Climate change: how we know it is us, and what the future holds
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Key vocabulary and concepts related to the human influence on climate change and future climate projections.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Greenhouse Gases (GHG)
Gases in the atmosphere, like CO2, that absorb and re-emit longwave (infrared) radiation, trapping heat and warming the planet.
More GHG = atmosphere becomes more opaque
Radiation to space occurs at higher altitudes - colder here
Less radiation is emitted to space
More radiation comes in than leaving to space
=atmosphere warms
Climate Models
Computer models that use equations to represent processes and interactions within the climate system to simulate past, present, and future climate conditions.
Allow us to ask what if questions of the climate system
Climate Change Attribution
The process of identifying and quantifying the causes of observed climate changes, often distinguishing between human and natural factors.
We want to prove it is us, not other factors
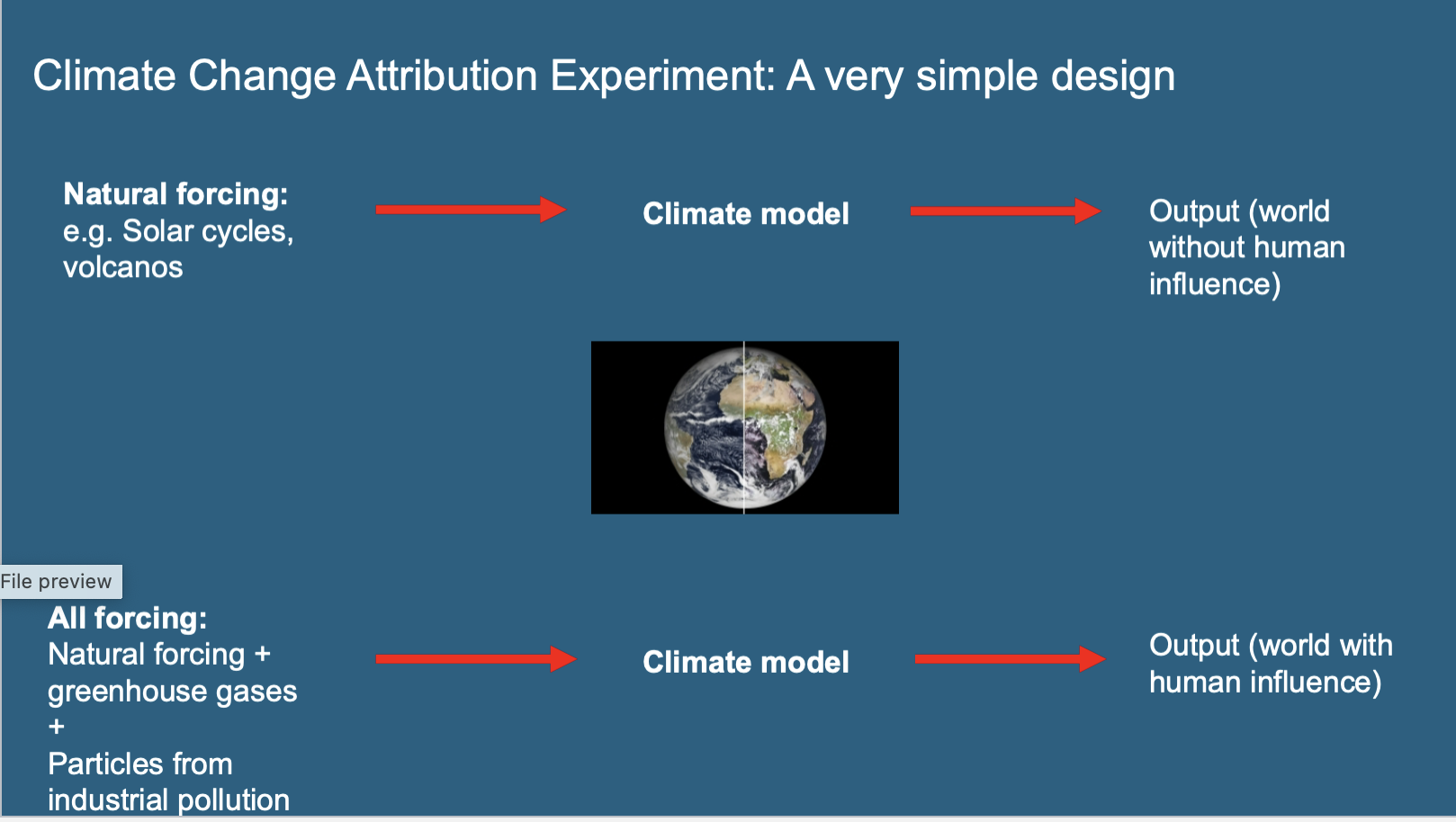
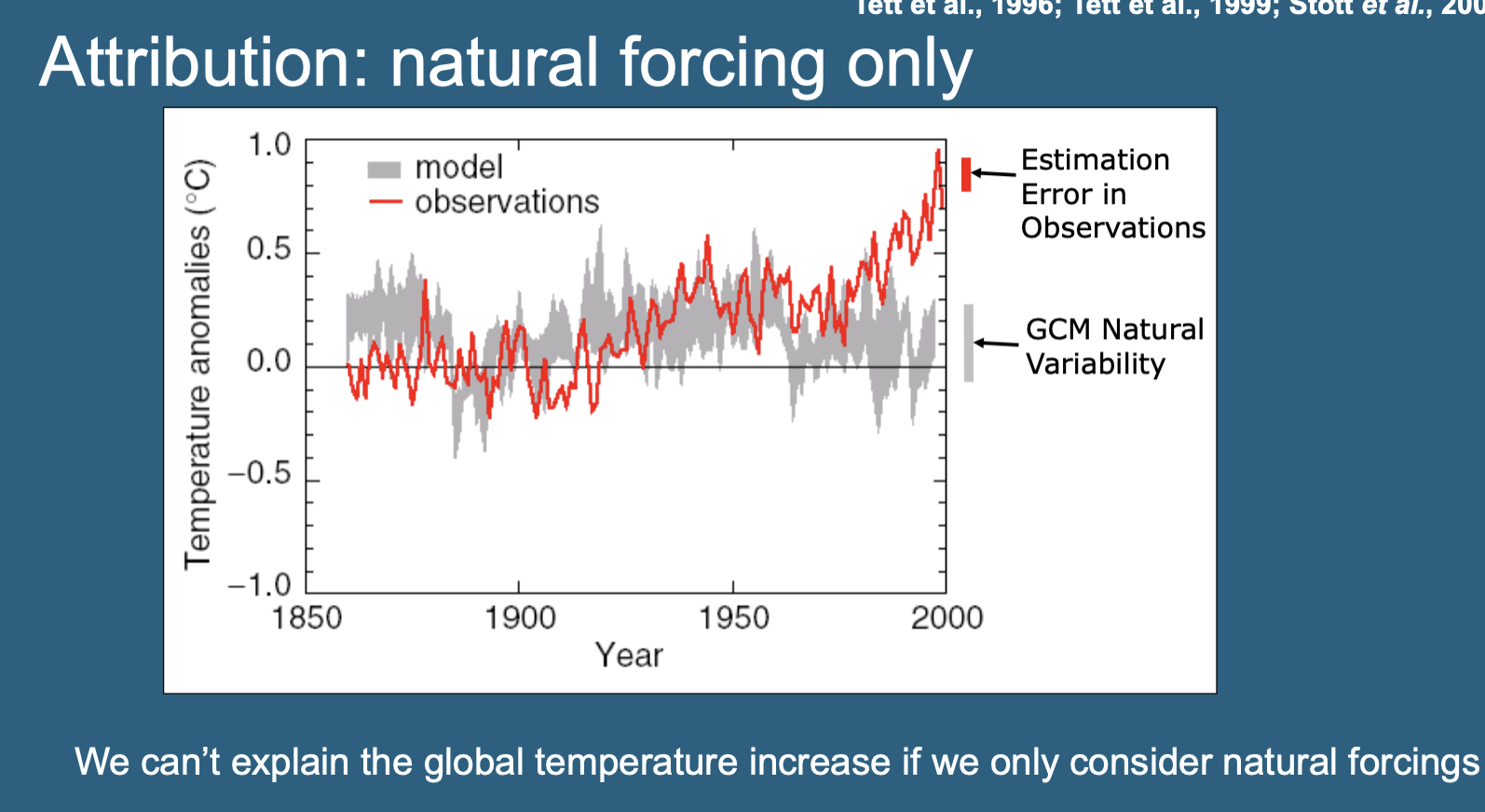
Natural Forcing
External factors that influence the climate system, such as solar variations and volcanic eruptions, excluding human-caused factors.
All forcing
natural + GHG + particles from industrial pollution put into the model shows output with human influence
Extreme Events
Unusual or rare weather events, the frequency and intensity of which may be altered by climate change, potentially causing significant damage to society.
E.g. we do not feel the 1 degree change, but we feel the impact of these extreme events
Future Climate Change Projections
Estimates of potential future climate conditions based on climate models and various emissions scenarios, used to understand possible impacts and inform policy decisions.
Future simulations are more uncertain - we do not have observations to check models are doing the right things
Combat uncertainty - use many models + average the results of the models
Coupled Model Intercomparison Projects (CMIPs)
Coordinated efforts to run multiple climate models with the same experiments, allowing for comparison and evaluation of model results to improve future climate projections.
Future forcing
emissions scenarios - put into climate model to generate what the future looks like

Problem of future forcing
We do not know how societies will evolve over the next century
Need to develop several emissions scenarios and asses climate response
Emissions Scenarios
Different possible future pathways of greenhouse gas emissions, based on assumptions about population growth, economic development, and technological change.
SRES (Special Report on Emission Scenarios) 1990s
4 different possible future trajectories of population, economic growth and GHG emissions
Now dated and lack large changed to society
RCP (Representative Concentration Pathways)
Scenarios that outline different levels of carbon dioxide concentration by the year 2100, each corresponding to a specific level of radiative forcing.
Do not take into account what happens in society
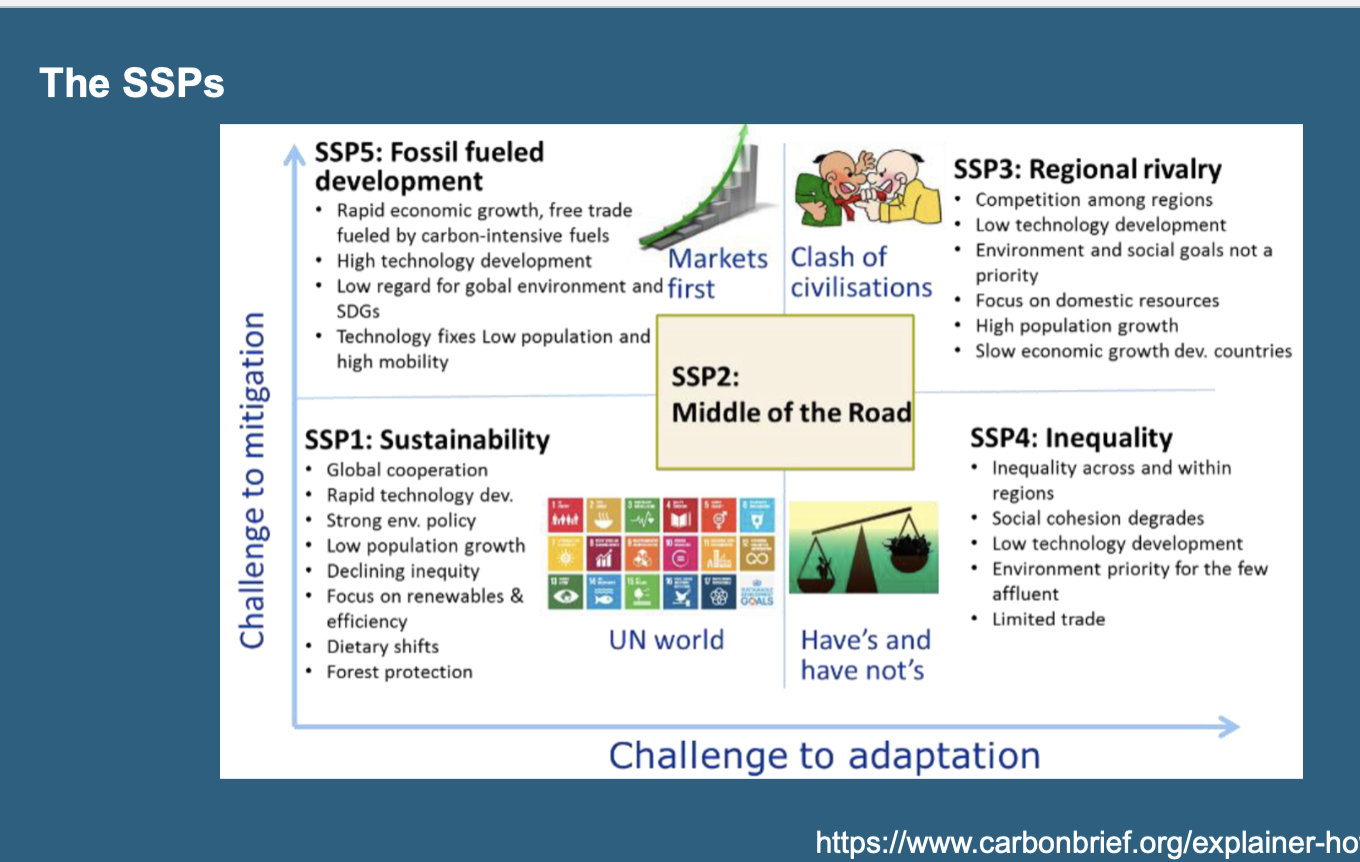
SSP (Shared Socioeconomic Pathways)
Scenarios that describe how the world might evolve in the absence of climate policy, influencing the ease or difficulty of implementing climate policies.
Polar Amplification
The phenomenon where the Arctic region experiences more pronounced warming compared to other parts of the globe due to climate change.
Projections of dangerous heat stress
humans sweat to cool down, a process that is less efficient at relative humidity
Heat stress indices consider coincidence of temperature and relative humidity
Projections for rainfall
precipitation change is more uncertain than temperature
Midlatitudes and poles get wetter
Subtropical oceans drier
Tropical rain belt wetter
Changes to rainfall extremes
In the future extreme rainfall is going to be heavier
Future climate of the UK
Wetter, warmer winters
Hotter, drier, summers
increase in frequency and intensity of extremes
Winter rainfall increasing - thermodynamic