c6 - improving reactions + organic chemistry + earth systems
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
what 3 elements do plants need
nitrogen
phosphorus
potassium
what are symptoms of mineral deficiencies for the different elements
nitrogen - poor growth, yellow leaves
phosphorus - poor root growth - discoloured leaves
potassium - poor fruit growth, discoloured leaves
what are fertilisers
substances that replace elements used by plants as they grow that are in water-soluble form so they can be absorbed by plant roots
what are examples of water-soluble minerals and their formulas
nitrate ions NO3- / ammonium ions NH4+
phosphate ions PO43-
potassium ions K+
what does the haber process do and what is its equation
manufactures ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g)
what are the 3 raw materials used for the haber process
steam, natural gas, air
how is nitrogen and hydrogen manufactured for the haber process
nitrogen - through the fractional distillation of liquefied air
hydrogen - through reacting natural gas with steam
what percent of the haber process is used to make fertilisers
over 80%
what are 4 examples of compounds in fertilisers
ammonium nitrate
ammonium phosphate
ammonium sulfate
potassium nitrate
draw a flow diagram to show how the 4 mineral compounds are made
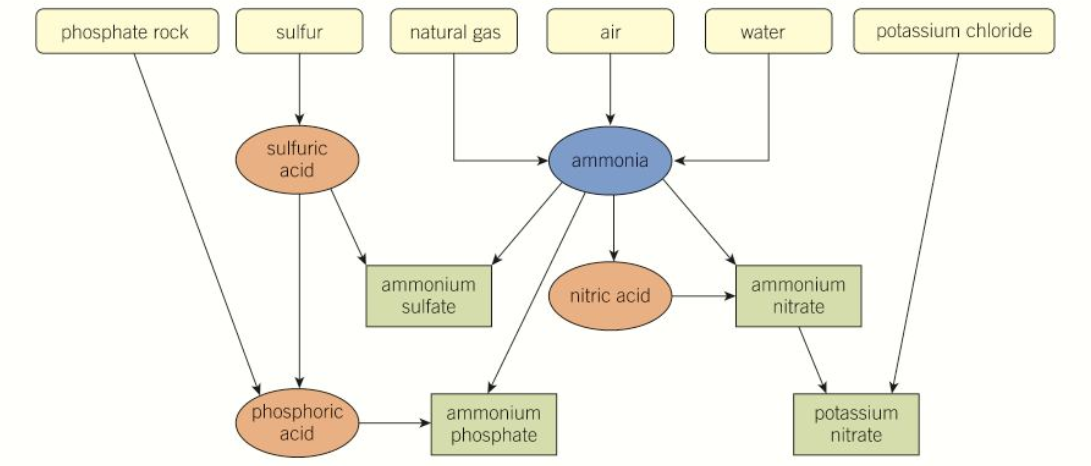
what are the 3 conditions used for the haber process and what equilibrium yield does this achieve
iron catalyst present
pressure of 200 atmospheres
temperature of 450 celsius
achieves a 30% equilibrium yield
how is the temperature chosen a compromise
its low enough to achieve a reasonable equilibrium and high enough to achieve a reasonable rate of reaction
why is 450 celsius chosen for the haber process
the forward reaction is exothermic so if temperature is increased, equilibrium moves to the reactants and yield decreases
what are the raw materials needed for the contact process
sulfur, air, water
what happens in each of the 3 stages of the contact process (include equations)
stage 1:
sulfur burns in air to produce sulfur dioxide
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
stage 2:
sulfur dioxide and oxygen react to form sulfur trioxide
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2SO3 (g)
stage 3:
sulfur trioxide is converted to sulfuric acid
H2O (l) + SO3 (g) → H2SO4 (aq)
what are the conditions needed for reacting sulfur dioxide and oxygen to form sulfur trioxide in the contact process and what equilibrium yield does this achieve
pressure of 3 atmospheres
temperature of 450 celsius
a vanadium oxide catalyst
the equilibrium yield is about 96%
how are the hazards of reacting sulfur trioxide with water controlled
it’s carried out in 2 steps:
sulfur trioxide is passed through concentrated sulfuric acid to form oleum
the oleum is added to water so the reaction makes a larger volume of concentrated sulfuric acid
what is the hazard of reacting sulfur trioxide with water
it produces a hazardous acidic mist
how is ethanol made from renewable raw materials
in fermentation using plant sugars
what is the equation for glucose turning into carbon dioxide and ethanol
C6H12O6 (aq) → 2CO2 (g) + 2C2H5OH (aq)
how is ethanol made from non-renewable raw materials
from crude oil through the hydration of ethene
what is the equation for making ethanol from ethene
C2H4 (g) + H2O (g) ⇌ C2H5OH (g)
what is yeast
single-celled fungi containing enzyme that catalyse the conversion of glucose to ethanol
why is fermentation carried out at 35 degrees celsius
if the temperature is above 50 enzymes will denature and if it’s too low they will go inactive
what conditions is the hydration of ethene done at
300 degrees celsius
60 atmospheres
phosphoric acid catalyst
what is an ore
a rock or mineral that contains enough metal to make it economical to extract the metal
(the value of the metal is more than the cost of extracting it)
what are 3 examples of ores and the metals they contain
malachite - copper carbonate
bauxite - aluminium oxide
haematite - iron(III) oxide
what is the reactivity series
potassium
sodium
calcium
magnesium
aluminium
(carbon)
zinc
iron
tin
lead
copper
silver
gold
platinum
what are the 2 ways copper can be extracted from copper(II) sulfide
by heating it with methane or hydrogen
OR
roast the copper(II) sulfide in air
heat the copper(II) oxide with carbon
how are copper or iron extracted
by heating their compounds with carbon or carbon monoxide
when is electrolysis used for extraction
when the metal is more reactive than carbon
draw a diagram of a blast furnace
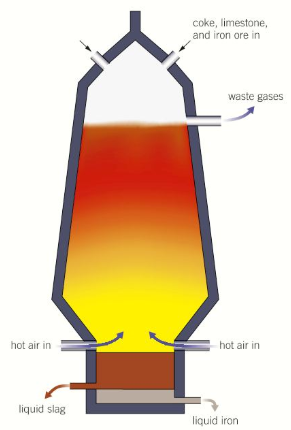
what is added to a blast furnace
iron ore, coke, limestone to the top
hot air is forced in at the bottom
what is coke
mostly carbon made by heating coal in the absence of air
what happens in a blast furnace (5)
coke burns in hot air making carbon dioxide
more coke reduces the carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide
carbon monoxide reduces iron(II) oxide to iron at 1500 celsius
molten iron and impurities (which are removed with limestone) trickle downwards
they are then removed separately from the bottom of the furnace
how does limestone remove impurities (2)
calcium carbonate (limestone) decomposes to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide
calcium oxide reacts with silica from impurities to form calcium silicate (slag)
how is aluminium found in nature
as aluminium oxide in bauxite ore
how is aluminium extracted
through electrolysis after dissolving it in molten cryolite
why does electrolysis need to be used
because aluminium is more reactive than carbon so cant be displaced
why is cryolite used
because the aluminium oxide must be in liquid form for electrolysis but its boiling point is too high normally so cryolite reduces it
what is the electrolysis cell for the electrolysis of aluminium like
the cell is made from steel and has a graphite inner lining which acts as the cathode
a series of large graphite blocks act as the anode
what happens during the electrolysis of aluminium oxide
aluminium is produced at the cathode
oxygen is produced at the anodes
oxygen reacts with hot graphite anodes and makes carbon dioxide
what are the half equations for the electrolysis of aluminium oxide
cathode - Al 3+ + 3e- → Al
anode - 2O2- → O2 + 4e-