BIOL 1021 Lab Final
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
what caffeine and ethanol did to the heart rate of Daphnia
caffeine - increased heart rate, ethanol- decreased heart rate
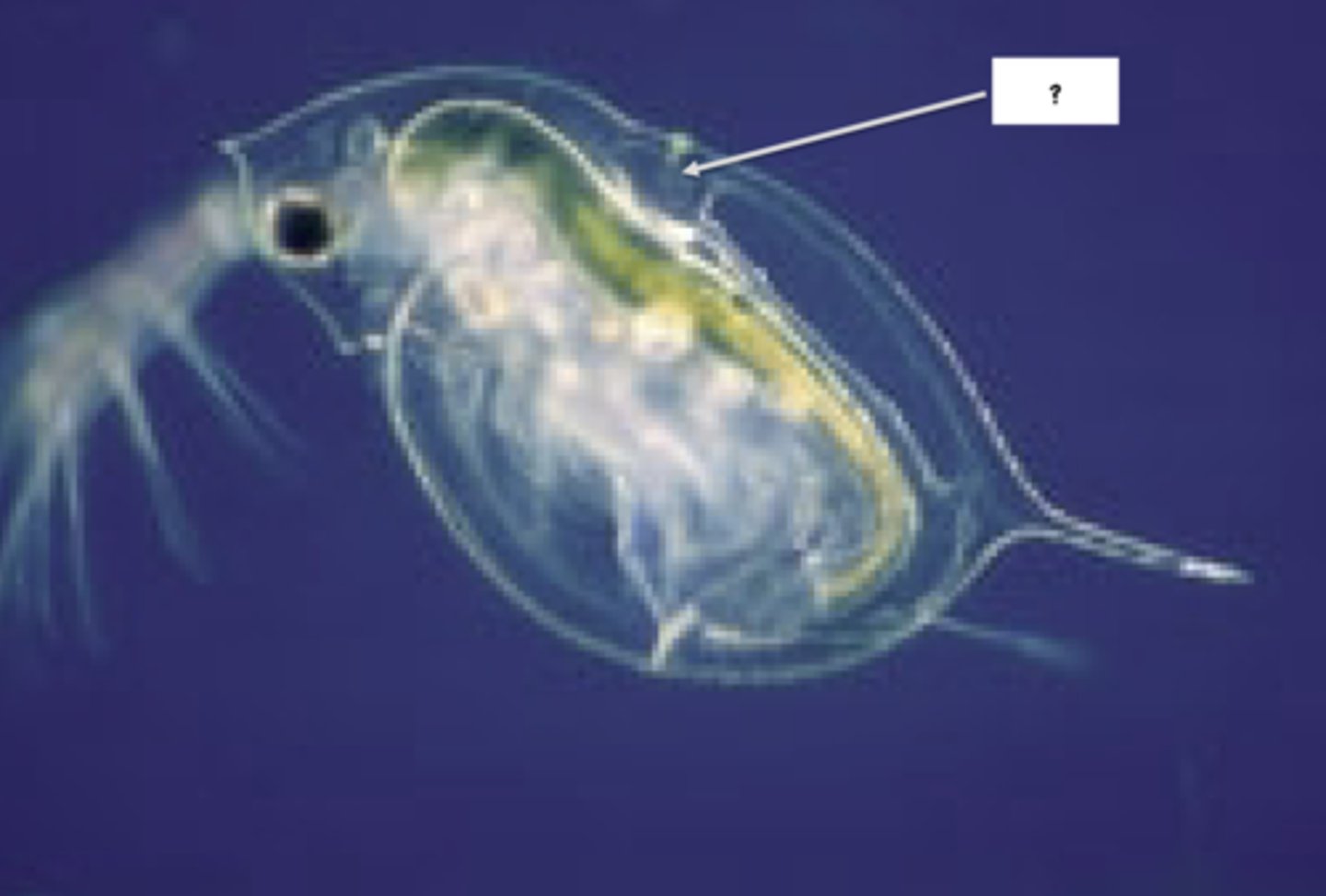
heart
knurled ring
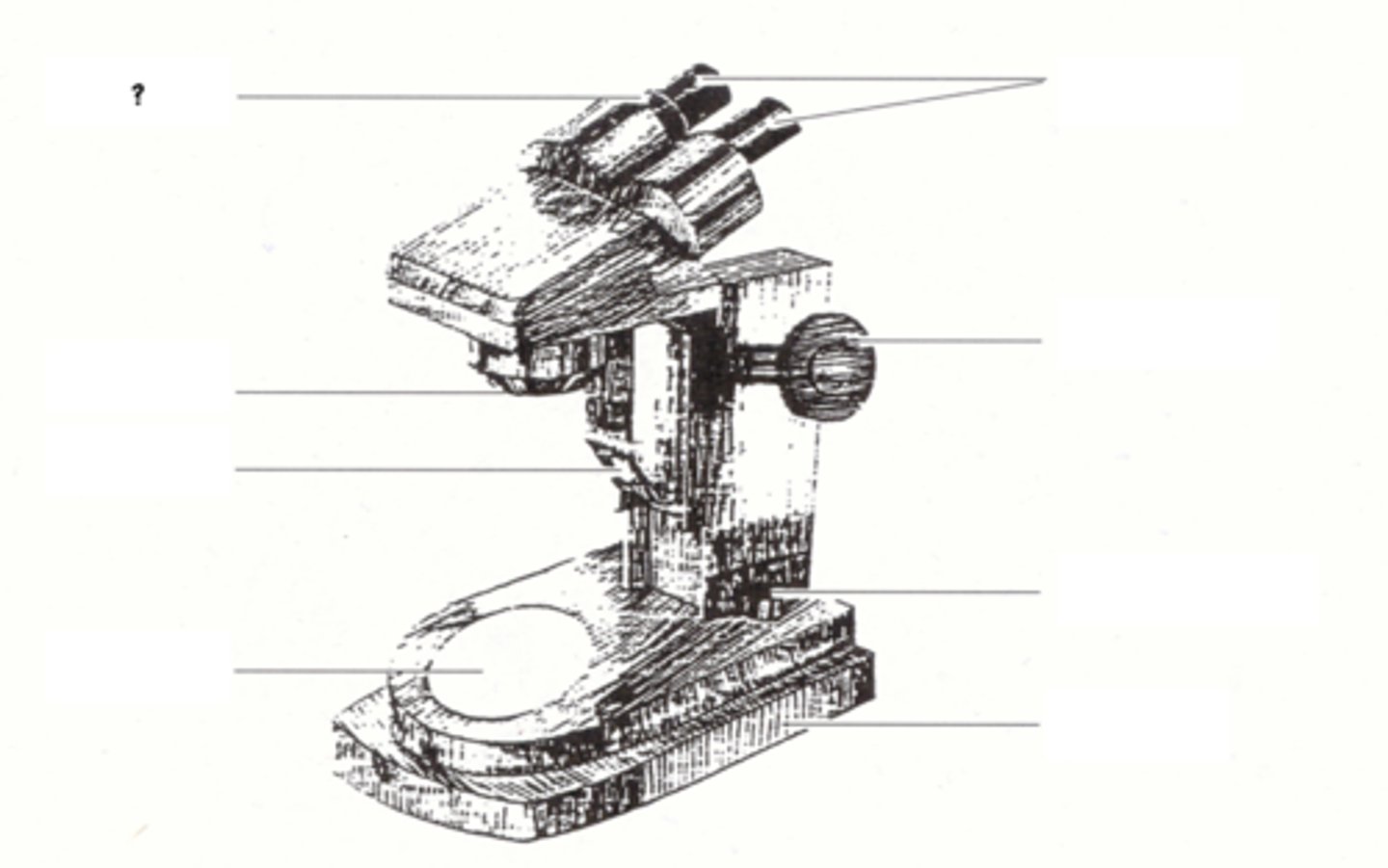
eyepieces
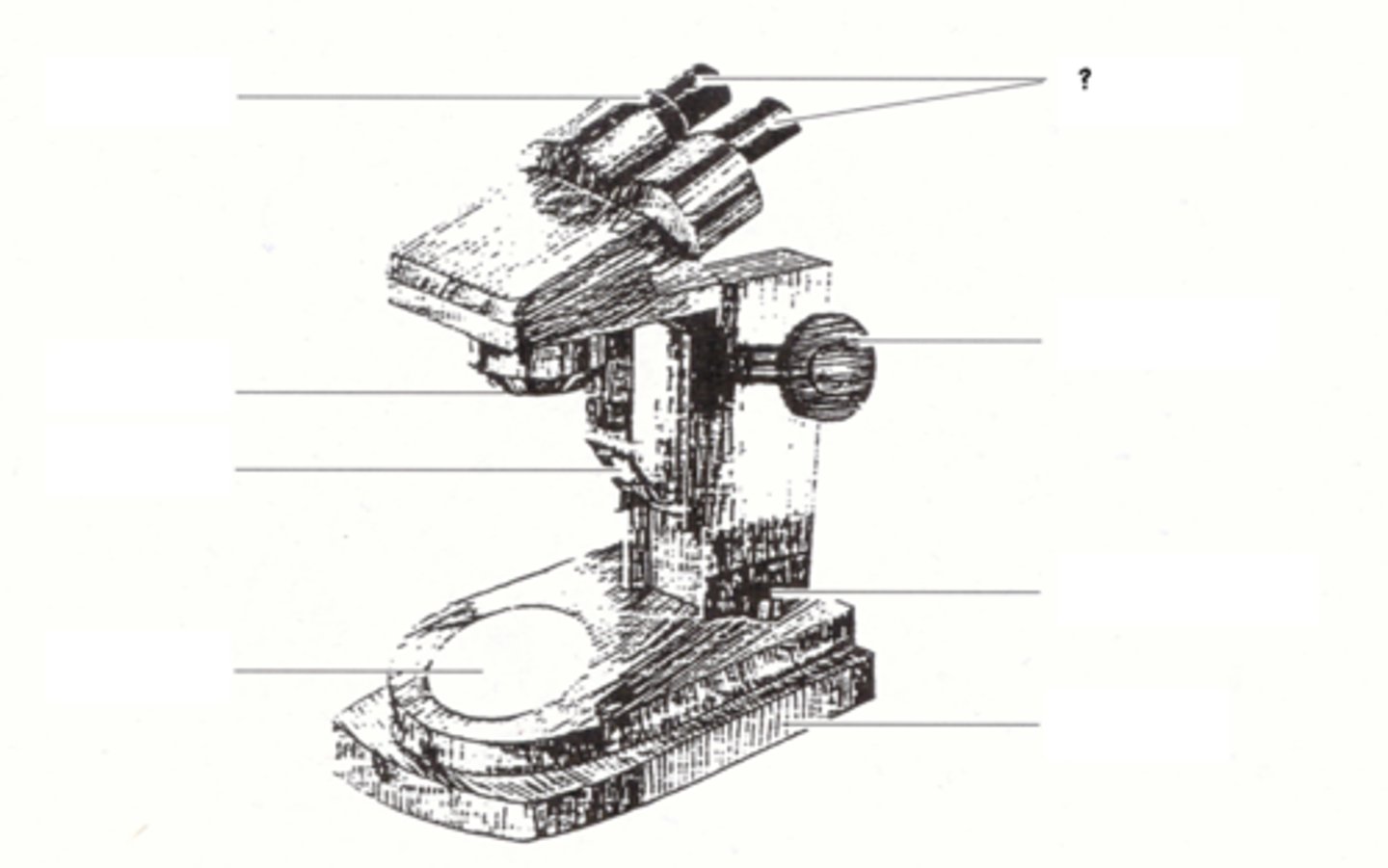
objective
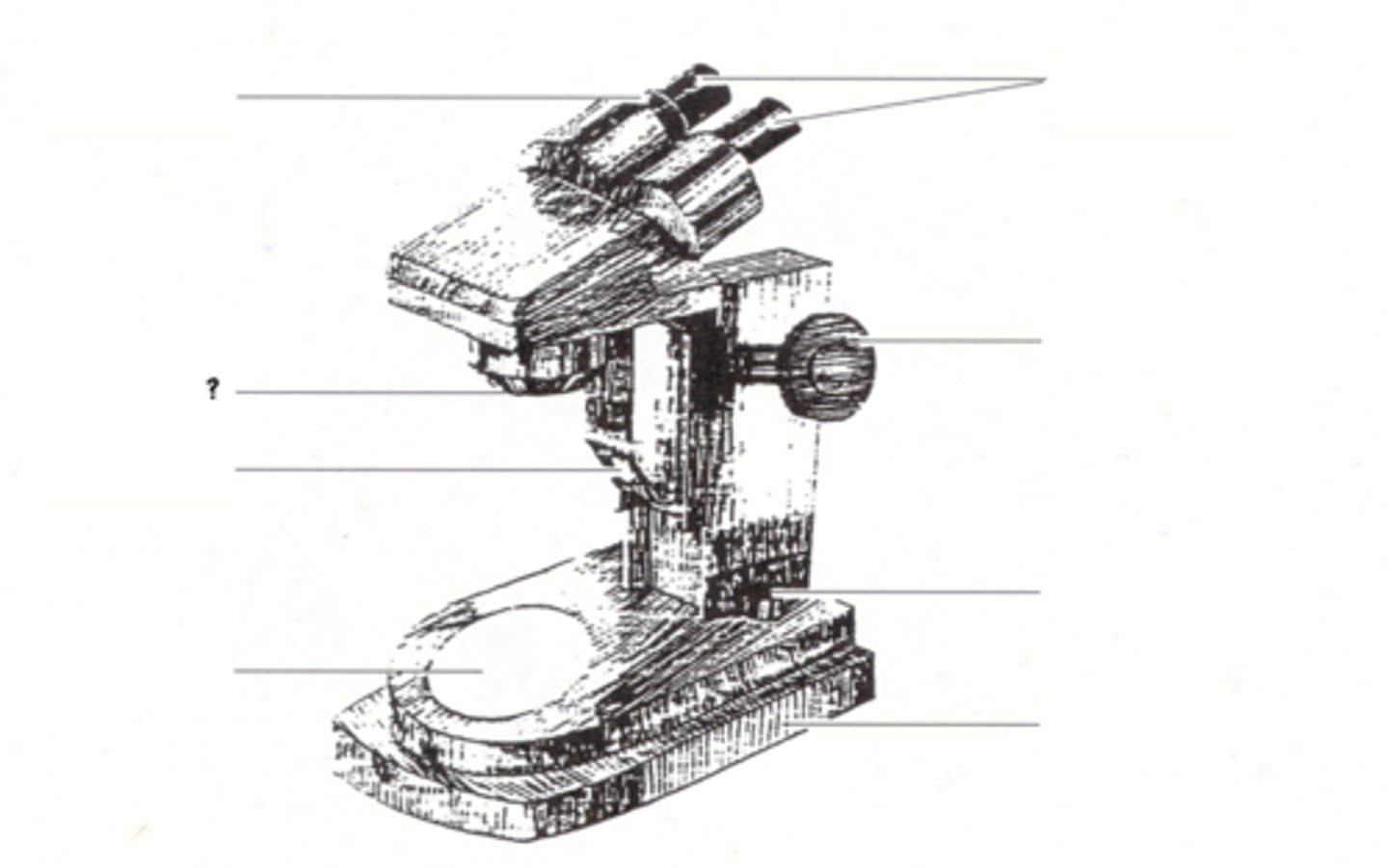
focusing knob
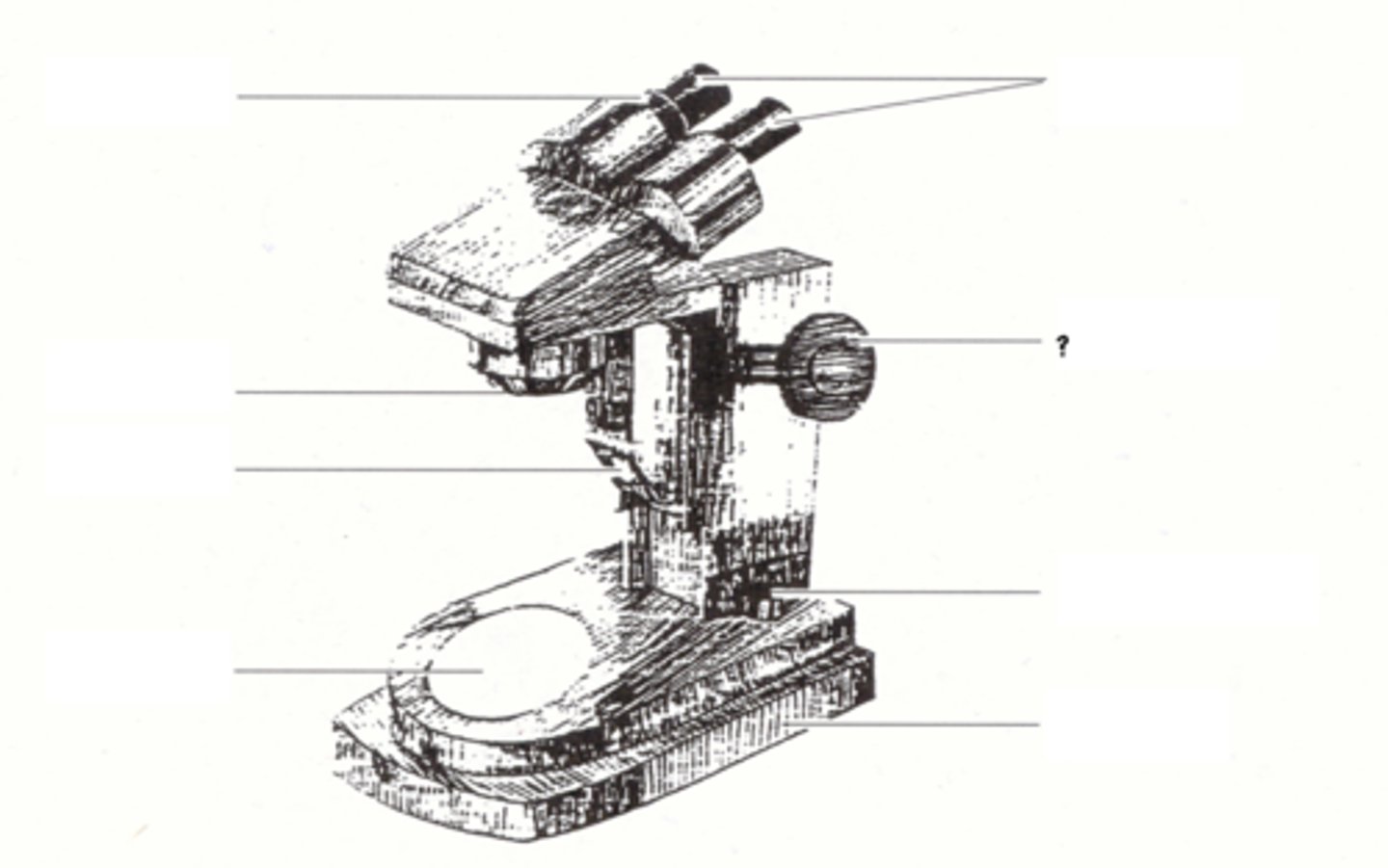
illuminator
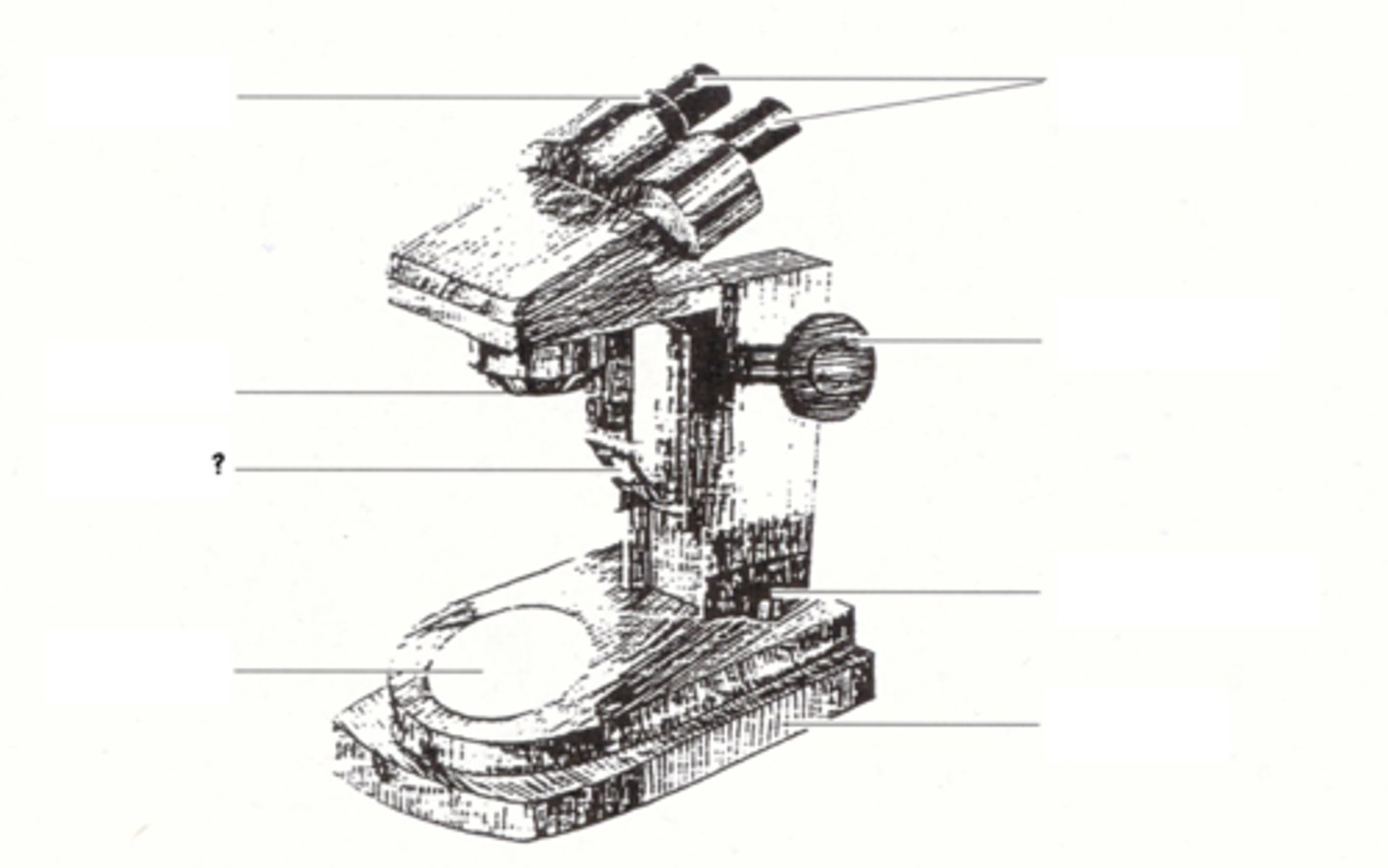
illuminator switch

stage
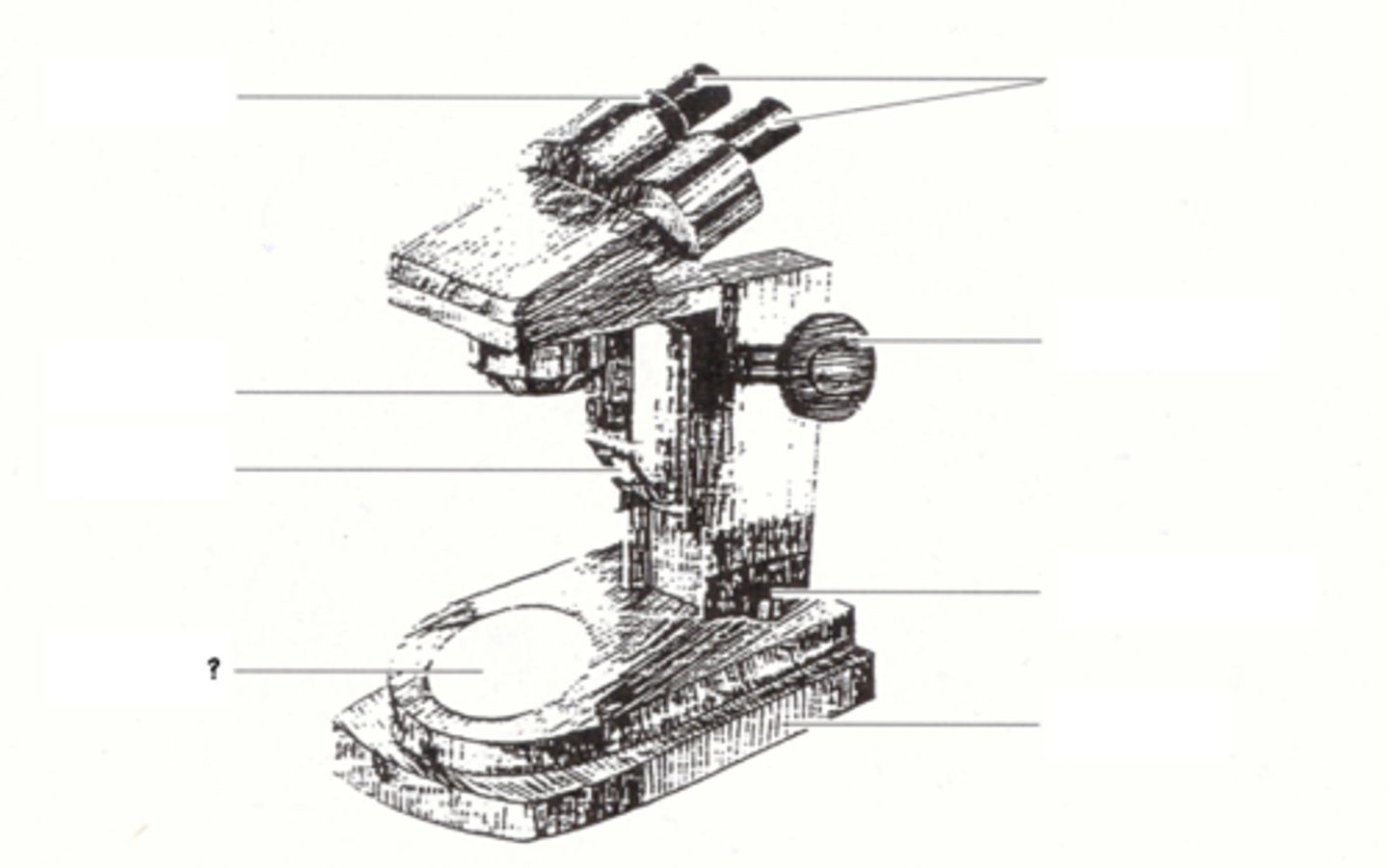
base
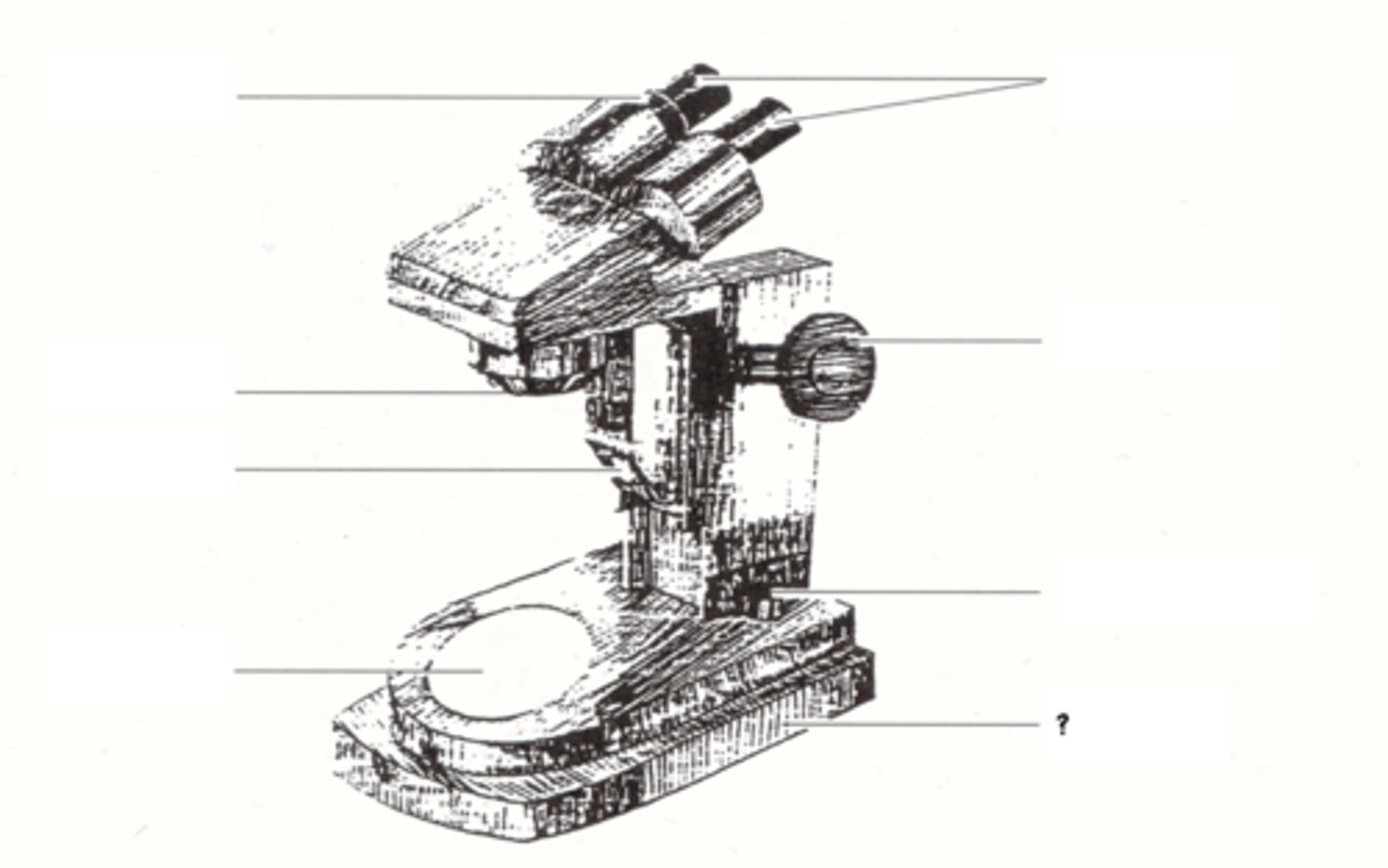
independent variable
variable that is manipulated
dependent variable
a variable whose value depends on that of another
mean
average
median
middle number
mode
the most frequently occurring
range
the difference between the highest and lowest
Benedicts test
testing for reducing sugars - stays clear blue
iodine test
testing for starch - turns green/brown
Biuret test
test for proteins - turns bright purple
brown paper test
test for lipids - leaves translucent spot
hydroxyl
OH-
carboxyl
COOH
amino
NH2
phosphate
PO4 3-
carbonyl
C=O
methyl
CH3
kilo
10^3 (1000)
base unit
10^0 (1)
deci
10^-1 (0.1)
centi
10^-2 (0.01)
milli
10^-3 (0.001)
micro
10^-6 (0.000001)
nano
10^-9 (0.000000001)
Celsius to Fahrenheit
F= 1.8 (C) +32
Fahrenheit to Celsius
C=(F-32)/1.8
compound scope magnification equation
eyepiece lens mag x objective lens mag
how to estimate length of an object by using the value for diameter of field on a compound scope.
multiply the diameter by one-tenth
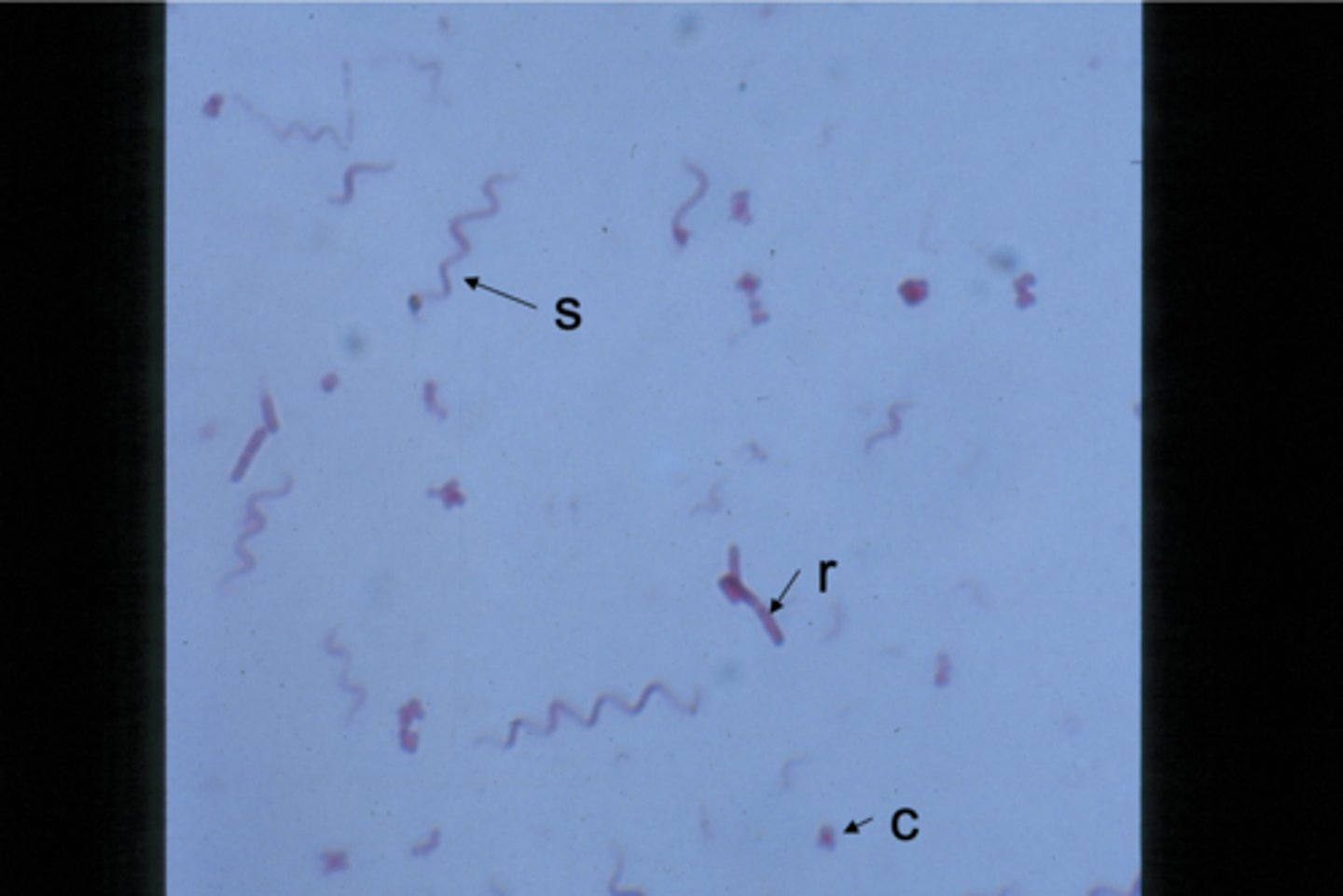
r - rods, s - spirilla/spirillum, c - cocci/coccus
Anabaena

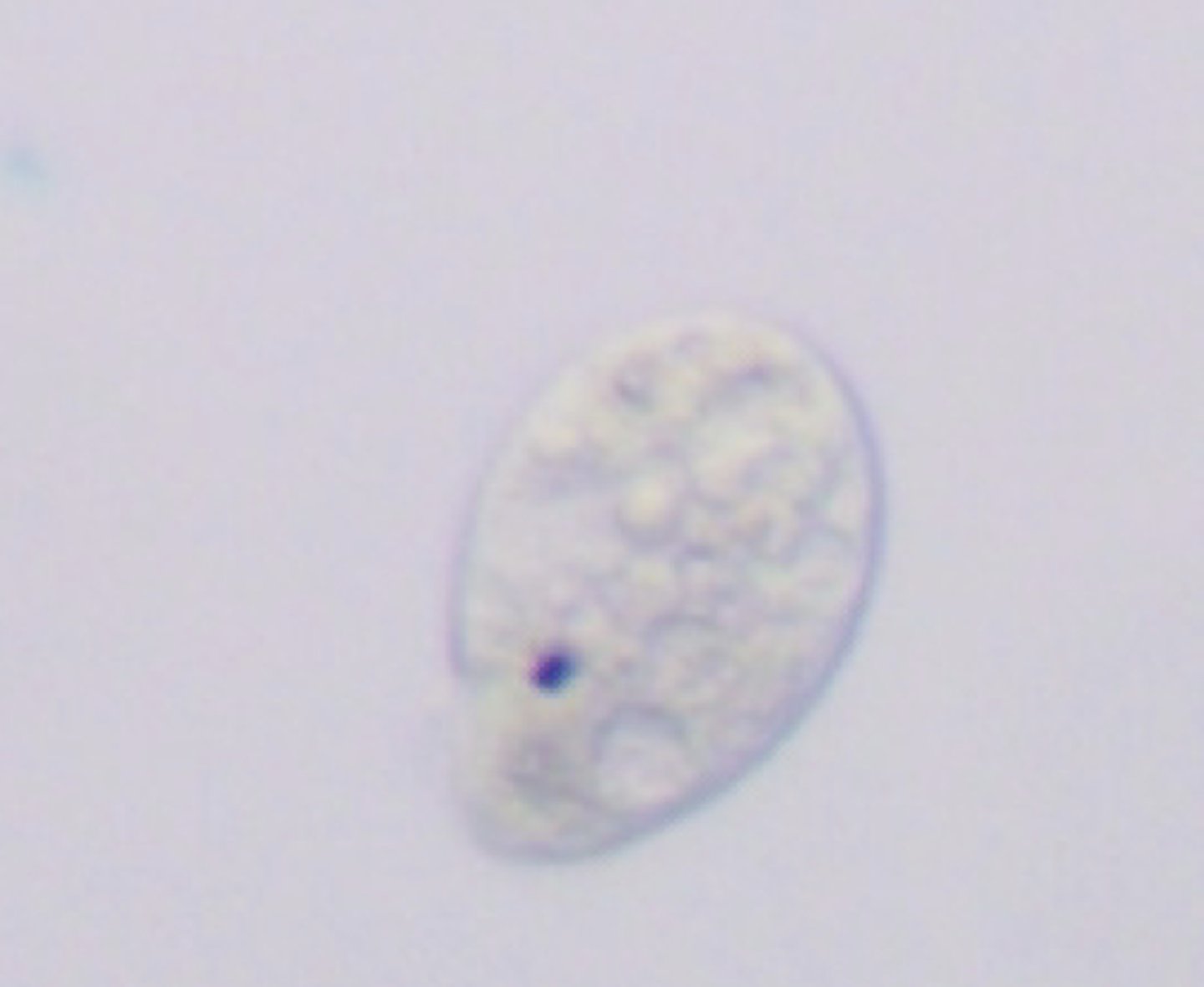
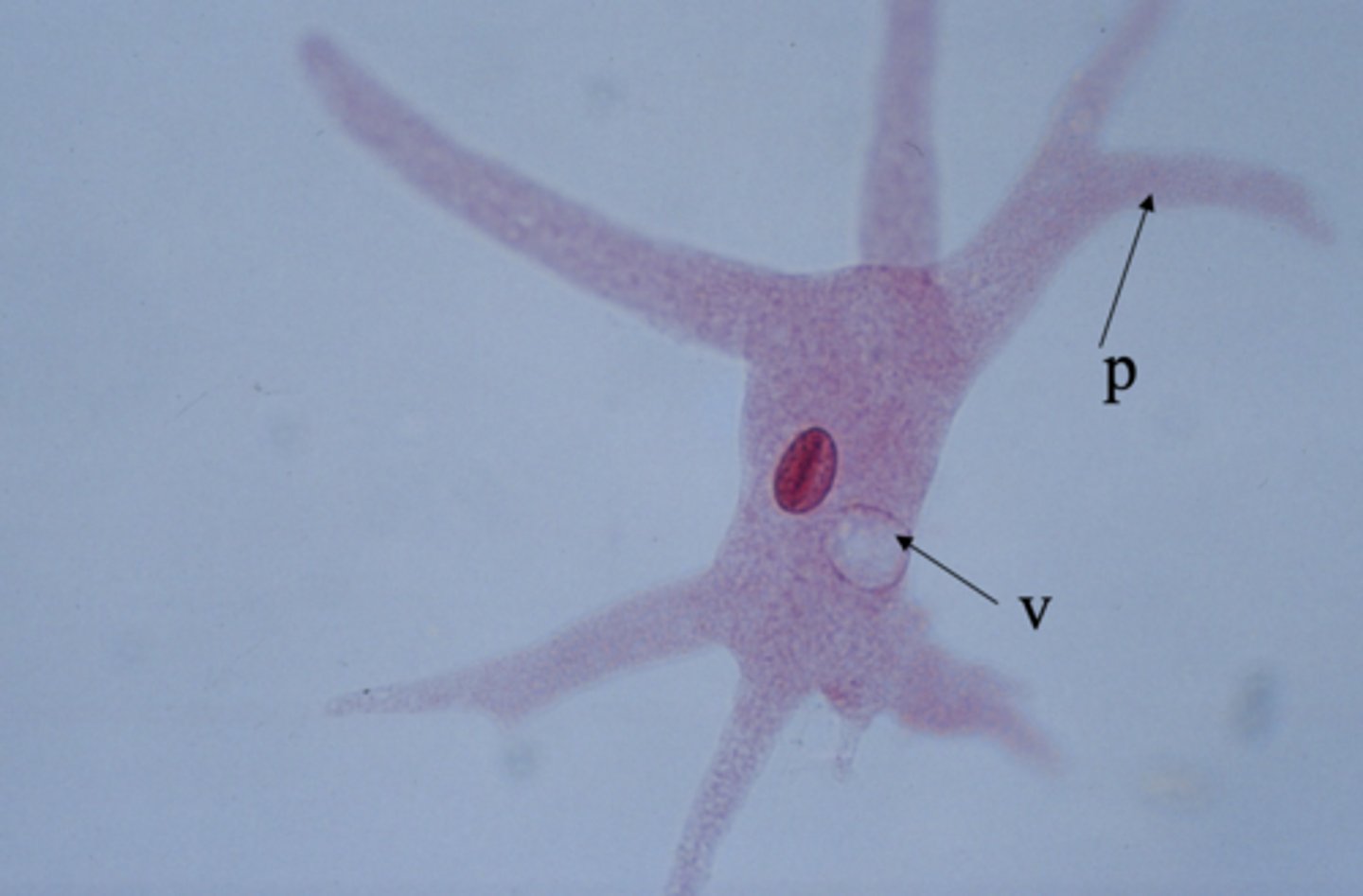
Tetrahymena
v=food vacuole, p=pseudopod
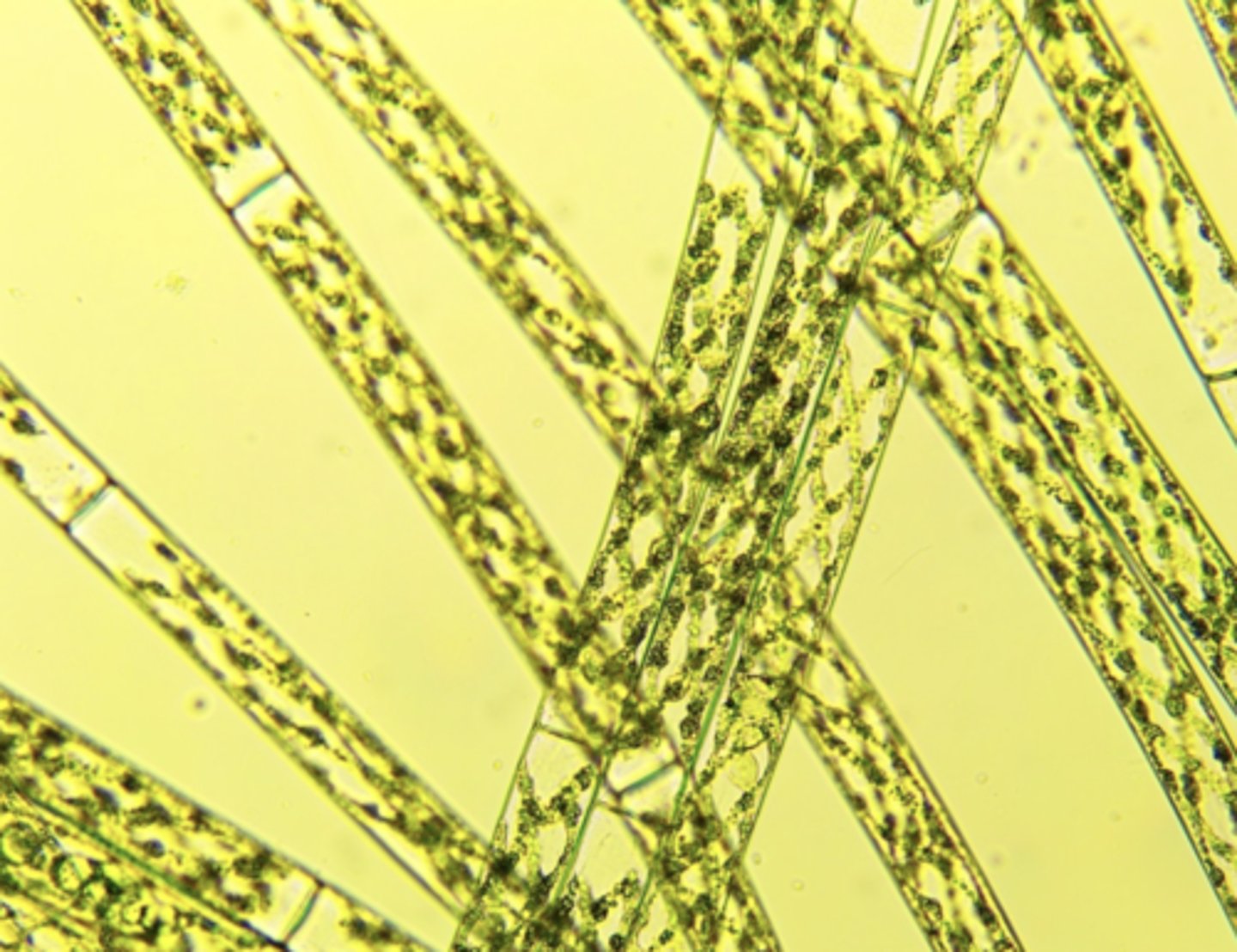
Spirogyra
Volvox
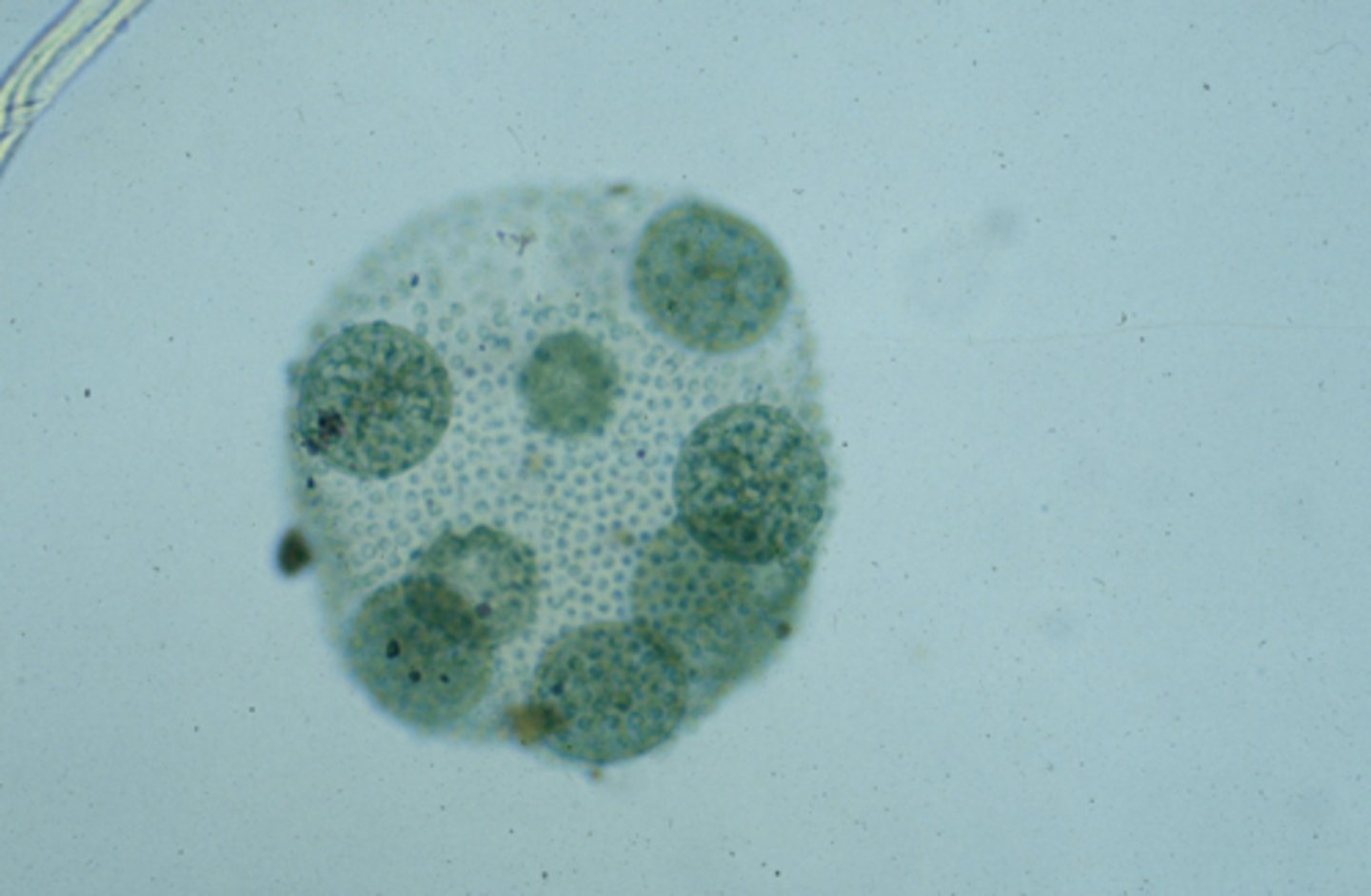
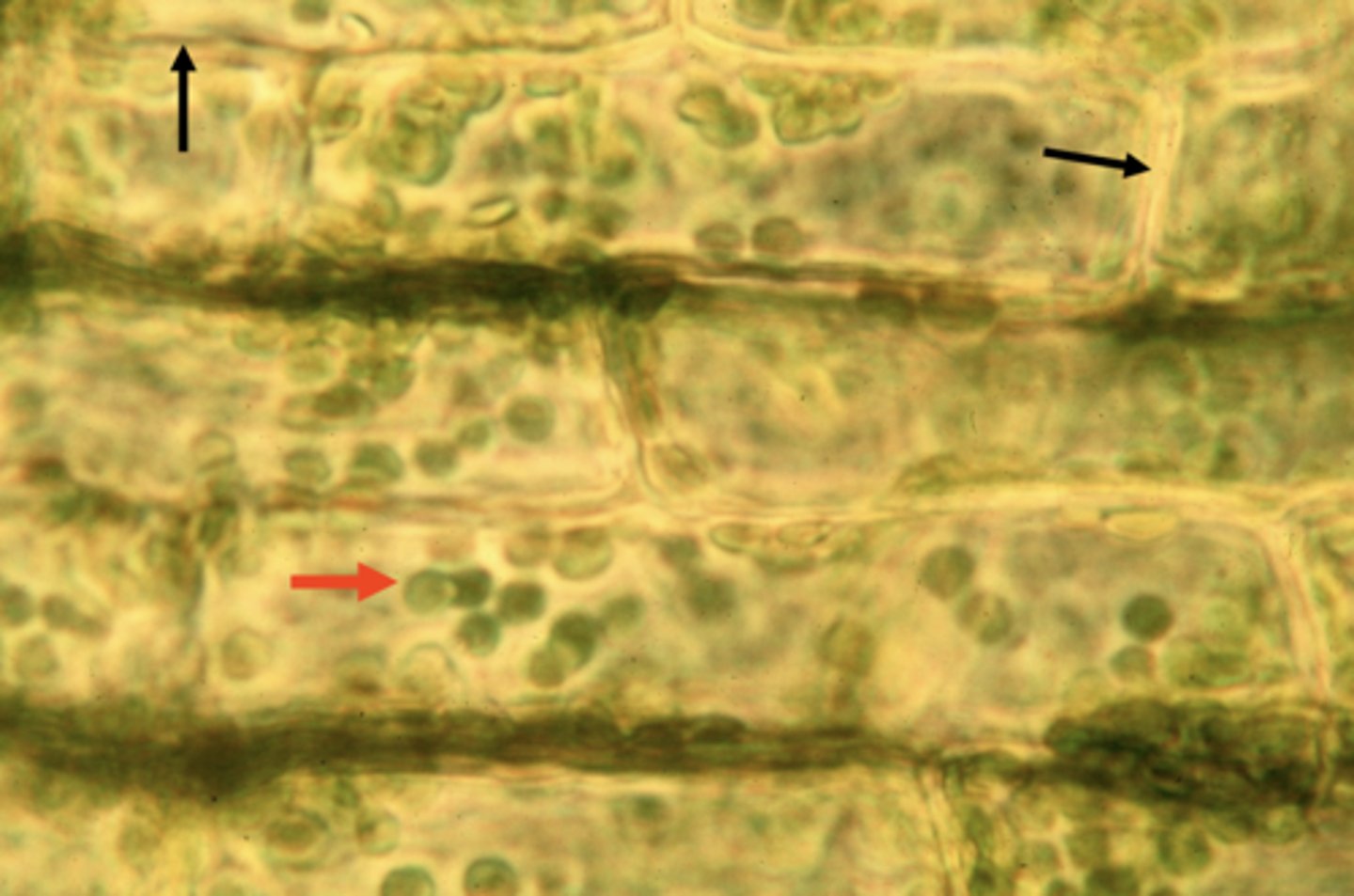
Elodea
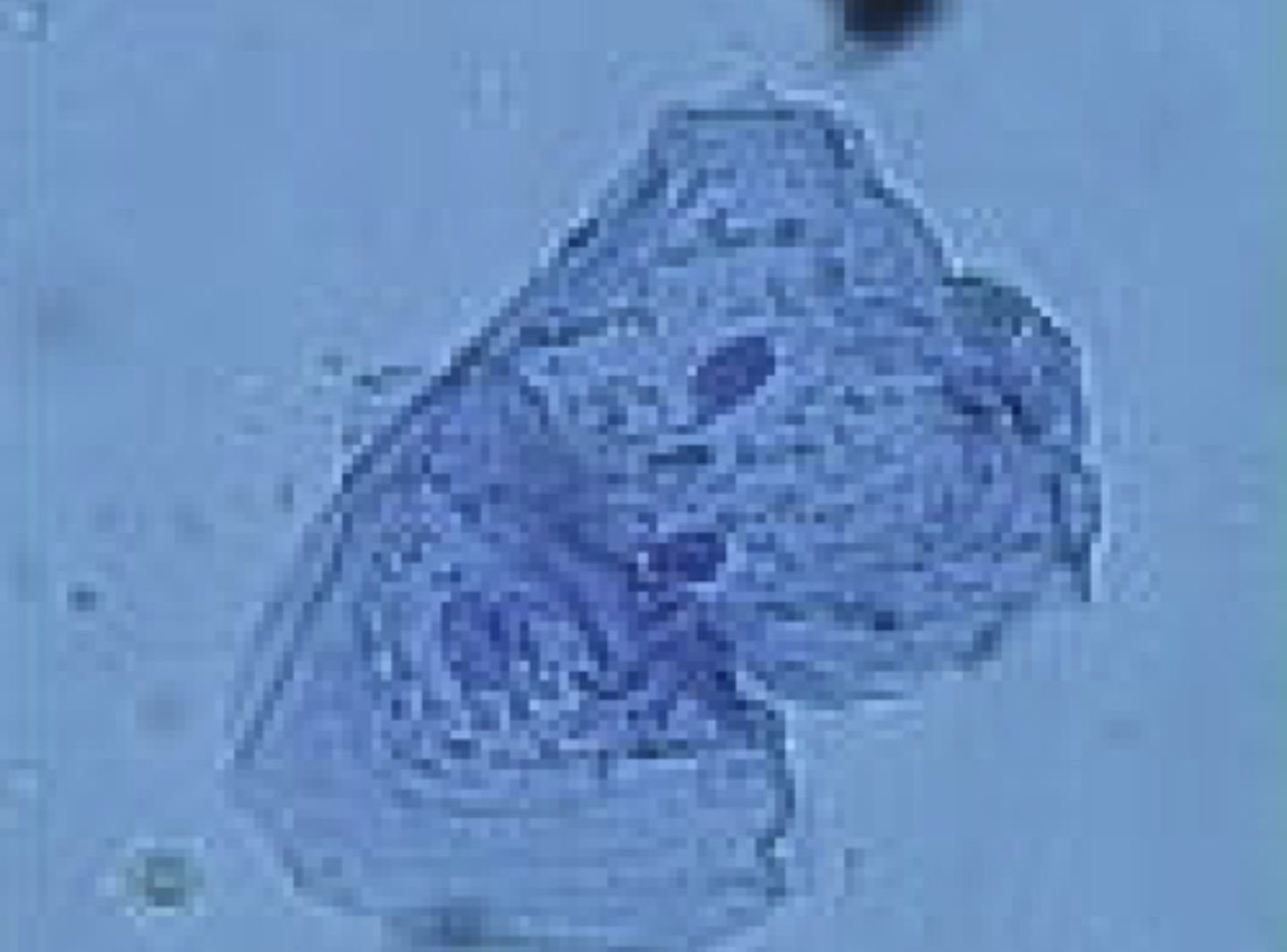
squamous epithelia
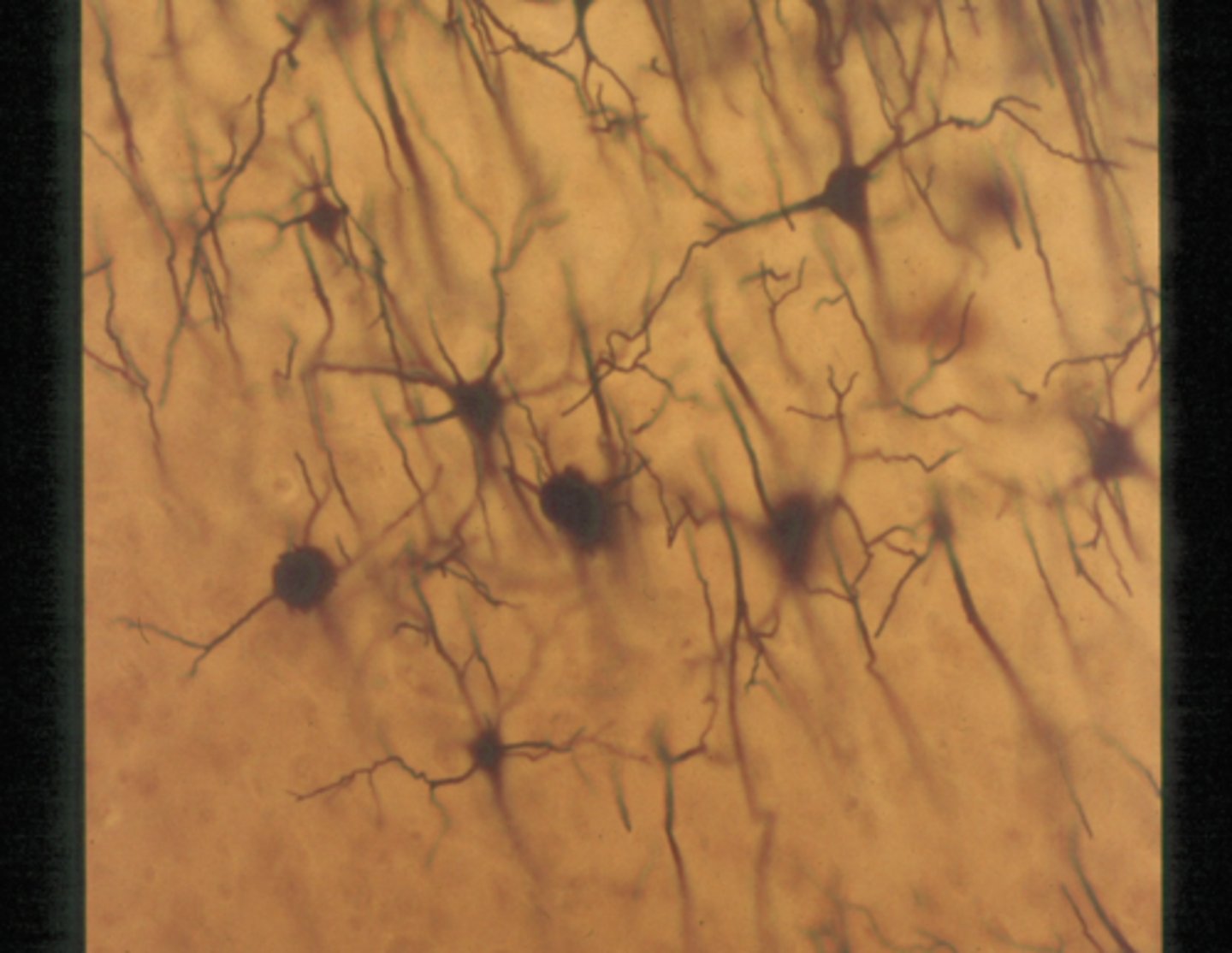
nerve cells from brain
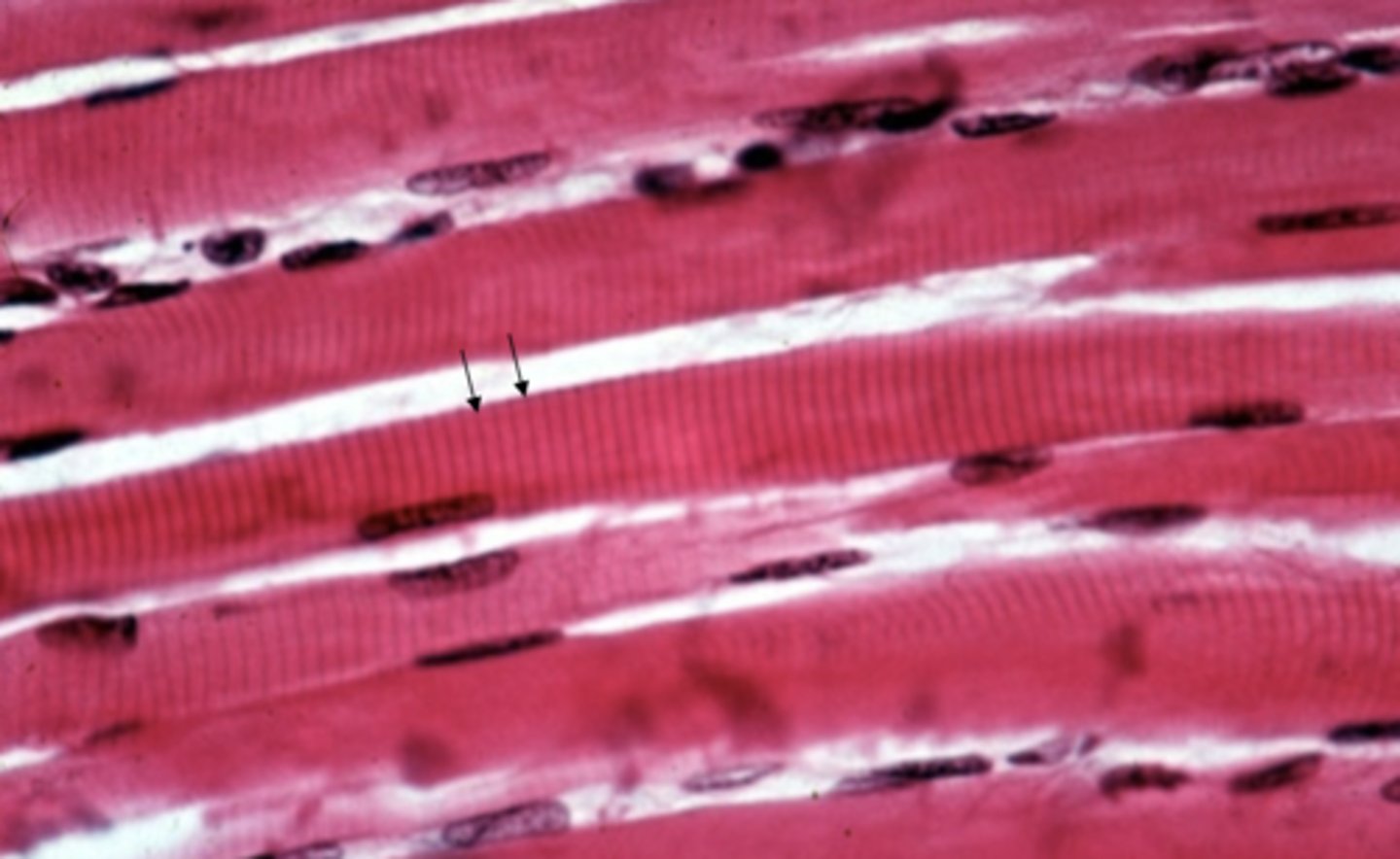
skeletal muscle
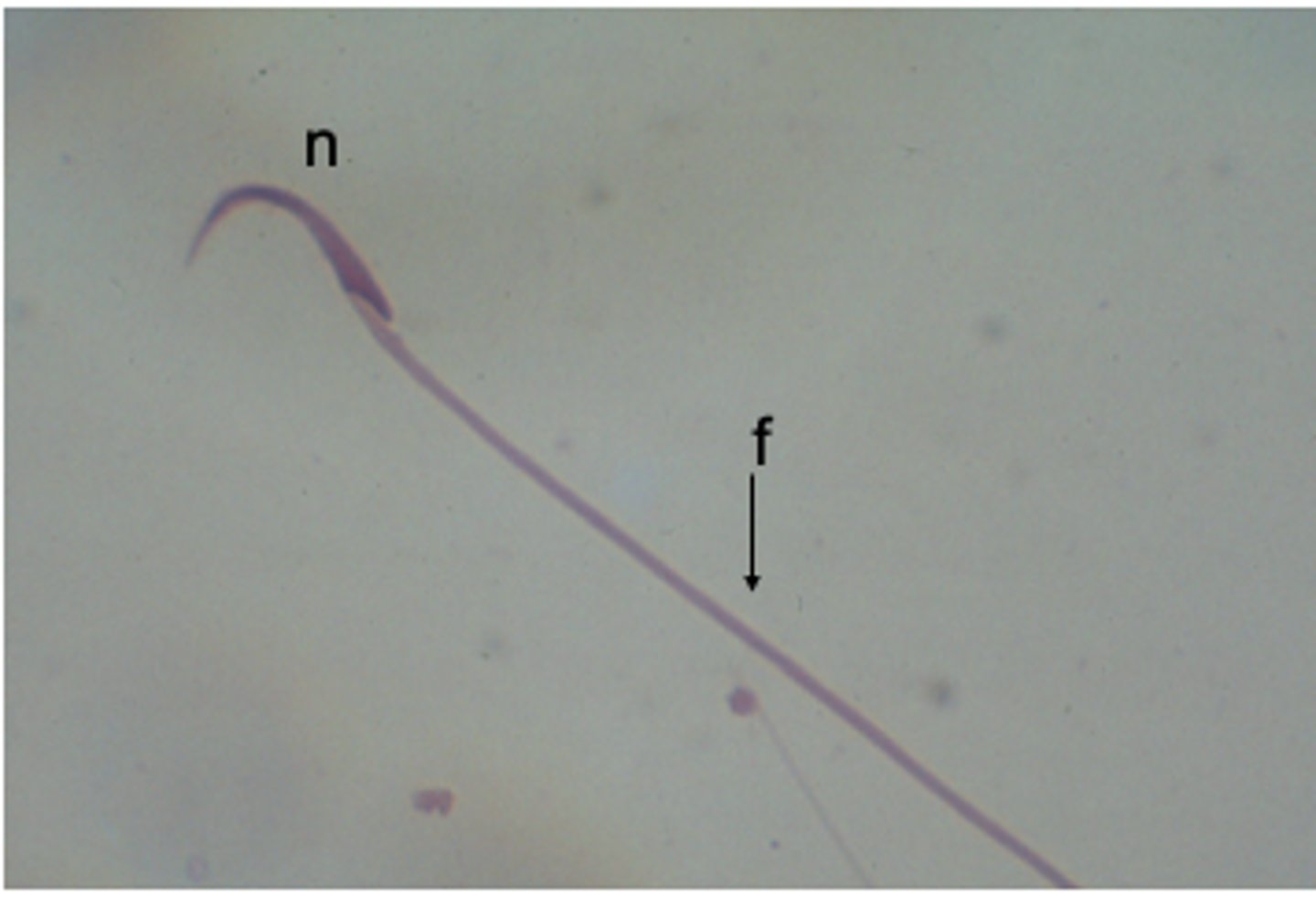
sperm, Note flagellum (f) and area of nucleus (n)
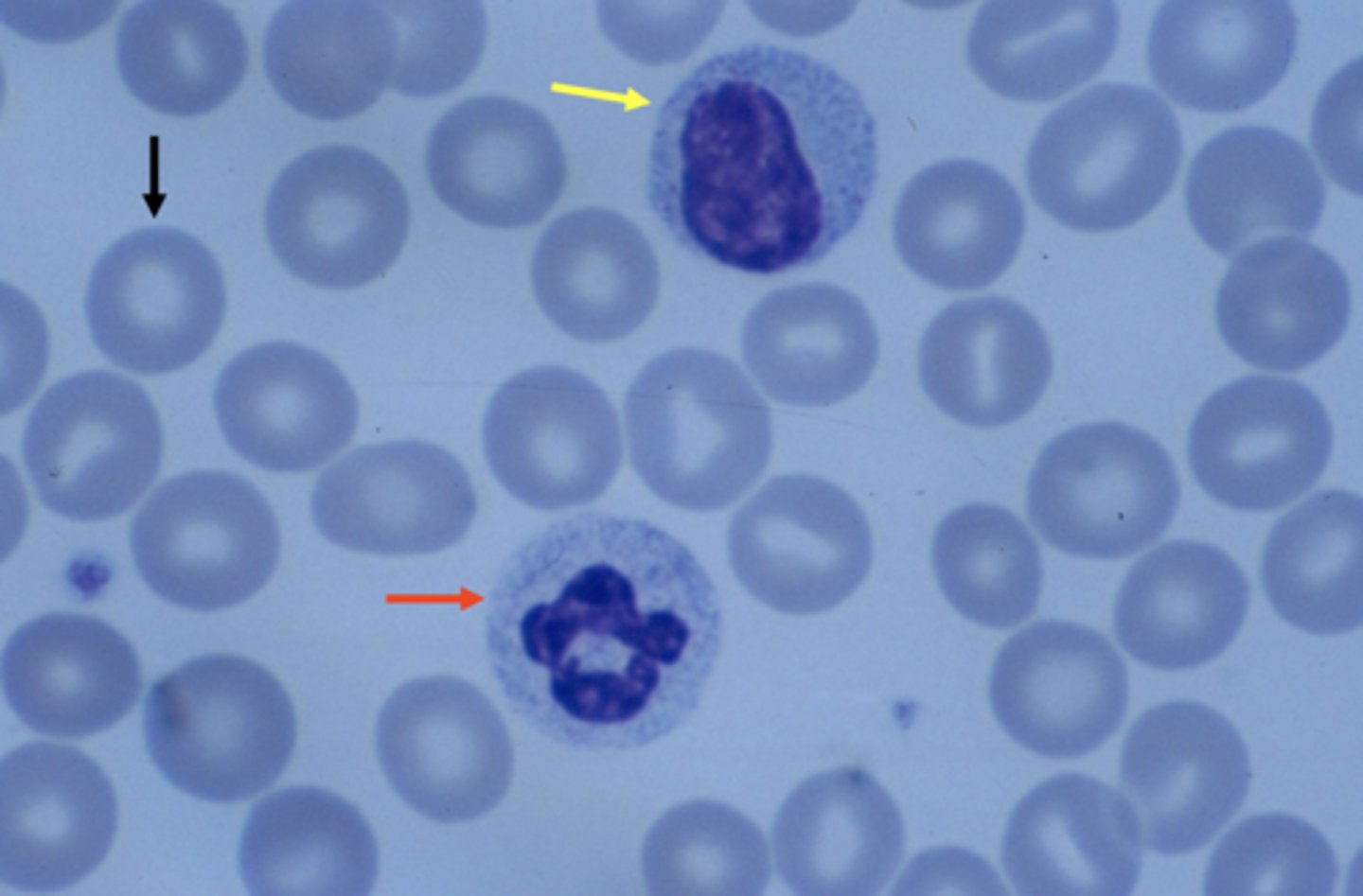
ed blood cells(black arrow), neutrophil (red arrow), and lymphocyte(yellow arrow)
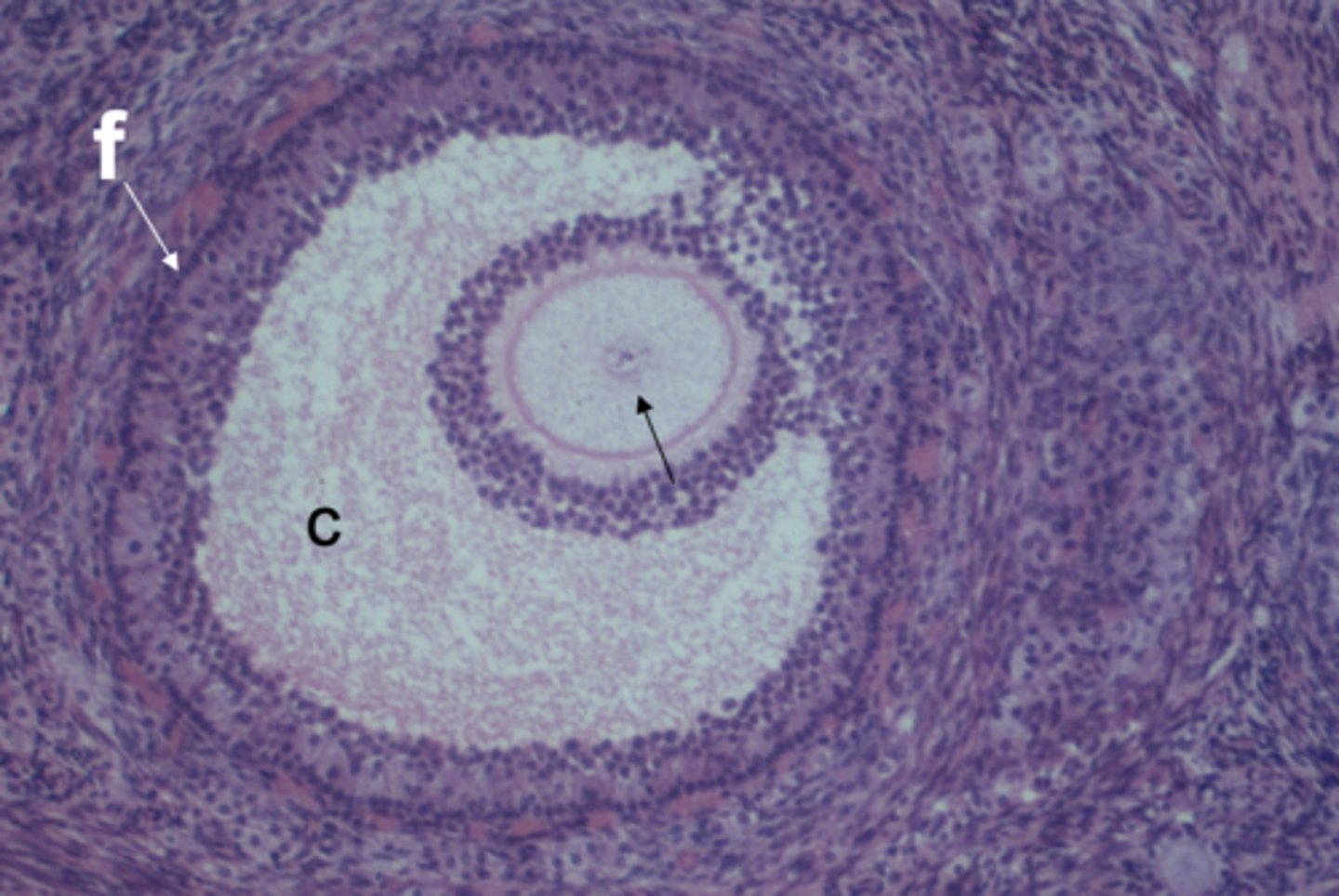
Ovary tissue. Note follicle (f), cavity of follicle (c), and eggcell (arrow)fc
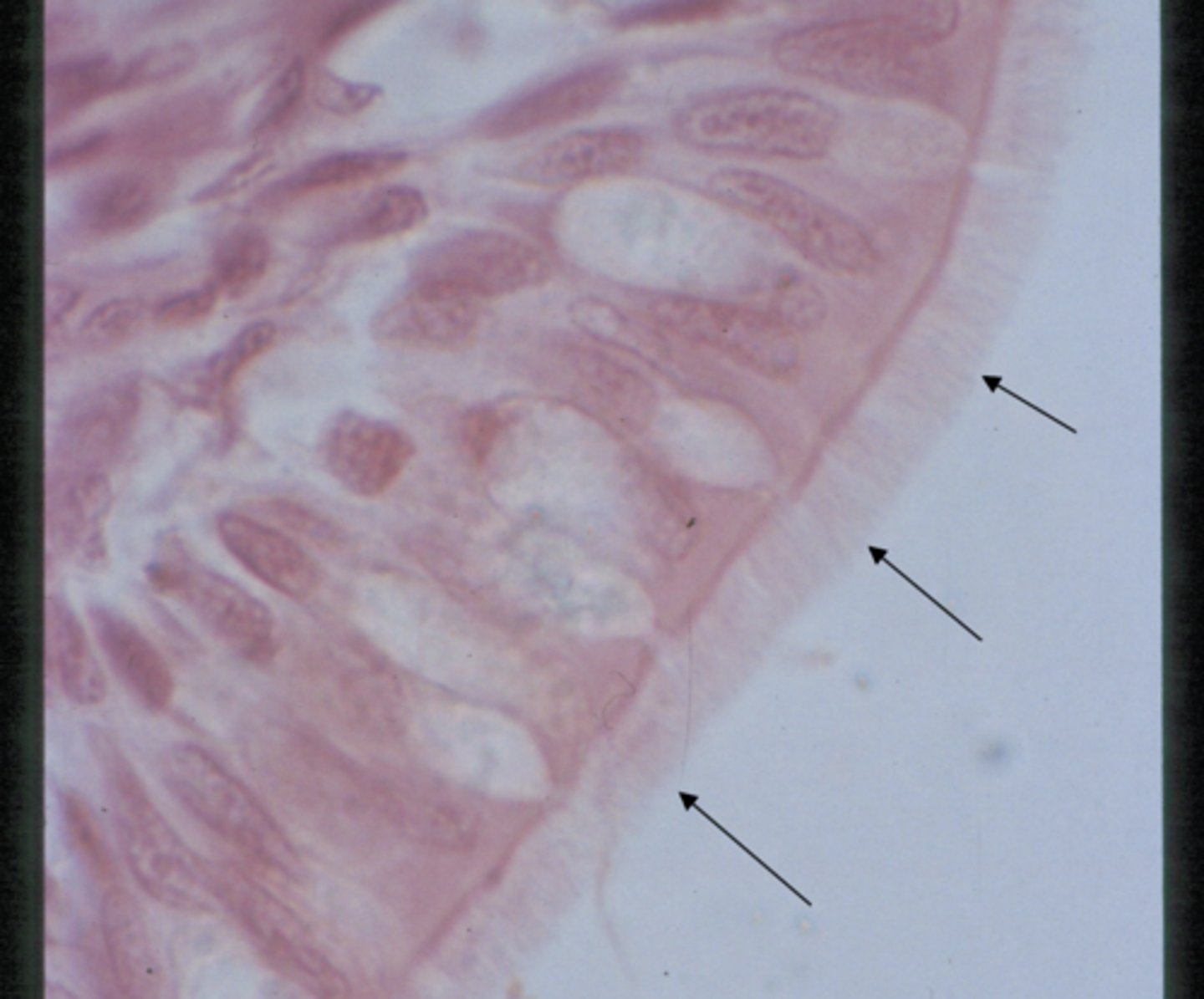
Ciliated epithelium
how temperature and molecular weight affect the rate of diffusion
higher temperatures increase the rate of diffusion, while higher molecular weight decreases the rate of diffusion
osmosis
diffusion of water
diffusion
movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
a bag containing a solution with a higher solute concentration (hypertonic)
will gain mass due to osmosis, as water moves from the hypotonic solution into the bag
a bag with a lower solute concentration (hypotonic)
will lose mass to the surrounding hypertonic solution
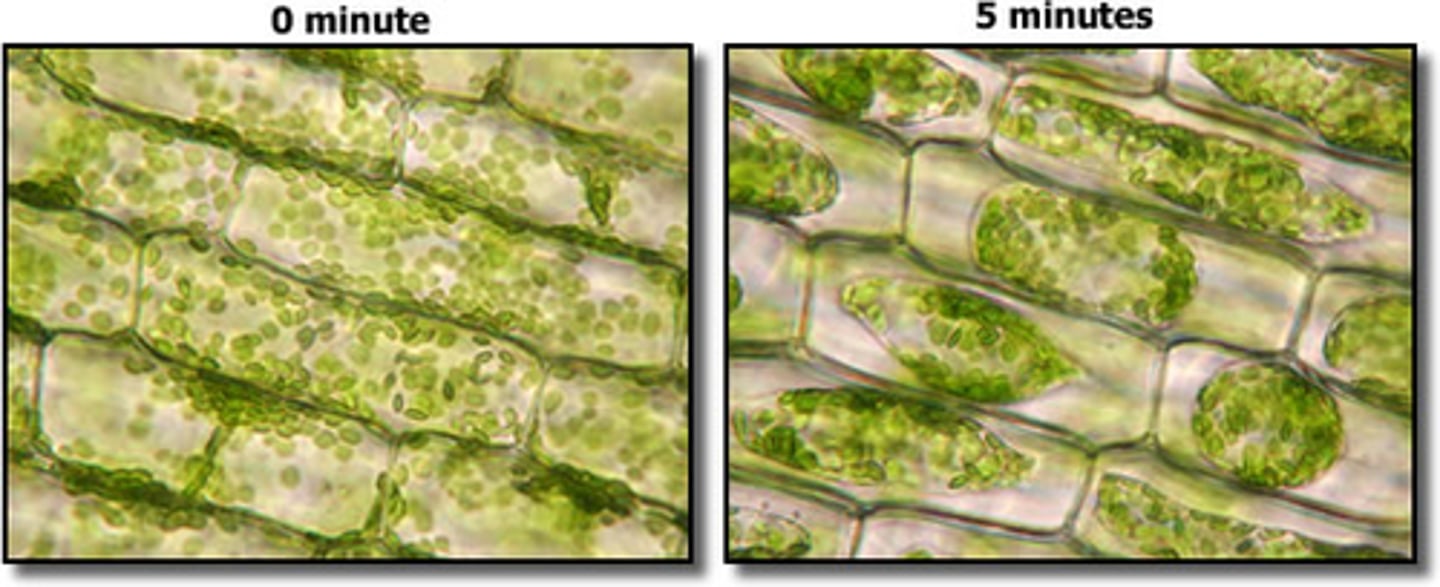
salt solution plasmolyzed Elodea
salt creates a hypertonic environment, causing water to move out of the cells
enzymes
proteins that speed up chemical reactions
when testing potato extract
enzyme is catalase, the substrate is hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and the products are water (H2O) and oxygen (O2)
changing temperature when testing potato extract
increasing temperature generally increases enzyme activity until a certain point where extreme heat causes the enzyme to denature and lose its function
changing pH when testing potato extract
changing the pH away from the optimal range (around neutral) will significantly decrease enzyme activity due to disruption of the enzyme's protein structure and its ability to bind to the substrate
measuring CO2 production relates to respiration and fermentation in yeast
produces carbon dioxide and ethanol as byproducts
measuring CO2 production relates to respiration and fermentation in germinating beans
undergo cellular respiration, using oxygen to break down sugars and produce energy, with CO2 as a waste product
measuring CO2 production relates to respiration and fermentation in crickets
crickets produce CO2 through cellular respiration during their normal metabolic activities
aerobic respiration
respiration that requires oxygen
fermentation
process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen
heat of respiration represents
energy released as a byproduct of the cellular respiration process
when bromothymol blue experiment yields green
some CO2 is present
when bromothymol blue experiment yeilds yellow
has been in the dark - lots of CO2 is present
chromatography
technique that is used to separate the components of a mixture based on the tendency of each component to travel or be drawn across the surface of another material
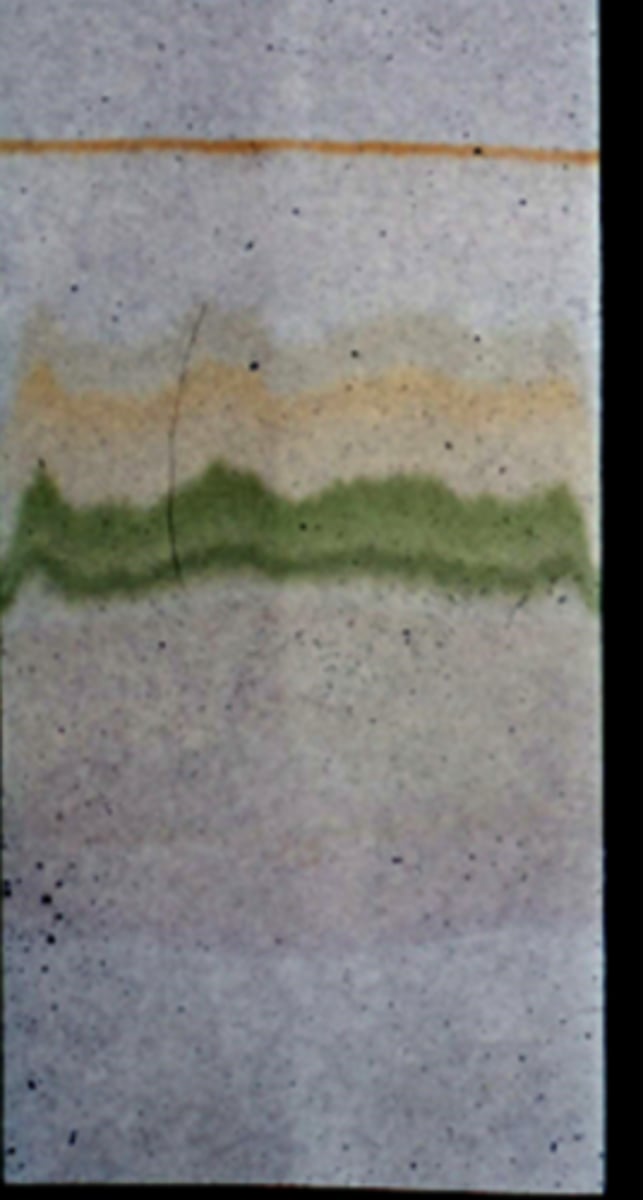
pigments in chromatography
have color based on what wavelength they do not absorb well
top to bottom: carotene, xanthophyll, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b
what fluorescence is and what causes it
the emission of light by a material after it absorbs radiation, usually ultraviolet light, brought about by absorption of photons in the singlet ground state promoted to a singlet excited state
what color is least useful for photosynthesis
green
reflected light
light that is thrown back or bounced off an object
absorbed light
light that enters but does not leave an object
where starch is stored
stored in plant leaves within the chloroplast
how light vs. dark affects starch storage
light - Photosynthesis occurs and more starch is produced, dark - Photosynthesis does not occur and less starch is produced
how measuring O2 levels relates to photosynthesis
more O2, the faster the rate of photosynthesis
mitosis
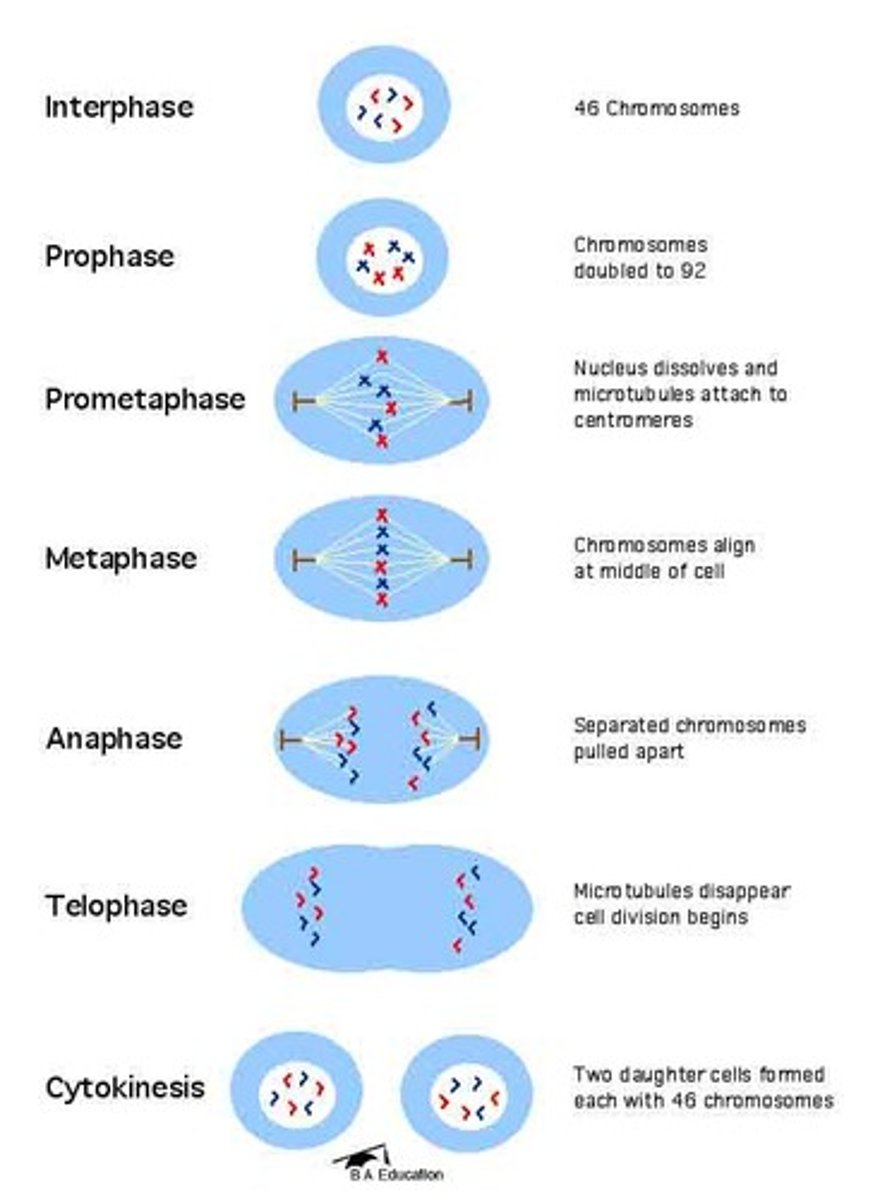
meiosis
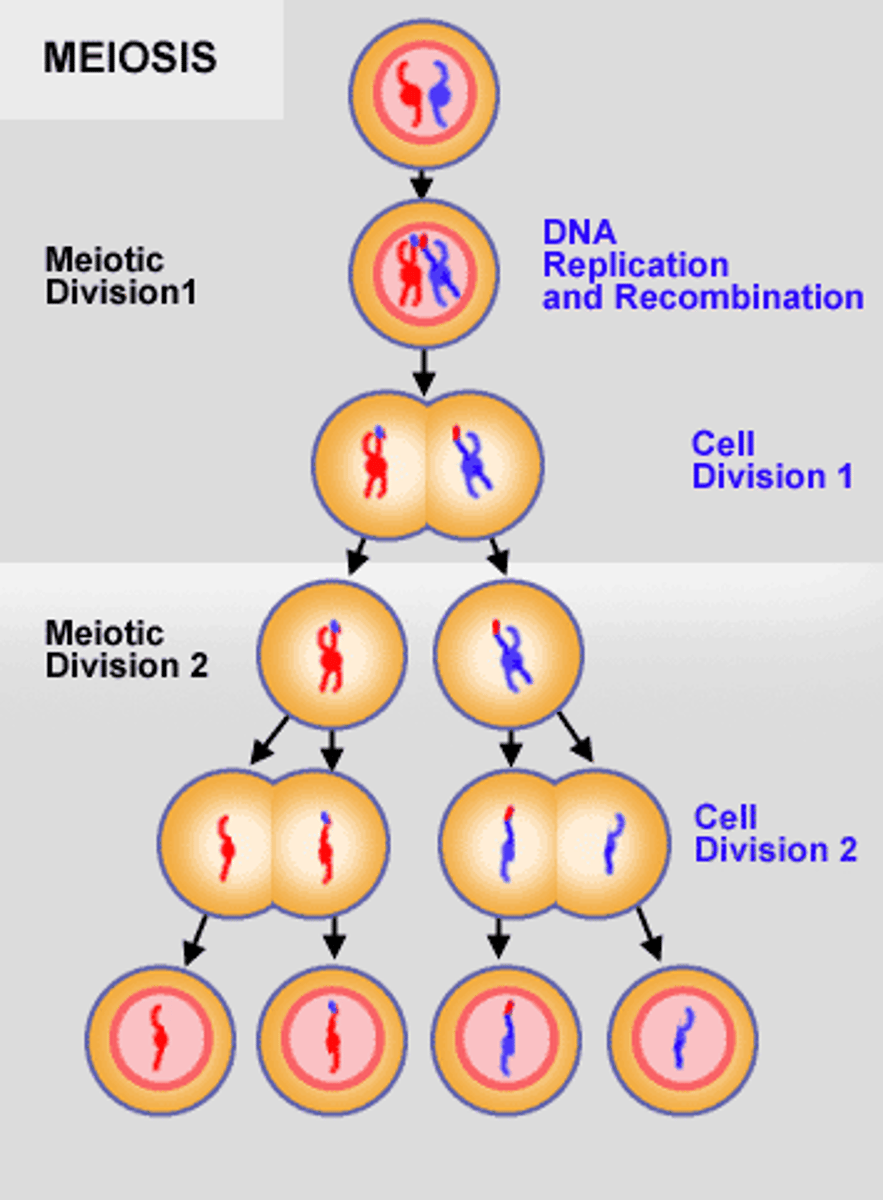
interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions
prophase
chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
prometaphase
nuclear envelope fragments and the spindle microtubules attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes
metaphase
chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
anaphase
chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
telophase and cytokinesis
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed
diploid
2 sets of chromosomes
haploid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
homozygous dominant
both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and dominant (AA)
homozygous recessive
both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and recessive (aa)
heterozygous
organism that has two different alleles for a trait
allele
different forms of a gene
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism
how to predict genotypic and phenotypic ratios for "monohybrid" crosses
use a Punnett square by identifying the genotypes of the parents, then filling in the square to see all possible combinations of alleles for the offspring
how to work backwards to determine the likely genotypes of parents
use a Punnett square by analyzing the known phenotypes of their offspring, considering the dominant and recessive traits involved, and then filling in the squares to find the most probable parental genotypes that would produce those offspring
how to predict phenotypic ratios for "dihybrid" crosses
use a Punnett square and expect a 9:3:3:1 ratio
how to work backwards to determine the likely genotypes of parent
use a Punnett square by analyzing the known phenotypes of the offspring, considering the dominant and recessive traits, and then filling in the squares to find the possible parental genotypes that would produce those offspring
X-linked (sex-linked) trait
gene is contained within the X or Y chromosome