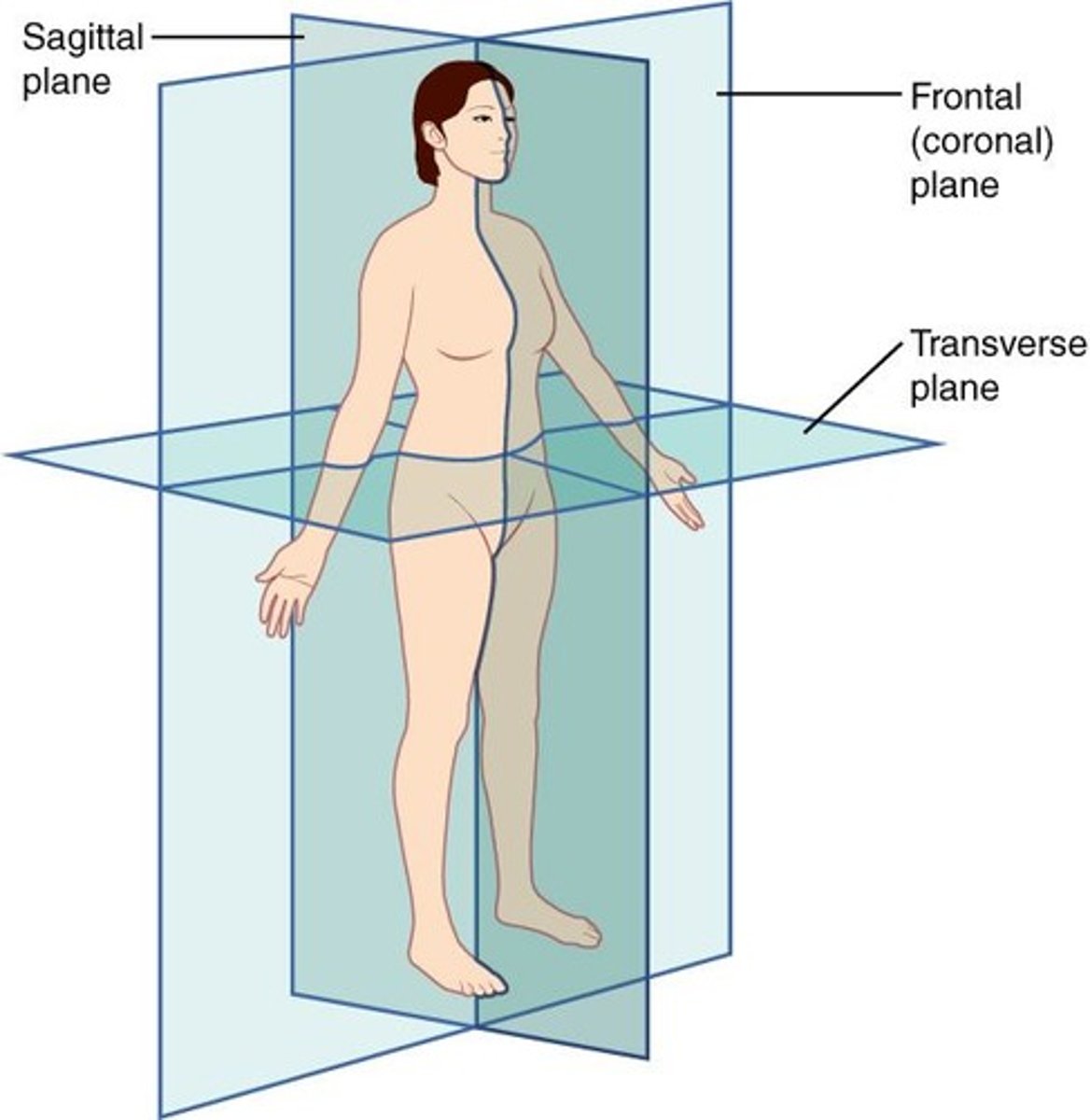
Frontal
divides body into front and back
Transverse
divides body into top and bottom
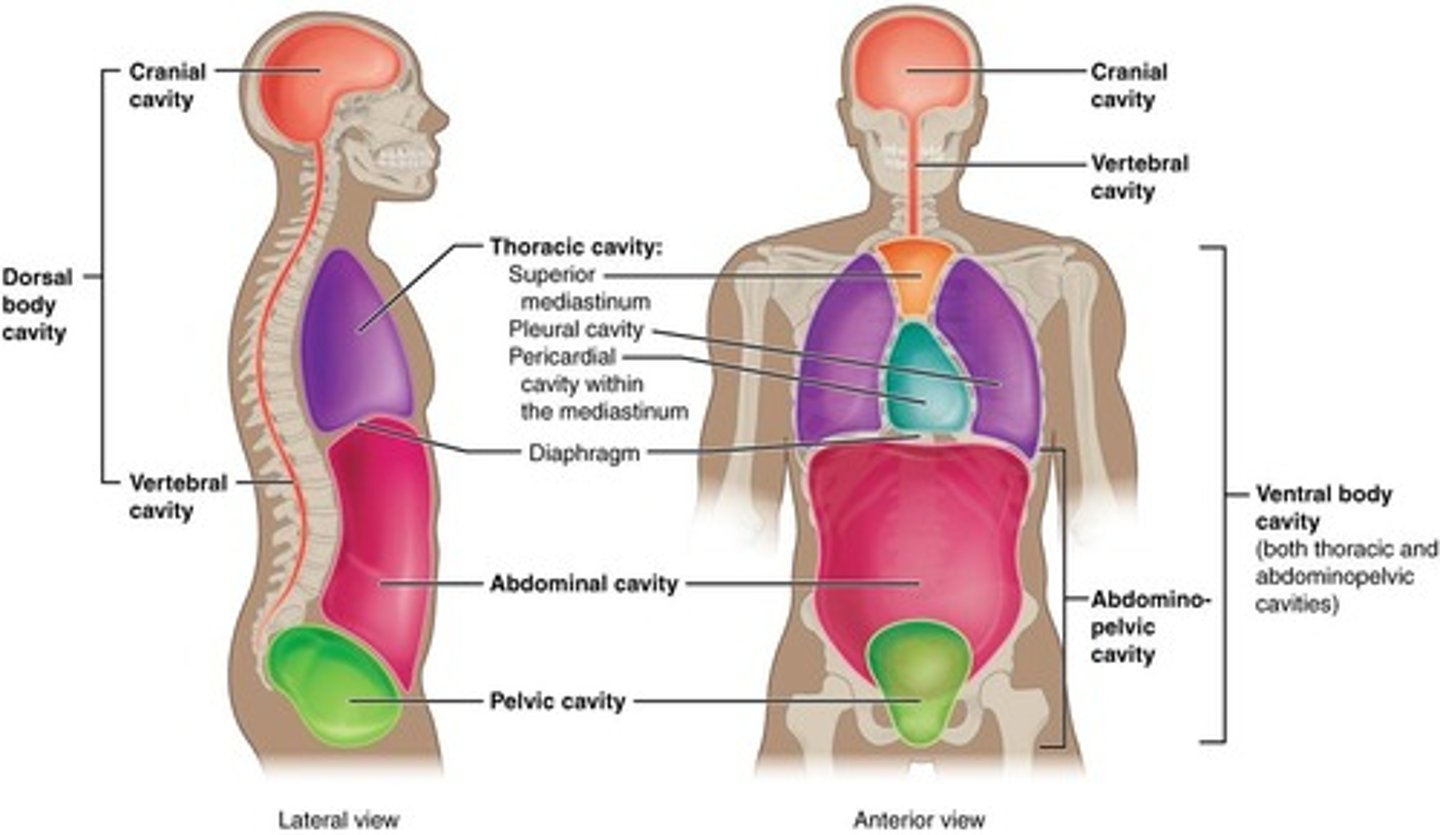
Dorsal cavity
contains cranial cavity (brain) and spinal cavity (spinal cord)
Ventral cavity
contains thoracic (lungs, heart, ribs, diaphragm) and abdominopelvic (digestive and reproductive organs) cavities
Serous membrane
thin membranes that cover walls and organs, reducing friction by secreting fluid
X-ray
high energy EMR with a short wavelength that can penetrate solids and ionize gases, darkening a metallic plate
Computed tomography
computers analyze several cross-sectional X-rays at once
Magnetic resonance imaging
matter exposed to magnetic fields and radio waves emit radio signals
fMRI
detects concentration of blood flow in the body
Position emission tomography
using substances that emit radiation allows physiologic activity to be visualized
Ultrasonography
transmission of high frequency sound waves into the body to generate an echo signal converted by computers into imaging
Anatomy
The study of body structure.
Surface Anatomy
Study of the form & markings of the body surface.
Gross (Macroscopic) Anatomy
Study of structures that can be examined without the use of a microscope.
Systemic Anatomy
Study of a specific system of the body such as the digestive system.
Radiographic Anatomy
Study of the body that includes the use of x-rays.
Developmental Anatomy
Study of development from the fertilized egg to adult form.
Embryology
Study of development from the fertilized egg through the eighth week in utero.
Histology
Microscopic study of tissues.
Cytology
Microscopic study of cells.
Pathological Anatomy
Study of structural change associated with disease.
Atom
Smallest unit of matter; composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Molecule
Combination of 2 or more atoms (same or different) bonded together.
Compound
Combination of 2 or more molecules bonded together.
Organelle
Tiny structures within cells which carry out specialized cell functions.
Cell
Smallest living unit of structure and function of body.
Tissue
A group of similar cells plus their intercellular material (matrix) which carry out a particular function.
Organ
Structure composed of two or more different tissues carrying out a specific function.
Organ System
Related organs that work together to carry out a particular function.
Cardiovascular system
An example of an organ system.
Organism
what all the organ systems working together compose
Anatomical Position
standing erect (feet are near each other), face forward, arms at sides, palms forward
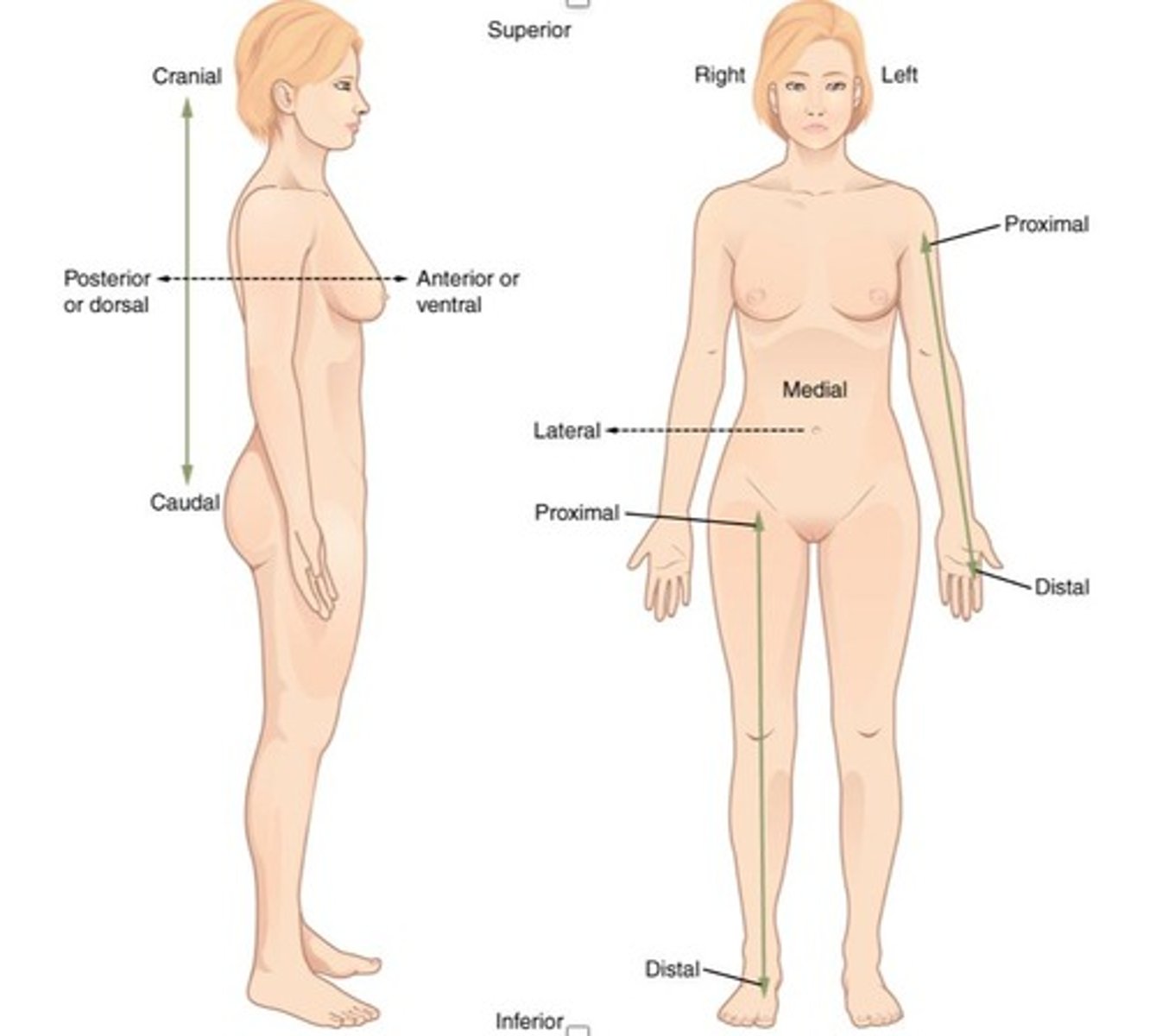
Superior (cephalic or cranial)
toward head or upper part of a structure
Inferior (caudal)
towards feet or lower part of a structure
Anterior (ventral)
towards front
Posterior (dorsal)
towards back
Ipsilateral
on same side of body as another structure
Contralateral
on opposite side of body from another structure
Intermediate
between two structures
Central
situated at the center of the body or an organ
Peripheral
situated away from the center of the body or an organ; can also mean near surface (eg. peripheral blood vessels or nerves)
Sagittal Plane
vertical plane (lengthwise cut); divides body into right and left sides or sagittal sections
Midsagittal Section
if equal right and left halves
Parasagittal Section
if unequal right and left halves
Frontal (coronal) Plane
vertical plane; divides body into anterior and posterior portions; produces frontal sections
Transverse Plane
horizontal plane (parallel cut to the floor) occurring anywhere along length of body; divides body into superior and inferior portions; produces cross sections
Oblique Plane
Cut made along a plane intermediate between a vertical and horizontal plane; produces oblique sections.
Bilateral Symmetry
Exterior left and right sides are mirror images.
Cranial Cavity
Located within the skull; contains the brain.
Vertebral Canal
Located within the vertebral column; contains the spinal cord.
Meninges
Three membranes composed only of connective tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord.
Dura Mater
The outer membrane of the meninges.
Arachnoid Mater
The middle membrane of the meninges.
Pia Mater
The inner membrane of the meninges.
Meningitis
Inflammation of meninges due to bacterial or viral infection.
Diaphragm
A horizontal sheet-like skeletal muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities; major muscle of inspiration.
Serous Membranes
Composed of simple squamous epithelium (called mesothelium) overlying a layer of areolar connective tissue.
Visceral Layer
Covers organs within the cavity.
Parietal Layer
Lines the cavity wall.
Pleura
Serous membrane associated with the lungs in the thoracic cavity.
Pericardium
Serous membrane associated with the heart in the thoracic cavity.
Peritoneum
Serous membrane associated with most (but not all) of the viscera in the abdominopelvic cavity.
Pleural Cavities
Two cavities, each surrounding a lung.
Pericardial Cavity
Cavity surrounding the heart.
Mediastinum
Tissue-filled space between lungs, vertebral column, and sternum containing the heart, esophagus, trachea, thymus gland, large blood vessels, bronchi, lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and nerves.