OPT 714 Peds Visual Perception Final
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
True or false: binocular vision is critical for learning to read
false, binocular vision is not as critical unless small font and/or extensive near work
True or false: form perception is NOT a major factor in reading to learn
True
According to the AOA, what is the ultimate goal of optometry in helping learning related vision problems?
"reduce the risk of vision problems interfering with the learning process"
In what order should these issues be addressed in?
Oculomotor/ BV disorders
Rx / lens correction
visual perception issues
Rx/lens -> BV -> visual perception
Visual form discrimination
ability to discriminate among different shapes and remember what shapes mean

Visual form constancy
The ability to identify a form even though it may be sized differently, rotated, reversed and/or hidden among other forms as compared to the original stimulus

Figure-Ground
identifying a specific detail from surrounding information
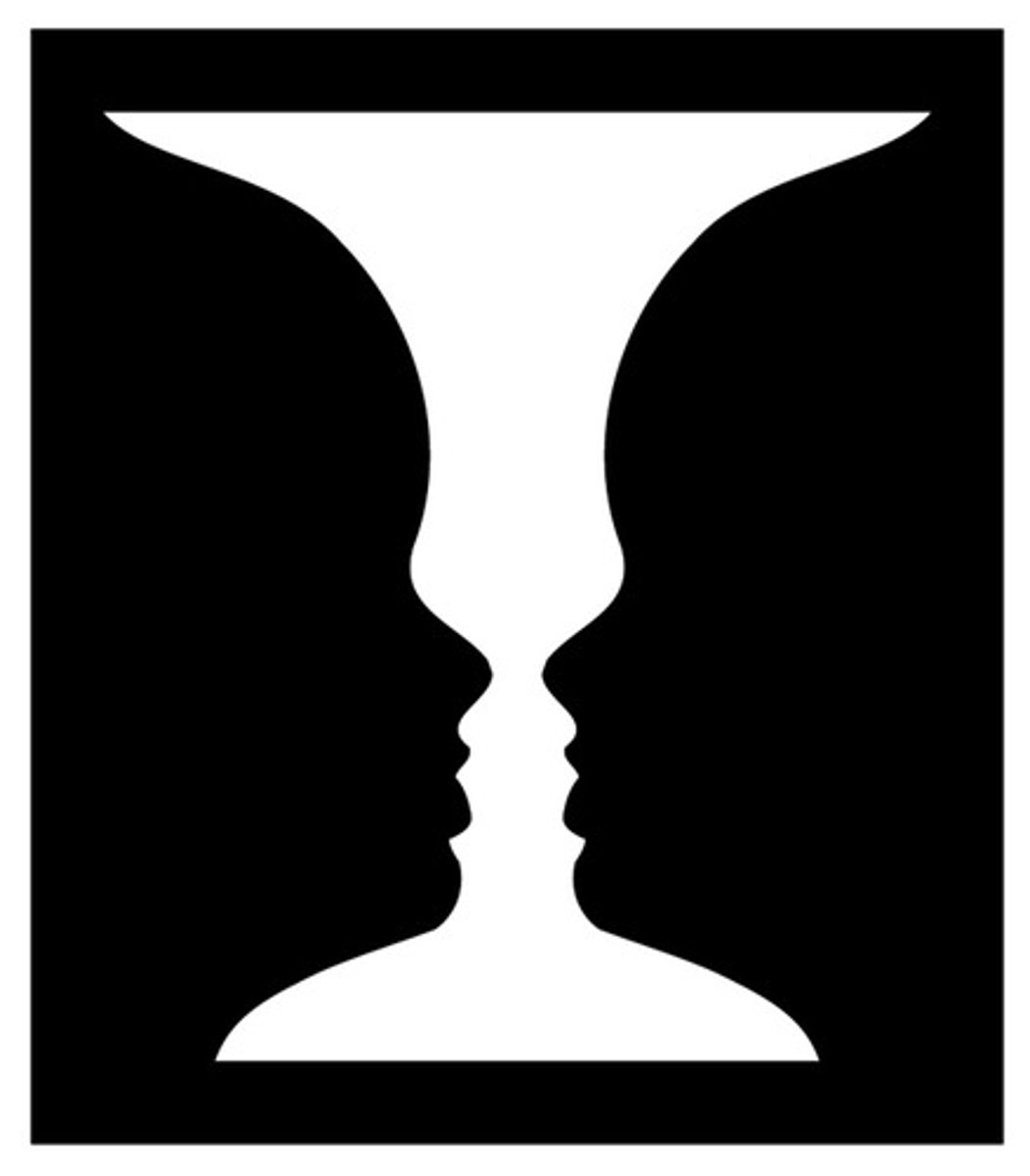
Visual Closure
ability to fill in an incomplete piece of info or come to a conclusion with limited visual info

Visual Memory
ability to remember what has been seen (aka when you do a tachistoscope or try to memorize the password for the Amazon locker lol)
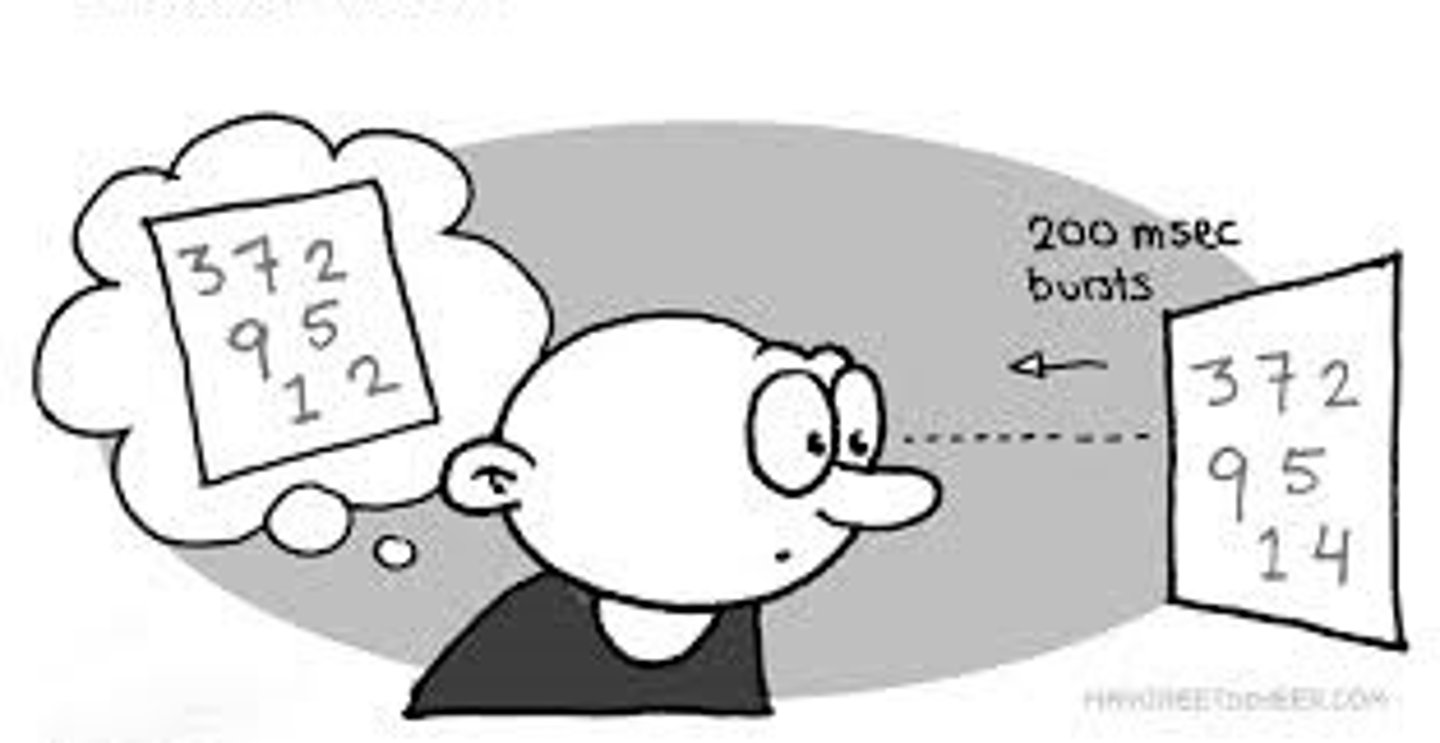
Visual sequential memory
ability to remember sequences (like a phone number or pattern of symbols)
Visualization
"mind's eye" or acting something out in your head even if you've never seen it before
****Most impact on reading visual analysis skills happens in what grades?
1-3
Form perception
ability of the individual to analyze specific features of forms and determine differences between forms
Feature Analysis
part of form perception where you take an internal representation of similarities and differences until a match is made
ie trying to recognize your car in the parking lot, you're looking at the make, model, year, color, size, etc

Discrimination
comparing multiple items simultaneously to figure out which ones match or not
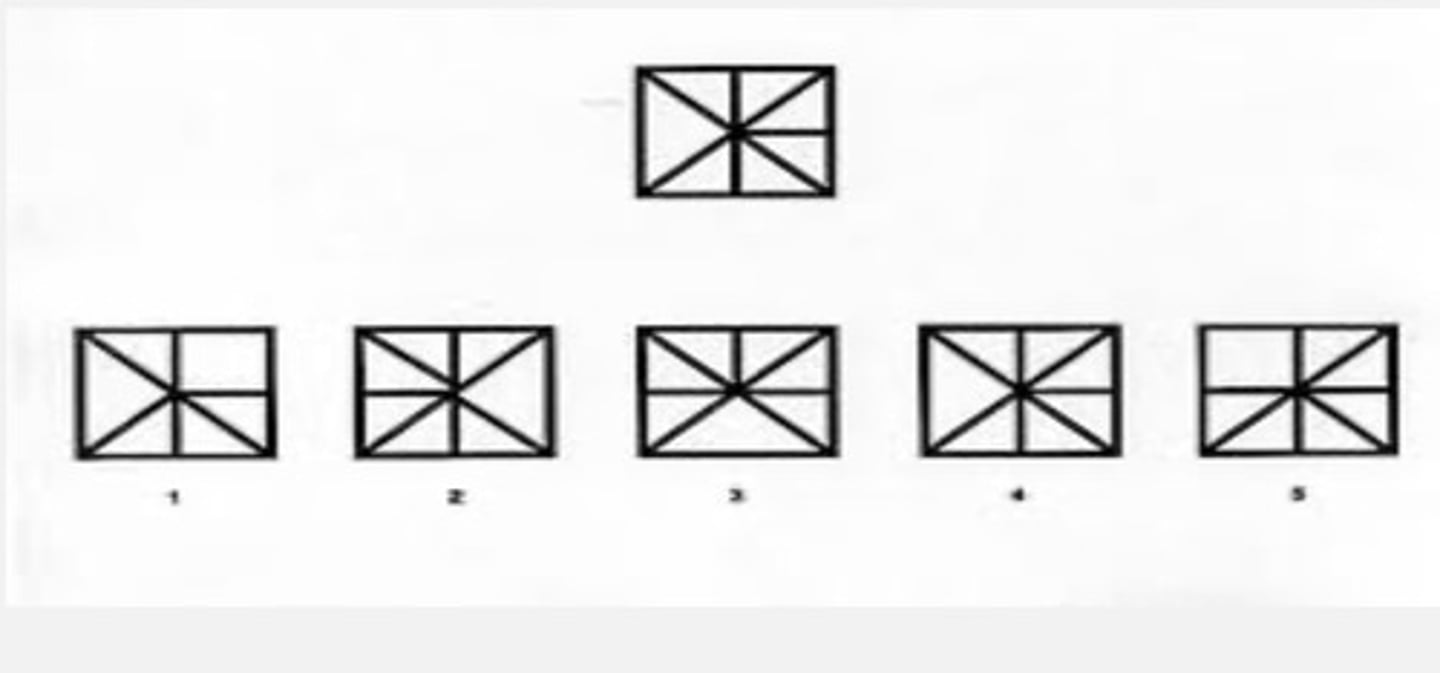
Recognition
harder than discrimination; you have to recognize the form and compare to internal representations in your memory
ie recognizing someone and having to remember you met them at a party

Identification
harder than discrimination, more detailed processing of recognition that leads to an appropriate label
ie you recognize someone, know they were from the party, and identify them as being Susie
Recognition of form is present by what age
6 mo
Size and shape constancy is present by what age
6-8 mo
Basic form perception is intact by
7-8 mo
Vuripollot experiment
-children younger than 5 years old have incomplete and unsystematic search patterns
-children younger than 6 yo tend to scan the same number of windows regardless of the number of differences
-children older than 6 use a complete and systematic search pattern influenced by number of differences between the houses
3 types of memory
Sensory information store: (<1s to a few sec, lasts the same duration as the stimulus)
Short term (working memory); requires ACTIVE attention
Long term
Scaled Score (ss)
used when there are subtests, derived from z score (mean = 10, standard dev = 3)
Standard Score (SS)
a transformation of the raw score whose score distribution in a specified population has known values for the mean and standard deviation
(mean = 100, SD = 15)
Children under the age of ____ yo tend to not use as many active memory strategies such as cues or chunking
7
Basal Rule
establishes a STARTING POINT based on the patient's age or performance from previous tests
ie if the child is older than 10, start on question 5 and assume 1-4 are correct
Ceiling Rule
how many items child needs to answer incorrectly in order to end the test; do not count points that occur after reaching the ceiling rule
MVPT
Motor Free Visual Perception Test (screening non motor test)
TVPS
Test of Visual Perception Skills (Diagnostic non-motor test)
MVPT-4 Test
4 years to 80 + years allowed
-NO TIME LIMIT!
-20-30 min test, 10 min scoring
-8 demo plates (not scored) and 45 test plates

****The MVPT test is a screener for motor free visual perception and assesses what 5 perception categories?
Visual discrimination
-look at image, pick the one that looks like it exactly
Figure Ground
-"how many circles do you see (can be different sizes) in this mess of images?"
Visual Memory
-short term memory, show them a symbol for 5 seconds, then ask them to pick it from the next page
Visual Spatial Relationships
-spatial orientation: which one can't be turned to face the same direction as the rest?
-form constancy: look at symbol, find it in the image even if it changes size or orientation
Visual closure
-finish the drawing in your head by connecting the gaps
***MVPT-4 ceiling rule and basal rule
None, they must take the entire test!!!!
***What scores are concerning for MVPT-4?
1 SD below standard score or percentile
Standard score <85
Percentile <16th%
****Limitations of the MFVP-4
1) yields only a single raw score
2) it is a screener because it creates an overall view of a person's VP skills
3) DOES NOT PINPOINT SPECIFIC TYPES OF VP DIFFICULTIES
TVPS vs. MFVP-4
Both of them do not have a time limit. Similar ~30 min test time on avg. MFVP-4 is a screener, while the TVPS is diagnostic! MFVP can be scored from 4-80+ yo, but TVPS only has norms for 4-21.11 yo
True or false: the TVPS has SUBTESTS SCORED SEPARATELY WITH ITS OWN NORMS vs the MFVP which lumps everything into one score
True!
What are the 7 parts of the TVPS?
Visual discrimination
Visual Memory
Visual spatial relationships
Visual form constancy
Visual sequential memory
Visual figure ground
Visual closure
Which TWO parts of the TVPS are different from the 5 available in the MFVP screener?
Form constancy and sequential memory
-Form constancy = recognize object despite change in size / location
-Sequential memory = recall visual sequence such as phone numbers or spelling
Basal Rule for TVPS
Ages 5-11: start at item 1
Ages 12-21: start at item 4 (assume 1-3 correct for scoring) unless they have a known VP or memory issue
-if 12+ pts do not correctly answer first 3 plates, administer the plates BACKWARDS until they get 3 in a row correctly, then return to last item tested and continue forward without re-administering any plates
Ceiling rule for TVPS
Discontinue when 5 out of 7 incorrect
********concerning scores for TVPS
SS: <85
Percentile: < 16th%
Scaled score: <7
How to convert TVPS percentile into a descriptor
0-16 needs improvement
17-31 below avg
32-68 avg
69-99 above avg
Developmental Test of Visual Perception (DTVP)
- Not a TRUE non-motor test (some sections require patient to use hands to draw or trace)
- Can measure their abilities for visual-motor
-has both timed and untimed components
_____ year old children rely on tactile / kinesthetic senses / motor senses to interpret the world, but by age _____ a child should be using vision and hearing as their dominant sensory systems without much reinforcement by tactile info
1-2, 6
****What are the 2 primary visual perception pathways in the brain?
VISUAL SPACIAL (where)
Dorsal stream to parietal lobe
VISUAL IDENTIFICATION (what)
ventral stream to inf. temporal lobe
DPSM
dorsal -> parietal lobe, spatial (where), magnocelluluar
The rest is ventral -> temporal lobe, ID (what), parvocellular
Dorsal stream primary purpose
Direct action
Dorsal stream is dependent on what 4 visual motor systems?
1) magnocellular processing of peripheral vision (attention)
2) fixation / saccade / pursuit
3) vergence
4) stereo
A child learns the concepts of up/down/over/under/position during ages _________ by working to overcome gravity
1-3
By _______ yo, kids can correctly IDENTIFY up/down/front/back on THEMSELVES and OBJECTS
3-4
Laterality vs. Directionality
Laterality = knowing right from left based on concept of symmetry
Directionality = APPLICATION of laterality to understand relationship between body and environment for navigation
Understanding laterality of own body comes by age _____
4-6
What part of the brain develops at age 4-5 that helps with understanding laterality?
Corpus callosum (RL hemispheres communicate better)
When does hand dominance emerge?
around 4-5 yo
By age ____, correctly can ID right and left on SELF. By age ____, can correctly ID R and L with external objects
6-7, 7-12
****Occasional reversal errors are normal in ________ grade but should NOT PERSIST into _______ grade
K-1st, 2nd
Which is more common: letter/number reversals around the y or x axis?
Y axis
-ie b and d, p and q
X axis reversals less common, such as 2 vs 5 and 6 vs 9
Reversals are more common in dyslexic children. What may this be due to?
-Lag in laterality awareness
-manifestation of poor visual memory specific to language symbols or bottleneck in translation of symbol to sound
****What test do we use to evaluate laterality and directionality?
Piaget Right-Left Awareness test
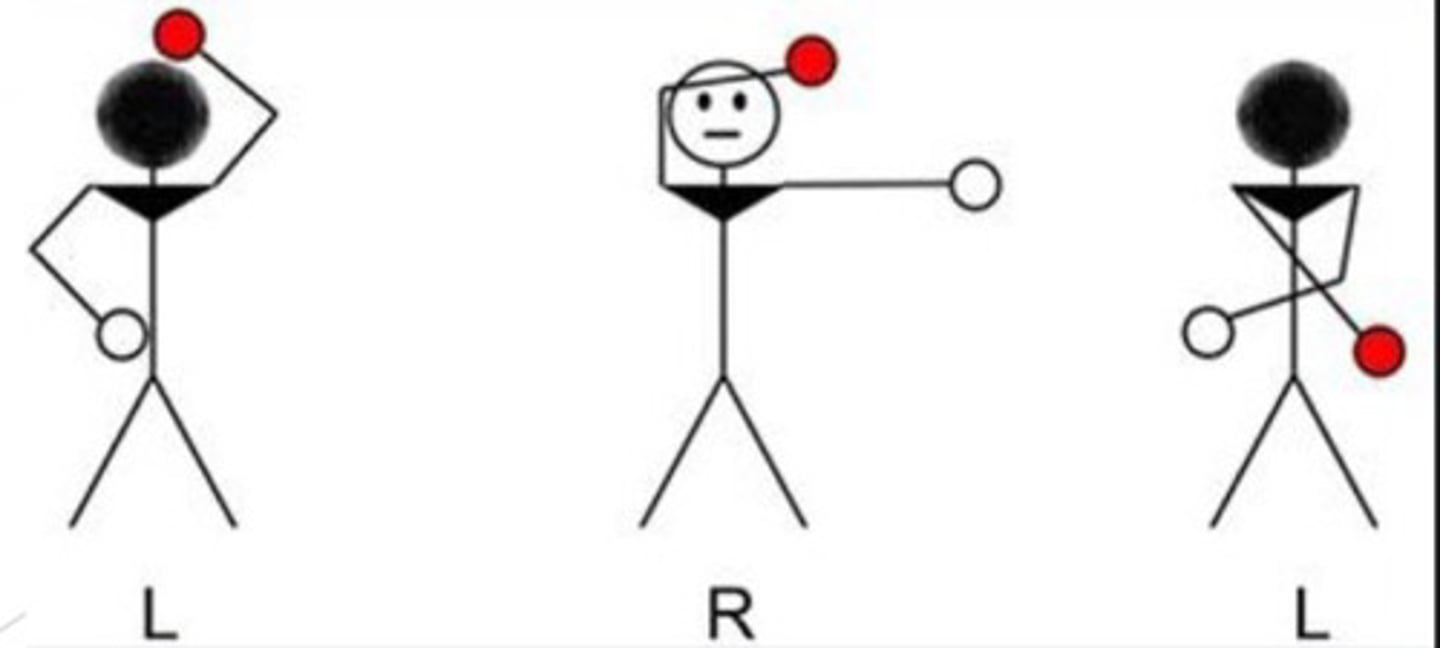
What do you need to test for Piaget-RL awareness?
Pencil, key, coin, bracelet
***To get full credit for a section in Piaget's test, the child must get
all questions correct in that section
True or false: Part C of Piaget's test is actually easier than Part B
True
How is Piaget's Laterality test scored?
You only give them credit for sections they can complete with 100% accuracy then compare to the age norms.
ie a 5 year old is expected to get 100% on section A, but a 7 yo is expected to get 100% on A and C minimum!
Gardner Reversals Frequency Test
paper pencil test with execution, recognition, and matching subtests for reversals

Execution subtest of Gardner Reversals
Verbally instruct child to write out scripted numbers and small letters. Count total reversals and unknown errors.
Execution subtest of Gardner reversals: cannot be graded if the sum of reversal and unknown errors is greater than
16
Recognition subtest of Gardner Reversals
can the child cross out letters or numbers that have been typed out in a reversed manner
Matching subtest of Gardner Reversals
Child must look at symbol on the left and then circle the correct symbol that exactly matches the symbol on the right
If the Piaget test comes back abnormal, you can assume the child has
delayed laterality development
If the Piaget test comes back normal, you can assume the child has
language processing issues such as dyslexia (but also check for eye movement, non-motor VIP, and VMI skills)
Visual motor integration (VMI)
ability to integrate visual info processing skills with fine motor movement (aka hand eye coordination!)
Remember: when do these skills develop by?
-reaching for targets
-pincer grip
-4-6 months
-7-8 months
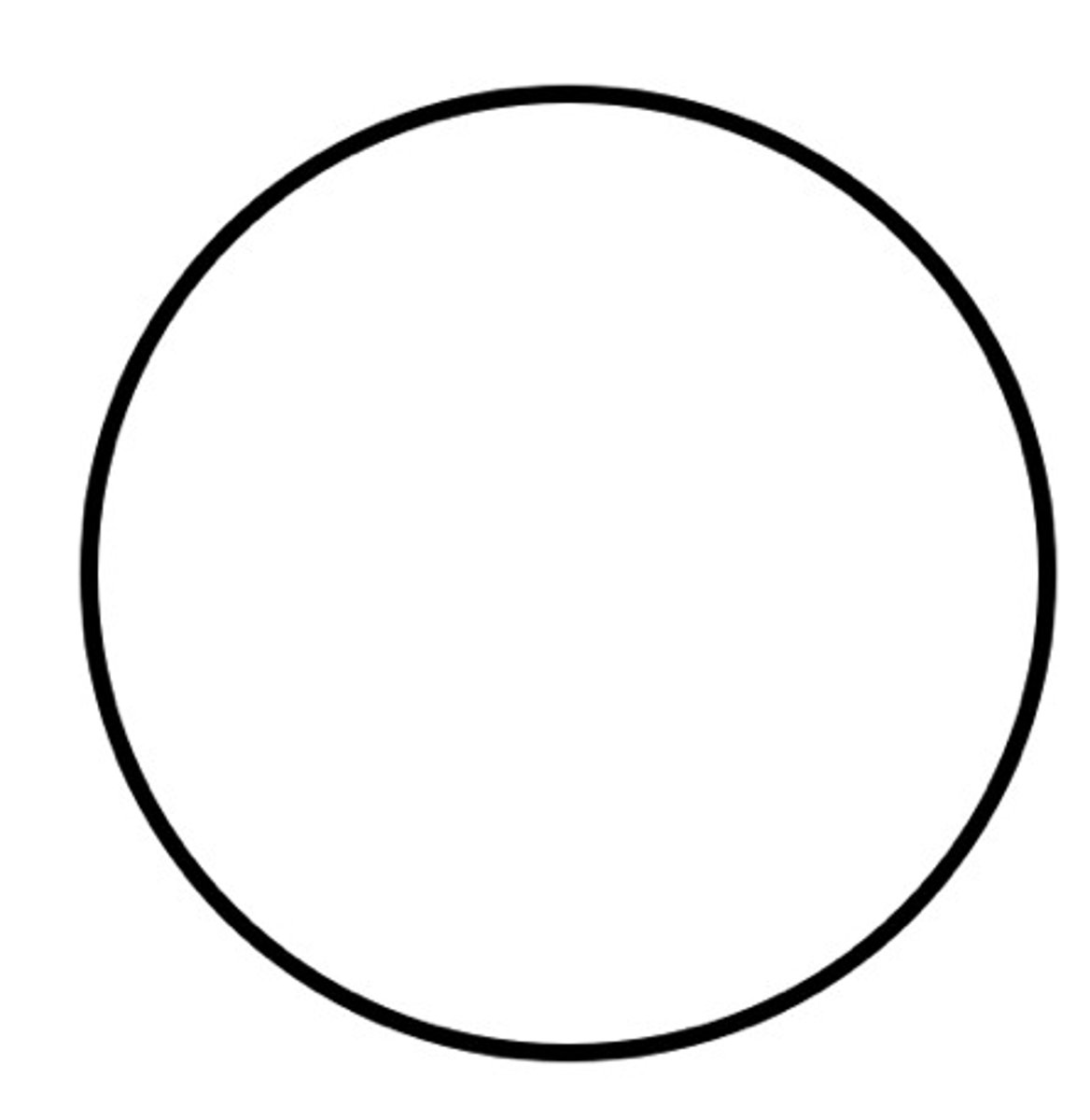
********When would you expect a child to be able to draw a CIRCLE
3 years
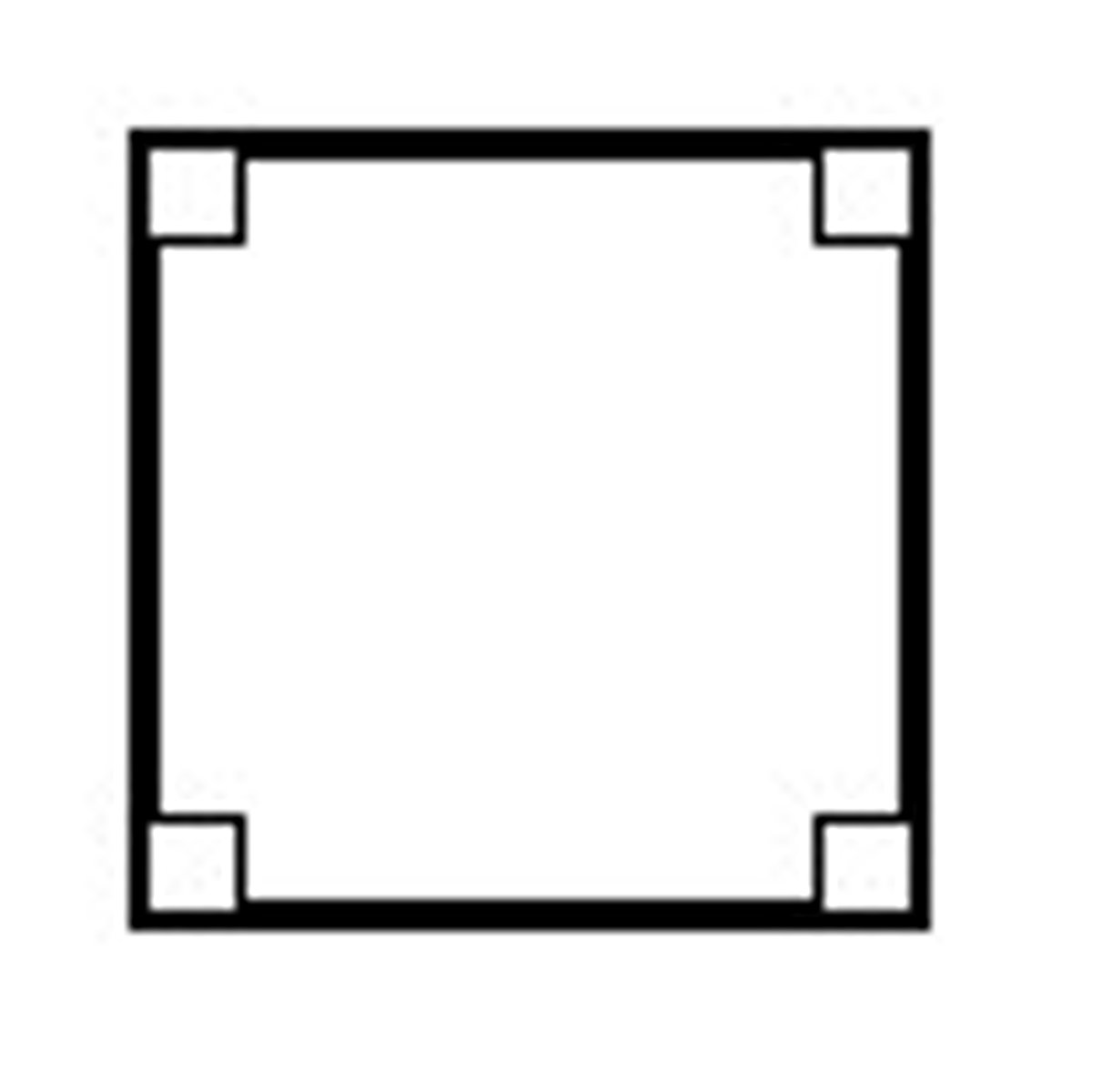
********When would you expect a child to be able to draw a SQUARE
4 years (4 corners 4 years!!!!)
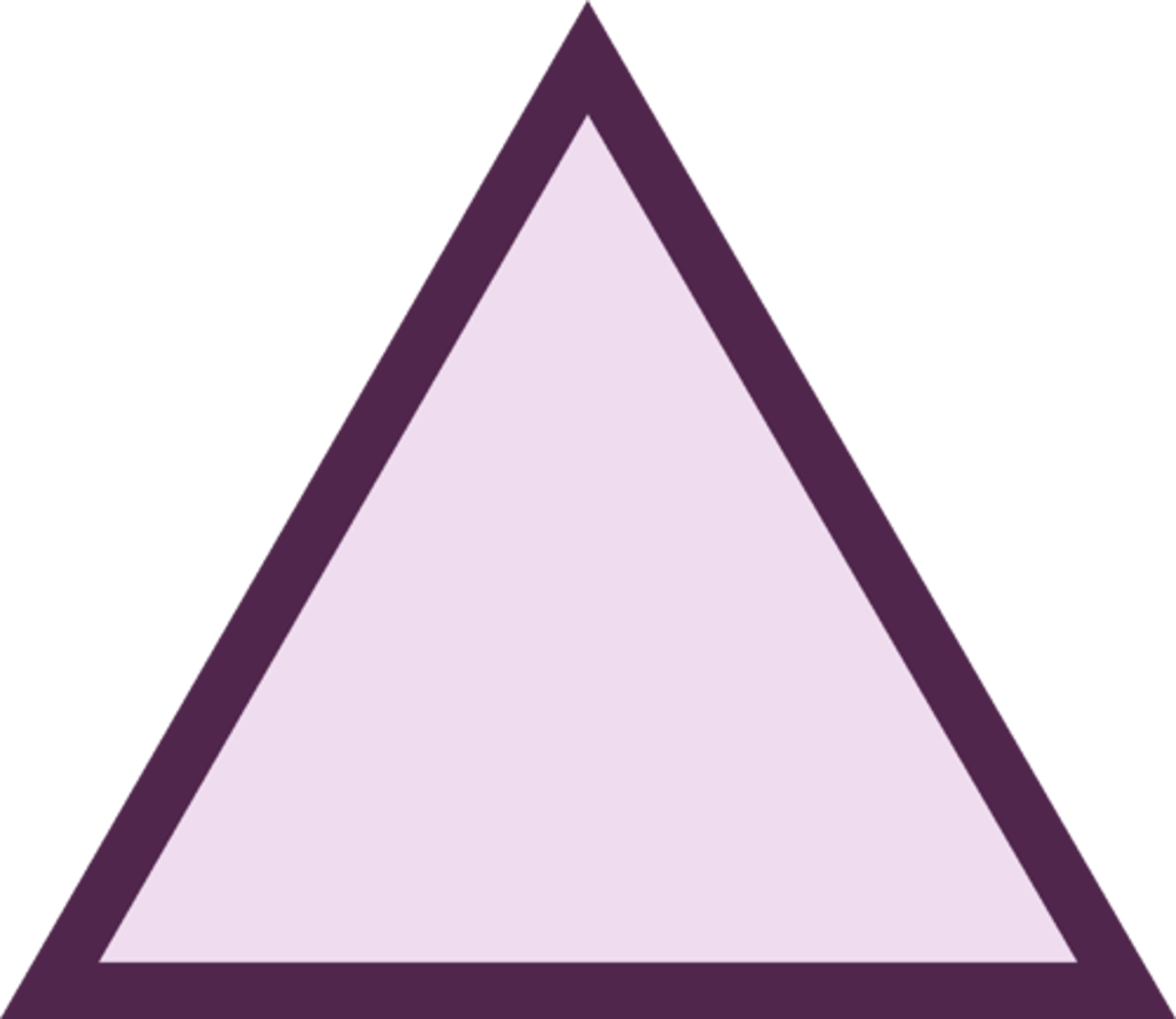
********When would you expect a child to be able to draw a TRIANGLE
5 years
********When would you expect a child to be able to draw a DIAMOND
8 years

Children with poor VMI also tend to have poor ___________
non motor visual perception skills
True or false: VMI is correlated with IQ, arithmetic, and early reading
true
True or false: deficient VMI is commonly seen in children with special education learning disabilities
true
****What test is specifically for VMI?
Beery VMI
Beery VMI
Beery Developmental Test of Visual-Motor Integration; consists of geometric shapes that the person reproduces; measures visual perception and handeye coord
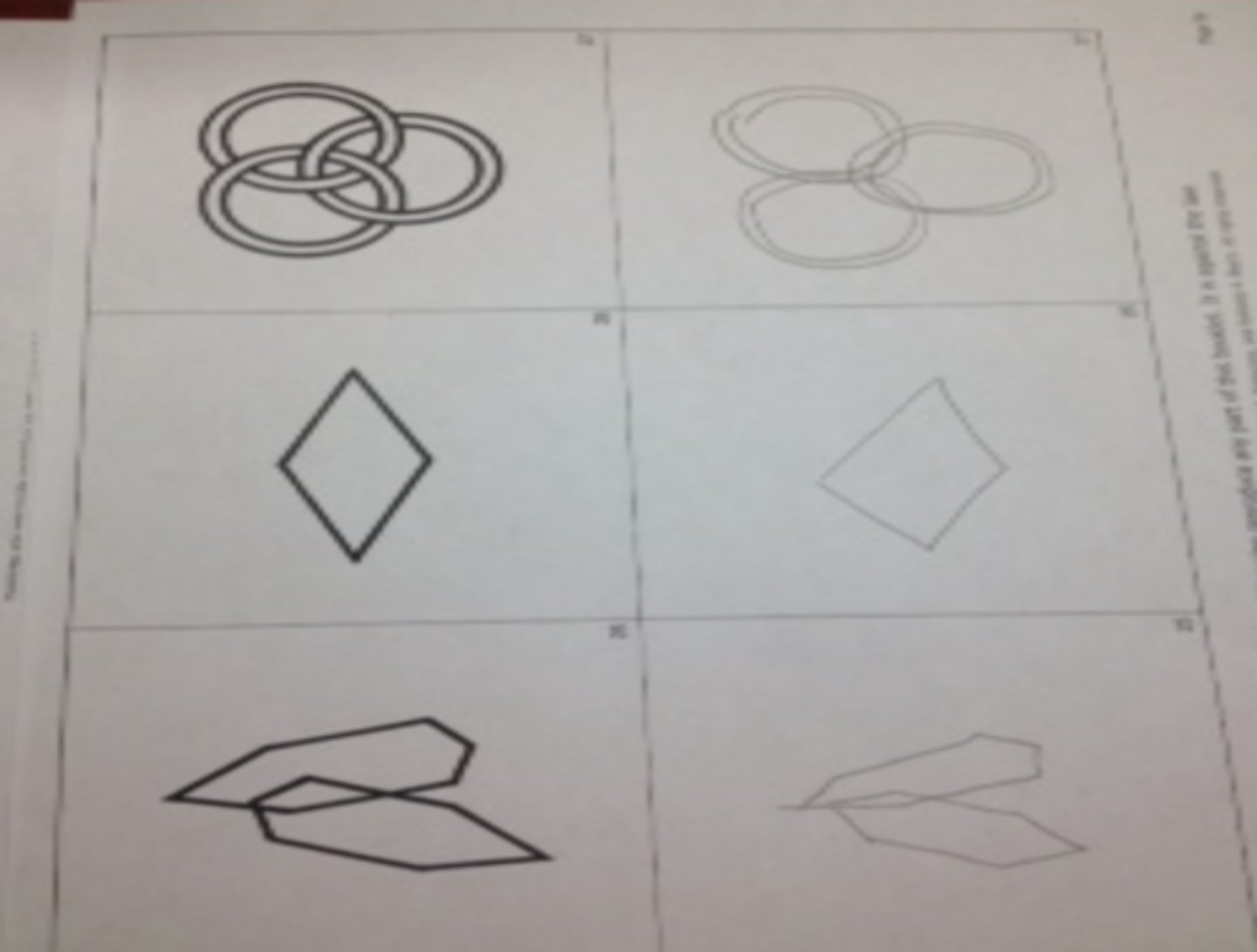
How to score the (evil) Beery shapes
if ALL the crazy criteria are met, 1 point total. No partial credit.
Why is the max points on Beery VMI 30 if only 24 shapes exist?
children 5 and under can earn 3 pts for "imitating" the first 3 forms, and another 3 pts for simply drawing within the box borders for the first 3 forms. If the pt is 6 years or older, they get the 6 points for free, since it is assumed they are capable of imitation.
*** 6 POINTS FOR 6 YEARS AND OLDER!
Beery VMI ceiling
3 consecutive failures in a row (only points below ceiling count!)
Raw score = sum pts below ceiling + 6 bonus if older than 6 yo
Motor Coordination Subtest of Beery VMI
TIMED starting at item #7
-5 minutes
-1 pt for drawing inside the lines of the dot shapes, lines can touch edges but not cross over, item 27 and 30 require overlap
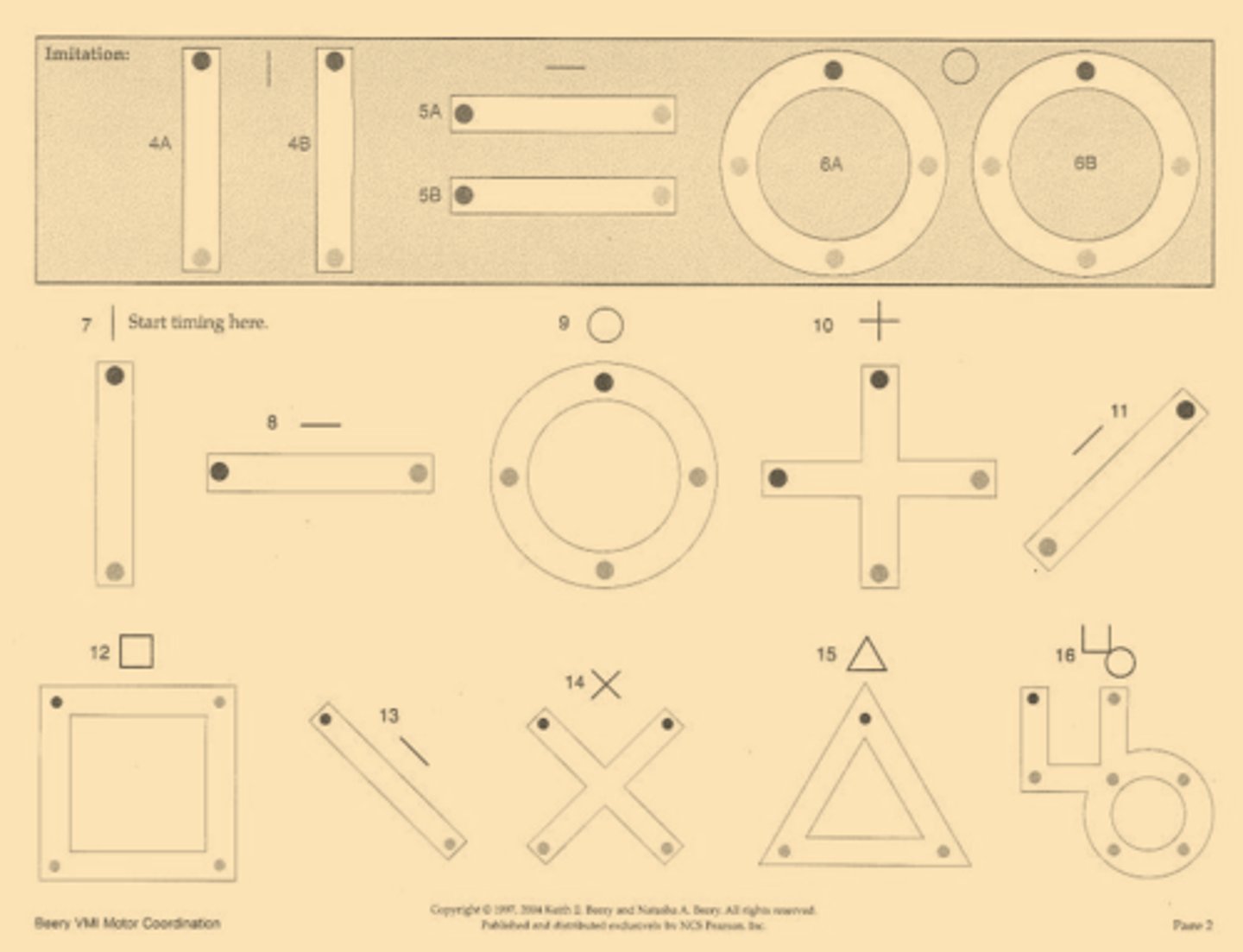
****Poor Beery VMI scores can be due to:
-poor non motor form perception
-poor fine motor coordination
-poor integration of above visual and motor skills
-any combo of the ones above!
****Why is there a motor coordination subtest of the Beery VMI?
to help determine if poor fine motor control is the cause or not
****If the overall Beery VMI score is ________, ALWAYS run the Motor Coordination Subtest to determine how much the score is influenced by ___________
low, fine motor skills
For the motor coordination subtest, is the ceiling the same as the regular Beery VMI?
No, the Beery VMI has a 3 miss ceiling, but since the motor subtest is timed, there is no 3 consecutive fails ceiling! The time is the ceiling.
True or false: we use the Beery's non motor perception to determine if the patient is having poor non motor form perception issues
False, we actually use the TVPS or MVPT to cover non motor testing since they are more comprehensive than the Beery non motor subtest
Simian grip
closed fist grip with thumb wrapping around index finger, control from gross movement at the ELBOW or above!!!!!!
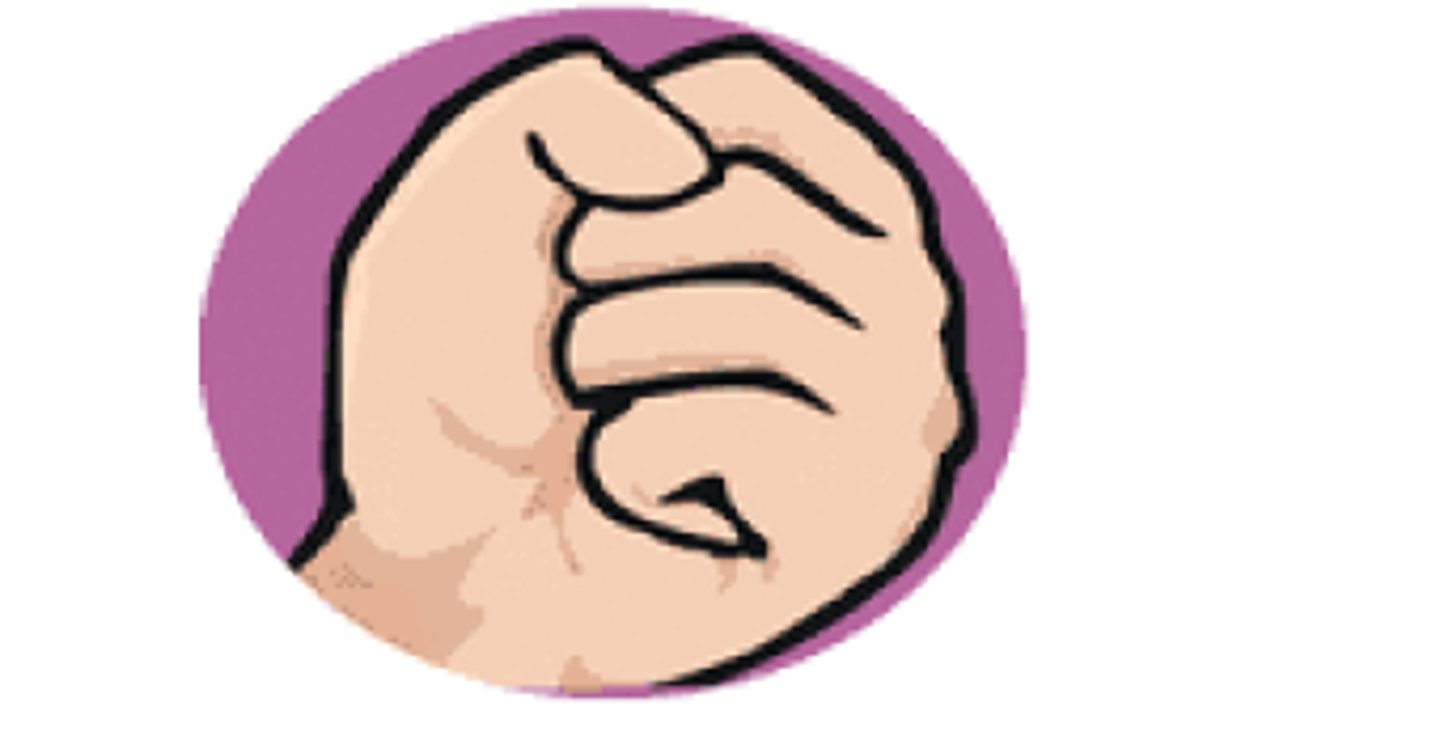

When is the simian grip common?
preschool
Intermediate grip
3 fingered (thumb index and 3rd finger), control from the FOREARM
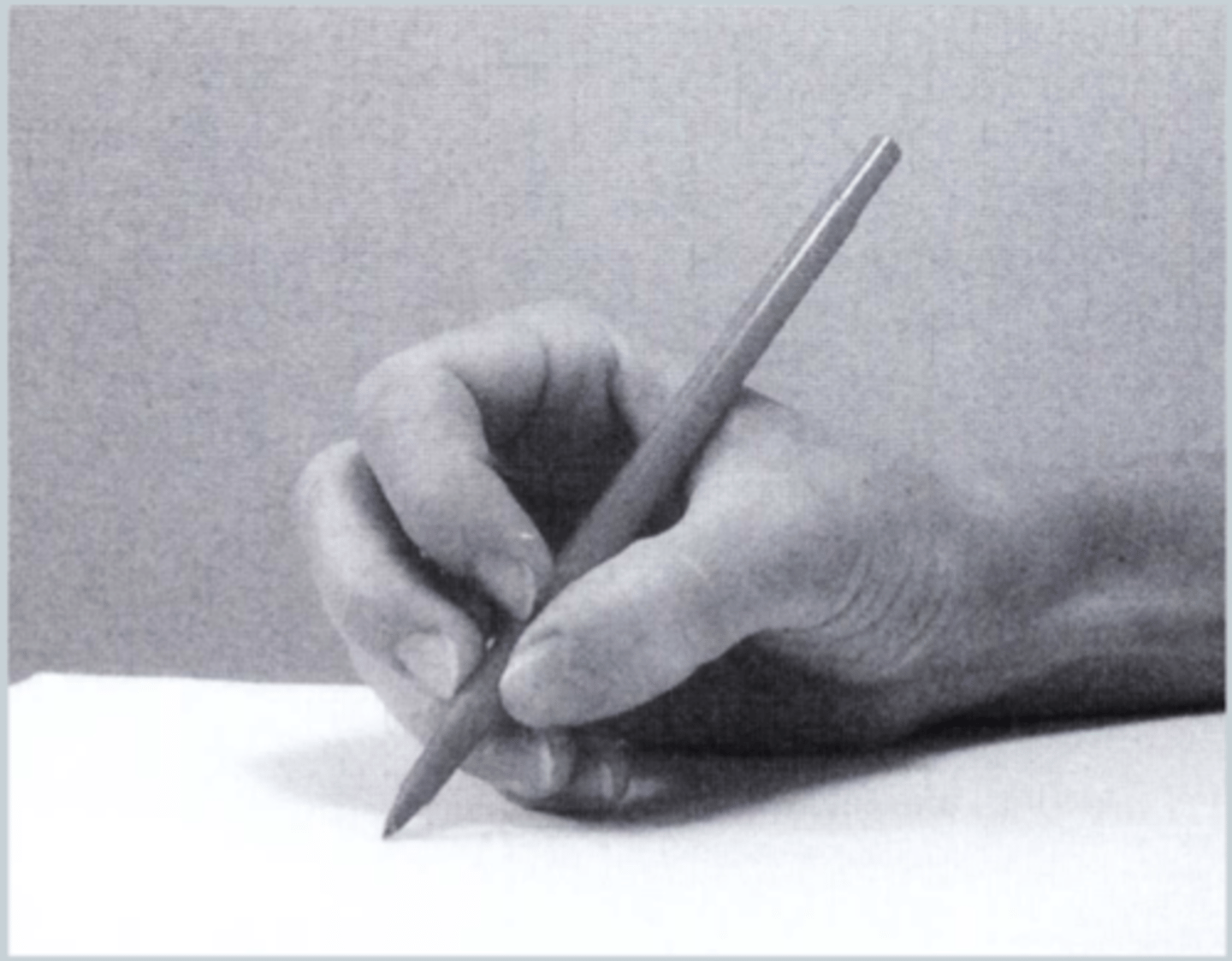
Tripod grip
the way in which a pen or pencil should be held, using the thumb, forefinger and middle finger, sophisticated fine motor control!
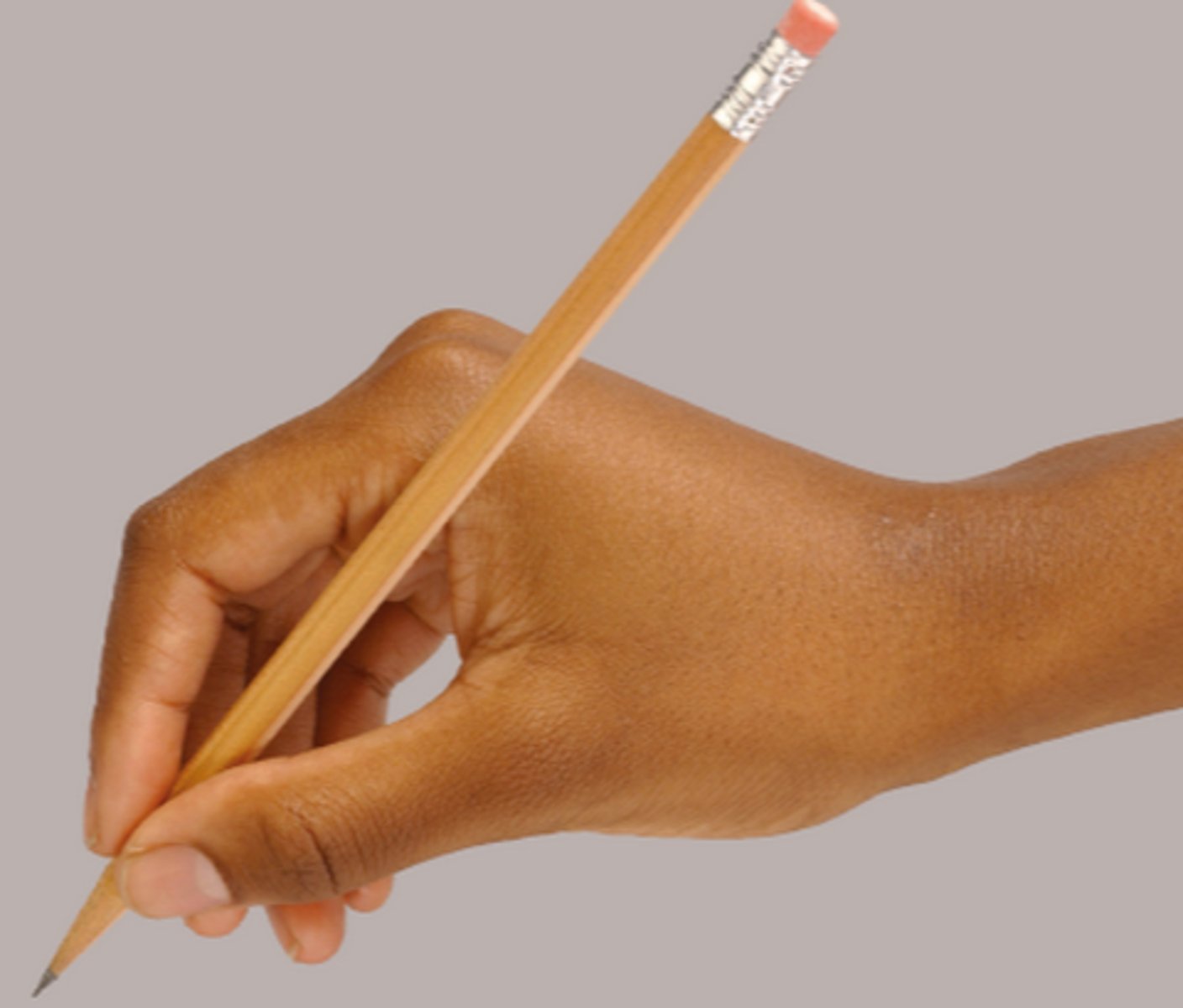

At 5 years old, how many children use these grips?
Simian
Intermediate
Tripod
Simian 13%
Intermediate 30%
Tripod 57%
At 7 years old, how many children use these grips?
Simian
Tripod
Simian 11%
Tripod 70%
At 9 years old, how many children use these grips?
Simian
Tripod
Simian 5%
Tripod 90%
Babies are born with saccades then display pursuits by
6-8 weeks
NSUCO test
5 cycles of saccades, 2 rotations of pursuits
For NSUCO, is a 1 or a 5 a good score?
5
SCCO 4+
optional fixation test of 10 seconds on a bead, then 5 cycles of saccades, then STAR PATTERN pursuits
