Audiology- EXAM 1
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
audiologist
diagnoses hearing loss, educates about hearing loss/impairment, prescribes and fits amplification devices, provides the latest hearing aid technology, accessorizes the latest hearing technology, programs cochlear implants, diagnoses balance disorders, educates about hearing conservation, and search for cures for hearing loss
medical audiology
employs the largest number of audiologists
-focus: diagnostic assessments to identify cause of hearing and balance disorders
educational audiology
provides identification of kids with hearing loss and referral to proper care, rehabilitation activities, counseling and guidance for parents, students and teachers, selection and evaluation of individual and group amplification
pediatric audiology
provide pediatric testing and empathy to help guide parents and families through a difficult time
dispensing/rehabilitative audiology
dispenses, distributes, sale, and appropriately fit hearing amplification
industrial audiology
design hearing conservation programs, fit hearing protection, monitor employee hearing levels, etc.
tele-audiology
increasing access to audiological services in remote areas
sound
a common type of energy that occurs as a result of pressure waves that emanate from some force being applied to a sound source
requirements for sound
1. source of vibratory energy
2. a medium that has mass and is elastic
intensity
perception of loudness, the higher the magnitude of the compression wave, the higher is the intensity of the signal
pressure level of a sound that is barely audible
approximately 20 upa
pressure level of a sound that is so intense that it is painful
approximately 200,000,000 upa
intensity is measured in
decibels (dB)
Bel
logarithmic unit of measure of sound intensity
frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
-perception of pitch
the higher the speed of vibration of the compression wave
the higher the frequency of the signal
frequency is usually expressed in
cycles-per-second or Hertz (Hz)
auditory system
outer ear, middle ear, cochlear duct, inner and out hair cells, cranial nerve VIII, auditory brainstem, auditory cortex
inner ear
the innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs
osseous labyrinth
the channel in the bone
membranous labyrinth
composed of soft tissue fluid-filled channels within the osseous labyrinth that contain the end-organ structures of the hearing and vestibular systems
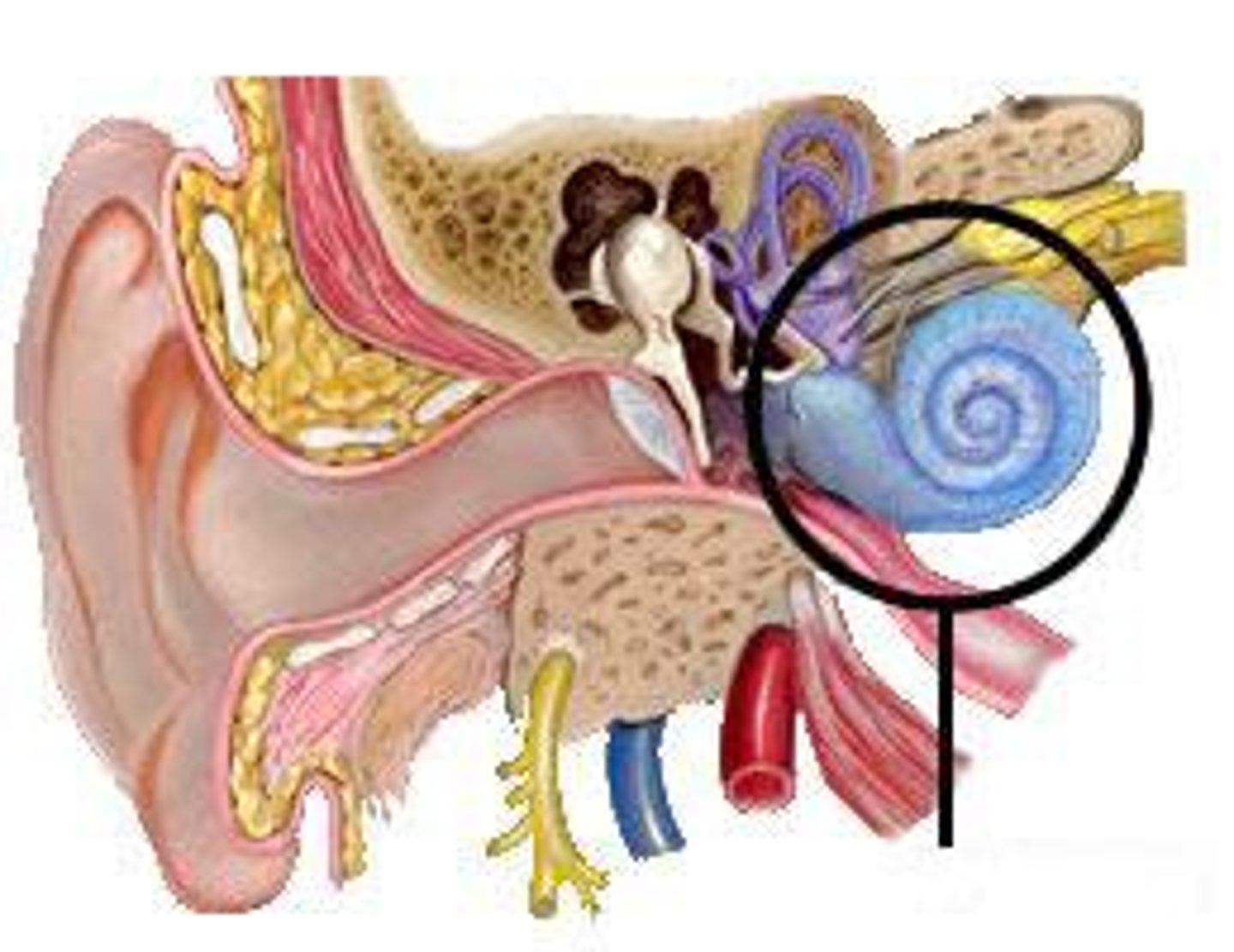
the cochlea
the auditory labyrinth and is the sensory organ of hearing
a fluid-filled space within the temporal bone, the shape of a snail shell
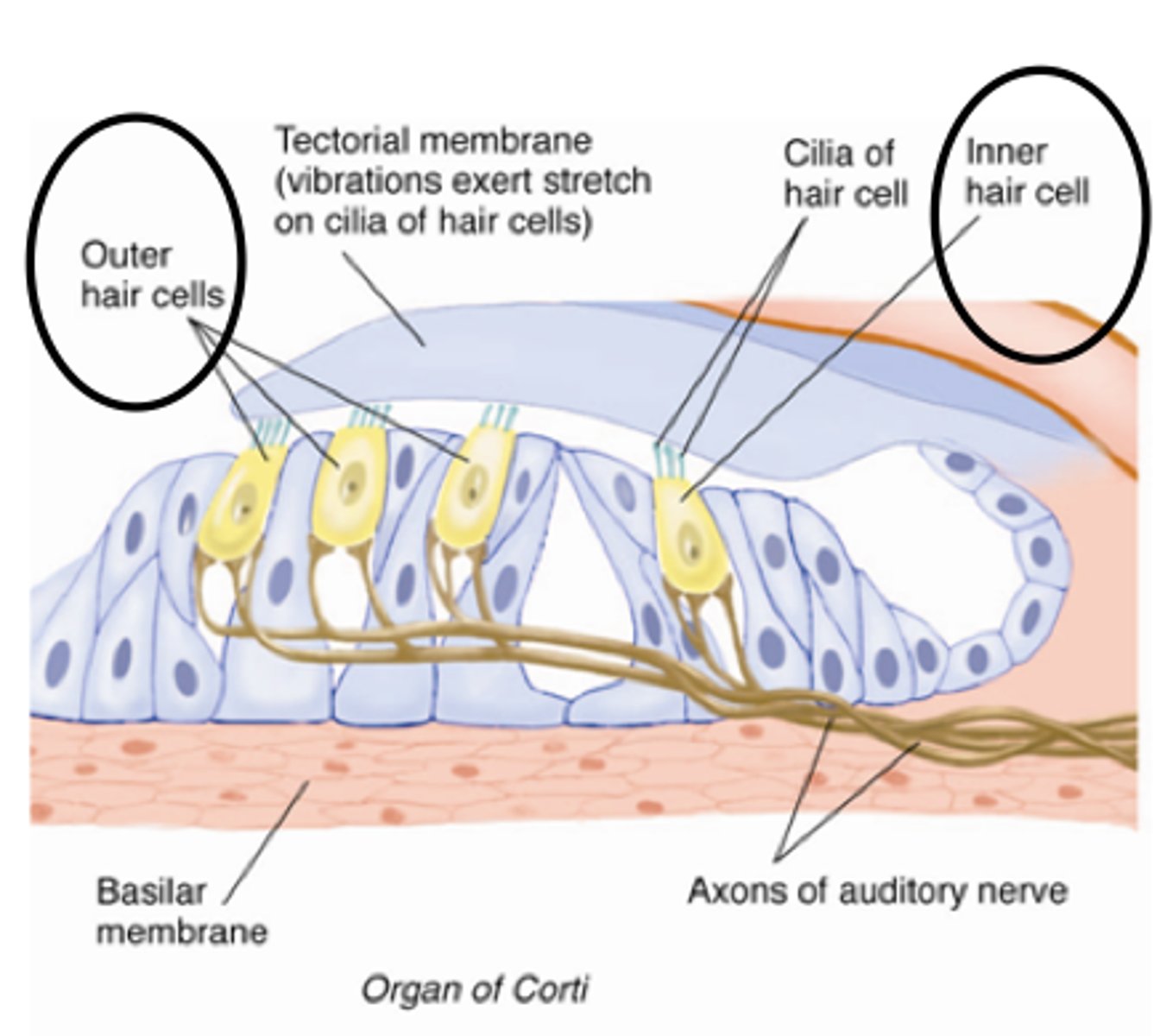
outer hair cells
elongated in shape and have small hairs (cilia), attached to their top, three rows, innervated mostly by efferent (motor fibers of the nervous system), about 13,000
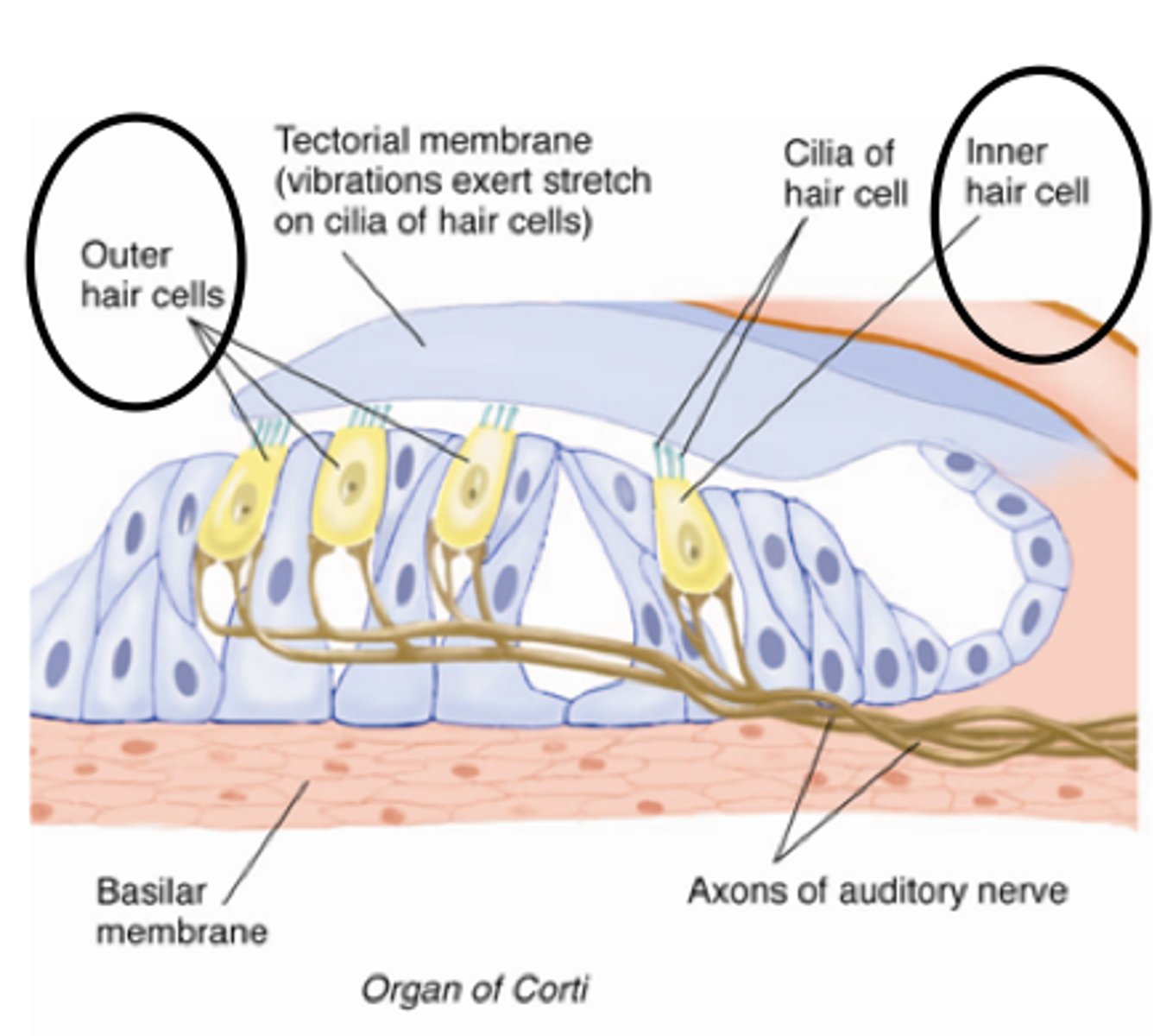
inner hair cells
elongated and have an array of cilia on top, single row, cilia in proximity to (but not direct contact with) the tectorial membrane, innervated by mostly afferent (sensory fibers of the nervous system), about 3,500
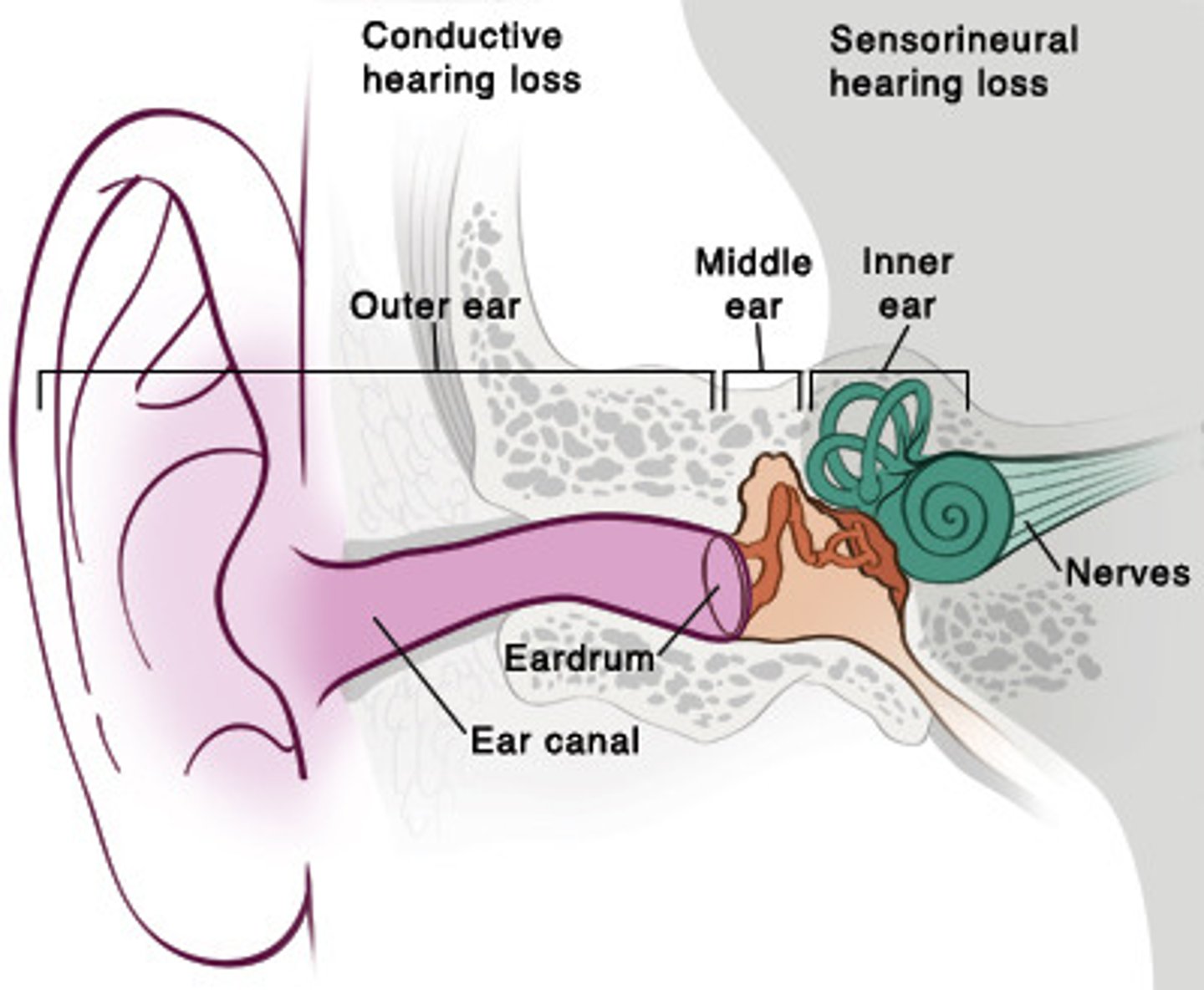
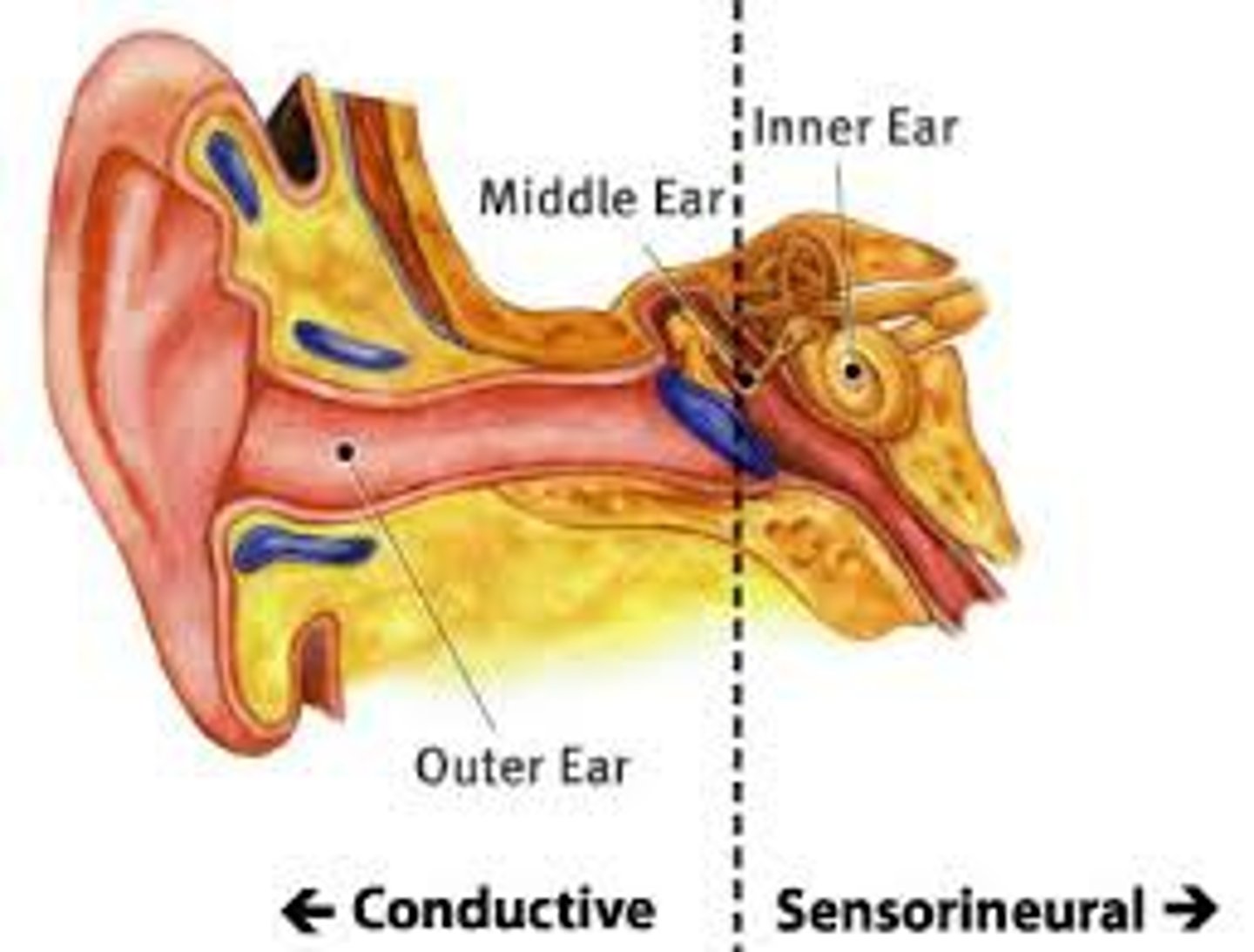
conductive hearing loss
hearing impairment caused by interference with sound or vibration in the outer ear or middle ear,
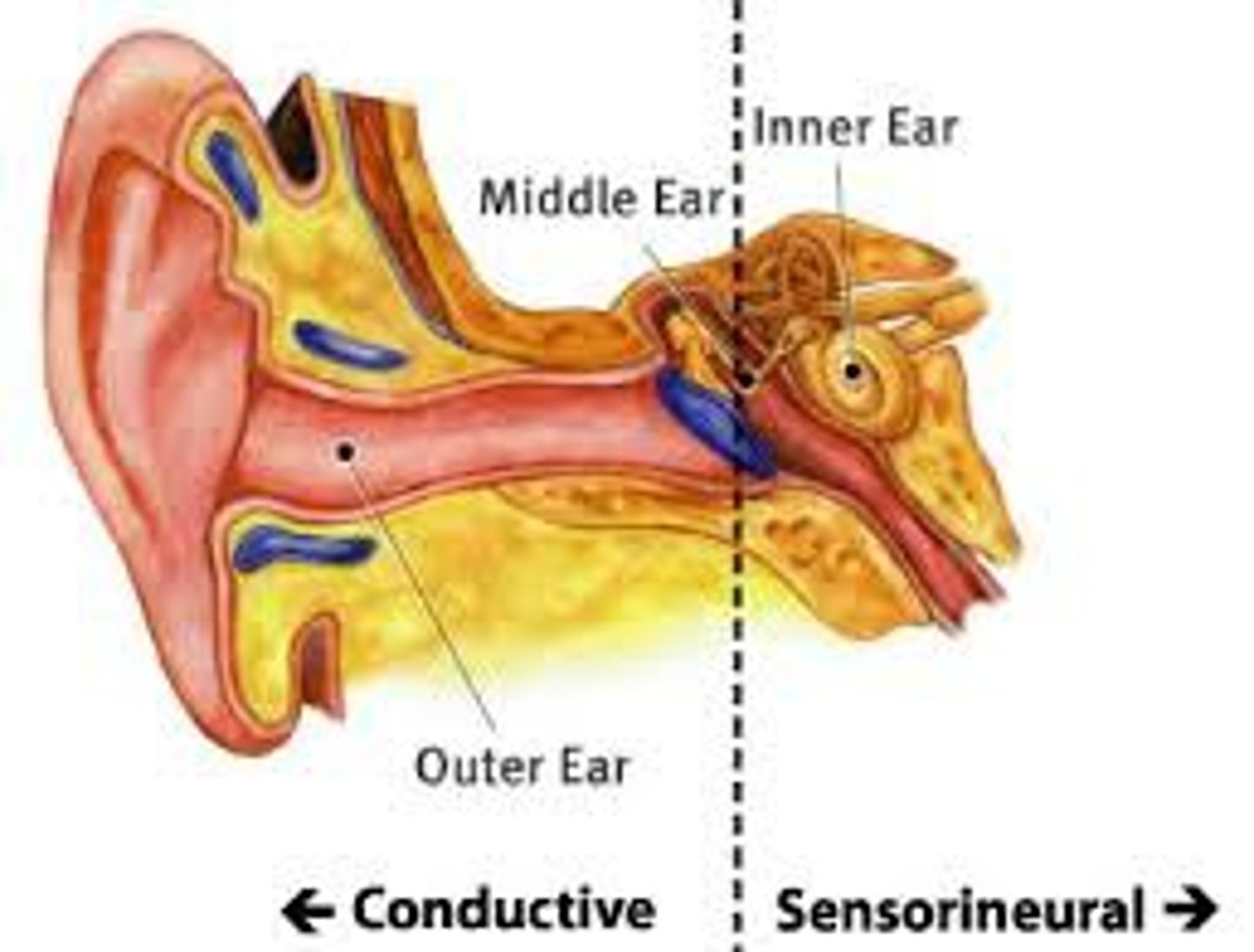
sensory/neural hearing loss
hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve
outer ear purpose
conducts sound energy
middle ear purpose
conducts sound energy and increases soudn intensity
inner ear purpose
converts mechanical to hydraulic to electrochemical energy
auditory nerve purpose
transmits electrochemical (nerve) impulses to brain
Schwabach Test
tuning fork test that compares patients BC to normal, placed by the mastoid process
Rinne Test
tuning fork test that compares patients AC to BC, alternate placement between mastoid process and opening to ear canal
Bing Test
tuning fork test used to determine presence or absence of occlusion effect, placement by the mastoid process
Weber Test
tuning fork test used to check lateralization of tone in unilateral losses, placement in the midline of head
audiogram
a tool used to illustrate hearing sensitivity relative to average hearing ability
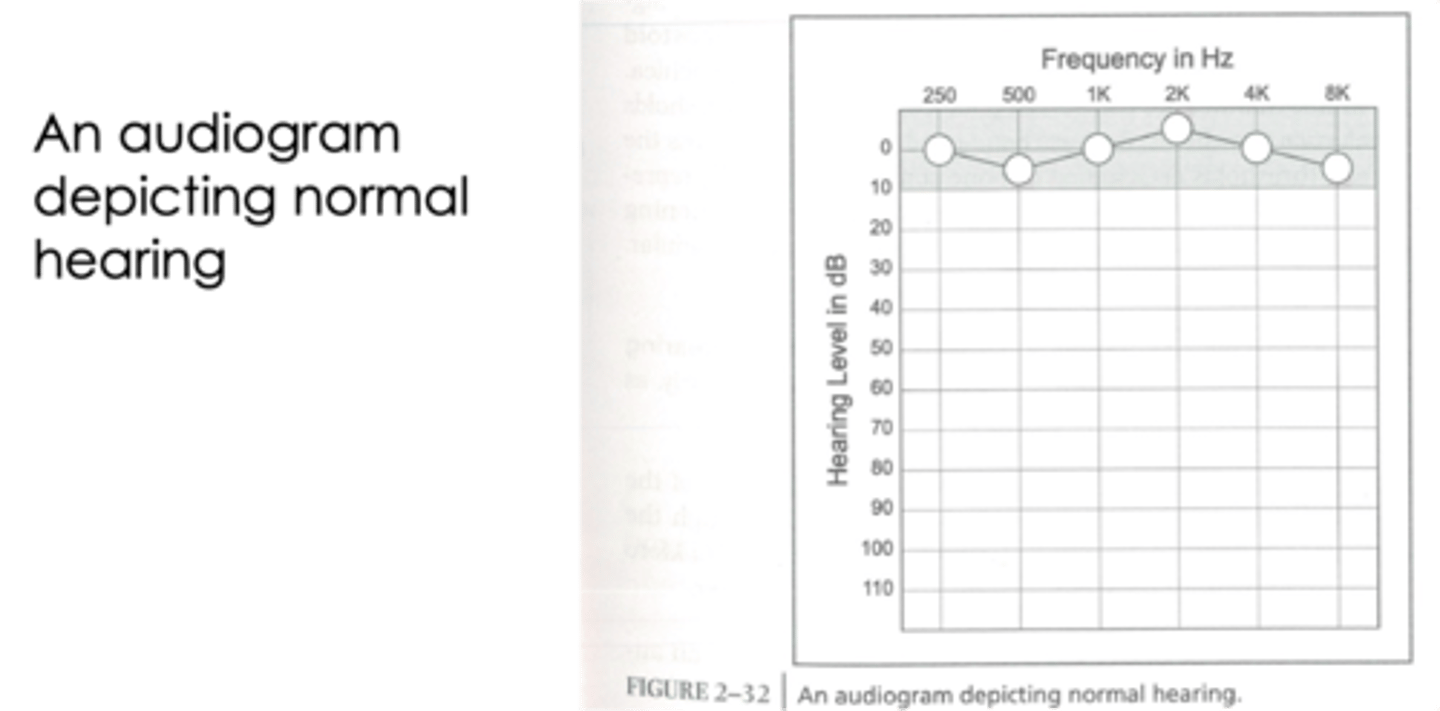
audiogram depicting normal hearing
lying in 0-10 dB
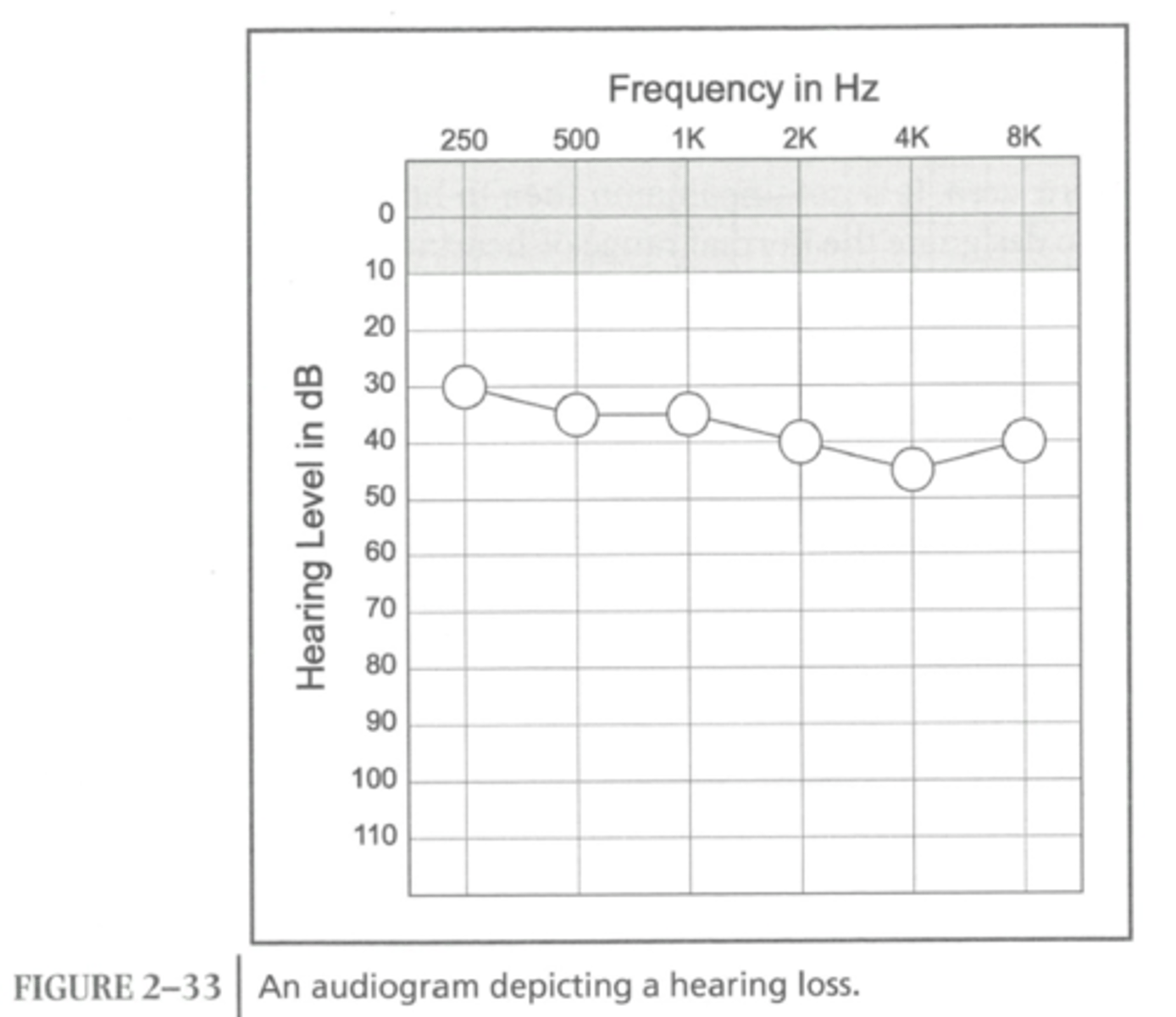
audiogram depicting a mild to moderate hearing loss
lying from 30-50 dB
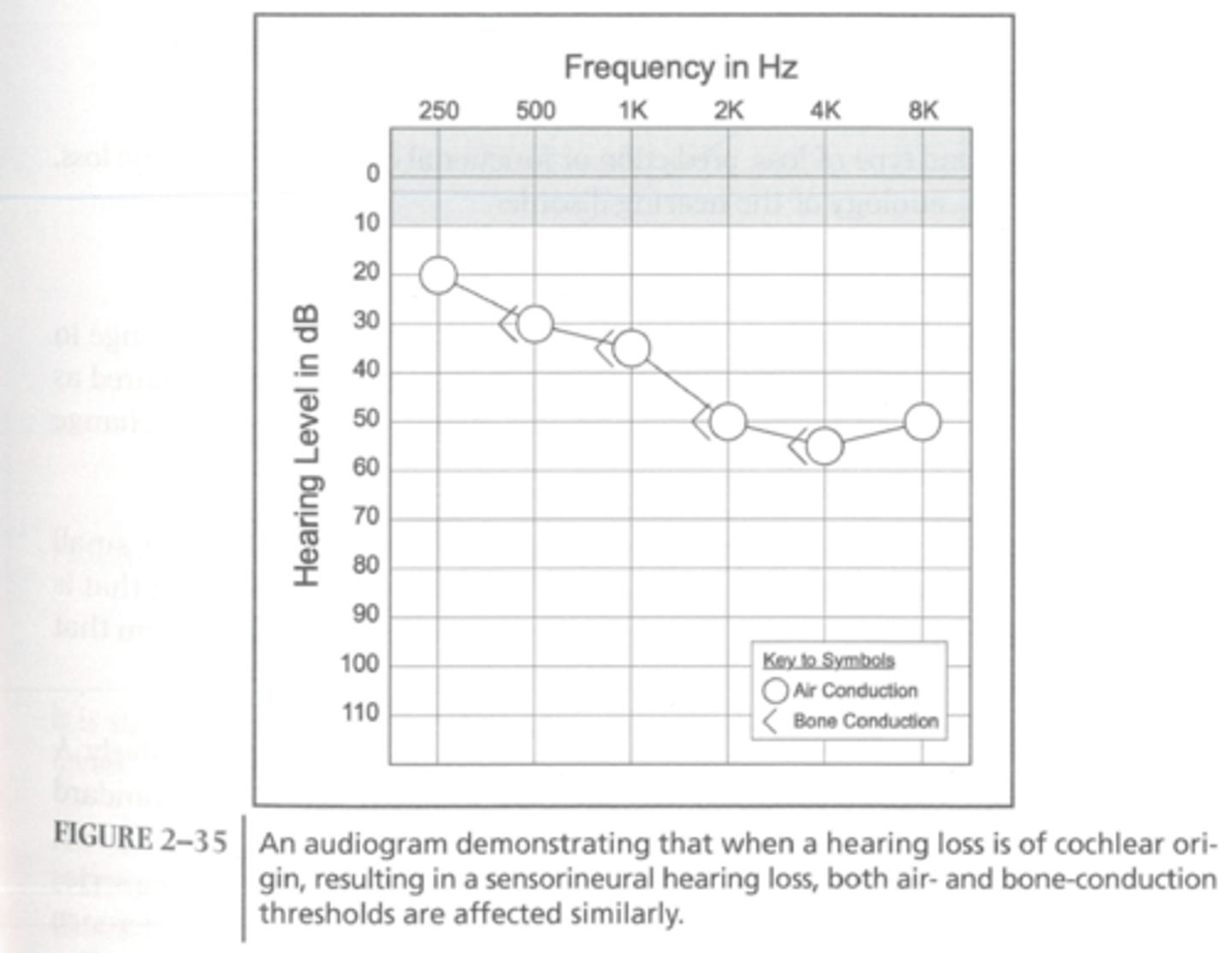
audiogram depicting a mild to moderately-severe sensory/neural hearing loss
lying from 20-60 dB
acoustics
the study of the physical properties of sound in the environment
physical characteristics of sound
intensity, frequency, energy, velocity, phase
perceptual characteristics of sound
loudness, pitch, quality/timbre
period (T)
time, in seconds, required to complete one cycle
wavelength
distance, in meters, it takes to complete one cycle
-relationship between frequency and time
sound velocity
speed of sound from the source to another point within the medium
-measured in m/s
speed of sound in air
344 m/s
speed of sound in water
1433 m/s
cycle
a complete vibration consisting of one compression and rare-fraction totaling up to 360 degrees
λ calculation
=c/f
f calculation
=c/λ
beats
the noticeable increase and decrease in sound intensity when two tones of almost identical frequency are presented slightly "out of phase"
complex sounds
vibrations that contain two or more frequencies
oscilloscopes are used to
measure and analyze sound
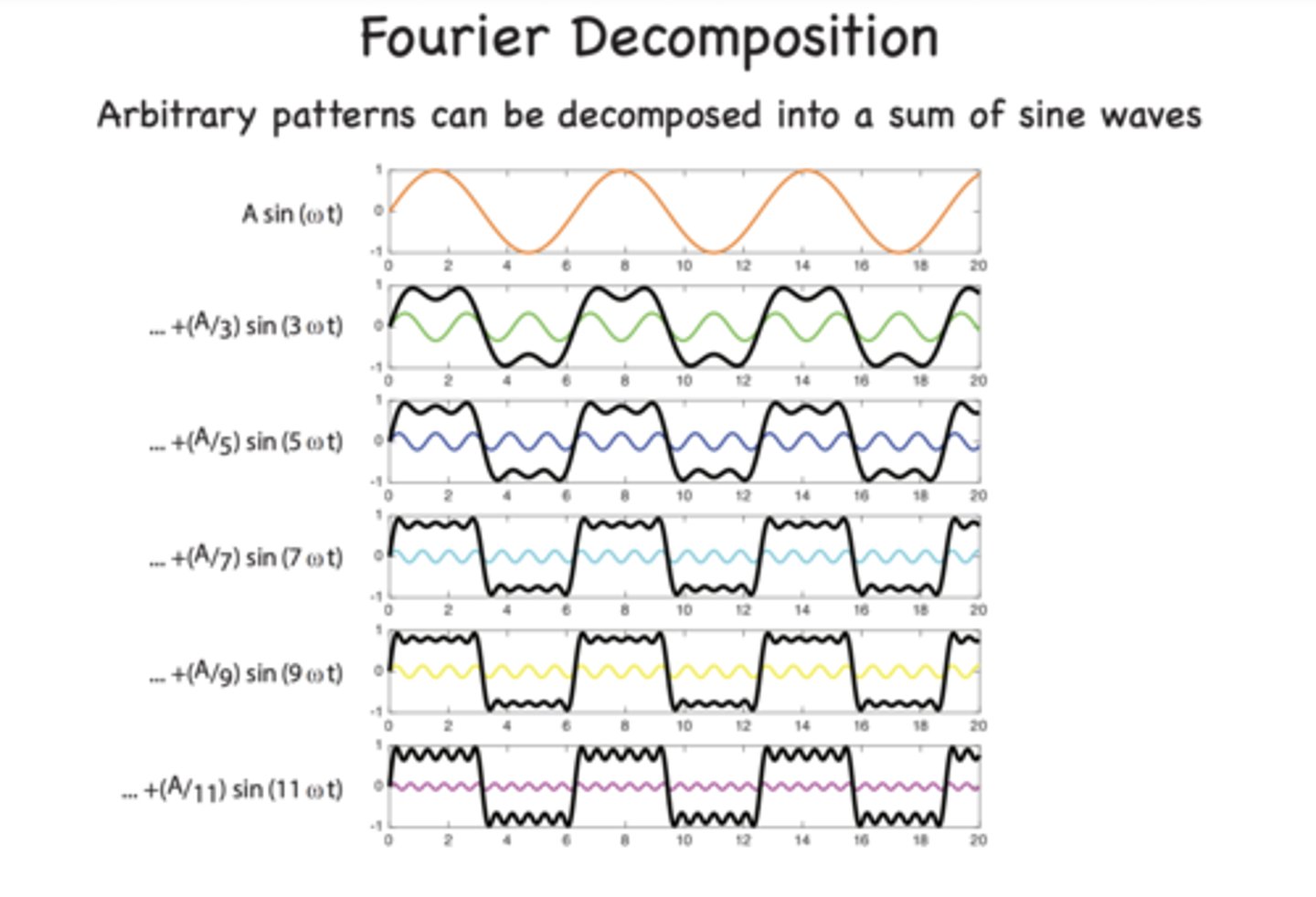
fourier analysis
the breakdown of a complex wave into its simplest (sinusoidal) components
harmonics/overtones
whole number multiples of the fundamental frequency (F0)
1st harmonic
=fundamental frequency (F0)
2nd harmonic
=F0 x 2 = 1st overtone
3rd harmonic
= F0 x 3 = 2nd overtone
4th harmonic
= F0 x 4 = 3rd overtone
5th harmonic
= F0 x 5 = 4th overtone
speech formants
peaks of energy above the fundamental frequency in vowel sounds, results from altering the shape of the vocal tract
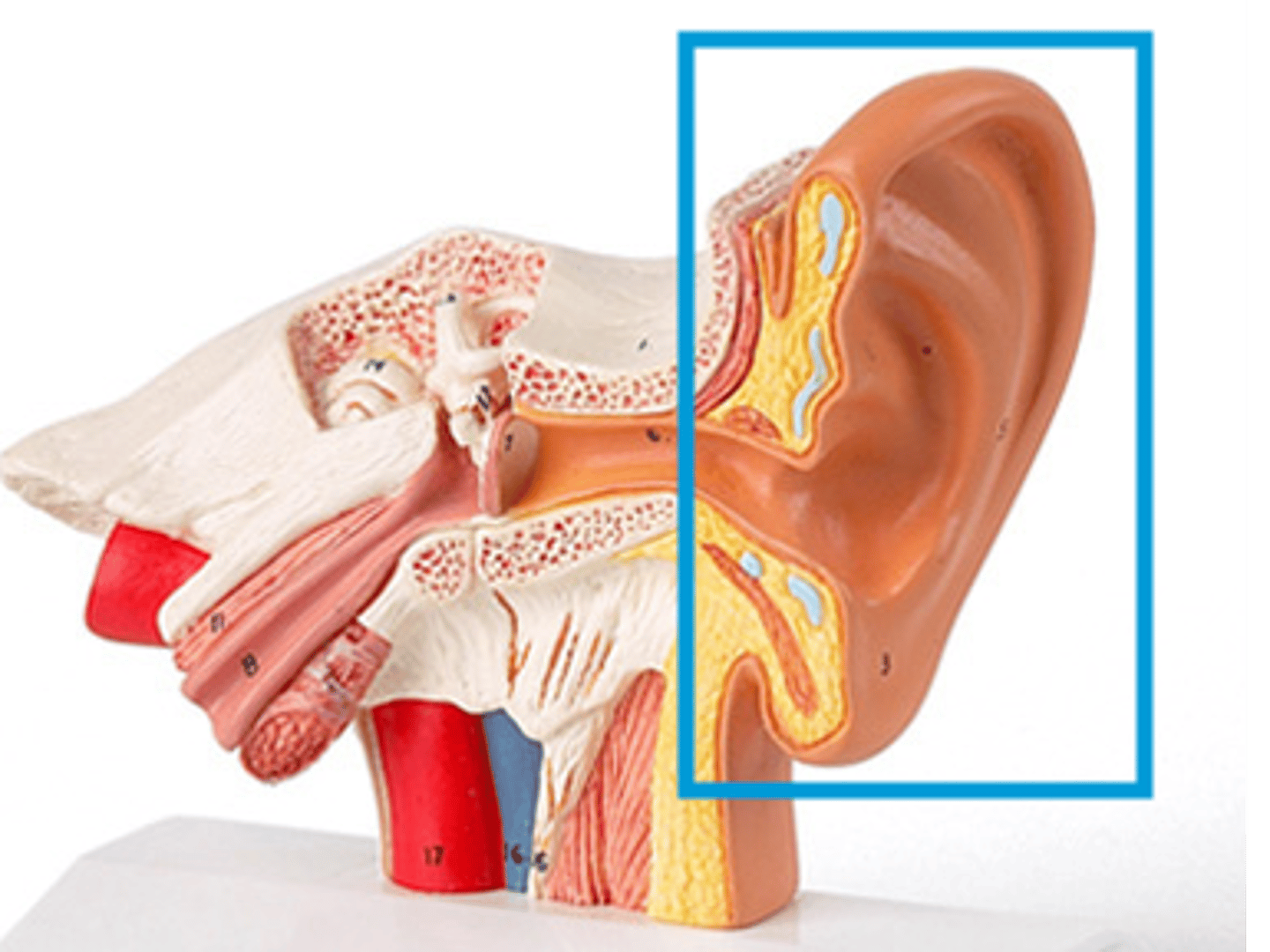
pinna
the cartilaginous portion of the outer ear that collects sound waves from environment and directs them to the ear canal
-aids in sound localization
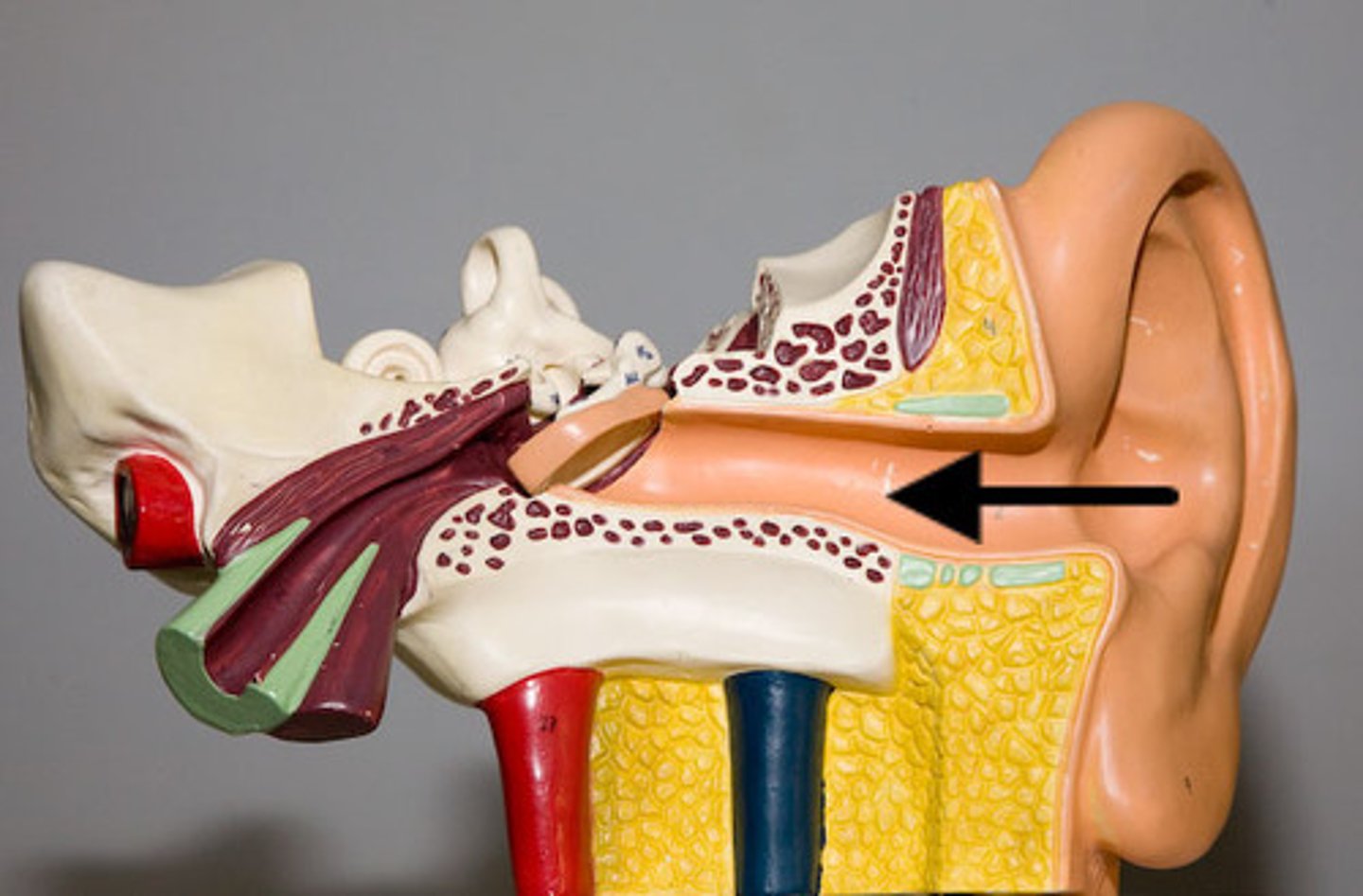
external auditory canal (EAC)
housed in the temporal bone, the first and second "bends" provide some protection of TM against foreign objects
-slightly curved
-approximately 1 inch in length
outer 1/3 of EAC
cartilaginous, hair follicles, sebaceous glands make earwax
inner 2/3 of EAC
bone
tympanic membrane (TM)
eardrum; a semitransparent membrane that vibrates to transmit sound waves to the ossicles; separates the external auditory canal from the middle ear cavity
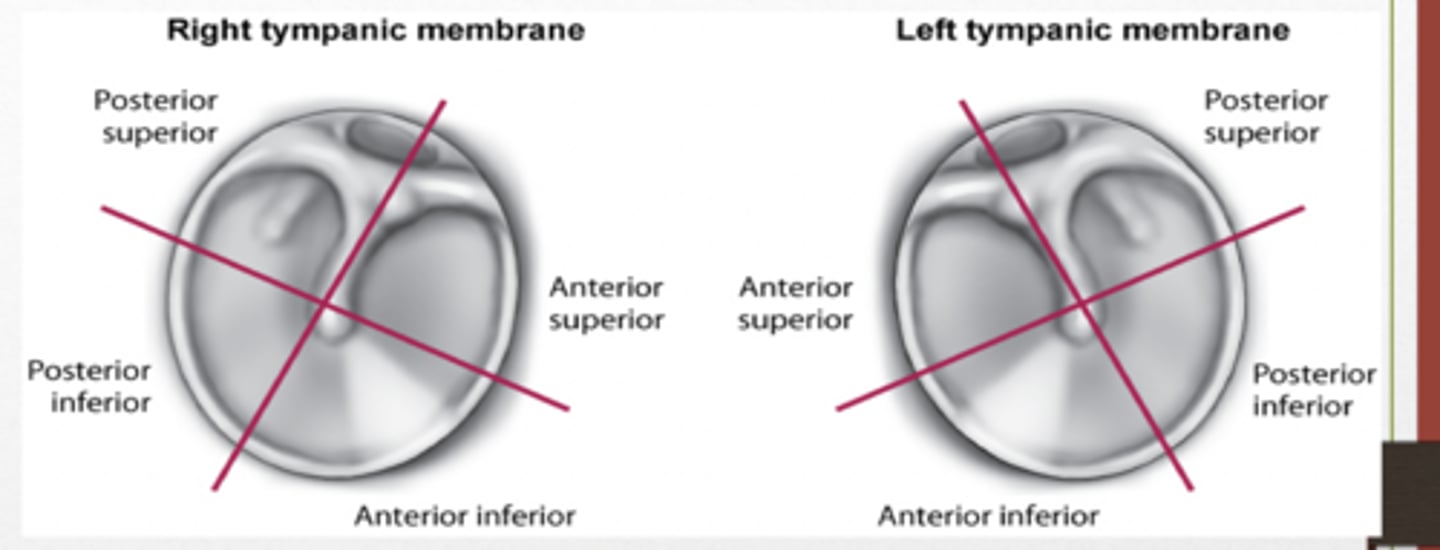
quadrants of tympanic membrane
posterior superior, posterior inferior, anterior superior, anterior inferior
artesia of EAC
absence of EAC, could result in conductive hearing loss
stenosis of EAC
narrowing of EAC
-only leads to conductive hearing loss if EAC stenosis leads to closure of canal or if there is blockage of the small EAC by cerumen
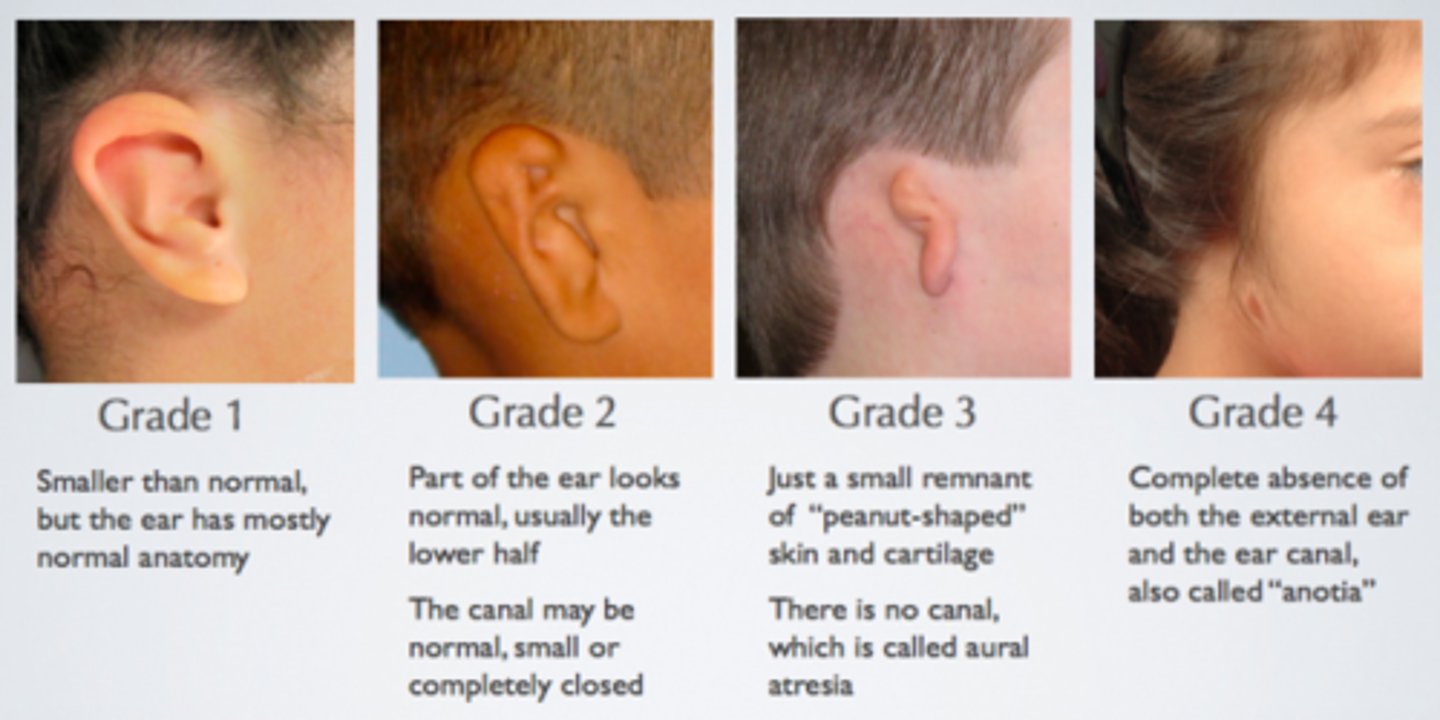
microtia/anotia
congenital deformity where the pinna is underdeveloped (microtia) or completely absent (anotia)
anotia-pinna
squamous cell carcinoma of the EAC
considered a tumor
symptoms:
-Ear drainage (otorrhea)
-Ear pain (otalgia)
-Hearing loss
-Facial nerve paralysis
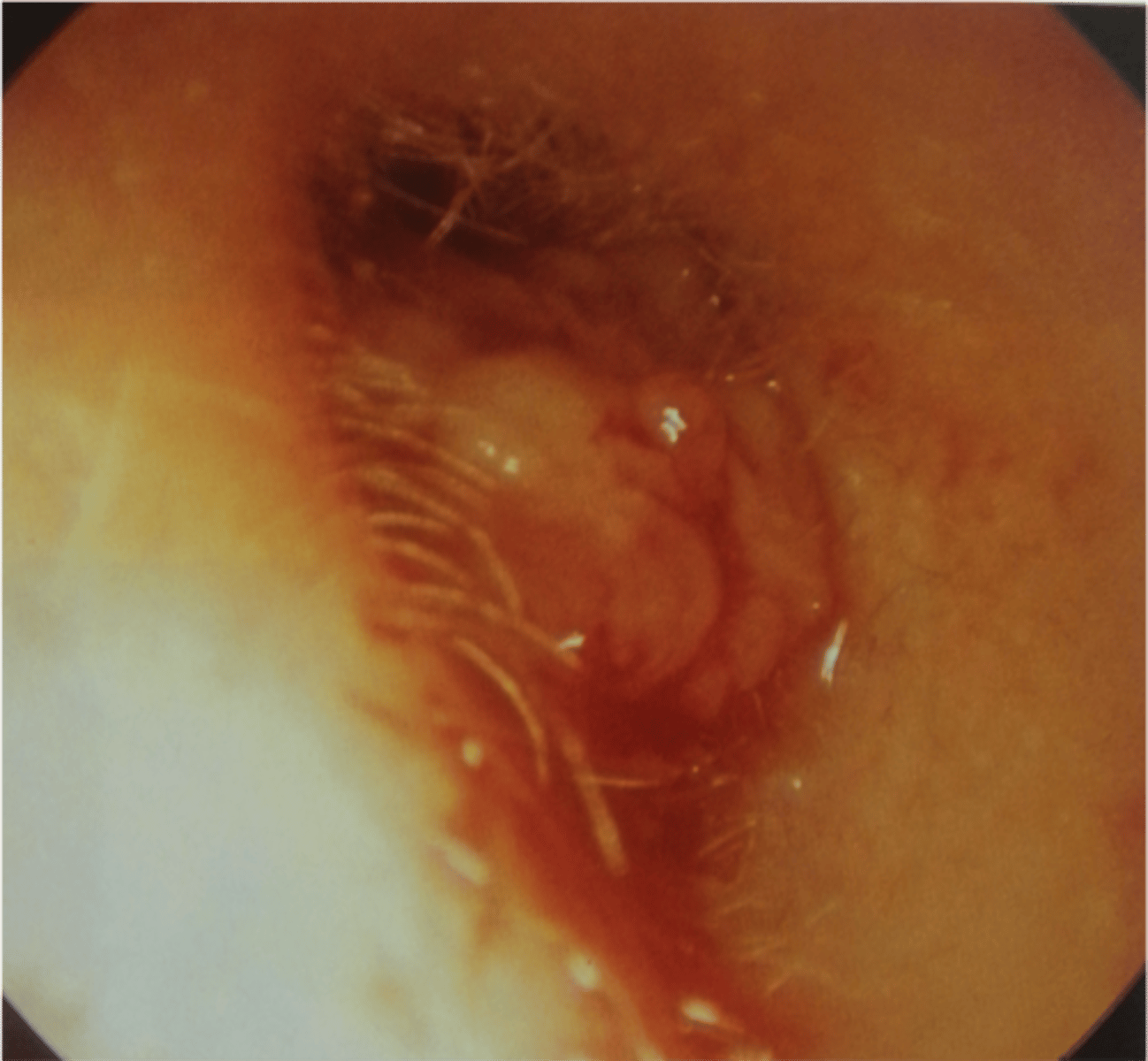
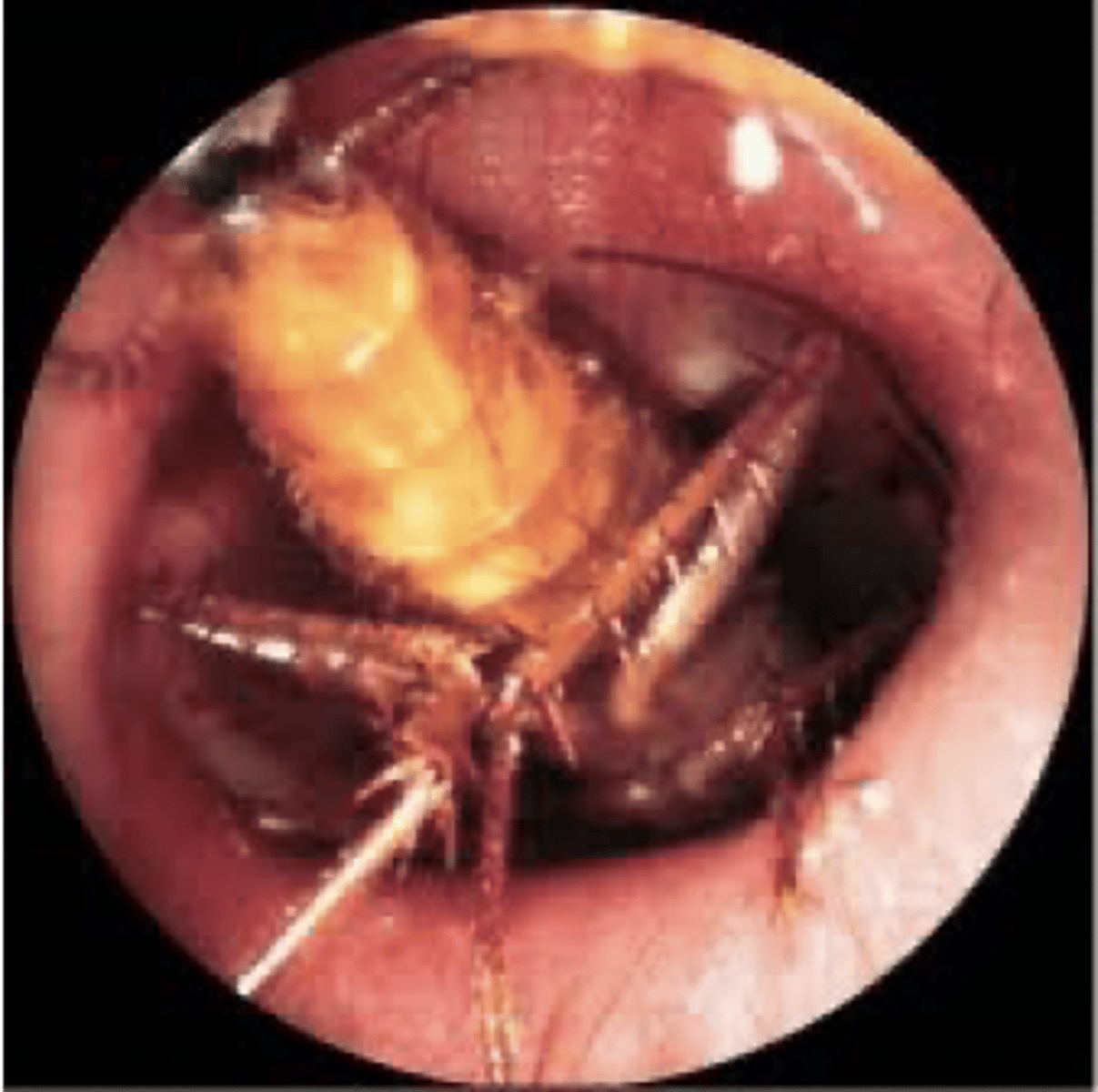
foreign body in EAC
can cause hearing loss if _______ occludes EAC, causes TM rupture, or substantial EAC swelling
external otitis
infection occurring in the skin of EAC, caused by allergic reactions to ear plugs, hearing aid molds, soap, pool water
symptoms:
-ear pain (otalgia)
-ear drainage (otorrhea)
-TM can become inflamed
-itching sensations
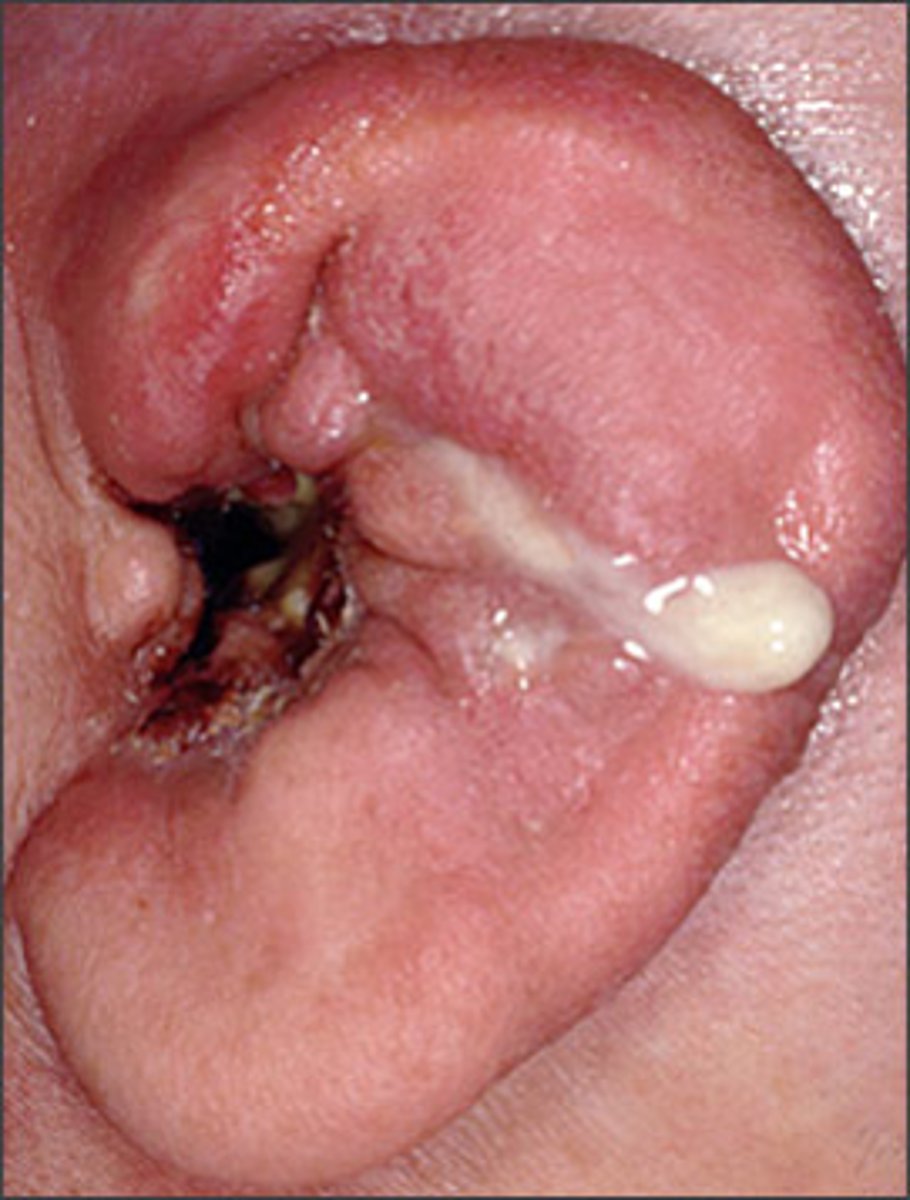
otomycosis
fungus in external ear
symptoms:
-otorrhea (ear drainage)
-otalgia (ear pain)
-itching sensations
-conductive hearing loss if fungus accumulation and drainage occludes EAC
air conduction
the process by which sound waves enter the ear through the pinna
bone conduction
occurs as the eardrum vibrates and moves the auditory ossicles
Compression
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are close together.
rarefraction
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are far apart
the decibel
a unit for expressing the ratio between two sound pressures or two sound powers
1 dB is = to how many Bels?
1 dB = 1/10 of a Bel
3 important characteristics of the decibel scale
1. ratio between two numbers (not additive)
2. logarithmic scale
3. decibel levels can be specified with various references
intensity level (dB IL)
decibels can be expressed with intensity references based on output and references levels
dB (IL) = 10 log (IO / IR)
specified referenced for dB IL measurements
10^-12 watt/m^2
output capabilities of speakers are commonly described in
watts
sound pressure level (dB SPL)
intensity is proportional to the square of sound pressure
pressure reference
dB (SPL) = 10 x log (PO^2/ PR^2)
measurement tool for sound pressure level (dB SPL)
sound level meter
Pascals
common unit to used to describe pressure changes in air
Po
pressure observed (measured)
Pr
pressure reference (set references for pressure in air)
atresia of EAC
absence of EAC (canal)
Fourier decomposition
the classical tool for decomposing a given surface or more generally a signal into its basic components, the surface is broken down into different scales using a set of sine and cosine functions with different frequencies.