11 - Thermodynamics & Thermochemistry
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key concepts, definitions, and important equations related to thermodynamics and thermochemistry as discussed in the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Thermodynamics
The field of physics that studies how heat, work, energy, and entropy interrelate for chemical or physical processes.
can determine if a reaction or process will happen
can NOT determine how fast a reaction will occur (that is kinetics)
R (Ideal Gas Constant)
8.314J/molK
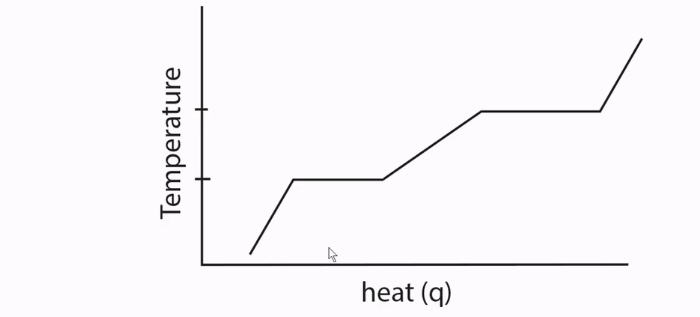
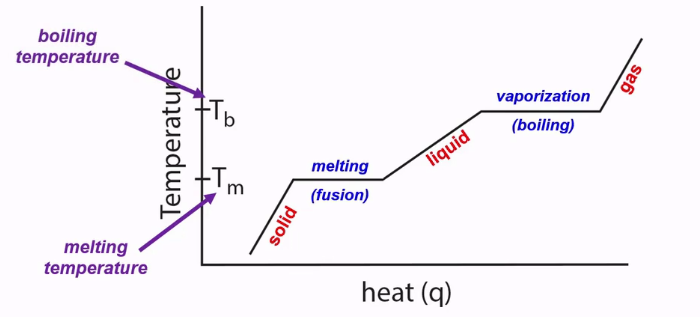
Heat Curves
A diagram that shows how a substance changes phases (from a solid to a liquid to a gas) as temperature is raised.
Conduction
Heat transfer due to direct contact
ΔG is Negative
Reaction will occur spontaneously
ΔG is Positive
Reaction will not occur spontaneously
ΔG is 0
Reaction is at equilibrium
Convection
Heat transfer due to the motion of a liquid or gas
Circulation hot air; air fryer
Radiation
Heat transfer via electromagnetic radiation
transfers heat with no medium in between through forms of radiation; microwaves
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Entropy;
The entropy of the universe is always increasing. If one system becomes more ordered, it does so by making another system (or surroundings) more disordered.
3rd Law of Thermodynamics
For a perfect crystal that’s been cooled to absolute zero (-273 K) its entropy is close to or approaching zero
Thermochemistry
The specific application of thermodynamics to chemical processes.
Universe
the system + surroundings
Heat
A form of energy associated with the movement of atoms and molecules.
Work
Energy transferred to or from an object via a force acting on it.
Energy
The capacity to do work or transfer heat.
Entropy (S)
A measure of disorder or randomness in a system.
A state function
Cannot be negative (but Delta S can)
(Direct) Entropy Increases = Disorder Increases = Atomic Movement Increases
State Functions
Properties that depend only on the initial and final state of a system, not on how it got there.
ΔE
The change in internal energy of a system.
1 st Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another.
ΔSuniverse
The total change in entropy of the universe.
Greater than zero
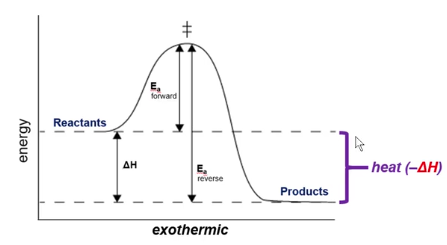
Exothermic Reaction (- H)
A reaction that releases heat to its surroundings.
Favorable
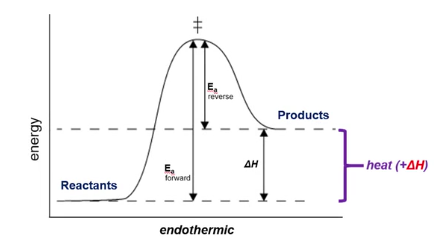
Endothermic Reaction (+ H)
A reaction that absorbs heat from its surroundings.
Unfavorable
Enthalpy (H)
The total heat content of a system.
Positive ΔH
Indicates that a reaction is endothermic. (absorbs heat)
Unfavorable
Negative ΔH
Indicates that a reaction is exothermic. (gives off heat)
Favorable
Calorie (cal)
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 °C.
Calorie (Cal)
Equal to 1,000 calories; used in nutritional contexts.
Calorimetry
A technique used to measure the heat of chemical reactions.
Bomb Calorimeter
A device used to measure heat produced by a chemical reaction.
Phase Change
A transition of a substance from one state of matter to another.
Fusion
The process of melting; transition from solid to liquid.
Endothermic (+)
S +
Vaporization
The process of boiling; transition from liquid to gas.
Endothermic (+)
S +
Sublimation
The transition from solid to gas without passing through the liquid phase.
Endothermic (+)
S +
Deposition
The transition from gas to solid without passing through the liquid phase
Exothermic (-)
S -
Condensation
The process of gas transforming into a liquid.
Exothermic (-)
S -
Crystallization
The process of transforming liquid into solid
Exothermic (-)
S -
What two elements are liquid at standards state?
Mercury (Hg)
Bromine (Br)
ΔS
The change in entropy of a system.
Can be positive or negative
Spontaneous Reaction
A reaction that occurs without external influence.
Nonspontaneous Reaction
A reaction that does not occur without external influence.
Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG)
A thermodynamic quantity that indicates the spontaneity of a reaction.
Standard Conditions
Conditions of 298 K (25 °C) and 1 atm used for measuring ΔG, ΔH, and ΔS.
Enthalpy of Formation (ΔH°f)
The change in enthalpy when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements at standard conditions.
Equal to 0 kj/mol when an element is in this standard state
Hess's Law
The principle that the total enthalpy change in a reaction is the sum of the changes in the individual steps.
Specific Heat (C)
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by 1 °C.
Varies from one substance to another
Varies from different phases (solid, liquid and gas) of the same substance
Positive q
Indicates that heat is absorbed by the system.
Negative q
Indicates that heat is released from the system.
Work (w)
Energy transfer resulting from a force applied over a distance.
Entropy Change (ΔS)
The difference in entropy of products and reactants in a reaction.
System
The part of the universe being studied in thermodynamics. The substance or region you are examining
In thermochemistry, this would be the products and reactants
Surroundings
Everything outside the system that can exchange energy with it.
Heat Transfer Methods
Conduction, convection, and radiation.
Spontaneity of a Reaction
Determined by the signs and magnitudes of ΔH and ΔS.
ΔG° (/ΔS°/ΔH°)
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)
273 K and 1 atm
ΔG > 0
Indicates a nonspontaneous reaction under given conditions.
ΔG < 0
Indicates a spontaneous reaction under given conditions.
Gibbs Free Energy Equation
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS.
Work Done to the surroundings by the System
Occurs when a system expands against an external pressure.
W is +
Work done to the system by the surroundings
Occurs when a system compresses
W is -
Calorimeter Constant (Ccalorimeter)
The specific heat capacity of the calorimeter used in calorimetry experiments.
Temperature Change (ΔT)
The change in temperature during a reaction or process.
Laws of Thermodynamics
Three main laws governing energy and heat in physical processes: conservation of energy, increase of entropy, and absolute zero states.
Endothermic vs. Exothermic
Endothermic absorbs heat; exothermic releases heat.
Heat Capacity (C)
The amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a certain amount.
Phase Transition
The transformation from one state of matter to another.
Enthalpy Change (ΔH)
The difference in enthalpy between the products and reactants.
Chemical Potential Energy
Potential energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance.
Kinetic Energy
The energy of motion.
Potential Energy
Stored energy based on an object's position or condition.
Ideal Gas Behavior
The assumptions that the gas particles are non-interactive and the volume of individual particles is negligible.
Molecular Motion
Movement of molecules that contributes to the thermal energy of a substance.
Gas Law Constant (R)
A physical constant that relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of an ideal gas.
Temperature (T)
A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed.
Activation Energy
The minimum energy required for a reaction to occur.
Chemical Equilibrium Expression
An equation that relates the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium.
Enthalpies of Reaction
The change in enthalpy when a chemical reaction occurs.
Molar Enthalpy of Fusion
The heat needed to melt one mole of a solid at its melting point.
Molar Enthalpy of Vaporization
The heat required to vaporize one mole of a liquid at its boiling point.
Thermal Energy Transfer
The flow of energy from a warmer object to a cooler one.
Temperature Scale
Units of measurement for temperature, such as Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin.
Heat of Reaction
The change in enthalpy during a chemical reaction.
Gibbs Free Energy Standard State
Conditions under which ΔG° is measured, typically 298 K and 1 atm.
Phase Diagram Components
Temperature and pressure as axes organizing phases of matter.
Chemical System Change
Alterations in reactants and products throughout a reaction.