1.2.3 Market equilibrium
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
market equilibrium
when there is a balance between supply and demand in a market
market demand
the total quantity demanded for a product in a market by all customers
market supply
the total quantity of a product supplied to a market by suppliers
what happens to equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity if demand increases
equilibrium price = higher
equilibrium quantity = higher
what happens to equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity if demand decreases
equilibrium price = lower
equilibrium quantity = lower
what happens to equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity if supply increases
equilibrium price = lower
equilibrium quantity = higher
what happens to equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity if supply decreases
equilibrium price = higher
equilibrium quantity = lower
what is equilibrium price
when the amount demanded matched the amount supplied
when the quantity that buyers demand is the same as the quantity sellers wish to supply - sometimes referred to as market clearing price
the equilibrium price (P*) and equilibrium quantity (Q*) is where the 2 curves meet
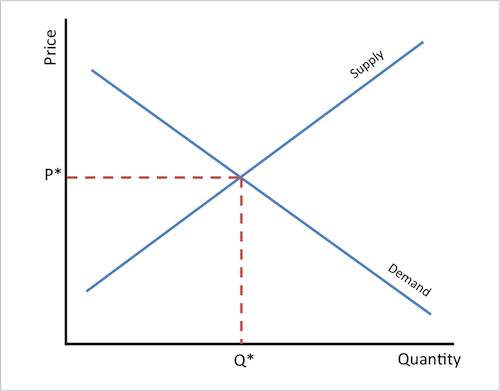
how does a surplus occur
when the price increases
in the price of a product increases this would cause movement to the right along the supply curve, and movement to the left along the demand curve
this would mean that quantity demanded (Qd) would be less than the quantity supplied (Qs) and so there would be excess supply - a surplus in the market

how does a shortage occur
when the price decreases
if the price of a product was decreases, this would result in movement to the left along its supply curve and movement to the right along the demand curve
this would mean that there would be more demand than supply, and so there would be excess demand an therefore a shortage in the market

what happens to the supply and demand curve if there is a rise in demand
shifts the demand curve to the right
the demand shift to the right form D1 to D2
but at a price of P1, there is a shortage in the market. the price needs to rise to clear the marker of excess demand
a new equilibrium quantity (Q2) is reached at a higher price than before - P2

what happens to the supply and demand curve if there is a fall in demand
shifts to demand curve to the left
a fall in customer demand shifts the demand curve to the left from D1 to D2
but at a price of P1 theres. asurplus in the market so the price needs to fall to clear the market of excess supply
a new equilibrium (Q2) is reached at a lower price than before (P2)

what happens to the supply and demand curve if there is a rise in supply
shifts the supply curve to the right
an increase in supply shifts the supply curve to the right from S1 to S2
at a price of P1, there’s a surplus in the market, so the price needs to fall to clear the market of excess supply
a new equilibrium quantity (Q2) is reached at a lower price than before (P2)

what happens to the supply and demand curve if there is a fall in supply
shifts the supply curve to the left
a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left from S1 to S2
at a price of P1 there is a shortage in the ,market so the price needs to rise to clear the excess demand
a new equilibrium quantity (Q2) is reached at a higher price than before (P2)
