AP Bio: Cell Division and Cell Communication
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Unicellular organisms: reproduction
Multicellular: development, growth, and repair
Why do cells divide?
Binary Fission
division of cells in a prokaryote
Mitosis
Division of the nucleus for eukaryotes

Interphase and Mitosis
What does the cell cycle include?
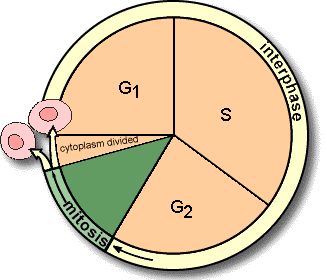
Interphase
Prep stage for cell division; happens 90% of the time
Mitosis phase
combines mitosis and cytokinesis; when the cell separates; 10% of the time
G1, S, and G2
What are the components of interphase?
G1
cell growth
S
Synthesis of DNA where it is duplicated and replicated
Need the same DNA in the new cell
Why does DNA duplicate?
G2
Cell growth/prep for division
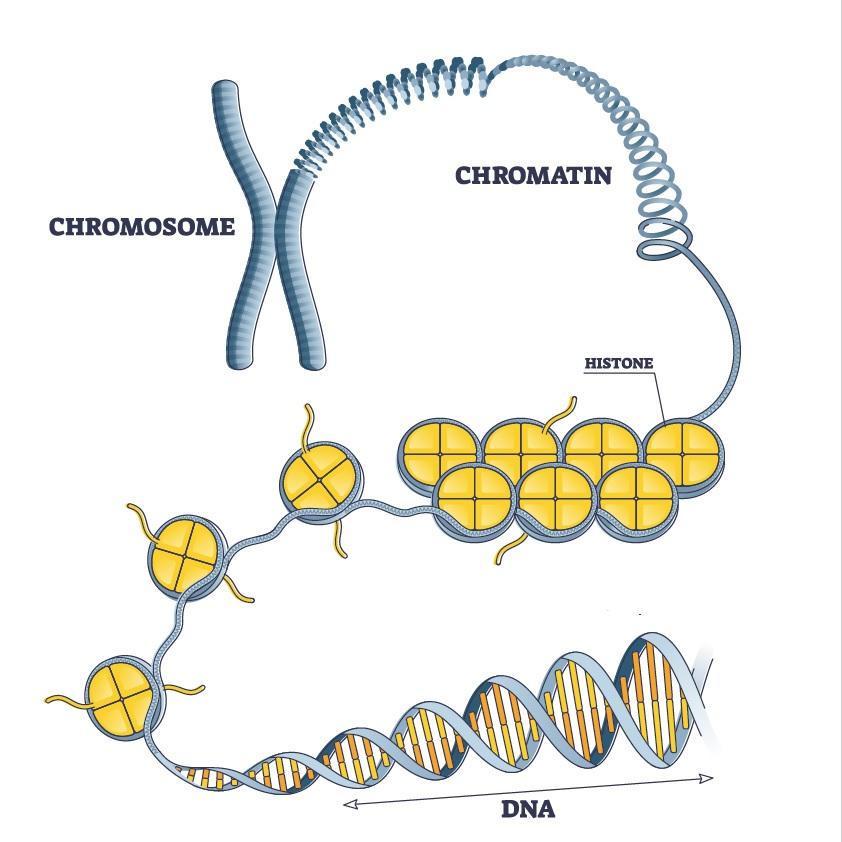
Chromatin
uncondensed DNA that spreads out; can’t see separate chromosomes
PMAT (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase)
Whats a good acronym for mitosis?
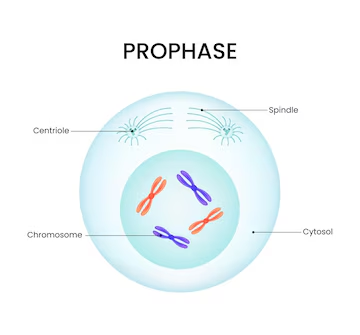
Prophase
already duplicated DNA condenses into 2 sister chromosomes
centrosomes move to the opposite sides of the cell and sprout microtubules
nuclear envelop disintegrates
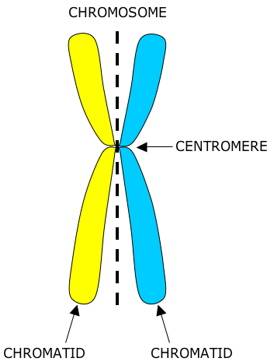
Centromere
waist of chromosome where sister chromatids are closely attached
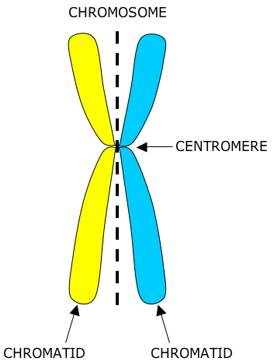
sister chromatids
identical copies
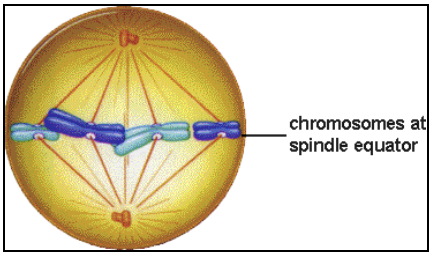
Metaphase
m = middle
protein kinetochore “anchor” forms at the centromere of each chromosome
microtubules from the mitotic spindle attach to the kinetochore
spindle fibers move chromosomes to the middle of the cells (to metaphase plate)
Some don’t attach
kinetochore
complex proteins associated with the centromere of a chromosome during cell division to which the microtubules of the spindle attach
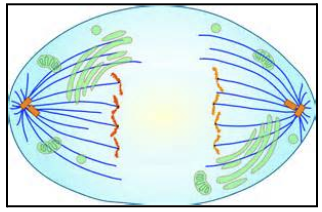
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and move along microtubules toward opposite sides of the cell
sister hromatids turn into daughter chromatids
microtubules shorten when they connect to the kinetochore
Telophase
nuclear envelop reforms
chromosomes unwind and go back into chromatic form

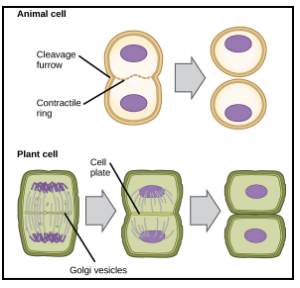
Cytokinesis
Animal Cells
contracting ring of proteins squeezes the cytoplasm and creates 2 cells
Plant Cells
vesicles form together to make a cell plate, which becomes the cell membrane and cell wall
contractile ring protein
squeezes the cytoplasm in half and creates to cells
G1,G2, and M
What are the three checkpoints in a cell
checkpoints
checks to make sure everything is fine in the cell process
if everything is okay the cell can proceed
if something is wrong they stop the cell and transport it to G0
G1
checks if the cell is big enough and has enough nutrients
most important checkpoint
passes failed cells to G0
G0
period where the cell doesn’t divide or prepare to divide
also serves as a resting place b/c of lack of nutrients
G2
makes sure that the cell is big enough and DNA is replicated properly
M checkpoint
checks for internal controls
crucial for correct cell division
internal controls show that there are external controls
external controls
signals that control cell growth and reproduction
density-dependent inhibition and anchorage dependence
What are the types of external controls/growth factors?
density-dependent inhibition
if there are too many crowded cells it will signal to stop dividing
signals are dependent on amount of other cells
growth factors
proteins released by certain cells that stimulate cells to divide
anchorage dependence
cells need to be on a surface in order to divide
cell division stops/pauses
damage repair system is activated
self destruct system is activated
What happens when there is a problem with the DNA or cell found at a checkpoint?
yes, it can just go back and repair itself
Can a cell repair itself if it has moderate damage?
cells undergo apoptosis
What happens to a cell if there is severe damage?
apoptosis
programmed cell death
cancer
unregulated cell division
requires 6-9 different mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes
doesn’t exhibit growth factors
genes that code for accelerator or brake proteins has a mutation that makes the protein function incorrectly
cell zooms though the checkpoints without stoping and ignoring signals that say to slow down
How does cancer appear?
oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes
Where do mutations typically appear?
proto-oncogene
protein that tells cells to divide moreo
oncogene
mutated proto-oncogene that causes cells to divide out of control
accelerator
loses a function
binds to more receptors and growth factors
tumor suppressor genes
encode proteins involved in suppressing cell division
if mutated it doesn’t tell cells to stop dividing
benign tumor
abnormal cells that stay at the original site
won’t grow or become dangerous
malignant tumor
invaded surrounding tissues
has potential to keep growing and spreading
stage 1-3
metastasis
malignant cells have spread from the original site to the other organs/body parts
secondary tumor presents
stage 4
surgery
radiation
chemotherapy
gene therapy
Types of cancer treatments
Asexual reproduction
1 parent
offspring identical to parent
mitosis/binary fission
pros: don’t have to find another mate which takes energy and resources
Sexual reproduction
2 parents
offspring NOT identical to parent
meiosis
pros: creates genetic diversity
46 chromosomes and 23 pairs
How many chromosomes and pairs do humans have?
Males have an XY
Females have XX
How do you tell a male from a female in chromosomes?
you have 3 copies of chromosome 21
What happens if you have down syndrome?
no sperm and egg is not made by mitosis.
you would end up have 92 chromosomes
Is sperm and egg made by mitosis?
zygote
egg fertilized by sperm
23 chromosomes
How many chromosomes are in an egg or sperm
meiosis
production of gametes
chromosome number decreases
diploid→haploid
46→23
2n→n
diploid
a full set of chromosomes
somatic cells
body cells that don’t include gametes
haploid
one set of chromosomes
gametes
egg/sperm cells
fertilization
chromosome number is restores
haploid → diploid
n → 2n
homologous chromosomes
same genes but different alleles
not identical
have same genes
two different copies of chromosomes
one from each parent
code for same inherited information
sister chromatid
two identical copies formed by the replication of a single chromosome
made during s phase so they have to be identical
Interphase→Prophase 1→Metaphase 1→Anaphase 1→Telophase 1→Cytokinesis 1→Interkinesis→Prophase 2→Metaphase 2→Anaphase 2→Telophase 2
What are the steps of Meiosis
2 cell divisions
How many cell divisions does meiosis have?
Prophase 1
DNA is already doubled
homologous chromosomes get together to form a tetrad
crossing over/recombination
crossing over
homologous pairs swap pieces of chromosomes at the inner chromatids at the tips at random
increases genetic diversity
DNA breaks and re-attaches
Metaphase 1
tetrads line up in the middle of the cell in pairs
the side that each chromosome lines up is random
same amount of chromosomes as mitosis
independent assortment
which side each chromosome lines up at random
increases genetic diversity
Anaphase 1
homologous chromosomes are pulled apart
still have a full set of chromosomes
Telophase 1
mitosis spindles go away
nuclear membrane reforms
Cytokinesis 1
cytoplasm divides to form two daughter cells
interkinesis
resting stage that certain cells go to between meiosis 1 and 2
meiosis 2
separation of sister chromatids
retain same number of chromsomes
basically mitosis
chromatids are no longer sisters becuase of recombination and random assortment
1n→1n
Crossing over, independent assortment, and random fertilization
What are the 3 ways genetic variation is introduced?
4 daughter cells
By the end of meiosis how many daughter cells should you have?