Nation-States, Sovereignty, and Globalization in PSCI 102
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is a state?
An independent, self-governing political community whose government can make binding rules for its population within a specific territory.
What three components make up a state?
Territory, people, and sovereignty.
What is a nation-state?
A sovereign state based on people living in a country who share a common identity as members of a nation.
What does state sovereignty entail?
States claim to be the highest authority for their population and territory, are not subject to external authority, and are viewed as legally equal regardless of power differences.
How many sovereign states are members of the United Nations?
193 sovereign states.
What are failed states?
States that cannot enforce laws, maintain order, protect citizens, or provide basic services.
What is the Fragile States Index?
An assessment created to evaluate a country's vulnerability to collapse, originally established in 2005.
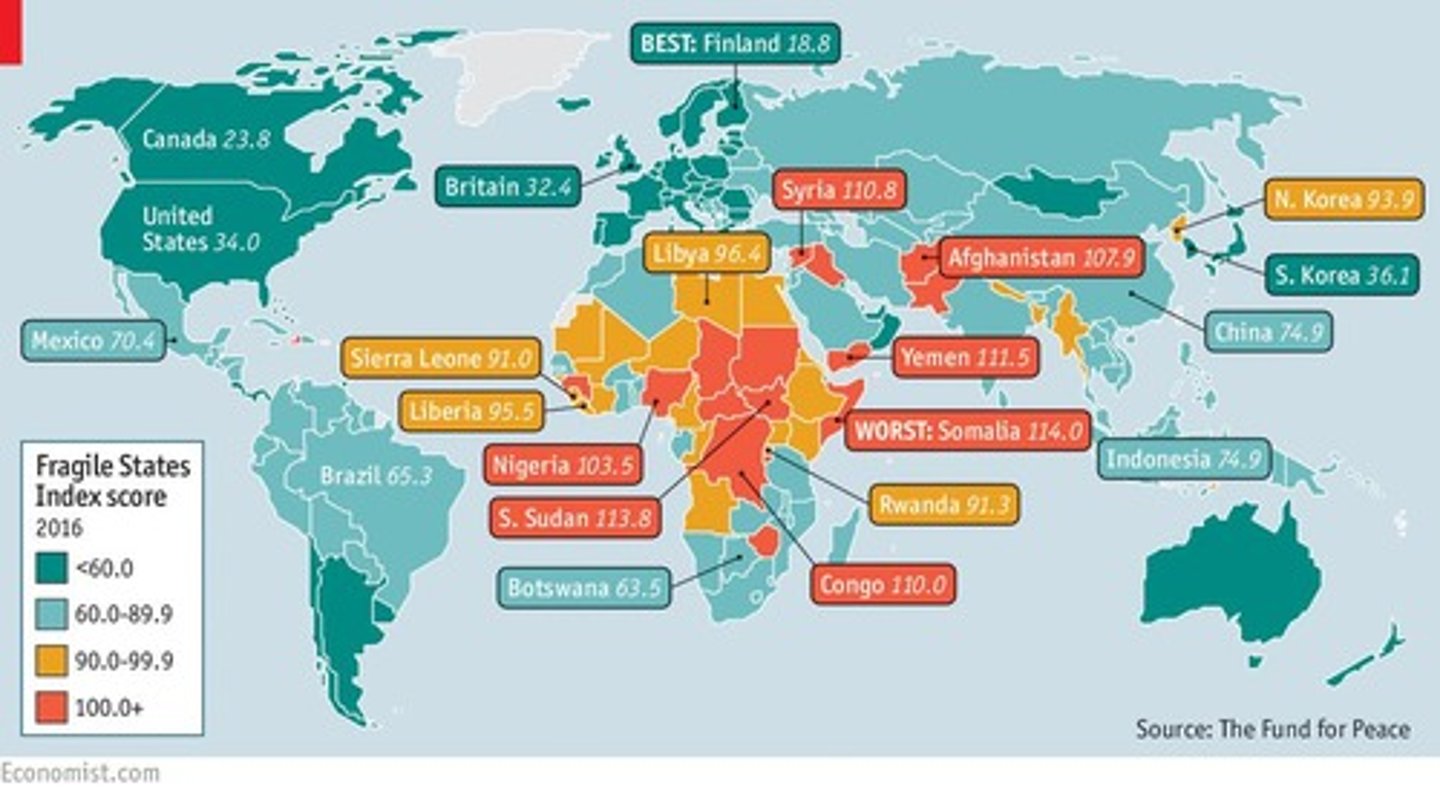
What is the impact of power disparities among states?
Weaker countries may find their sovereignty limited or ignored, leading to international intervention to protect human rights.
What is nationalism?
The belief that the nation-state is the best form of political community and that a nation should have its own self-governing state.
What are the two types of nationalism?
Ethnic nationalism, based on common ancestry, and civic nationalism, based on shared political values.
What is multiculturalism?
A policy recognizing and supporting the cultural diversity of a country, as opposed to forcing assimilation into a dominant culture.
What is the role of citizenship?
Citizenship involves being a full member of a political community with specific rights and duties, and it cannot be revoked in most countries.
What is statelessness?
A condition where no state recognizes a person as a citizen, affecting millions globally.
What is globalization?
Processes that increase the interconnectedness of the world in economic, political, and cultural realms.
How does globalization affect state power?
It erodes state power by shifting authority to global institutions and increasing the influence of global markets and corporations.
What are examples of international institutions formed due to globalization?
The United Nations, international financial institutions, and global NGOs.
What is the difference between patriotism and nationalism?
Patriotism is love for one's country, while nationalism emphasizes the interests and culture of a nation, often advocating for self-governance.
Can a person have multiple identities?
Yes, individuals can possess multiple identities simultaneously based on various factors such as ethnicity, nationality, and culture.
What challenges does multiculturalism face?
It is often challenged by societal responses to immigration, particularly from groups perceived as threats to social culture and values.

What is the significance of national identity?
It exists where people share common characteristics and ties to a territory, often promoted by governments to unify diverse populations.
What is the role of governments in creating national identity?
Governments may attempt to replace local cultures with a national culture to foster a sense of unity among citizens.
What is the impact of globalization on cultural values?
Cultural globalization allows for the wider distribution of cultural products and values, often promoting Western ideals globally.
What is the relationship between globalization and economic management?
Economic globalization reduces national governments' ability to manage their own economies due to the rise of global corporations.
What are contested states?
States that face disputes over their sovereignty or territorial integrity, often leading to conflict.
Is Canada a nation-state?
Canada is considered a multinational state due to its diverse population and multiple cultural identities.
What is the legitimacy of the state based on?
It is often based on the perception of a common national identity among the population.
What are the implications of small nation-states?
They may struggle with internal markets, government service costs, and military defense due to their size.