Biology - diseases*
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What are communicable diseases?
Diseases that can be spread from person to person or between animals and people.
What are communicable diseases caused by?
pathogens
What is a pathogen?
A microorganism that causes disease
How do communicable diseases spread?
- Direct contact
- Indirect contact
- Airborne transmission
- Vector-borne transmission
- Food and water-borne transmission
How can diseases spread from direct contact?
By touching an infected person, kissing, sexual contact, or coming into contact with bodily fluids
How can diseases spread from indirect contact?
By touching contaminated surfaces
How can diseases spread through airborne transmission
By inhaling droplets from coughing, sneezing or talking
How can diseases spread through vectors?
Through bites from infected insects, like ticks or mosquitoes
How can diseases spread through food and water?
By consuming contaminated food or water
Example of bacterial diseases
Salmonella, gonorrhoea, tuberculosis, meningitis, strep throat, cholera
What is tuberculosis?
Bacterial infection of the lungs
How is tuberculosis transmitted?
Inhalation of airborne droplets
What are the symptoms of tuberculosis?
Coughing, chest pain, weight loss, fever
How can tuberculosis be treated/prevented?
Antibiotics (e.g., Rifampicin), vaccination (BCG)
What is cholera?
An infectious disease of the small intestine caused by bacteria.
How is cholera transmitted?
contaminated water or food
What are the symptoms of cholera?
Diarrhoea, vomiting, dehydration
How can cholera be treated?
Rehydration therapy, antibiotics, improve sanitation
What is gonorrhoea?
a sexually transmitted disease caused by bacteria
How is gonorrhoea transmitted?
sexual contact
What are the symptoms of gonorrhoea?
-Thick yellow or green discharge
-Pain when urinating
How can gonorrhoea be treated?
antibiotics
What is Salmonella?
A type of bacteria that causes food poisoning
How is Salmonella transmitted?
contaminated food and water
What are the symptoms of Salmonella?
Fever, stomach cramps, vomiting and diarrhoea
How can Salmonella be treated?
The body's immune system usually manages salmonella itself, but antibiotics can be necessary if the symptoms persist for more than a week. Electrolytes can also be used to help ease dehydration.
What is strep throat?
a bacterial infection of the throat and tonsils
How is strep throat transmitted?
respiratory droplets
What are the symptoms of strep throat?
Fever, sore throat, swollen neck glands
How can strep throat be treated?
Antibiotics such as penicillin or amoxicillin
Examples of fungal diseases
Athlete's foot, ringworm, and candidiasis
What is athlete's foot?
fungal infection
How is athlete's foot transmitted?
Direct contact with infected skin or contaminated surfaces
What are the symptoms of athlete's foot?
Itchy, cracked skin between toes
How can athlete's foot be treated/prevented?
Antifungal creams, good foot hygiene
What is ringworm?
A highly contagious, fungal infection of the skin or scalp.
How is ringworm transmitted?
fomites and direct contact
What are the symptoms of ringworm?
Itchy, red, circular rash
How can ringworm be treated?
Antifungal creams, hygiene
What is candidiasis?
A yeast infection of the mouth or vagina.
What are the symptoms of candidiasis?
White patches in mouth, fatigue, itching
How can candidiasis be treated?
Antifungal medication (e.g., Fluconazole)
Examples of viral diseases
Influenza (flu), common cold, chickenpox, measles, HIV/AIDS, COVID-19
What is influenza?
flu
How is influenza transmitted?
via droplets generated when infected persons cough or sneeze
What are the symptoms of the flu?
pain, achy, fever, runny nose, sore throat, fatigue, muscle aches
How can the flu be treated/prevented?
Antiviral medication, vaccination
What is the common cold?
viral infection of the upper respiratory tract
How is the common cold transmitted?
Via airborne droplets, sneezing, secreting snot etc.
What are the symptoms of the common cold?
nasal stuffiness, scratchy throat, headache, sneezing, and coughing
What is COVID-19?
An infectious disease caused by the newly discovered coronavirus SARS-Cov-2
How is COVID-19 transmitted?
Through respiratory droplets.
What are the symptoms of COVID-19?
fever, cough, difficulty breathing, loss of taste/smell
How can COVID-19 be prevented?
Vaccination, quarantine, mask-wearing
What is chicken pox?
contagious viral infection
How is chicken pox transmitted?
via direct contact with the blisters, saliva or mucus of an infected person. The virus can also be transmitted through the air by coughing and sneezing
What are the symptoms of chicken pox?
fever and rash
What is measles?
infection of the respiratory system
How is measles transmitted?
respiratory droplets from coughing/sneezing
What are the symptoms of measles?
Fever and a red skin rash
How can measles be prevented?
vaccination
What is HIV?
HIV is a virus that affects the immune system and eventually causes AIDS
How is HIV transmitted?
- bodily fluids
- sexual contact
- blood
- breast milk
What are the symptoms of HIV?
Fever, weight loss, night sweats, diarrhoea, fatigue
How can HIV be treated/prevented?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART), prevention through safe sex
What is AIDS?
AIDS is the end stage of the HIV infection. At this point, the virus has attacked and weakened a person's immune system. People are classed as suffering with AIDS when their white blood cells drop below a certain level.
How is AIDS transmitted?
sexual contact, transfusion of infected blood, contaminated needles and syringes
How can AIDS be treated/prevented?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART), prevention through safe sex
Examples of protistic diseases
malaria and giardiasis
What is malaria?
Malaria is a disease caused by protist pathogens. The disease is carried from host to host by mosquitoes, and the protists enter the human bloodstream when they feed.
How is malaria transmitted?
Vectors (mosquito bites)
What are the symptoms of malaria?
Chills, sweating, fatigue, recurrent fevers and can lead to death
How can malaria be treated?
antimalarial drugs
How can malaria be prevented?
- Sleeping under mosquito nets
- Using insect repellents
- Killing mosquitoes using insecticide
- Eliminate standing water to destroy breeding grounds
What is giardiasis?
An intestinal infection caused by the Giardia parasite
How is Giardiasis transmitted?
contaminated water
What are the symptoms of giardiasis?
Prolonged diarrhea, malaise, weight loss, flatulence, cramps
How can giardiasis be treated/prevented?
prescription antiparasitic medications
How is the spread of disease is prevented?
- vaccination
- good hygiene
- quarantine
- disinfectants
- antiseptics
- keeping away from uncooked food or contaminated water
- Insect control
- insecticides
- Antibiotics and antivirals
What are vaccinations?
Weak or dead pathogens that are injected into your body
How do vaccinations prevent the spread of disease?
Vaccines help the body's immune system recognise and fight off specific pathogens before infection occurs.
How does good hygiene prevent the spread of disease?
Washing hands regularly with soap and water, using tissues when coughing or sneezing, and cleaning surfaces reduce pathogen transmission.
What are antibiotics?
Drugs that kill or prevent the growth of bacteria without killing healthy body cells
What are antivirals?
A Drug that interferes with the viral life cycle, preventing release of new viral particles, some antivirals alter cells DNA so that the virus cannot use the cell to multiply.
How does quarantine and isolation prevent the spread of disease?
Infected individuals should be isolated to prevent the spread of contagious diseases.
What are disinfectants?
chemicals that kill or inhibit harmful microorganisms on non-living surfaces
What are antiseptics?
substances that kill or slow the growth of microorganisms (like bacteria) on living surfaces (like skin) to prevent infection
What are insecticides?
chemicals designed to kill or repel insects
How does insect control prevent the spread of disease?
Using insect repellent, nets, and eliminating breeding grounds for vectors like mosquitoes can prevent diseases like malaria.
What are bacteria?
simple, single-celled prokaryotic organisms (no nucleus) with a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and loose genetic material (DNA/plasmids)
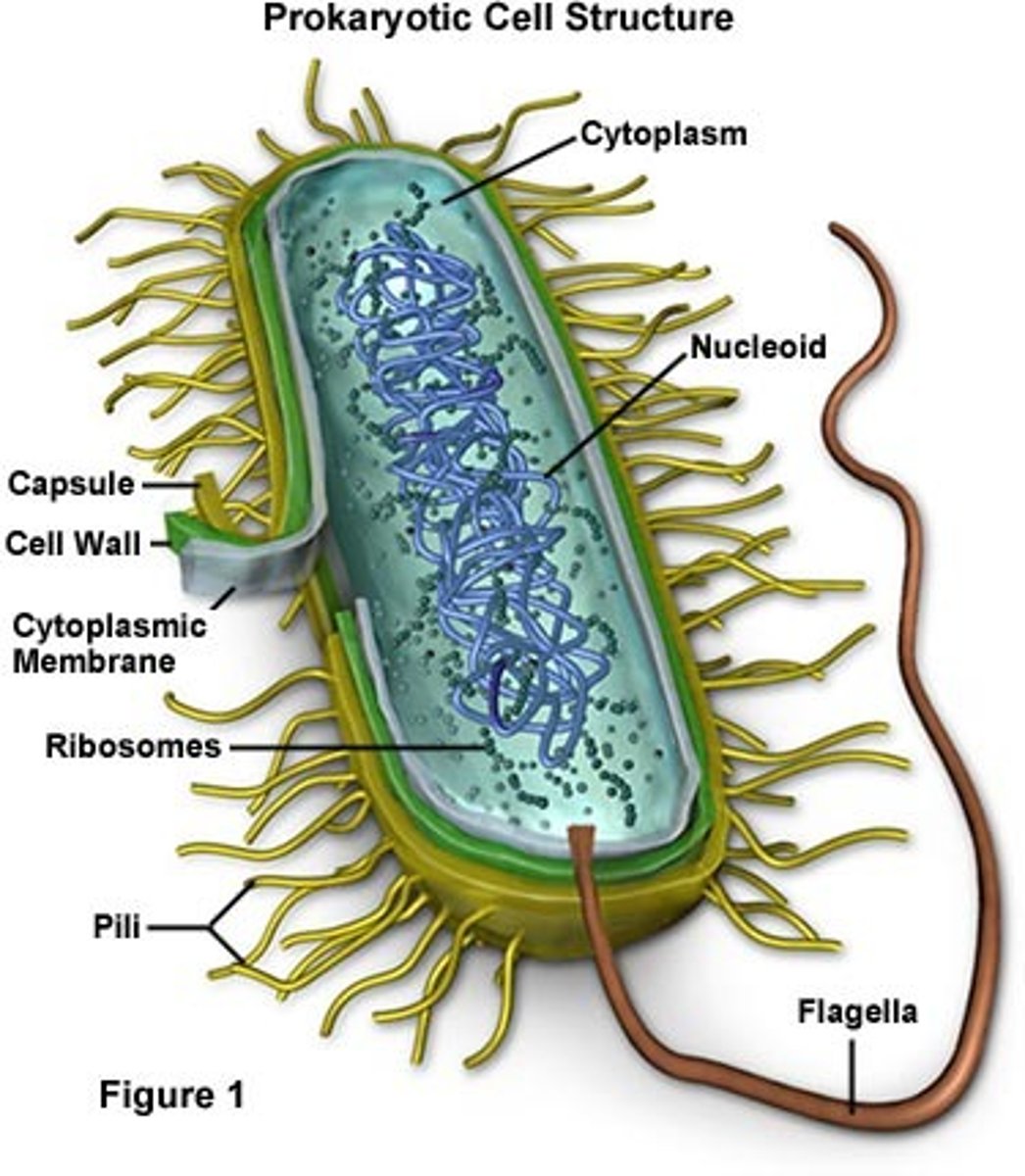
How do bacteria reproduce?
asexually through binary fission
How do bacteria enter the body?
- inhalation
- ingestion
- open wounds
- direct contact
What conditions are best for bacterial growth?
a warm, moist environment, like the respiratory tract, intestines or bloodstream
How do bacteria cause harm?
Bacteria can produce toxins that damage tissues, leading to symptoms like fever, inflammation, and pain.
How do viruses enter the body?
Inhalation
Body fluid exchange
Ingestion of contaminated food/water
Insect bites
How do viruses cause harm?
Viruses invade host cells and take over the cell's machinery to reproduce. This causes the host cell to burst or malfunction, leading to tissue damage and symptoms like fatigue and swelling.
Why do viruses take over host cells?
because they can't reproduce outside of host cells, because they have organelles. (However, they have DNA & RNA)
What are viruses?
tiny, non-living particles made of genetic material (DNA/RNA) that can't reproduce independently
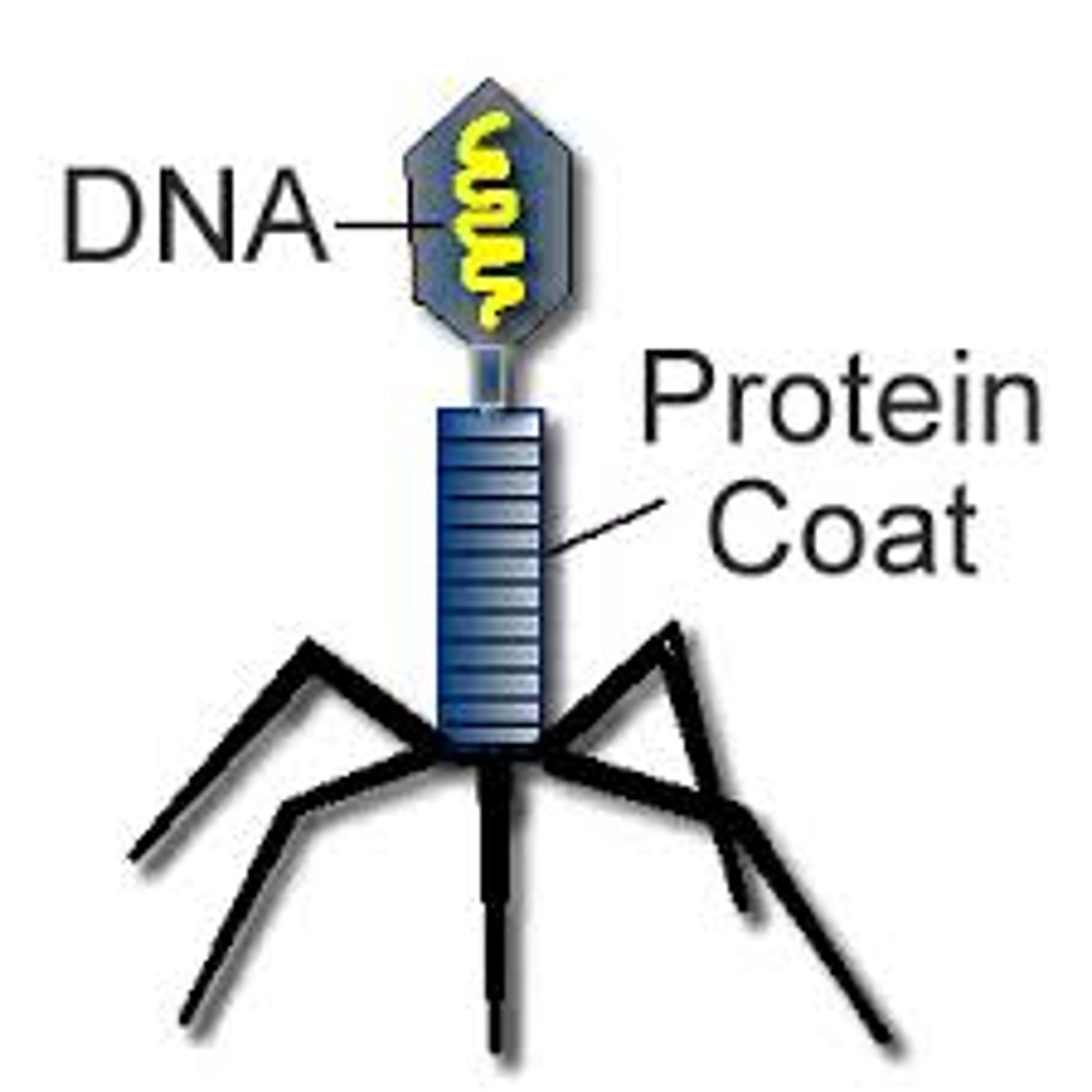
What are fungi?
eukaryotic organisms that are not plants or animals, have cells with a nucleus and cell wall, and get food by absorbing nutrients from dead or living matter
What are parasites?
an organism that lives on or inside another organism (the host) and benefits by taking nutrients or resources from the host, causing harm to the host in the process, without giving anything beneficial in return