N3: Unit 6: Module 4: Part 1: Care of the Patient with Musculoskeletal Trauma fully solved questions with 100% accurate solutions(Latest Update)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Fractures
A break or disruption in the continuity of the bone
-affects mobility (acute or long term)
-causes discomfort
-can occur anywhere in the body at any age (more likely to occur as we age as the skeletal system and bone structure starts to weaken)
-All of them require patient-centered, inter-professional collaborative care
-Many different kinds/classifications
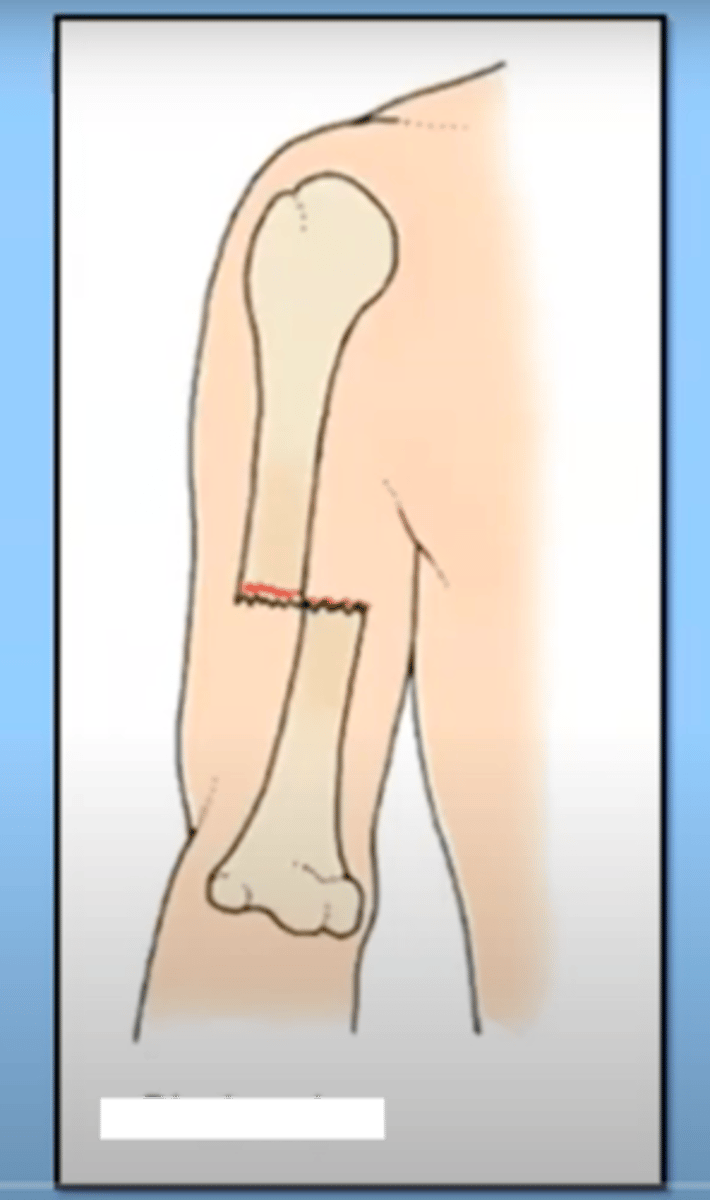
Complete fracture
the breaks goes through the entire bone
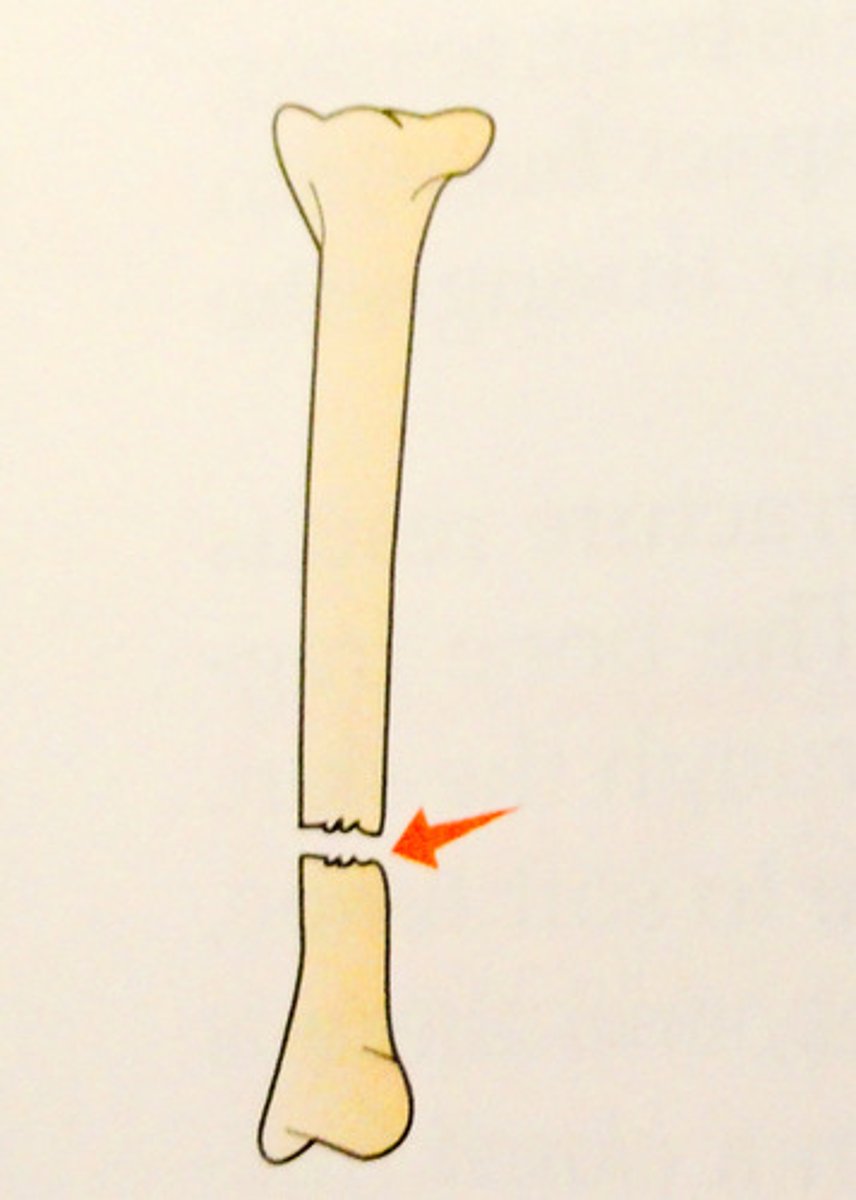
Incomplete fracture
bone is not broken all the way through
displaced fracture
the two main bone fragments are out of alignment
non displaced fracture
the separate fragments are in touch/aligned
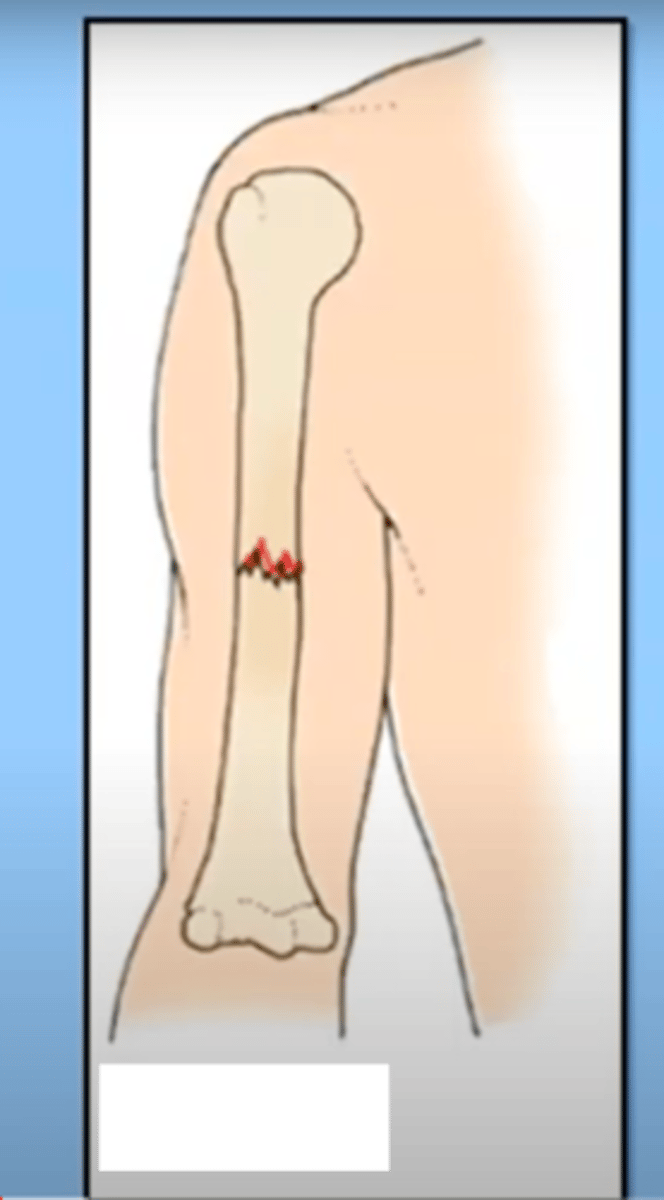
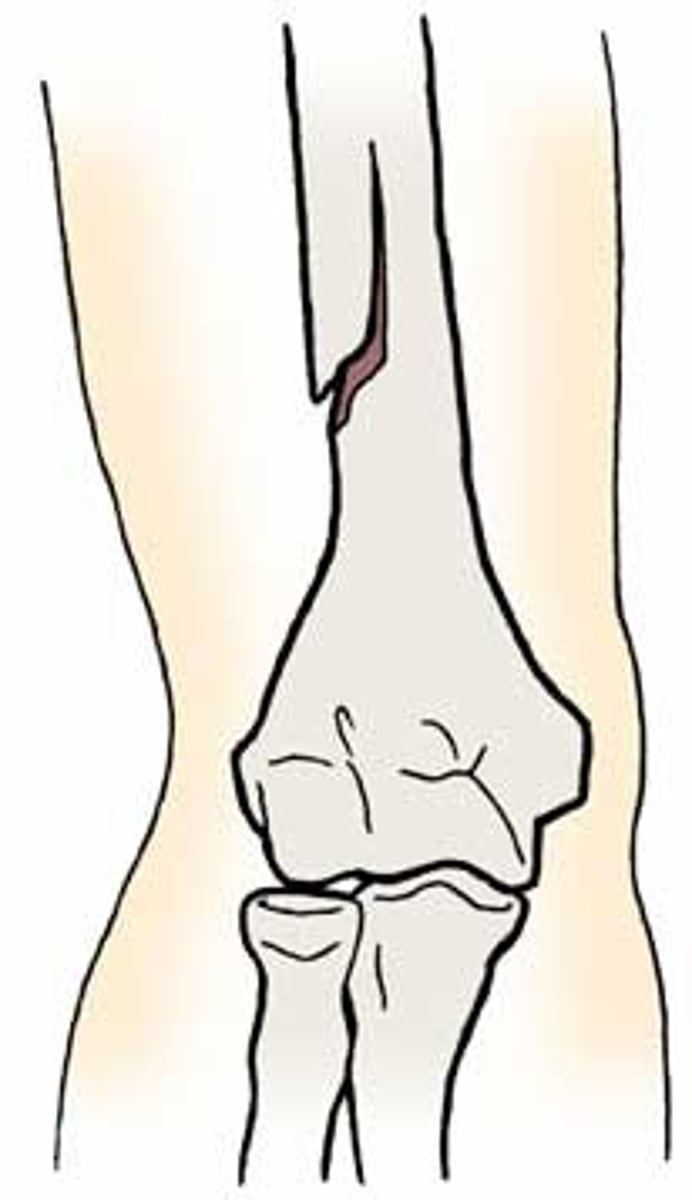
comminuted fracture
fracture in which the bone is splintered or crushed
-multiple fragments
-just 2 is not, that is clean break
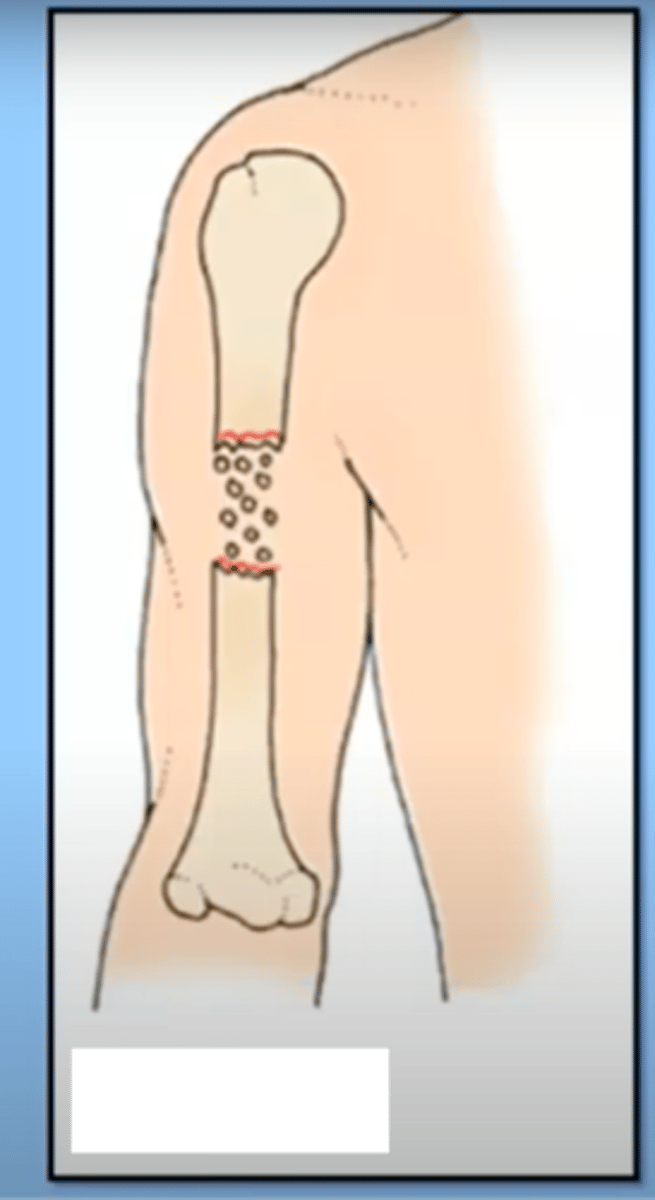
impacted fracture
fracture in which one bone fragment is pushed into another
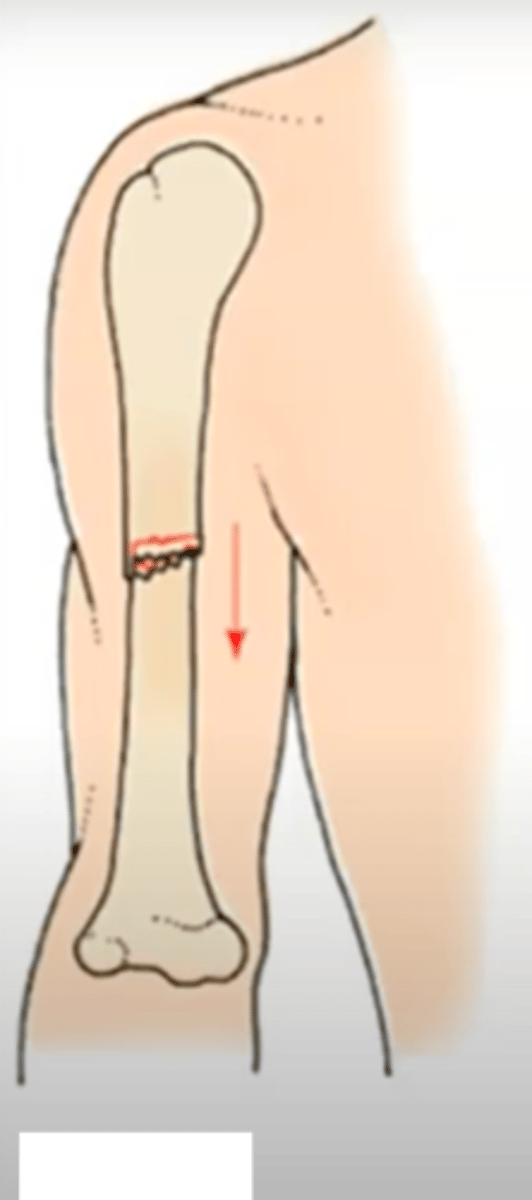
greenstick fracture
a fracture with an incomplete break, the bone bends, seen more in kids with more pliable bones
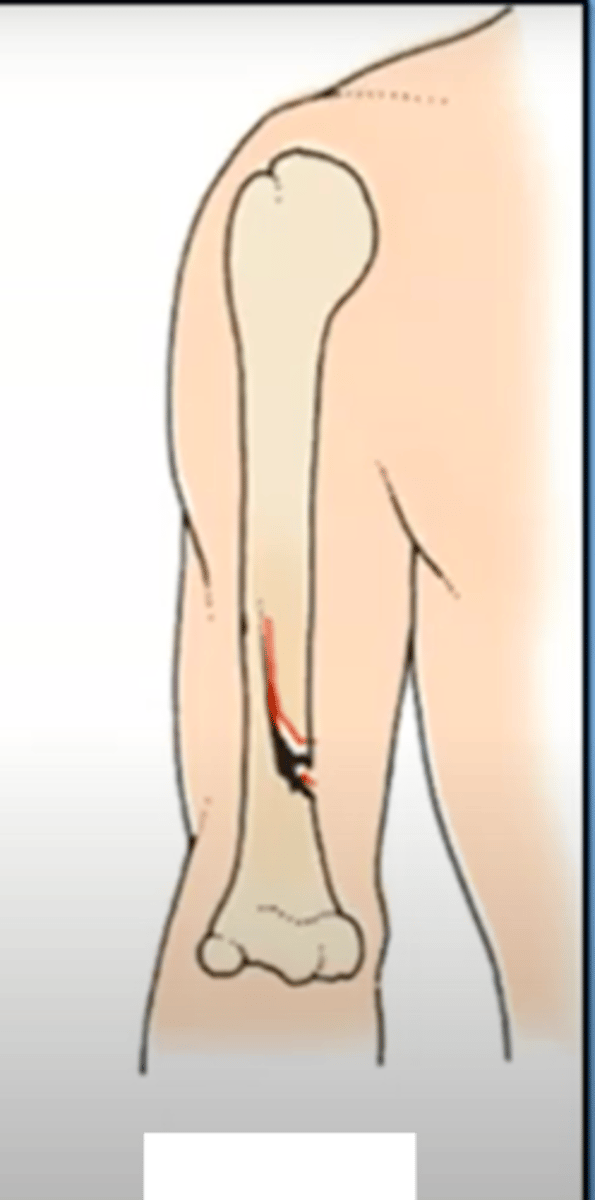
open/compound fracture
broken bone penetrates through the skin
major consideration to the complexity and healing process/risk to the patient
big infection risk
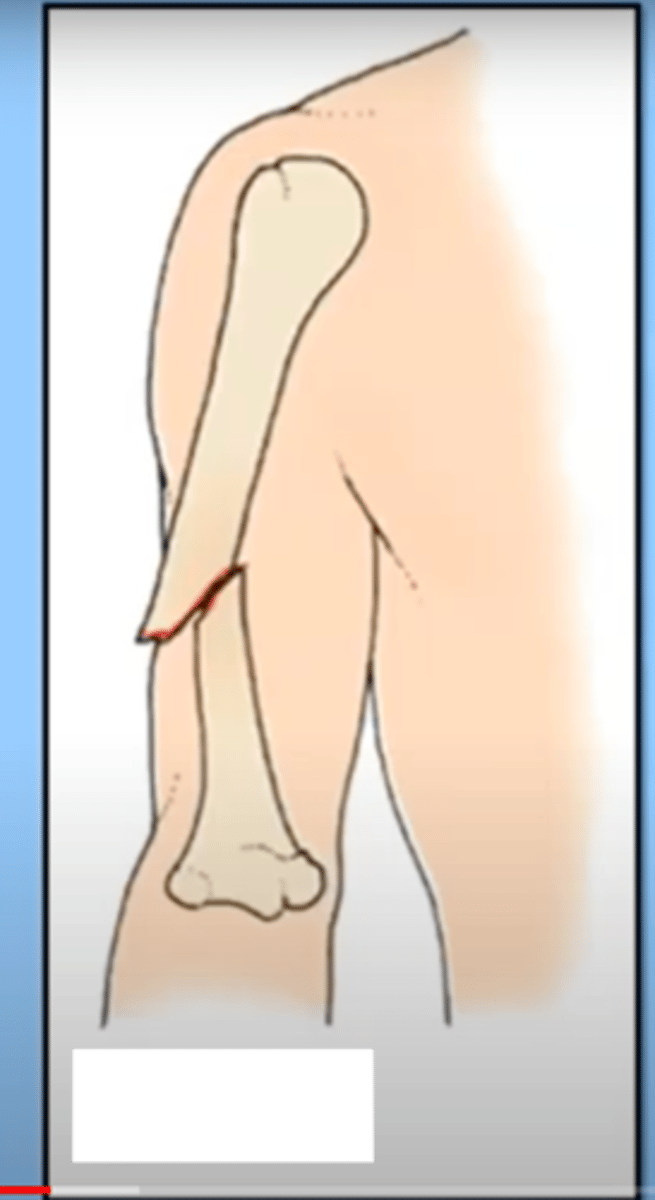
closed/simple fracture
break that does not penetrate the skin
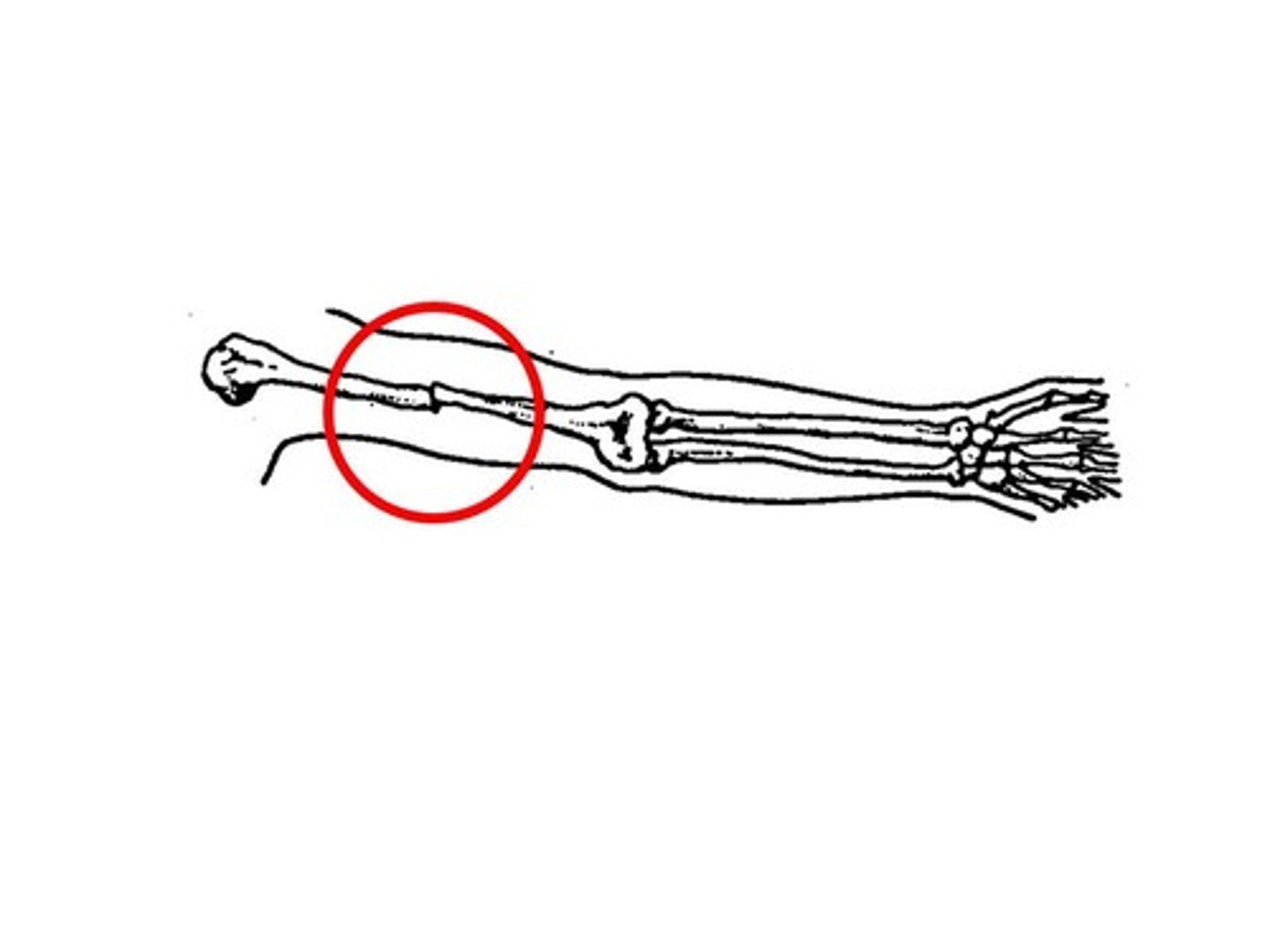
pathologic/spontaneous fracture
occurs when a weakened bone breaks under normal strain
may indicate an underlying condition ex: osteoporosis, malignancies
mechanism of injury
description of damage sustained by bone
-what it looks like
ex: stress (ppl who run), compression (of the vertebrae)
does the description of the injury occurrence match with the actual injury?
oblique fracture
occurs at an angle through the bone
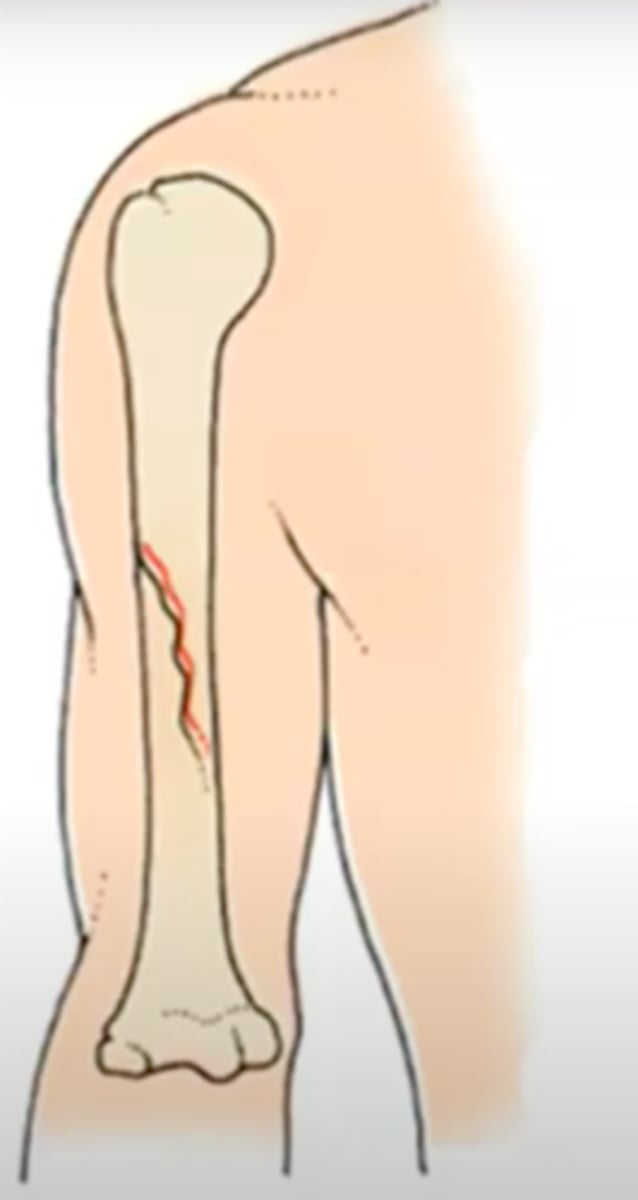
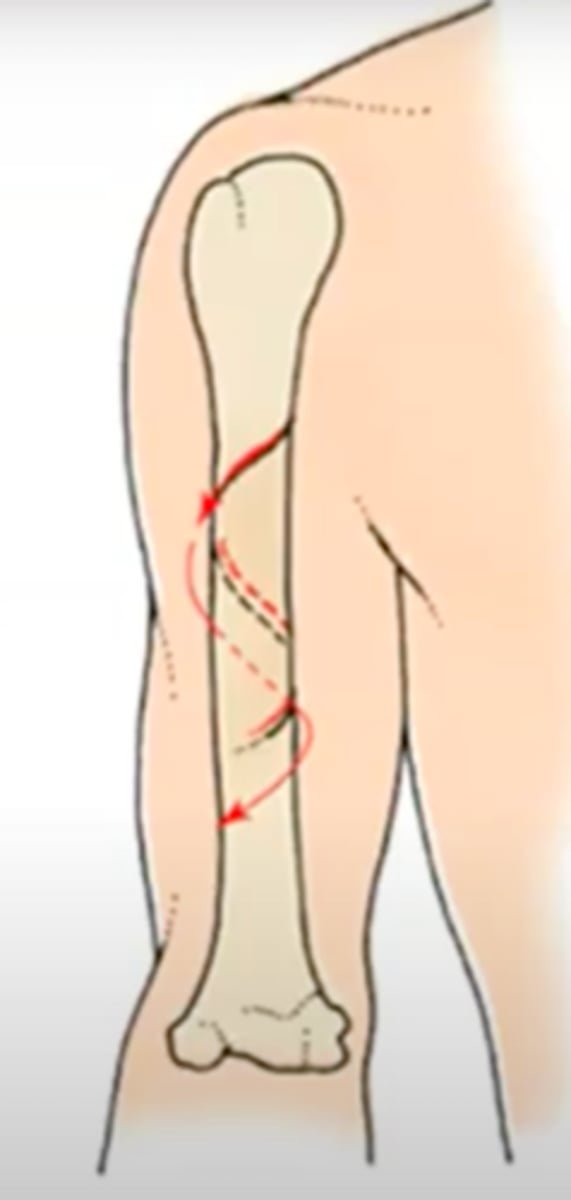
spiral fracture
a fracture in which the bone has been twisted apart
usually occurs when force is exerted on a bone while one end is stationary and the other end twists
sometimes associated with physical abuse, especially young children and elderly
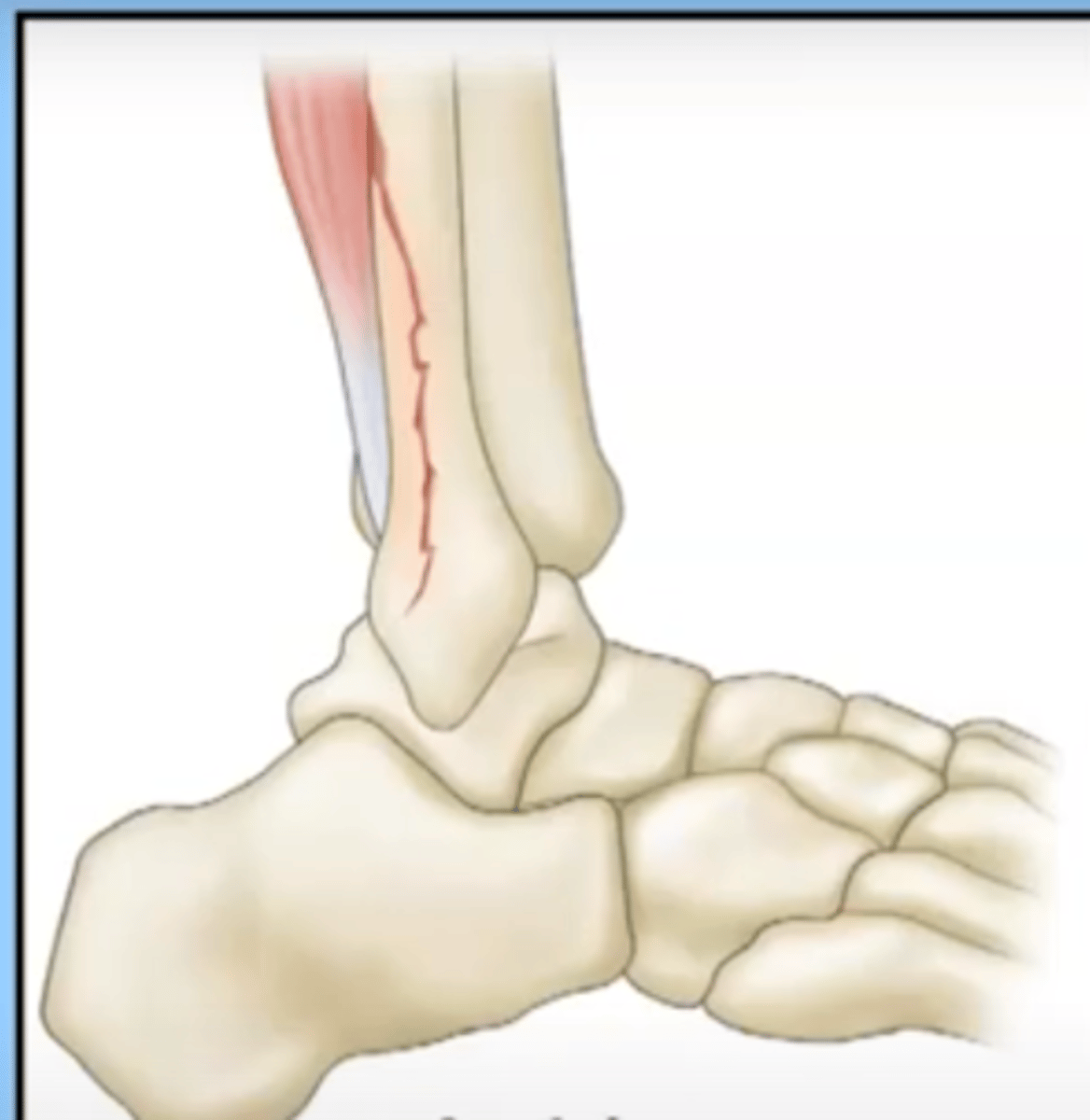
comminuted ulna and radial fractures
the muscles of the arm may simply pull the bone fragments up and away and create more of a gap
avulsion
a fracture in which a fragment of bone has been pulled away by a tendon and it's attachment
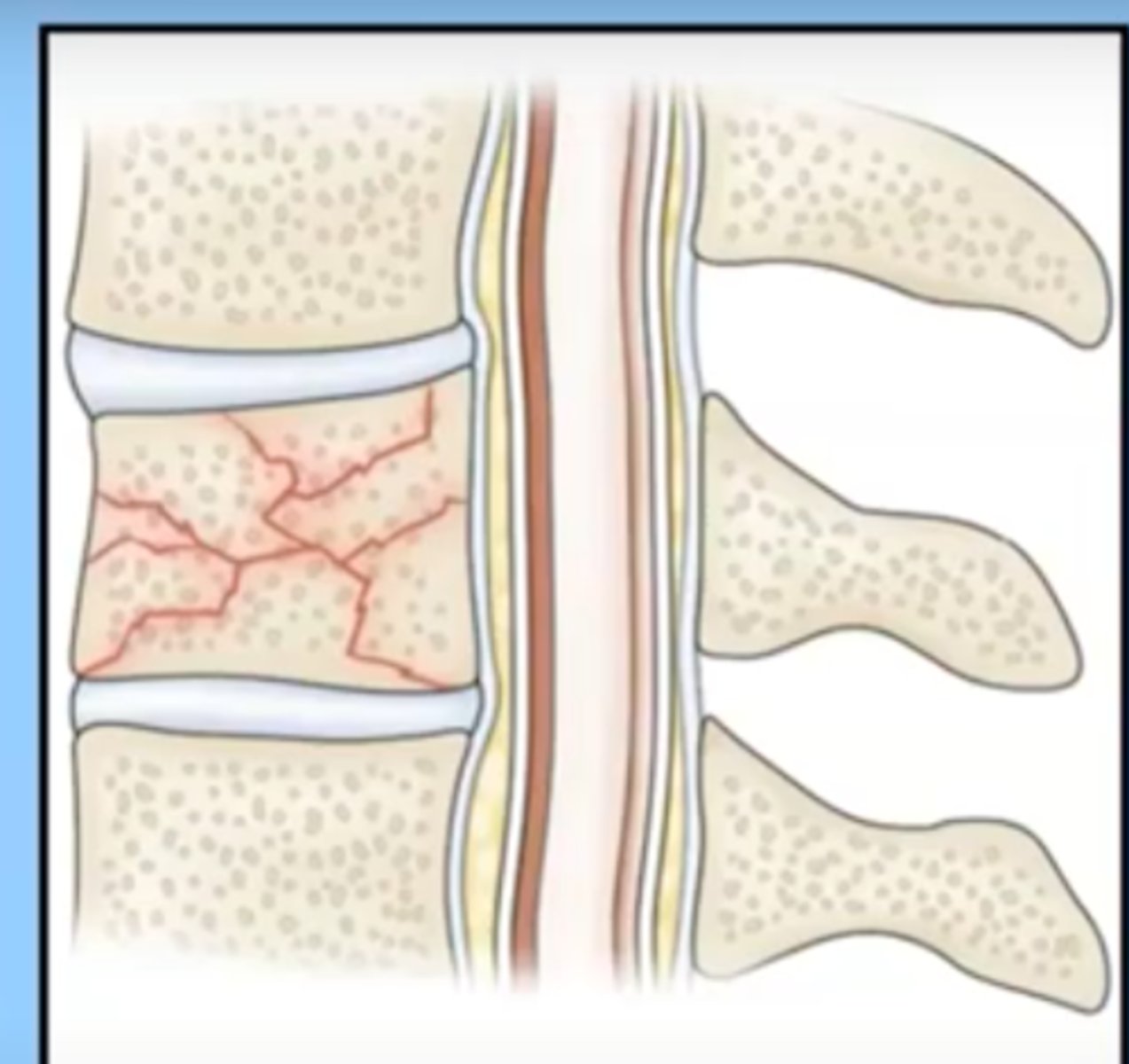
compression fracture
occurs when the bone is pressed together (compressed) on itself
seen in vertebral fractures, very common in osteoporosis (getting shorter)
signs and symptoms of a fracture
Often an obvious acute deformity, but not always (ex compression fracture)
Pain (has to be treated adequately to recover)
Loss of function
Shortening of the extremity (often seen in long bones or the hip)
Local swelling and discoloration (expect the swelling to be present for a while, want to try to minimize)
Diagnosis by symptoms, clinical exam, and x-ray (most often), or CT scan (more complex or questioning health of the bone), MRI (looking at surrounding tissues to gauge blood supply)
emergency management
ABC's
-patient's may have other life-threatening problems, especially with major trauma
immobilize the area of injury
-joints distal and proximal to the suspected fracture site must be supported
-don't want to make the situation worse
emergency management of open fractures
often happens pre-hospital
cover with a sterile dressing (if possible) to prevent contamination and minimize the dirt and pathogens that could get into the body
control bleeding if necessary
assess neurovascular status (ongoing intervention, does it seem like the blood supply or nerve supply was injured by the fracture)
remove potential constrictions (clothing is cut away)
secondary survey (what else is going on with the patient; ex: landed so hard they broke their femur but also ruptured their spleen)
shock
acute complication of fractures
r/o other injuries, hemorrhage, damage to arteries from the fracture
-ex: rupture of femoral artery from fracture
immediate assessment: is the person at risk for going into _______ or having some other problem because of the fracture
neurovascular assessment
continual
assessing distal to the injury
-skin color
-skin temperature
-movement distal to the injury
-sensation
-pulses
-capillary refill
-compare extremities
CSM (color/circulation, sensation, movement)
5 P's: pain, pulse, pallor, paresthesia, paralysis
expect edema (some long term)
-shouldn't be increasing in amount
patient assessment/plan
Patient history:
-other problems or conditions that will affect healing?
-other problems or conditions that need to be addressed?
-is the patient's report consistent with the injury? ex: frail elder in wheelchair that did not sustain a fall, does it make sense that they would have a spiral fracture of the arm?
Pain control is crucial
Treatment plan depends on injury and patient condition
-age is a big factor: children and young adults should recover at a slightly faster rate than older adults will
Medical management of fractures
Reduction
-closed
-open
Immobilization
-internal
-external fixation
-May require a surgical procedure to get the bone back in place and they have fixation (various devices, often screws or shafts that are put in place to maintain the bone in alignment so it can heal)
-some fixation devices are temporary, some permanent
Open/compound fractures require treatment to prevent infection
-bone is pierced through the skin
-Tetanus prophylaxis (check status)
-Antibiotics (prophylaxis due to high infection risk)
-Clean of the wound depending on damage
-Closure of the primary wound may be delayed to permit edema, wound drainage, and debridement prn
infection
-high risk with open/compound fractures (osteomyelitis)
-fixation devices (external, screws and rods going through the skin, usually protocol in place where they may be cleaned everyday an abx ointment applied, nursing responsibility to check for sx of infection)
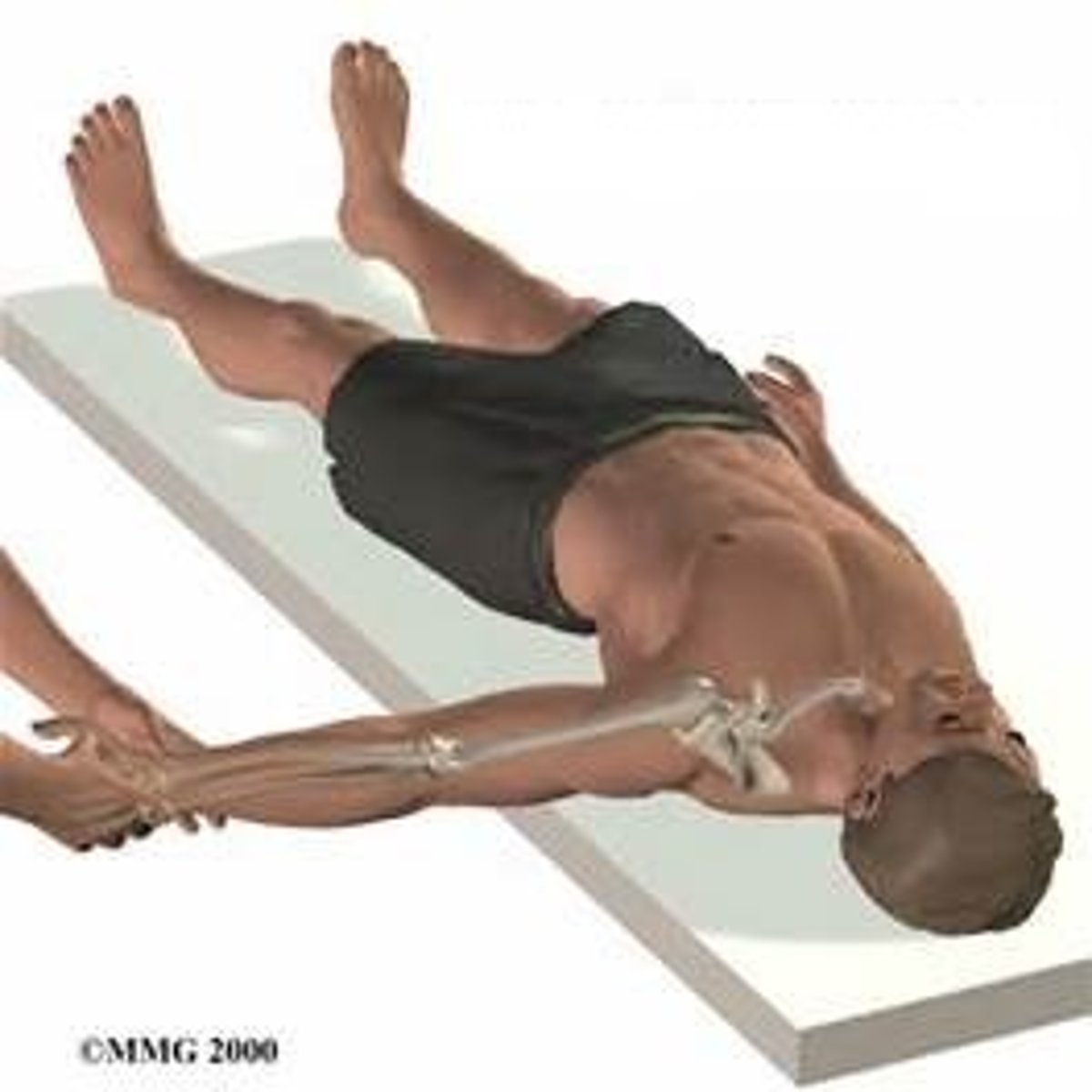
reduction
the term used to make sure the bones are in place/alignment/to get them back into place
closed reduction
done with the patient's limb numbed and orthopedist manipulates the bones to get them back into place

open reduction
requires surgical intervention through the skin to get the bone back into place
internal immobilization
placed in surgery and the skin is closed over
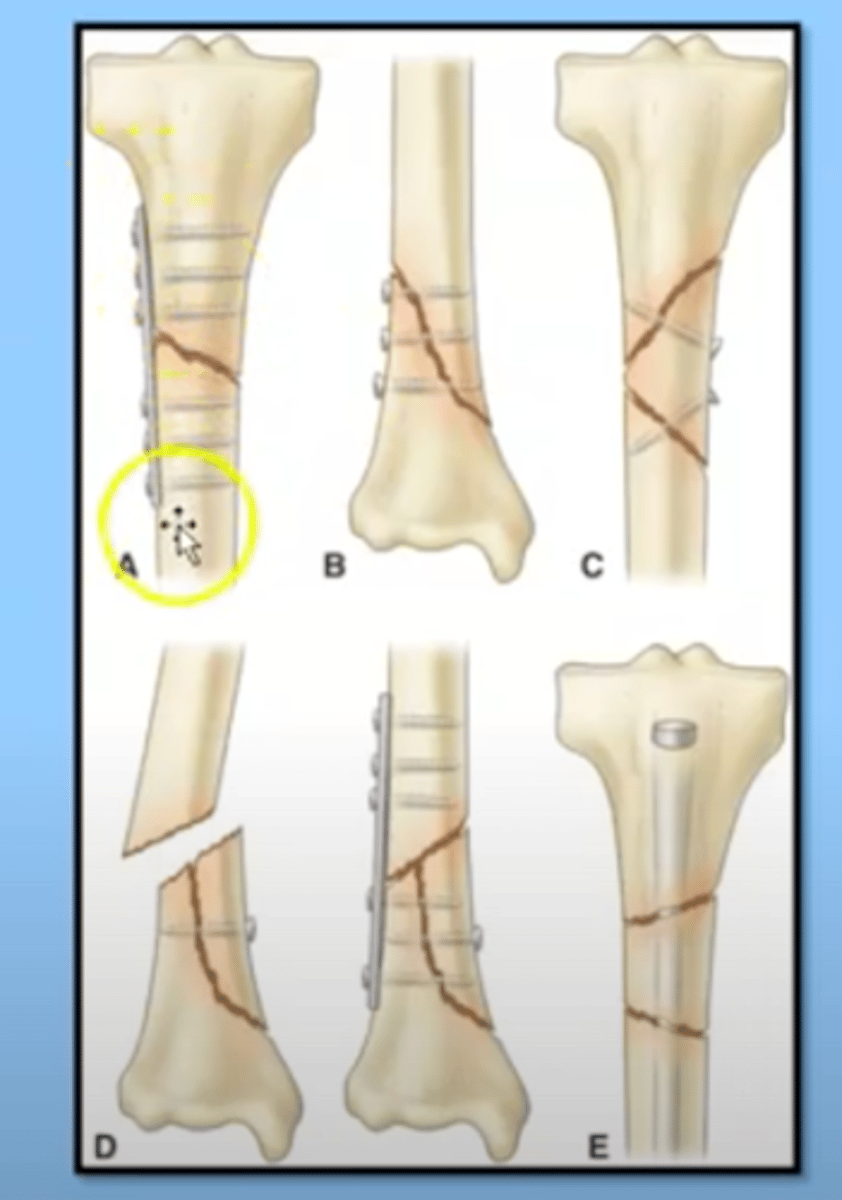
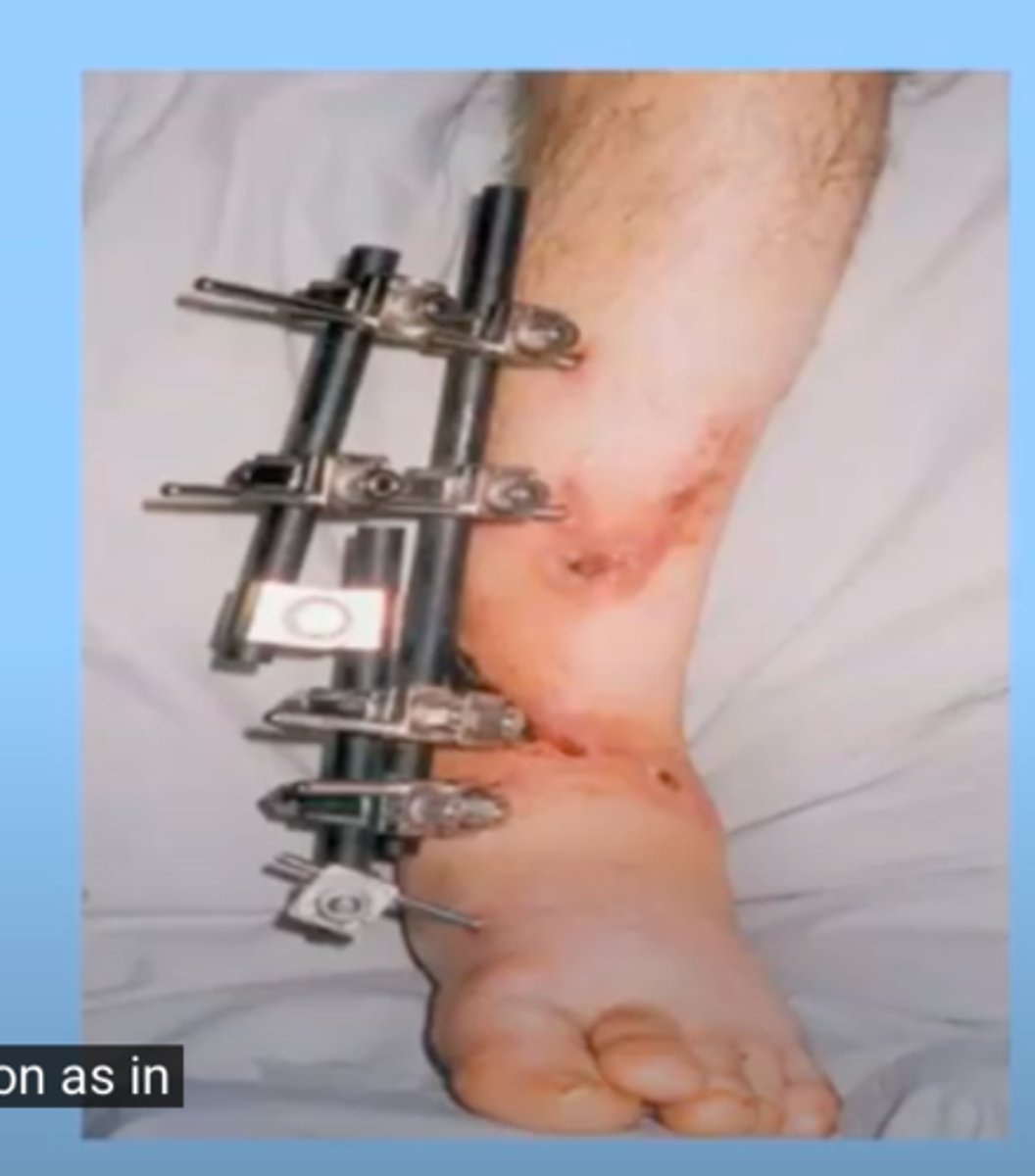
external immobilization
the usage of devices that go right through the skin to immobilize
Venous thromboembolism
complication of fractures
immobility increases risk
look for other risk factors - ex patient takes OC
early mobility is key to prevention
-if they cannot be mobile they may need anticoagulant for prophylaxis
pain
complication of fractures
Opioids often needed
NSAID, acetaminophen, either alone or in combination
-If taking combo agent ex Vicodin (acetaminophen and oxycodone), should be watching if they take any additional acetaminophen, do not want to overdose
Complementary therapies
-guided imagery, relaxation
Effective treatment may prevent development of chronic concern
elevating extremity, ice (even with cast)
Fat embolism
Globules of fat from bone marrow enter the blood stream
usually within 12-48 hours of injury
happens when there is a disruption usually to the long bones of the legs
Fat embolism syndrome
The globules clog vital organs, usually the lung
rare but life threatening
happens the most in young men up until age 40
first see hypoxemia, dyspnea, tachycardia, respiratory distress
red-brown petechial rash in non-dependent areas of the body late development
leads to pulmonary edema, respiratory failure, death
ICU treatment - no specific treatment other than supportive measures
compartment syndrome
increased pressure within sections of the extremities or abdomen, drastically reducing circulation to that area, causes edema which increases ischemia, tissue is at risk of necrosis. Anything that causes swelling can cause this.
Body parts are segmented into areas; muscle and blood supply are contained within fascia, so if there is a trauma/break and you have swelling into the tissue within these compartment, its a closed area and can cause necrosis
see: pain, paresthesia, pallor, pulses weaken, tightly swollen extremity; may/may not develop paralysis if nerve damage
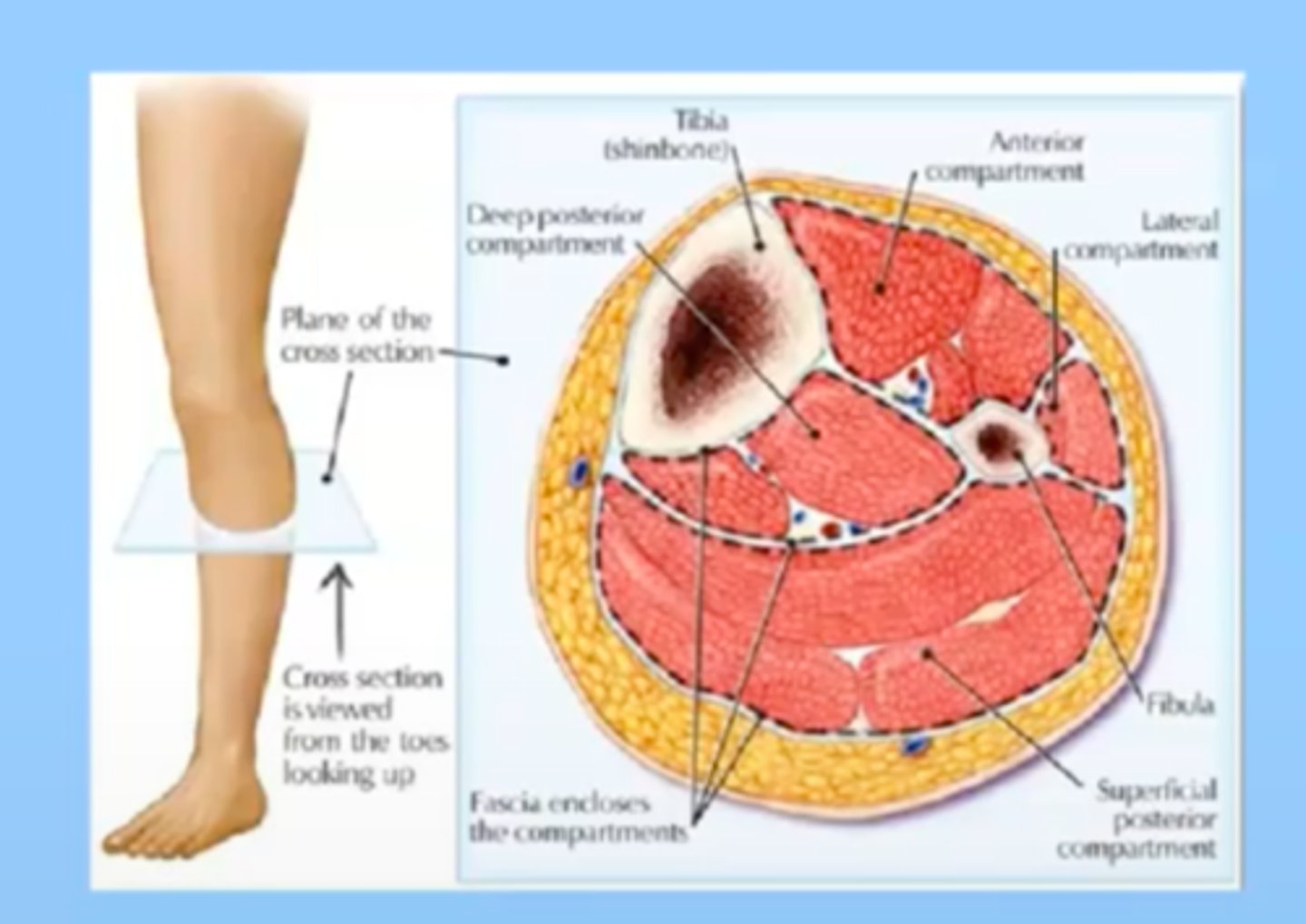
compartment syndrome surgical treatment
Fasciotomy
-cut through the fascia to relieve pressure
-meters can be placed to record the pressure within a compartment
long recovery, may need skin grafts
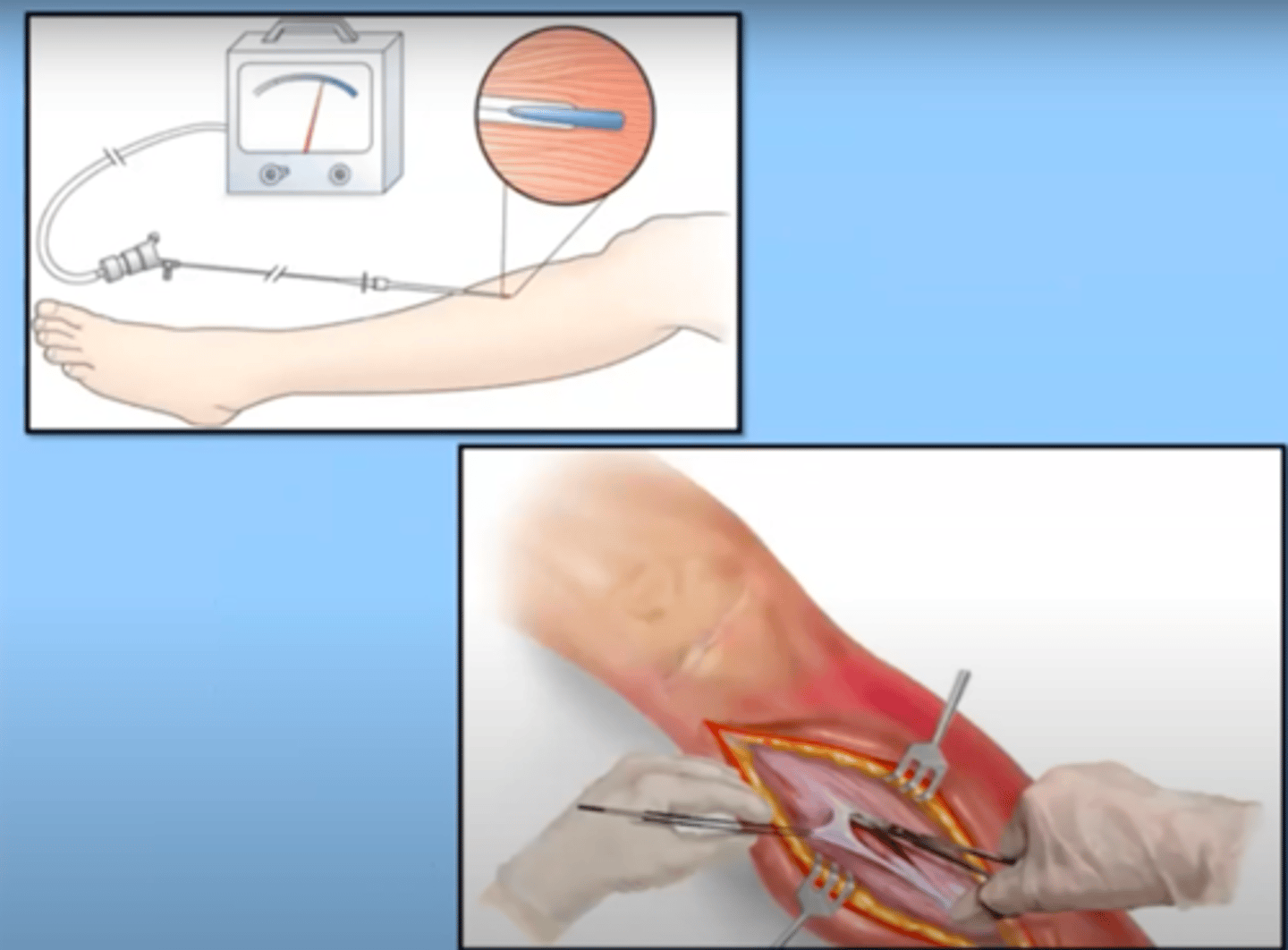
Crush injuries
Injury in which crushed/pinned against something
ex: a car accident
release of myoglobin from the muscle places the patient at high risk for developing rhabdomyolysis (destruction of muscle cells) and acute kidney injury
other complications include:
-hyperkalemia
-hypovolemia
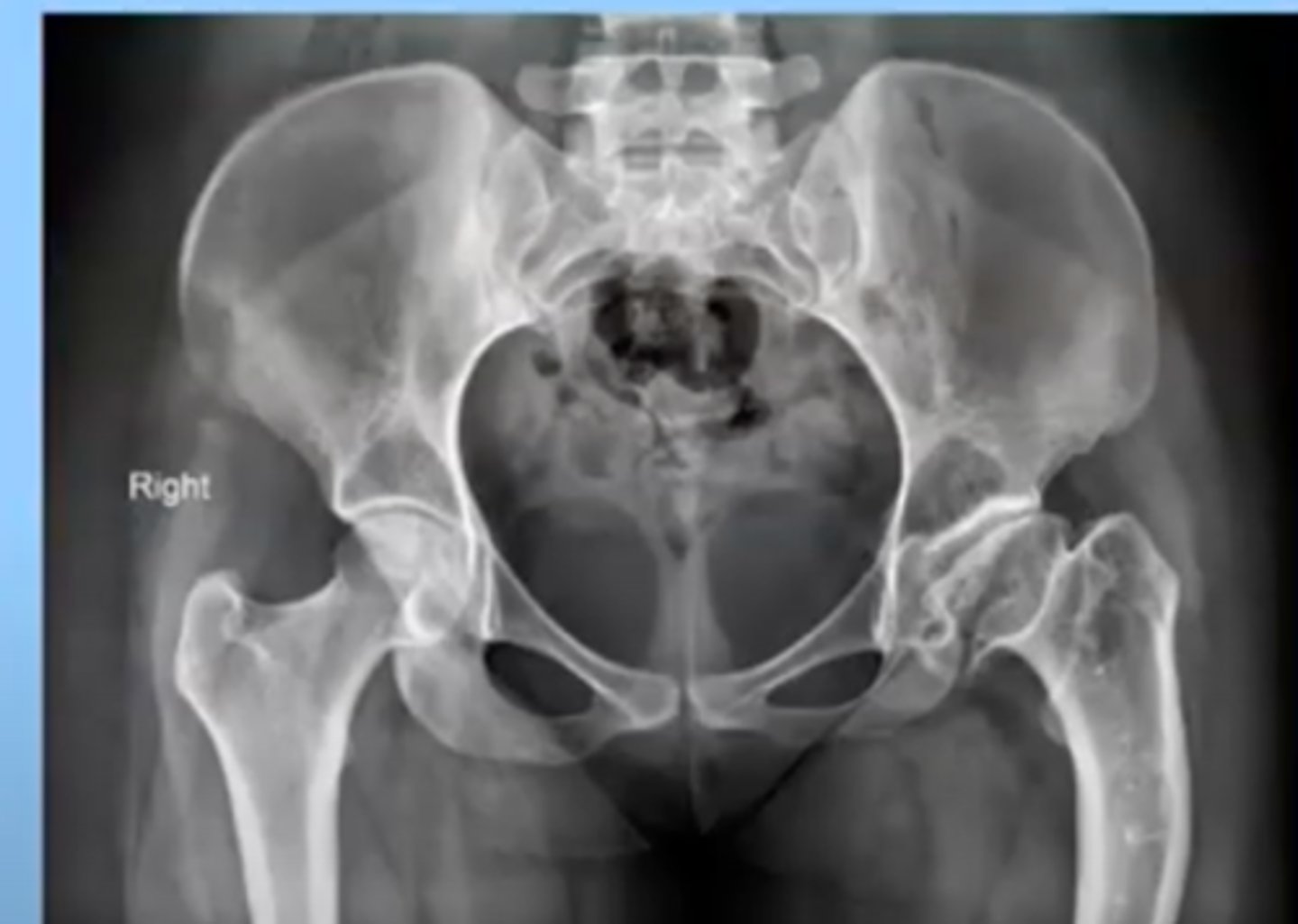
Avascular necrosis
Death of bone tissue because of a disruption in blood supply to the bone
femoral head of the hip is most common place
this can cause a fracture or be caused by a fracture or trauma to the bone (Acutely)
can also happen overtime
-ex: with a malignancy, chronic alcoholism, long term steroid use
-often have chronic pain in that area
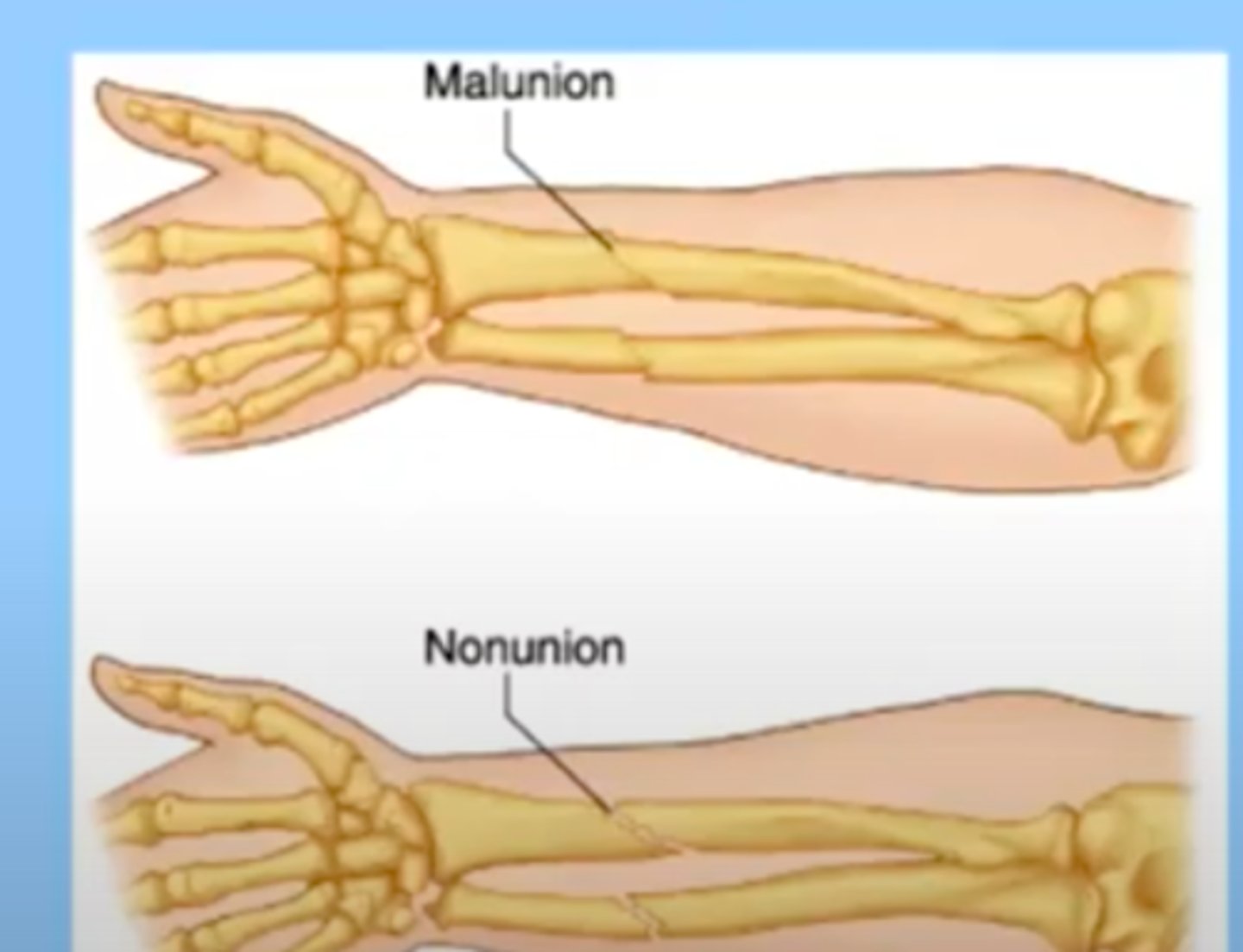
delayed bone healing
takes longer than expected for a bone to heal
can be causes by malunion or nonunion
malunion: the bones are healing, but they were not completely line up/don't stay lined up
-may or may not require surgical intervention
nonunion: the reduction has not been successful and the bone segments are not in contact with each other
complications of fractures
impaired physical mobility
peripheral neurovascular dysfunction
chronic pain
-complex regional pain syndrome
complex regional pain syndrome
usually occurs in an area of the body where there has been some injury and people have a heightened pain after that, some nerve involvement, not well understood
the area can have color changes, diaphoresis, etc.
not a lot of good treatment for it
nursing considerations
What medical-surgical treatment should the nurse expect to occur?
-based on injury
What complications could this fracture cause and teaching
How does this fracture affect mobility? (in healing process and long term)
How does this fracture affect patient safety? (are they safe to go home)
Frequent assessment of neurovascular status
Antibiotics as needed
DVT prophylaxis, especially in acute care setting
continued pain assessment and management
Goal is for patient to achieve optimal level of functioning
What other patient concerns and issues will affect healing?
-may need referral to SW, job concerns, childcare, etc.
what impact does this have on the patient's functioning and wellbeing? ex: older pts and independence/safety
Ensure appropriate discharge teaching
Discharge considerations
Continuing care
-orthopedic follow up
-often PT or OT (OT for below the shoulder, elbow and hand)
Is referral to home services needed?
Does the patient need acute rehab?
Social work needs?
VNA/PT safety assessment