Nucleic Acids
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
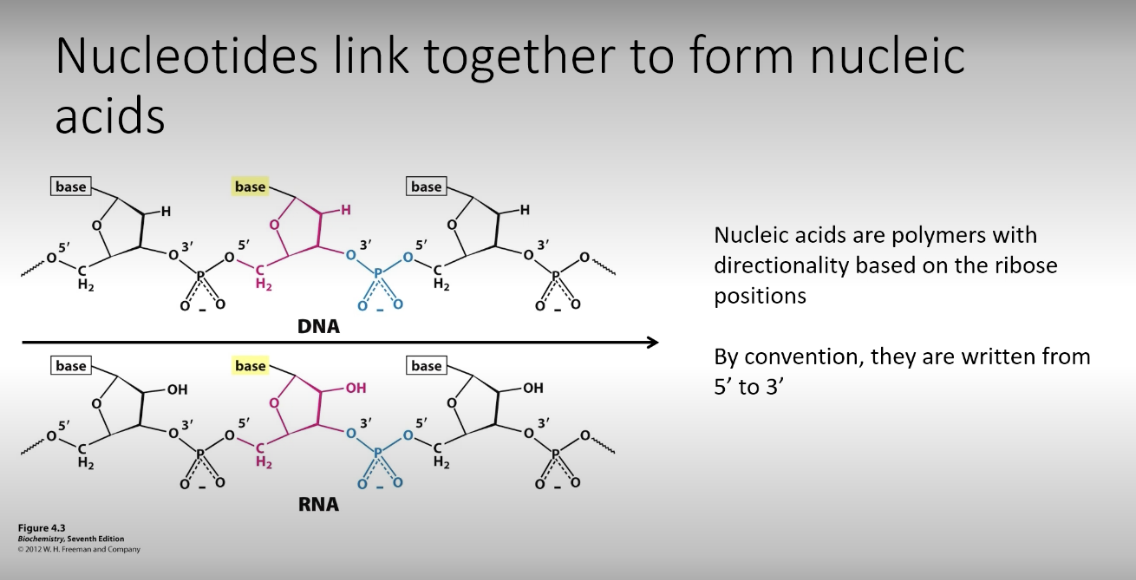
Nucleotides link together
to form nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are polymers with directionality based on the ribose positions
By convention, they are written from 5' to 3'
Nucleotides link together picture
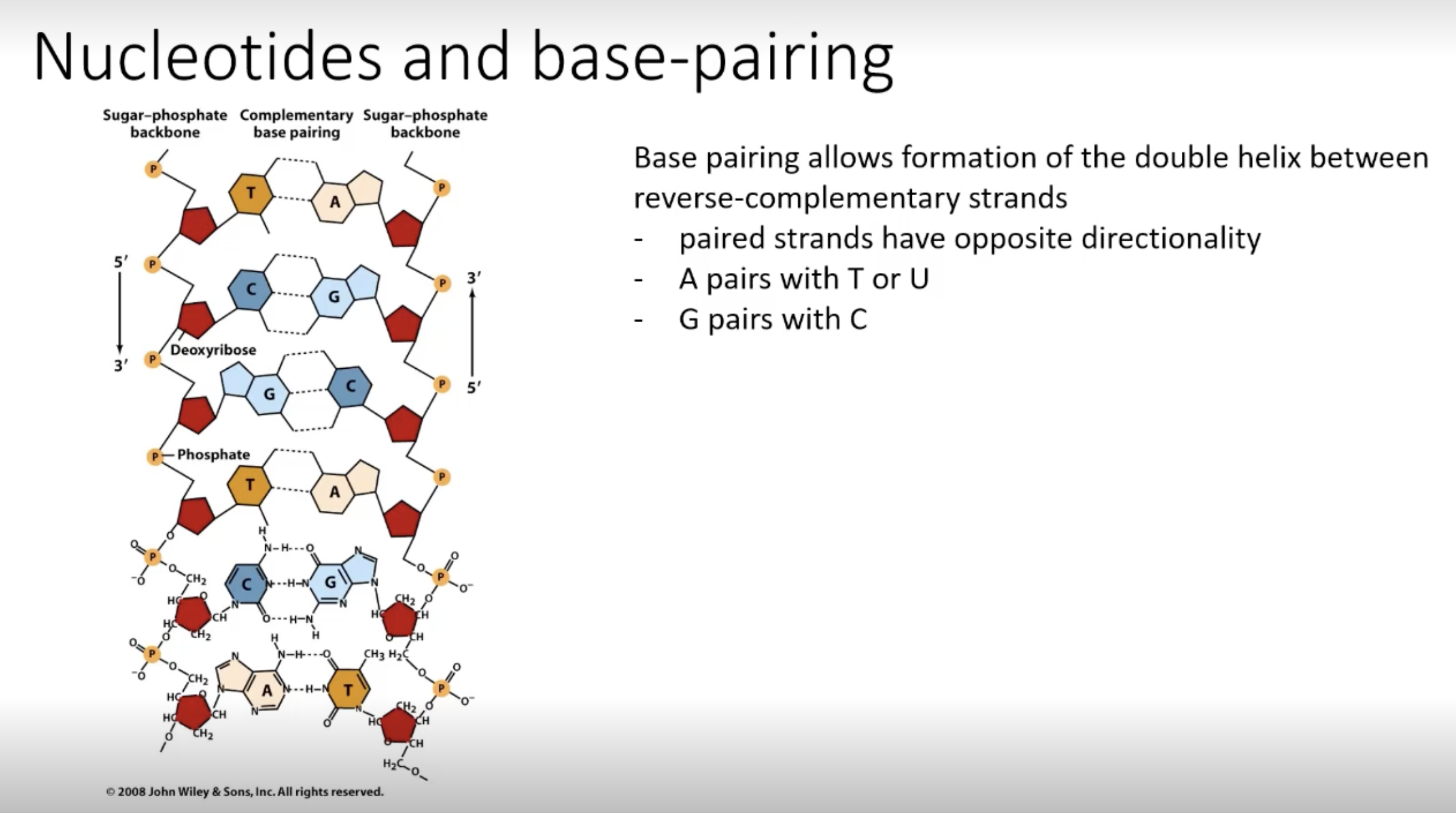
Nucleotides and base-pairing 1, what does base pairing allow, what bases pair with what
Base pairing allows formation of the double helix between reverse-complementary strands
- paired strands have opposite directionality
- A pairs with T or U
- G pairs with C
Nucleotides and base-pairing picture 1
bonds between bases
hydrogen
Intermolecular Duplex Formation
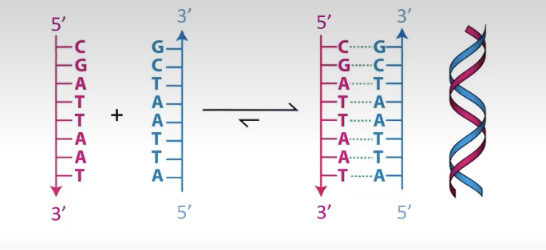
two strands base pairing together
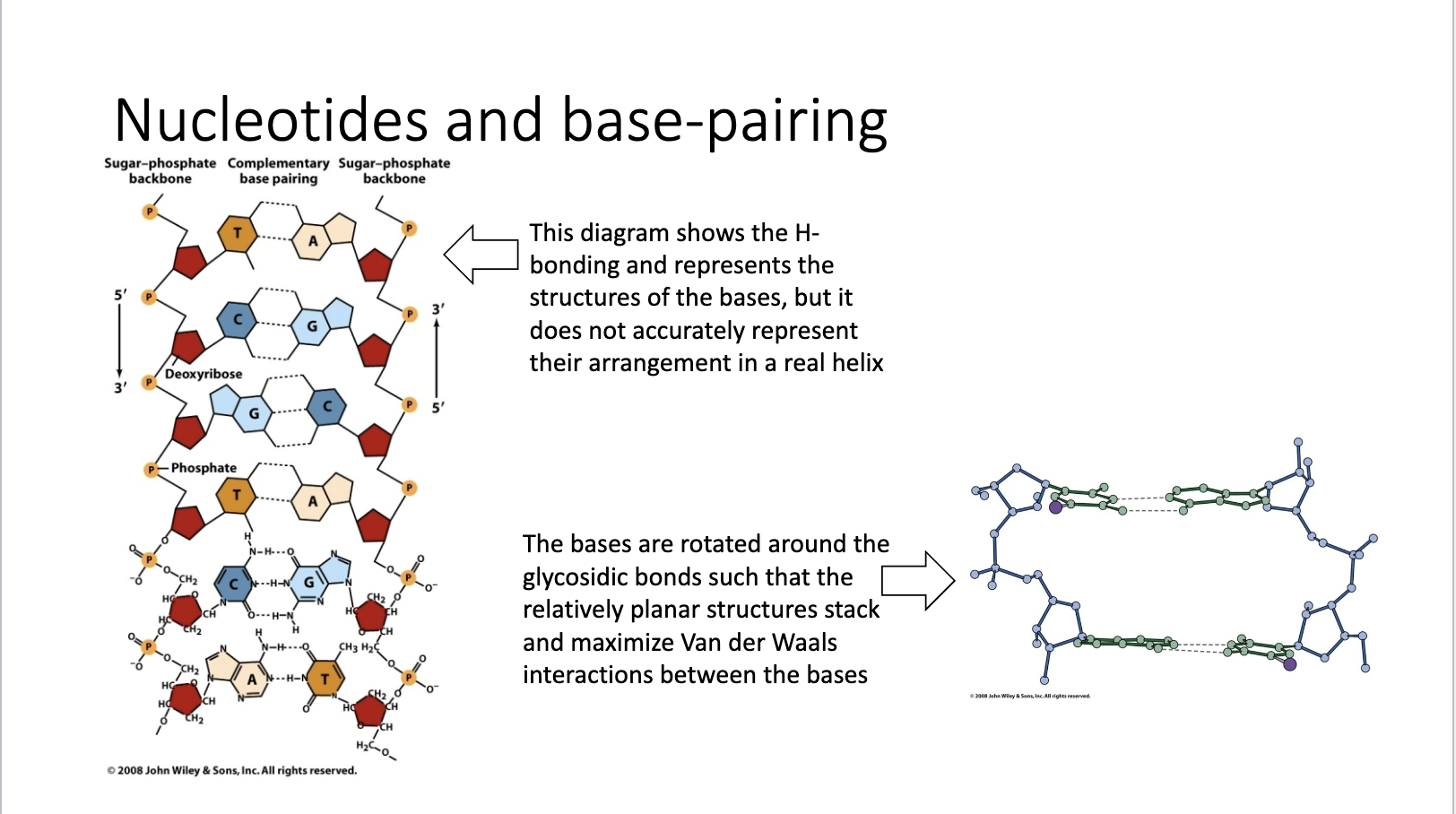
Nucleotides and base-pairing 2
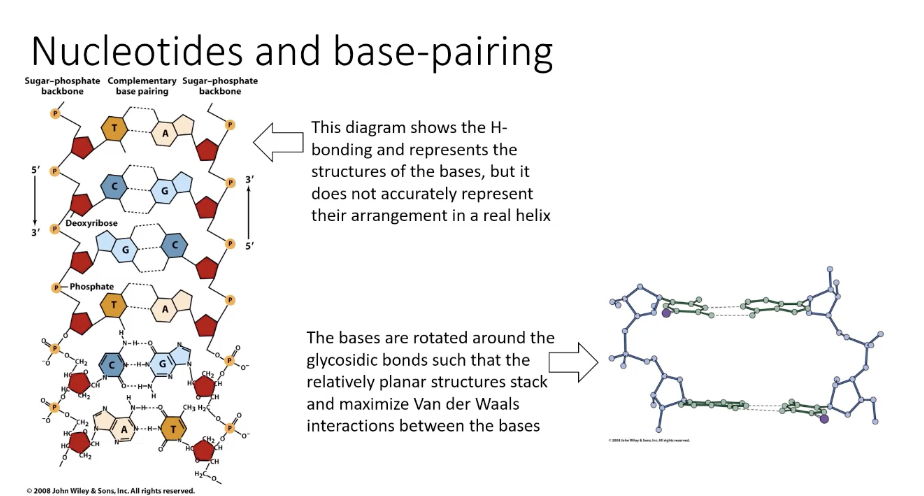
This diagram shows the H-bonding and represents the structures of the bases, but it does not accurately represent their arrangement in a real helix
The bases are rotated around the glycosidic bonds such that the relatively planar structures stack and maximize Van der Waals interactions between the bases
Nucleotides and base-pairing 2.1
bases are rotated around glycosidic bonds such that
Nucleotides and base-pairing 2.2
relatively planar structures stack
Nucleotides and base-pairing 2.3
maximize Van der Waals interactions between bases
Nucleotides and base-pairing 2 picture
Duplex Formation 1
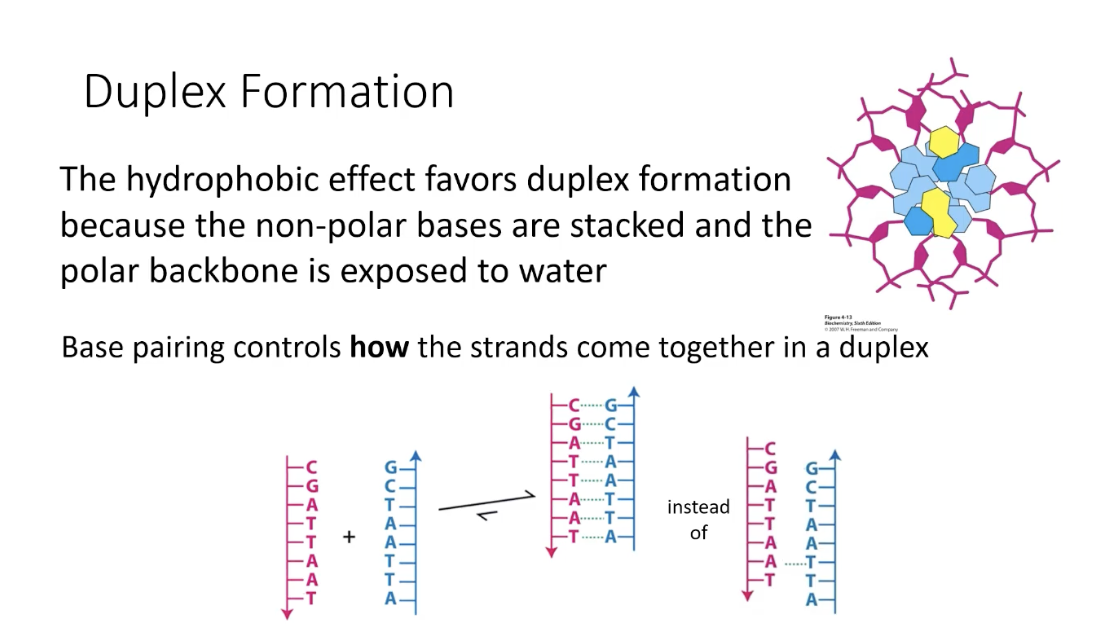
The hydrophobic effect favors duplex formation because the non-polar bases are stacked and the polar backbone is exposed to water
Base pairing controls how the strands come together in a duplex
Duplex Formation 1.1
hydrophobic effect favors duplex formation
Duplex Formation 1.2
because non-polar bases are stacked
Duplex Formation 1.3
and polar backbone is exposed to water
Duplex Formation text 2
Base pairing controls how the strands come together in a duplex
Duplex Formation 1 picture
Characteristics of the double helix 1
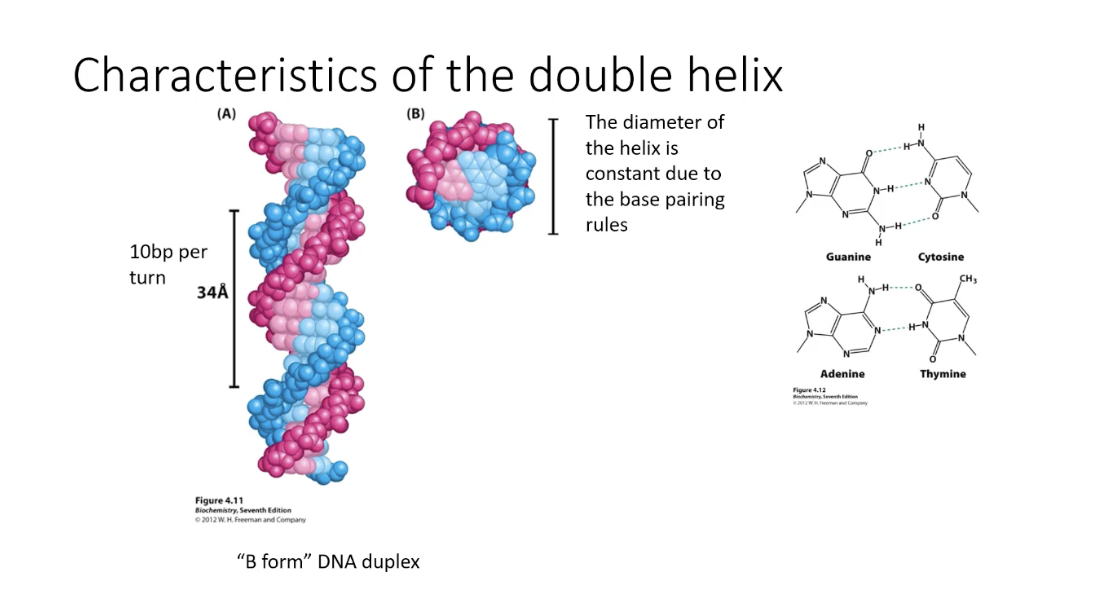
The diameter of the helix is constant due to the base pairing rules
Characteristics of the double helix 1 picture
Characteristics of the double helix 2
B form: the most common and stable form of DNA, characterized by its right-handed double helix structure that is the standard found in living organisms
A form: dehydrated DNA or DNA-RNA hybrid
Z-form: observed in vitro, but likely uncommon in cells
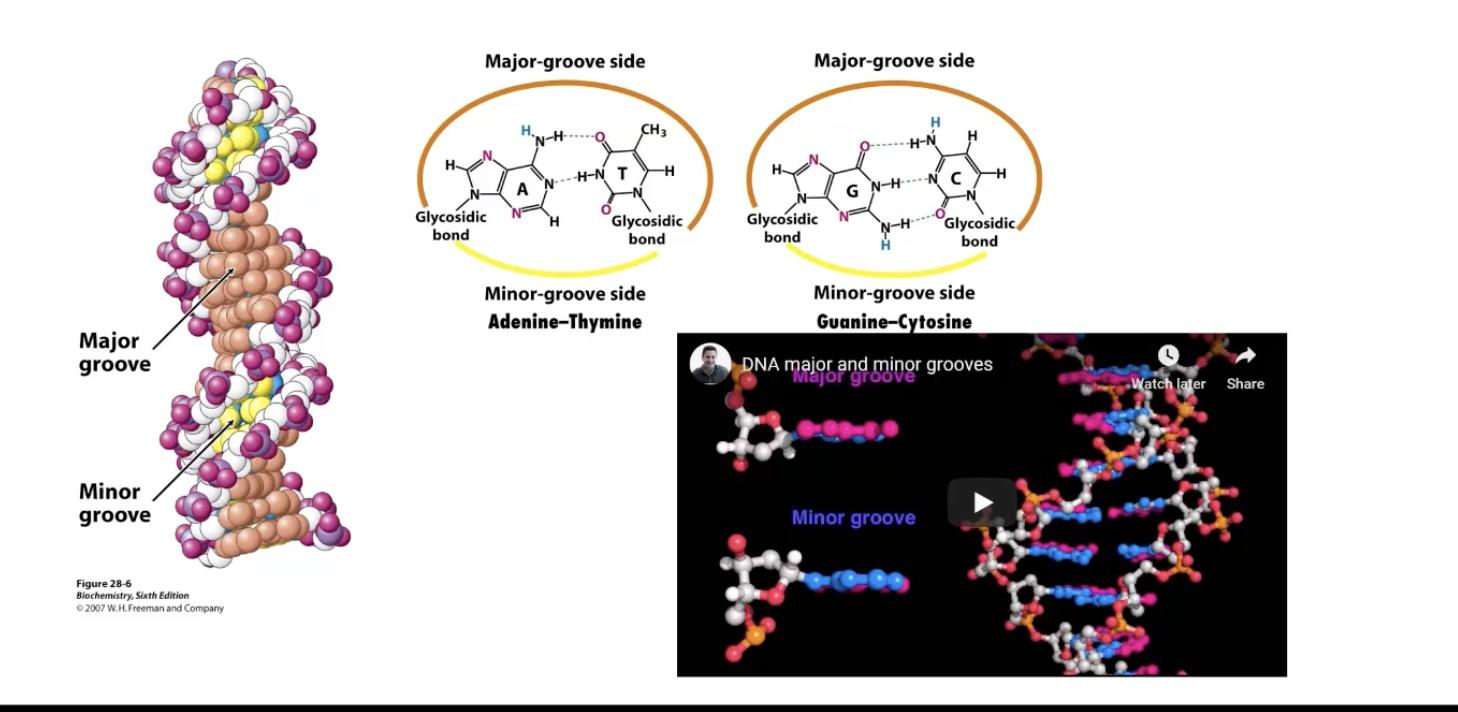
The double helix forms
a "major" and "minor" groove
Summary
Nucleotides link together to form nucleic acids
Base pairing between nucleic acids forms a double helix with defined parameters
Double helices have major and minor grooves