Nucleic Acids
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Cells + viruses
cells - use DNA, cells are living
viruses - not living, use DNA or RNA
Nucleic acids + Nucleotides
nucleic acids - polymers + macro molecules
nucleotides -monomers + building blocks, has a negative charge
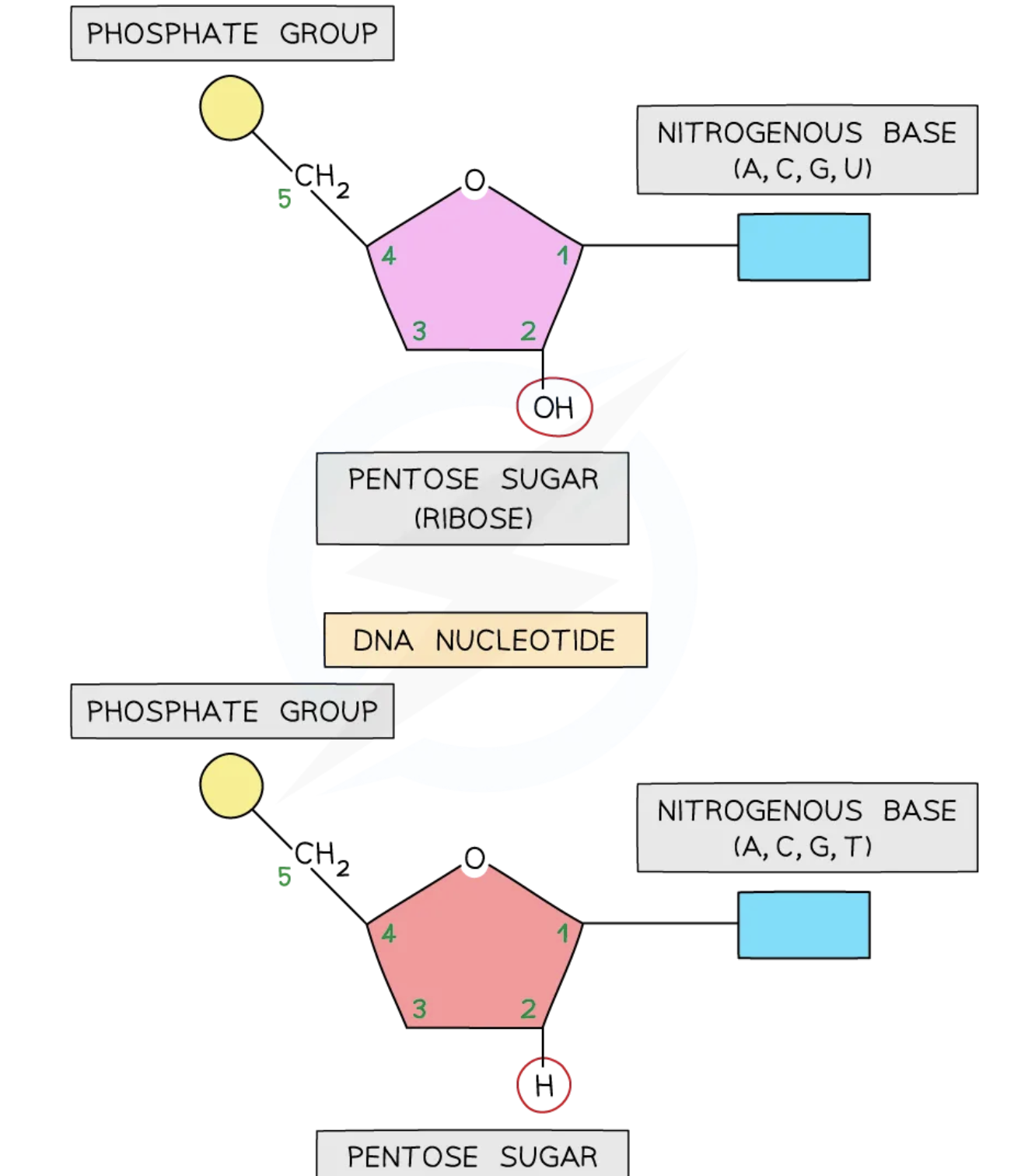
nucleotide structure drawing + components for DNA
phosphate group
nitrogenous base
pentose sugar
covalent bond - CH2
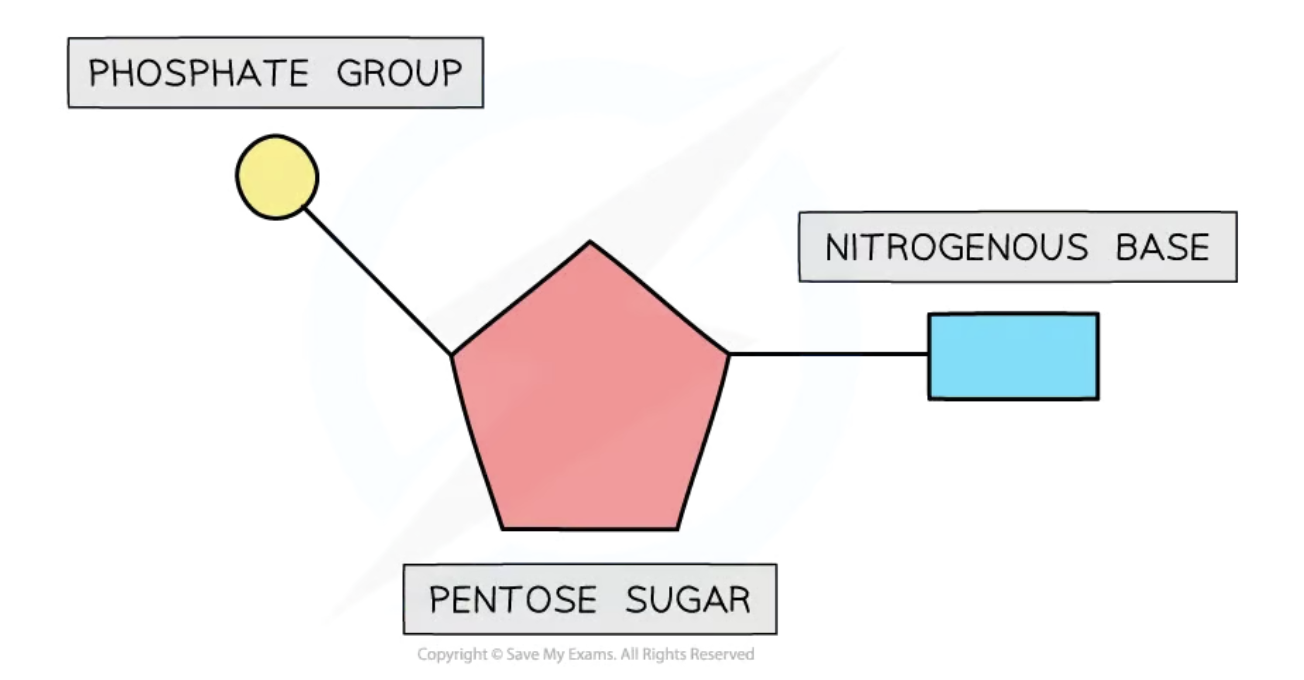
what is the pentose sugar called in DNA and RNA
DNA - deoxyribose
RNA - ribose
what are the nitrogenous bases for DNA + RNA
DNA - Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
DNA vs RNA strands
DNA - double stranded or single stranded, long strands, antiparallel
RNA - single stranded, short strands
Nucleotide to nucleic acid
condensation reaction - every time a new bond form (chemical reaction) a water molecule is produced
sugar phosphate bond/ phosphodiester bond
anti parallel strands of nucleotides
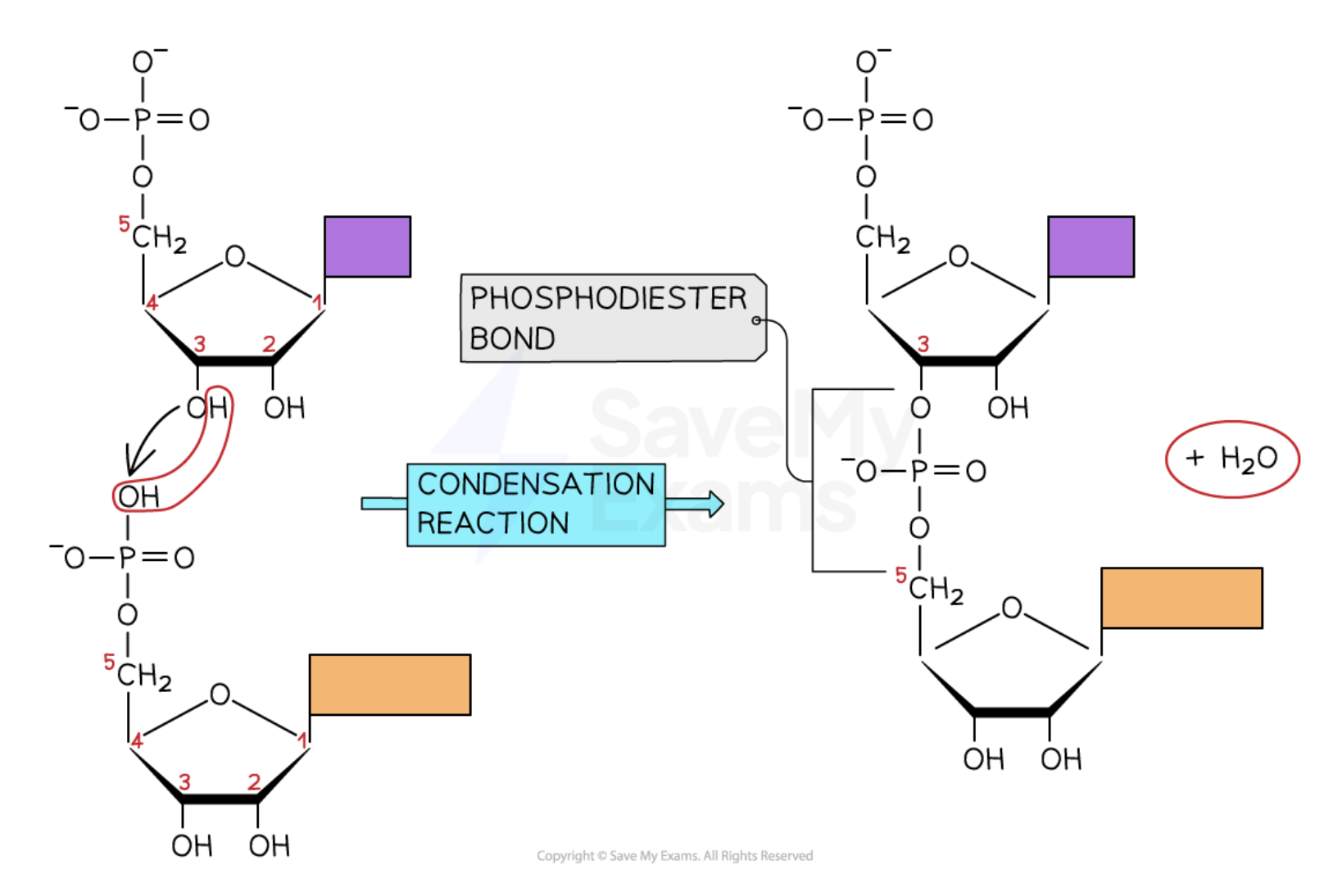
sugar phosphate backbone
alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups bonded together
messenger RNA (mRNA)
formed in the nucleus and transported to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
transfer RNA (tRNA)
is responsible for transporting amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis
ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
forms part of ribosomes
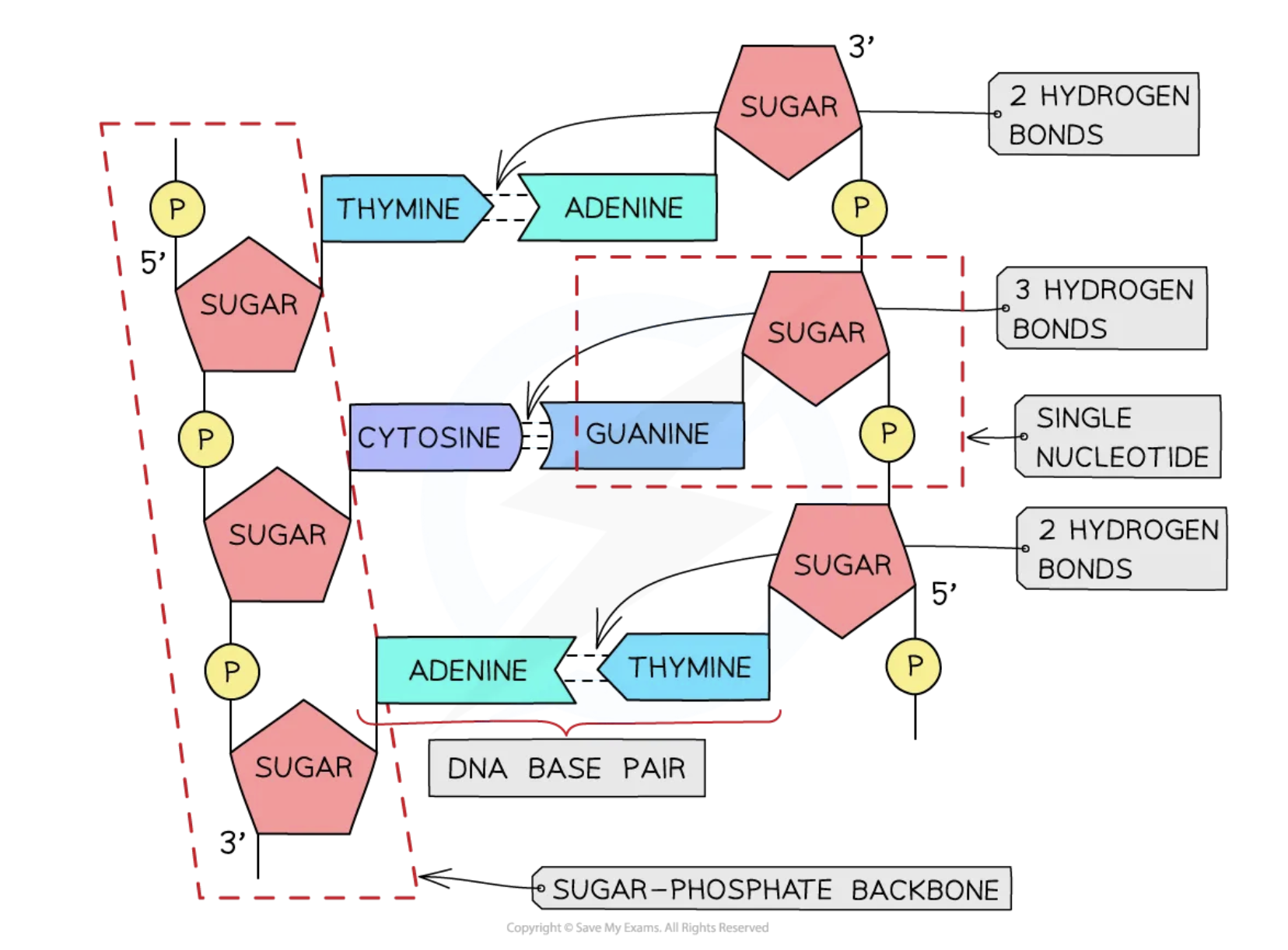
double Helix DNA
antiparallel strands of nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
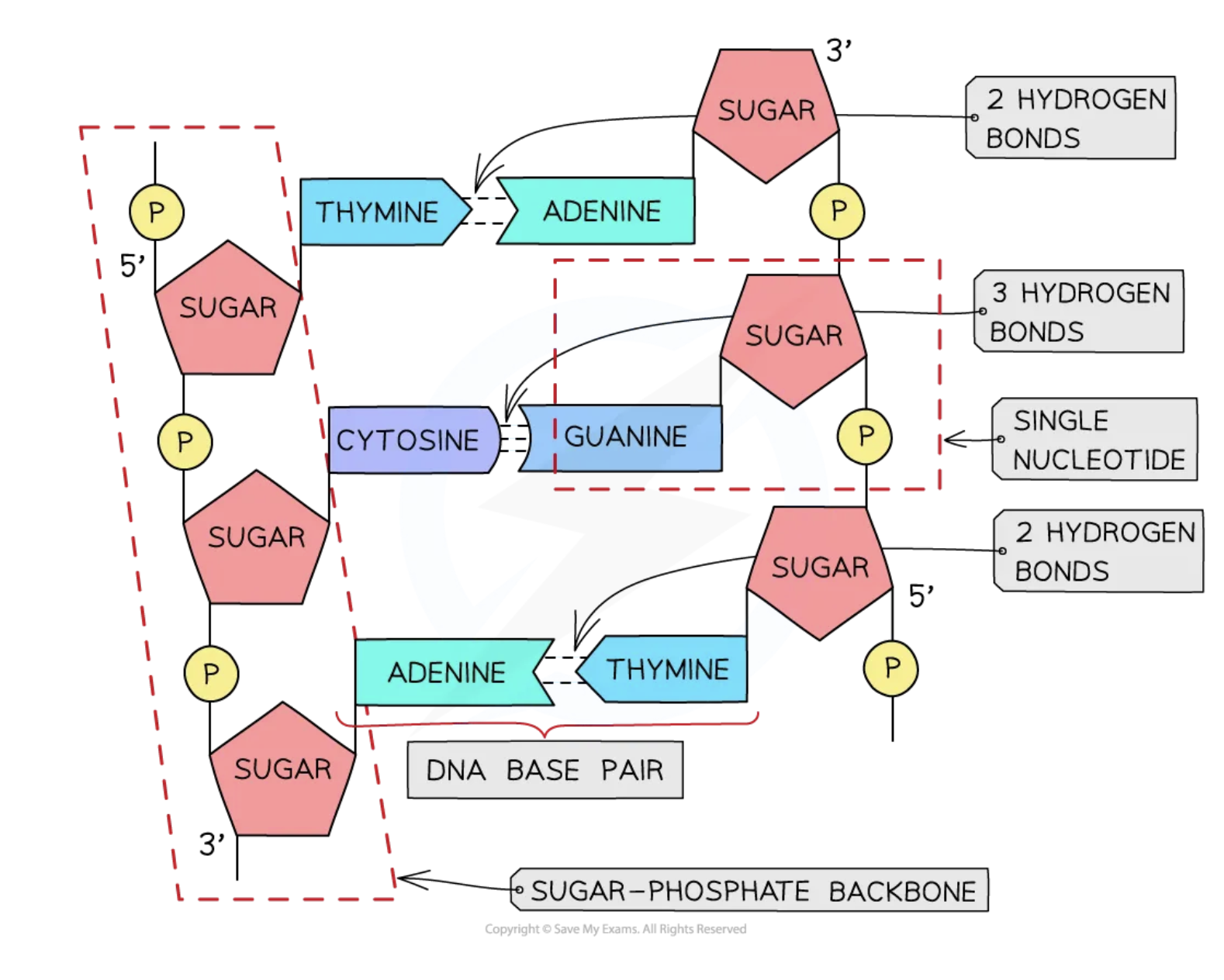
what are the complementary base pairs for hydrogen bonding in DNA
A-T : 2 hydrogen bonds
G-C : 3 hydrogen bonds
drawing DNA vs RNA
OH → RNA
H → DNA
Roles of complementary bonding
in gene expression
in DNA replication
Genetic code is universal
Roles of complementary bonding in gene expression
a strand of DNA is converted to complementary mRNA this is then read by complementary tRNA molecules
the tRNA is then split into groups which are 3 bases each.
each group codes for one amino acid
DNA → mRNA → tRNA
A → U → A
C → G → C
G → C → G
T → A → U
role of complementary bonding in DNA replication (inheritance)
each DNA strand is separated.
original DNA strand acts like a template
complementary nucleotides/bases build new strands → ľ identical DNA molecules.

DNA base sequence capacity
can hold limitless information
role of complementary bonding - Genetic code is universal
all organisms + cells use the DNA base sequence + express it in the same way
the genetic code evolved very early in the evolution of life in a last universal common ancestor from which all living species developed