4. EPITHELIAL CELLS
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
• Covering, lining, and protecting surfaces (eg, skin)
• Absorption (eg, the intestines)
• Secretion (eg, the parenchymal cells of glands)
• Contractility (eg, myoepithelial cells).
The principal functions of epithelial tissues are:
serous demilunes
Clumps of serous cells at the ends of some mucous tubules appear as crescent-shaped structures called _______________________
apical cytoplasm and plasmalemma
apocrine secretions are usually released as large lipid droplet that is usually discharged together with some of the _________________ and ___________________
lamina propria
serves to support the epithelium
lamina propria
provides nutrition and binds epithelia to underlying structures
lamina propria
identify the image
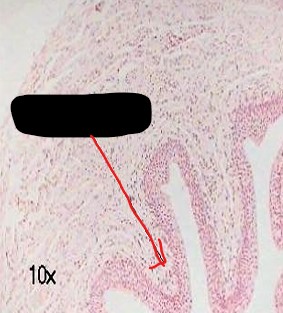
Papillae
small invagination's or irregularities in the connective tissue surface that increases area of contact between the connective tissue and the epithelial tissue
Basal pole
region of the cell contacting the connective tissue
adhesion
lamina propria has papillae that increases ____________
Apical pole
facing a space
Apical pole
project towards the external surface or the lumen of an organ which epithelia cover
Lateral surfaces
regions that adjoin the adjacent cells
Basement membrane
a felt-like sheet of extracellular material in the basal surface of epithelial cells
BASAL MEMBRANE
identify the image presented
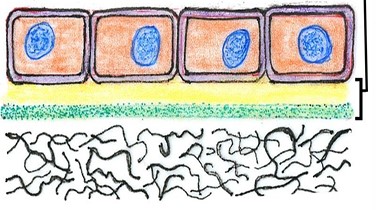
basal lamina
reticular lamina
Two structures of basement membrane:
basal lamina
(Two structures of basement membrane)
network of fine fibrils
reticular lamina
(Two structures of basement membrane)
a more diffuse and fibrous layer
collagen
most abundant protein in the body
kidney stones
too much use of collagen will lead to _________________ due to high levels of oxalate
False
T or F
basal lamina can be observed in light microscopy
Laminin
Type IV collagen:
The macromolecular components of basal laminae:
Laminin
(The macromolecular components of basal laminae)
These are large glycoprotein molecules that self assemble to form a lace-like sheet immediately below the cells' basal poles where they are held in place by the transmembrane integrins.
Type IV collagen
(The macromolecular components of basal laminae)
Monomers of type IV collagen contain three polypeptide chains and self-assemble further to form a felt-like sheet associated with the laminin layer
entactin/nidogen ; perlecan
laminin and type IV collagen network are held together by adhesive glycoprotein ________________ and by ____________, a proteoglycan
– Type III collagen
– Type VII collagen
Diffuse meshwork of reticular laminae contains:
albumin
most abundant protein in the blood
basal lamina
"_____________" is used to denote the lamina densa and its adjacent layers and structures seen with the TEM
Basement membrane
"__________________" is used to denote the structures seen with the light microscope.
occluding junctions
a junction that seals to prevent the flow of materials between the cells is called ________________
adhesive or anchoring junctions
sites of adhesion is called
gap junctions
is a junction that channels for communication between adjacent cells
Zonula occludens
Zonula adherens (intermediate junction)
Macula adherens (desmosomes)
enumerate the three distinct zones of the junctional complex
Zonula occludens
(three distinct zones of the junctional complex)
• important in transporting epithelium
• maintaining the structural integrity of epithelium
Zonula adherens (intermediate junction)
(three distinct zones of the junctional complex)
• “terminal web”
• Serves as a site of insertion for the contractile microfilaments that form the core of the microvilli.
• Aid in contraction of microvilli
Macula adherens (desmosomes)
(three distinct zones of the junctional complex)
• Appears as dense dots or fusiform thickening of the cells
• Site of attachment of the cytoskeleton to the cell surface
• Sites of cell to cell adhesion
“terminal Bar”
In LM ; entire structure of junctional complex is called _______________
1
6 connexins = __ connexon
Nexus (gap junction)
• Concerned with cell to cell communication
• “communicating junction”
Connexions
_____________ are protein subunits that make up gap junction channels (nexus).
between osteocytes, smooth and cardiac muscles, neurons
nexus (gap junction) is present in
skeletal muscle, blood
nexus (gap junction) is absent in
Cx46 and Cx50
Which connexins are important in the lens of the eye?
cataract
Mutation of Cx46 and Cx50 can cause ____________
Cx26
Which connexin is commonly associated with congenital deafness or ear dysfunction?
Gap junction
Which junction is affected when connexins are defective?
Microvilli
Delicate vertical striations in a refractile border of columnar epithelium
Microvilli
Prominent in cells whose principal function is absorption
Striated border
Which border is found in the intestinal epithelium?
Brush border
Which border is found in the epithelial cells of the kidney?
microvilli
Small finger-like processes that increase the efficiency of absorption
Stereocilia
Which long, pyriform tuft of slender processes projects into the lumen from epididymis epithelial cells?
Basal infoldings
Which basal structure increases surface area at the base of a cell to promote absorption?
cilia ; Stereocilia
larger than microvilli = __________
longer than mIcrovilli = ——————
Primary cilium
Which type of cilia is enriched with receptors for signal transduction complexes?
Motile cilia
Which type of cilia is found only in epithelia, abundant on the apical surface of cuboidal or columnar cells
Cilia
Function to propel fluid or coating of mucus towards the exterior
Covering (lining) epithelia
Secretory (glandular) epithelia
Main Groups of Epithelia
Simple
Pseudostratified
Stratified
(Classification of Covering Epithelia)
number of cell layers
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
transitional
(Classification of Covering Epithelia)
cell morphology
Simple Squamous Epithelium
• Very thin, flat cells
• Mosaic pattern
I. Simple Squamous Epithelium
• Attenuated cytoplasm with central bulging nucleus.
Endothelium
Which epithelium lines blood vessels and lymph vessels and the cavities of the heart?
Mesothelium
Which epithelium lines the serous cavities like pleura, pericardium, peritoneum, tunica vaginalis testis
Mesenchymal
Which epithelium lines the interior chamber of the eye, , perilymph spaces of the internal ear, subdural and subarachnoid spaces.
Flattened cells
Which epithelium consists of flattened cells lining the pulmonary alveoli and bowman’s capsule
–Facilitates the movement of the viscera (mesothelium)
–Active transport by pinocytosis (mesothelium and endothelium)
–Secretion of biologically active molecule
Main Functions of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
• Row of square or rectangular profile
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
• a classification of epithelial tissue wherein the nuclei tend to aligned at the same level in all of the cells, “box-like”, “cube-like”
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Which epithelium covers the surface of the ovary?
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Which epithelium covers the surface of the Thyroid follicles?
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Which epithelium covers the surface of the choroid plexus?
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Which epithelium is found in the pigmented layer of the retina?
– Covering
– secretion
Main Function of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
• a classification of epithelial tissue wherein the membrane composed of cylindrical cells possessing an appreciable height aside from length and width.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
• a classification of epithelial tissue wherein the nuclei are at the same level and situated nearer to the basal surface than the apical surface.
Simple plain tall columnar epithelial
which of epithelium is composed of mucosa of the stomach, small and large intestine, gallbladder, bigger ducts of glands
Simple plain low columnar epithelial
which of epithelium is composed of smaller ducts of glands, some excretory tubules of kidney
– Protection
– Lubrication
– absorption
– secretion
Main Function of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Which epithelium shows cells that become irregular and flattened as keratin accumulates?
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Which epithelium has cells that become hardened and cornified toward the surface?
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Which epithelium undergoes progressive removal of cells near the skin surface?
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Which epithelium consists of thin, metabolically inactive packets of keratin-lacking nuclei
– Protection
– Prevents water los
Main Function of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
epidermis
where is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium mostly distributed in the body?
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Which epithelium lines wet cavities where loss of water is not a problem?
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Which epithelium is found in the inner most surface of the body?
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Which epithelium has flattened cells of the surface layer that contain much less keratin, retaining their nuclei and metabolic function
– Protection
– Secretion
– Prevents water loss
Main Function of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
– Mouth
– Esophagus
– Larynx
– Vagina
– Anal canal
what parts of the body is lined by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
– Excretory ducts of salivary and sweat glands
– Developing ovarian follicles
what parts of the body is lined by Stratified Cuboidal Epithelia
– Protection
– Secretion
Main function of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelia
– Conjuctiva
what parts of the body is lined by Stratified Columnar Epithelia
– Protection
– secretion
Main Function of Stratified Columnar Epithelia
Transitional epithelium (urothelium)
Which epithelium has a thin basal lamina and lines distensible organs?
Transitional epithelium (urothelium)
Which epithelium appears very thin when the organ is distended and thicker when collapsed?
Transitional epithelium
Which epithelium consists of many layers in the contracted stage?
One or two rows of basal cells
In contracted urothelium, what is the deepest layer composed of?
– Bladder
– Ureter
– Rena calyces
Example of Distribution of Transitional (Urothelium) Epithelia
– Protection
– Distensibility
Main Function of Transitional (Urothelium) Epithelia
Pseudostratified Epithelia
Appears to be composed of several layers of cell when in reality, there is only one layer