Computer Science Test 2
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
Gate
Device that performs basic operation on electrical signals
Circuit
Gates combined to perform more complicated tasks
Boolean Expressions
uses boolean algebra to express two-valued logic
Logic Diagrams
graphical representation of a circuit with gate symbols
Truth tables
table showing all possible input and output values
NOT gate
accepts one input and returns the complementary signal
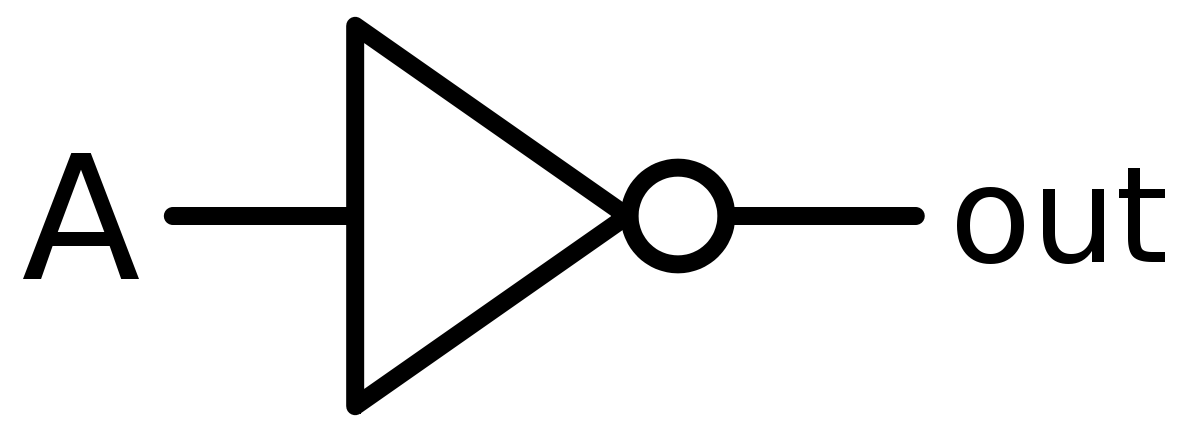
AND gate
accepts two inputs and outputs 1 only if both are 1
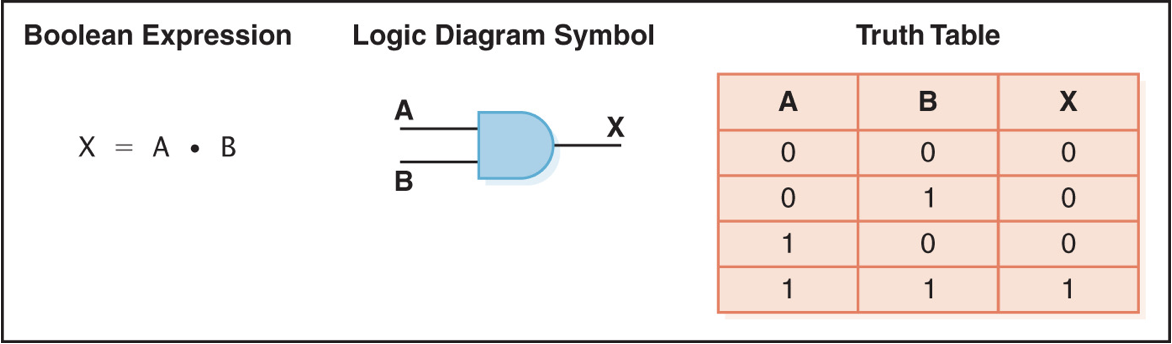
OR gate
accepts two inputs and outputs 1 if at least one is 1
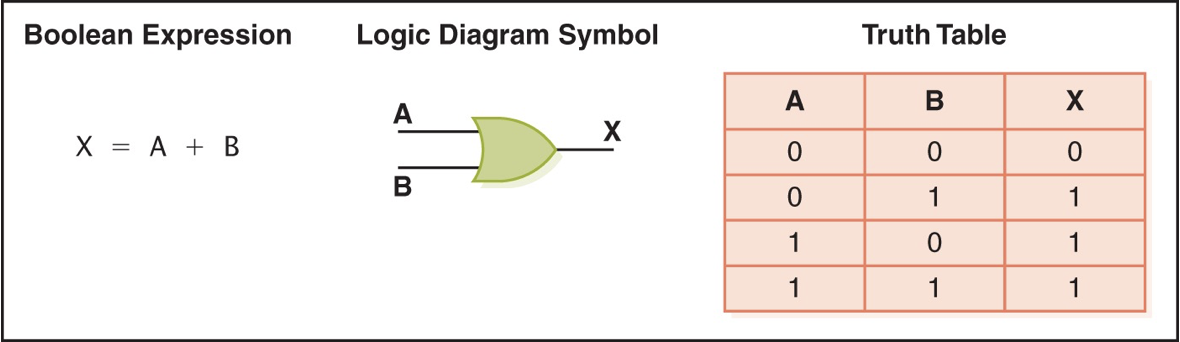
XOR gate
accepts two inputs and outputs 1 if inputs are different
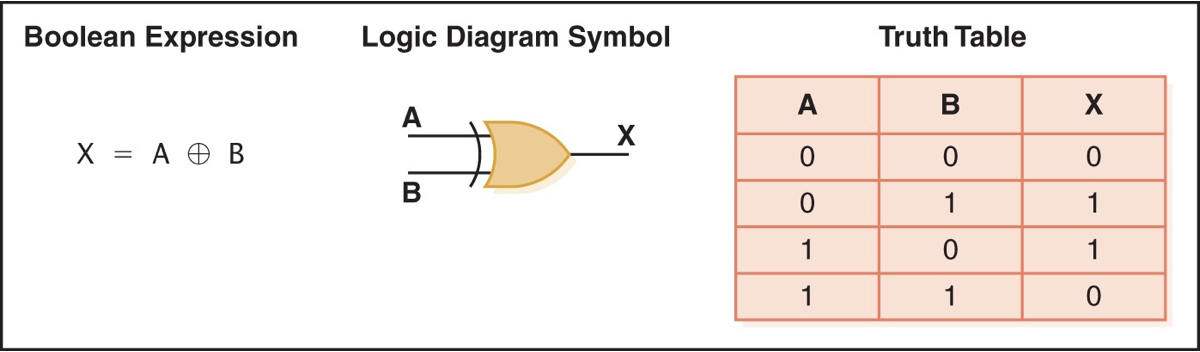
NAND gate
accepts two inputs and outputs 0 if both are 1
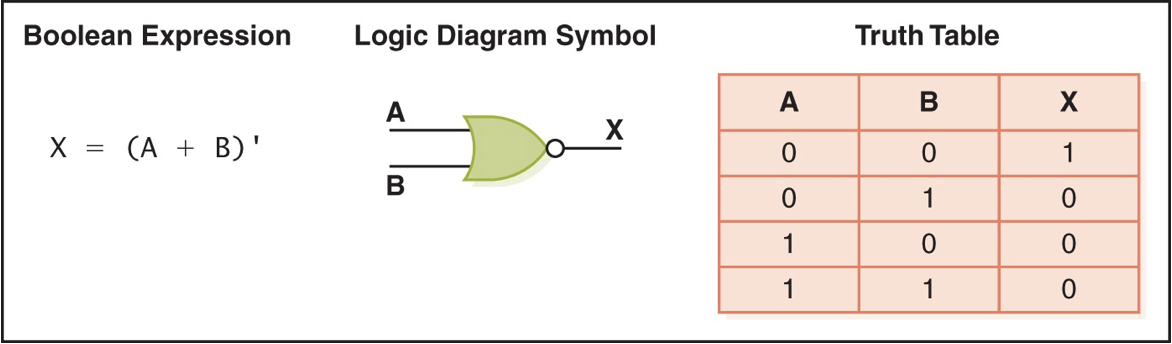
NOR gate
accepts two inputs and outputs 1 if both are 0
three-input AND gate
produces output of 1 only if all inputs are 1
transistor
acts are wire or resistor based on input voltage level
collector
terminal of a transistor
base
terminal of a transistor
emitter
terminal of a transistor
combinational circuit
output determined by input values
sequential circuit
output determined by input values and existing state
circuit equivalence
two circuits producing same output for identical input
Boolean Algebra
applies mathematical principles to design circuits
adders
special circuits for binary addition
half adder
computers sum of two bits and produces carry bit
full adder
takes carry-in value into account
Multiplexer(MUX)
routes input data based on input control signals
sequential circuit
circuit that stores information and uses output as input
S-R latch
circuit that stores a single binary digit
Integrated Circuit(IC)
silicon piece with embedded gates or transistors
Central processing unit(CPU)
most important IC in a computer system
NOT Gate
AND gate
OR Gate
XOR Gate
NAND gate
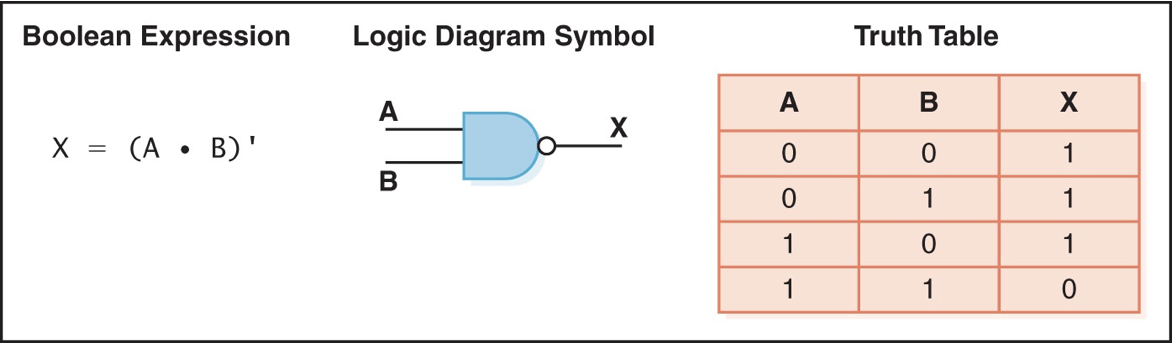
NOR gate
Admiral Grace Murray Hopper
Illustrated sizes in perspective
Coil of wire
Nearly 1,000 feet long
Distance traveled by an electron in a space microsecond
short piece of wire
travels in a space nonsecond
bag of grains of pepper
travels in a space picosecond
Intel Processor
“Faster is better“ applies here. A higher clock speed(GHz) generally indicates better performance for a processor, so a 2.66 GHz processor is better than a slower one
SDRAM
“Bigger is better“ applies to the size(4GB) if you need more memory for your tasks. However, “Faster is better“ also applies to the speed(800 MHz) because a higher memory speed can improve overall system performance
500GB SATA at 5400 RPM
“bigger is better“ applies to the storage size if you need more storage capacity. However “Faster is better“ applies to the transfer rate because a higher transfer rate because a higher transfer rate means faster data access and transfer speeds
Flat screen dot pitch
“smaller is better“ applies here. A smaller dot pitch means that the pixels on the screen are closer together, resulting in a sharper and more detailed display
What is an Intel Processor speed?
2.66 GHz
What is a SDRAM speed?
800 MHz
What is a SDRAM size
4GB
What is an 500 GB SATA at 5400RPM transfer rate?
300 MB per second
What is a Flat screen dot pitch size for pixels?
0.28mm
Memory
collection of cells with unique physical addresses
most computers are byte-addressable
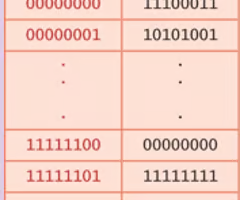
“Little-endian“ bit numbering
Arithmetic/Logic Unit
Performs functions such as addition and subtraction as well as AND, OR, and NOT
Registers
special storage units in ALUs
Input Unit
a device through which data and programs from the outside world enter the computer system
Name 3 Input Units
Keyboard, mouse, microphone
Keyboard
an input unit that allows users to input text and commands into a computer by pressing keys
Mouse
input device that allows users to move a cursor on the screen and interact with graphical user interfaces by clicking icons, buttons, and other elements
Mircophone
an input device that converts sound waves into electrical signals, allowing users to input audio data, such as voice recordings or voice commands into a computer
output unit
a device through which results stored in the computer memory are made available outside the computer system
Name 2 output units
monitor and printer
Monitor
an output unit that displays visual information including text, images, videos, and user interfaces to the user. it provides a visual representation of the computers output
Printer
output device that produces physical copies of digital documents, images, or other content. converts electronic data into a printed form on paper or other media
control unit
organizing force int he computer
Instruction Register(IR)
contains the executing instruction
Program Counter(PC)
contains the address of the next instruction
Central Processing Unit(CPU)
ALU and control unit
Bus
communication system transferring data between components
What does “bus“ connect?
connection between CPU, memory, I/O devices, and possibly other components(hard disk drive)
what is an N-bit processor?
this could refer to registers, ALU, addresses, or data bus
Fetch-Execute Cycle
fetch the next instruction
decode the instruction
get data if needed
execute the instruction
store the result of the instruction in memory
Why is it called a cycle?
it represents a repetitive and continuous sequence of operations that a computer’s central processing unit performs to execute instructions stored in memory
Random Access Memory(RAM)
each location can be accessed and changed; is volatile
Read Only Memory(ROM)
each location can be accessed but not changed; is not volatile
What does volatile mean?
the characteristic of the memory where data stored in RAM is temporary and is lost when the power to the computer is turned off or when the system is restarted
Why is it necessary to have secondary storage devices?
by providing persistent, high-capacity storage for data, software, and backups
Examples of secondary storage devices
Hard Disk Drive, Solid-State Drive, USB Flash Drive, External Hard Drive
Hard Disk Drive
one of the most common types of secondary storage devices. They provide high-capacity storage using spinning magnetic disks to store data. are found in desktop and laptop computers as well as external drives
Solid-State Drive
uses flash memory to store data. They are faster and more durable than HDDs but typically offer less storage capacity. are commonly used in laptops and desktops, and they are also available as external drives
USB Flash Drive
are portable secondary storage devices that connect to a computer's USB port. They are small, lightweight, and offer a convenient way to transfer and store data
External Hard Drive
connects to a computer via USB, Thunderbolt, or other interfaces. they are commonly used for backup, storage expansion, and data transfer
Magnetic Tape
first mass auxiliary storage device
The major problems with tape drivers
slow access speed, physical tape damage, limited random access, obsolete technology data deregulation
Magnetic Disks Access time
typically ranges from 2 to 15 milliseconds
seek time
time to read/write
latency
time for the second to be in position
transfer rate
rate at which data moves from the disk to memory
Optical Disks
CD, DVD, Blu-ray
CD
compact disk with laser reading
CD-ROM
CD read-only memory
CD-DA
CD digital audio
CD-WORM
CD write once, read many
RW or RAM
both read from and written to
DVD
Digital Versatile Disk, used for storing audio and video
Blu-ray
higher capacity DVD allowing higher resolution video, etc.
Flash Memory
nonvolatile, can be erased and rewritten
supports USB. mass storage standard
Touch screen
a computer monitor that responds to the touch of a finger or stylus
Resistive touch screen
two layer of conductive material, touch location determined by contact
capacitive touch screen
laminate conducts electricity, touch location determined by comparing current flow
Infrared touch screen
horizontal and vertical beams of infrared light, touch location determined by beam break
Surface Acoustic Wave(SAW)
high-frequency sound waves, touch location determined. by interruption
embedded systems
computers dedicated to perform specific functions
parallel computing
four forms: bit-level, instruction-level, data-level, task-level