U4 - motivation and emotion vocabs
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Motive
inner directing force; specific need or desire; arouses individual and directs behavior; ex. Hunger, thirst, achievement; can be environmental cues
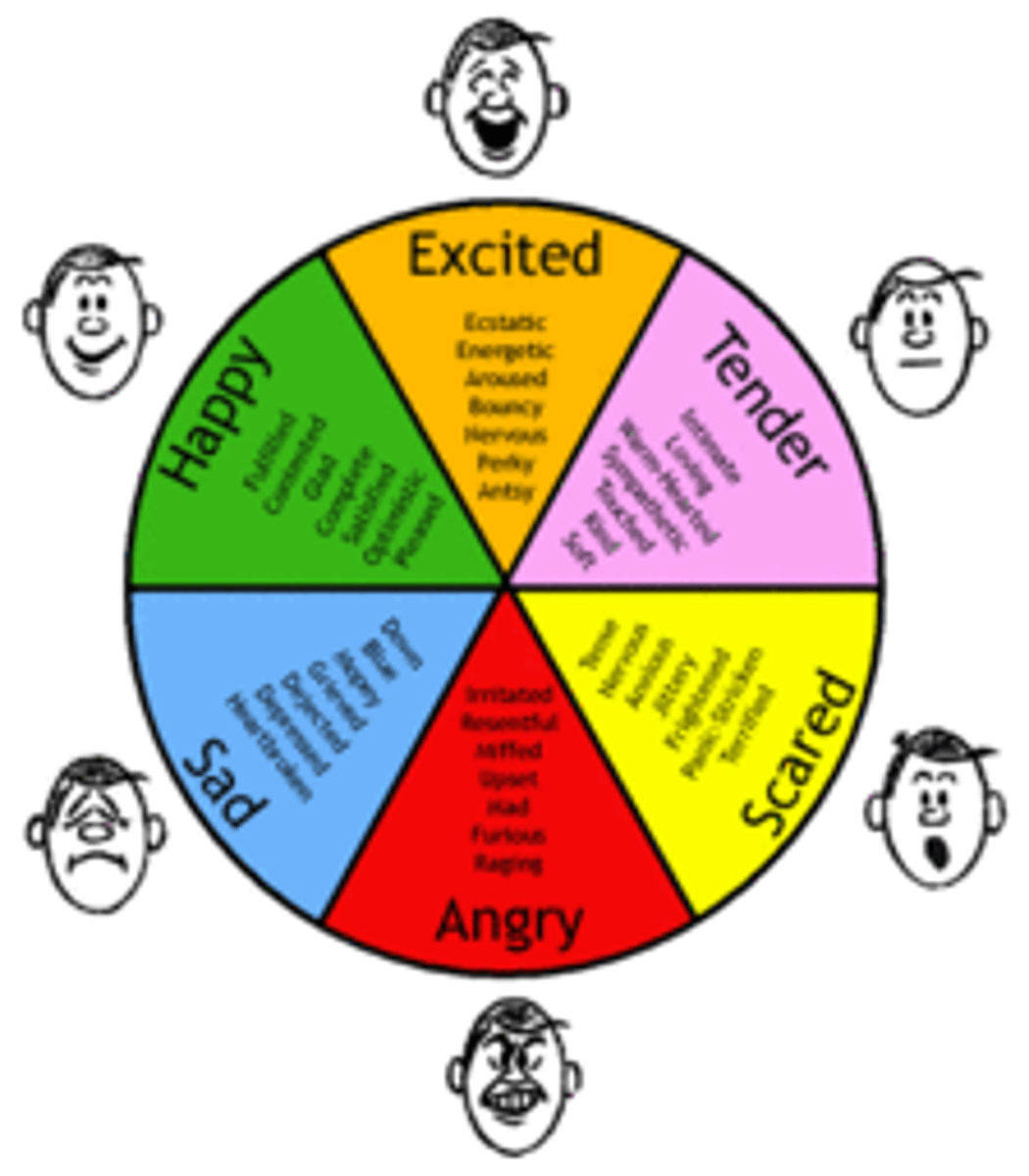
Emotion
experience of feelings that underlies behavior; activates and effects behaviors but difficult to predict behavior; ex. Fear, joy, surprise
Instinct
specific, inborn behavior patterns characteristic of an entire species; thought to account for human behavior until 1920s when it was learned that 1) behavior is learned, 2) behavior is rarely rigid and inflexible, 3) behavior to instinct means nothing; ex. Salmon swim upstream to spawn, spiders spin webs

Drive
state of arousal/tension that motivates behaviors; ex. Hunger, thirst
Drive-Reduction Theory
theory that motivated behavior is an attempt to reduce a state of tension/arousal in the body and return the body to a state of balance
Homeostasis
balance; stability; part of the drive-reduction theory; when individual functions effectively because drives are met
Incentive
external stimulus that motivates behavior; do not need to be aware of it to happen; does not have to be primary or an active, cognitive secondary drive; ex. Bakery, impulse buys, advertisements, Krispy Kreme

Intrinsic Motivation
internal motivation; completing the activity because it please you; ex. Singing, reading, crosswords, etc.; some people turn these things into extrinsic motivations like jobs but this is rare

Extrinsic Motivation
external motivation; completion of activity because of the consequence: reward or to avoid punishment; ex. Job, chores, school assignment, etc.

Primary Drive
unlearned; found in all animals and humans; motivates behavior that is vital to the survival of the individual/species; hunger, thirst, sex, sleep, BR needs

Set Point
idea that your body returns to a preprogrammed weight; this occurs naturally (after dieting and other events)

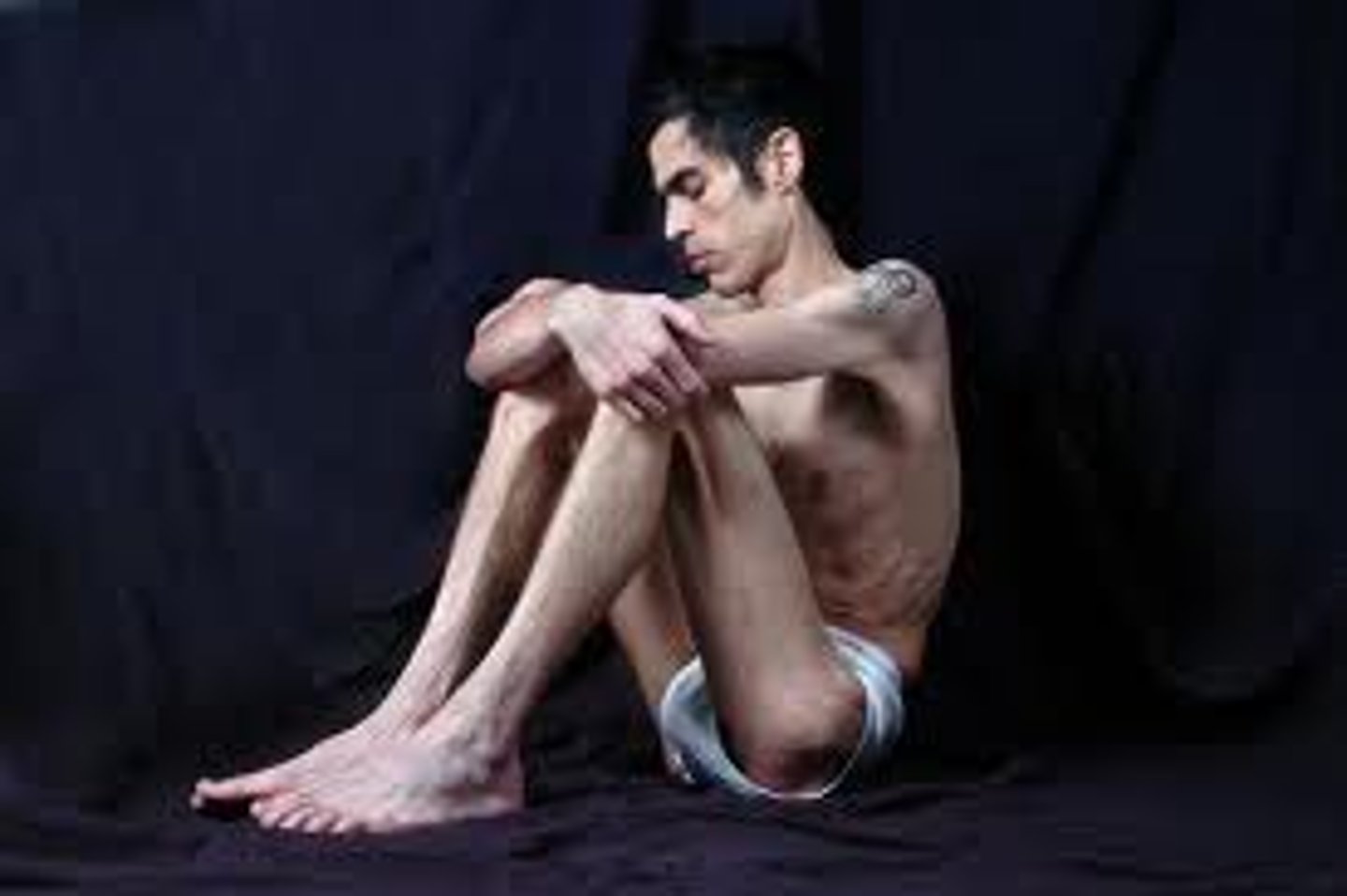
Anorexia Nervosa
eating disorder; severe weight loss accompanied by obsessive worrying about weight gain despite the fact the person is 10-15% below normal body weight; symptoms include: absence of 3 menstrual periods (females), distorted body image, intense fear of weight gain, dull eyes, baggy skin, dull hair, sallow skin, listlessness, overexercises, obsession about amount of food eaten; Onset: early adolescence, more white middle-class females; often comorbid with OCD
Bulimia Nervosa
eating disorder; recurrent episodes of binging and purging (massive eating in private, hiding out then throwing up or laxative usage), looks normal in weight (often) and is obsessed with maintaining weight not necessarily losing weight ; symptoms include: bruising on hand, suspicious behavior, binging/purging, smell from skin and mouth, lank hair, rotting teeth (eventually), puffy skin; Onset: late adolescence, more white middle-class females, but rising in white males

Testosterone
steroid hormone from the androgen group; in both men and women, testosterone plays a key role in health and well-being as well as in sexual functioning; Examples include enhanced libido, increased energy, increased production of red blood cells and protection against osteoporosis.
Pheromones
external stimuli; like primary drive, affects sex drive in animals; indirect evidence suggests that humans secrete pheromones to promote sexual pheromones to promote sexual readiness in potential partners; in sweat glands of armpits and genitals
Stimulus Motive
unlearned; responsive to external stimuli; pushes us to investigate, and often change, environment; ex. Curiosity, exploration, manipulation, and contact; males more likely to be aggressive probably because of socialization; collectivistic cultures are more likely to seek compromise
Social Motive
learned; need to fulfill intimacy and achievement through relationships; not to be confused with affiliation (need to be around people)
Aggression
behavior aimed at inflicting physical or psychological harm; intent is key element; ex. Road rage, passive aggressive acts, hitting

Achievement Motive
measured by Work & Family Orientation (WOFO) Scales; need to excel or overcome obstacles; often in areas of work, mastery, and competiveness; ex. GPA, award winners, standardized test scores (high), etc.

Power Motive
learned; need to be praised by those in authority or power

Affiliation Motive
need to be with others; anxious if isolated; affiliation increases if danger appears (spirit de corps-being with a sympathetic group); cant be alone; interplay of biological & environmental factors

Yerkes-Dodson Law
evidences arousal theory; the more complex a task, the lower level of arousal that can be tolerated without interference before the performance deteriorates; ex. used in class-driving to school, driving angry, finding a new location, boiling an egg
Cannon-Bard Theory
1920s; theory of emotion; processing emotions and bodily response occur simultaneously; ex. I see a bear, I feel afraid and my heart is racing
James-Lange Theory
1880s; William James and Carl Lange; theory of emotion; stimuli in environment cause physiological change in bodies, then emotion comes; ex. I see a bear which cause my heart to race, then I become afraid
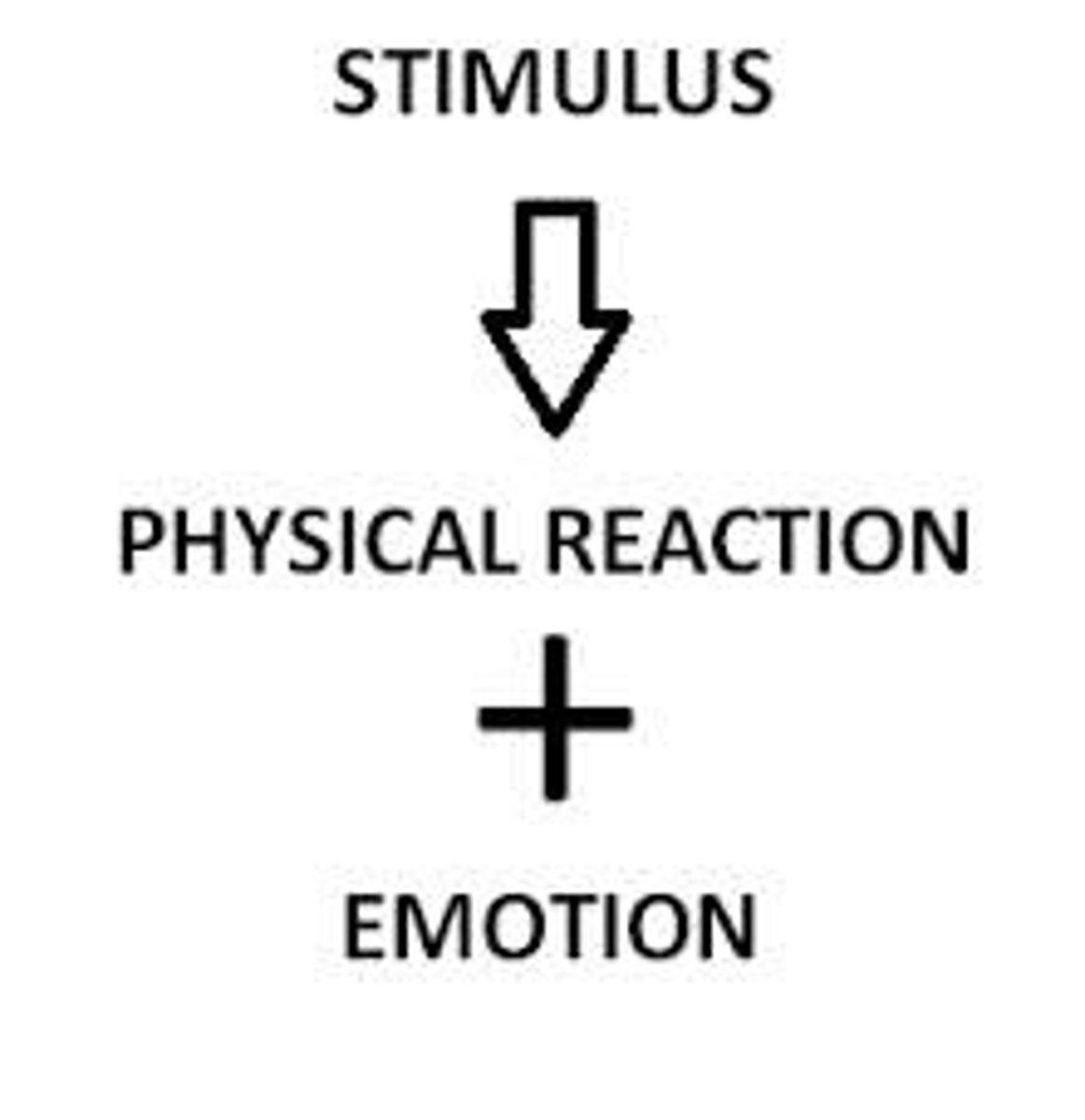
Cognitive Theory
perception of situations that is essential to emotional experiences; Cannon-Bard is an example; experience depends on one's perception of how to interpret arousal
Display Rules
facial expressions of primary emotions; fairly constant from one culture to another, yet people still get confused; refer to circumstances which it is appropriate for people to show emotions; ex. during surgical procedure Americans show true emotions but Japanese withhold emotions

Two Factor Theory of Emotion
Schacter & Singer (1962); cognitive theory; there are bodily emotions, but we use the emotions/information to tell us how to reaction in the situation; only when we think, recognize, do we experience the emotion
Explicit Acts
nonverbal cues to emotion; gestures; but can be misconstrued, ex. crying over onions, laugh at wrong time
Emotional Labor
sociological in nature; Hochschild (1983); jobs, typically held by females, often have the employees regulate, manage, or alter emotional expression; likely due to service or helping occupations
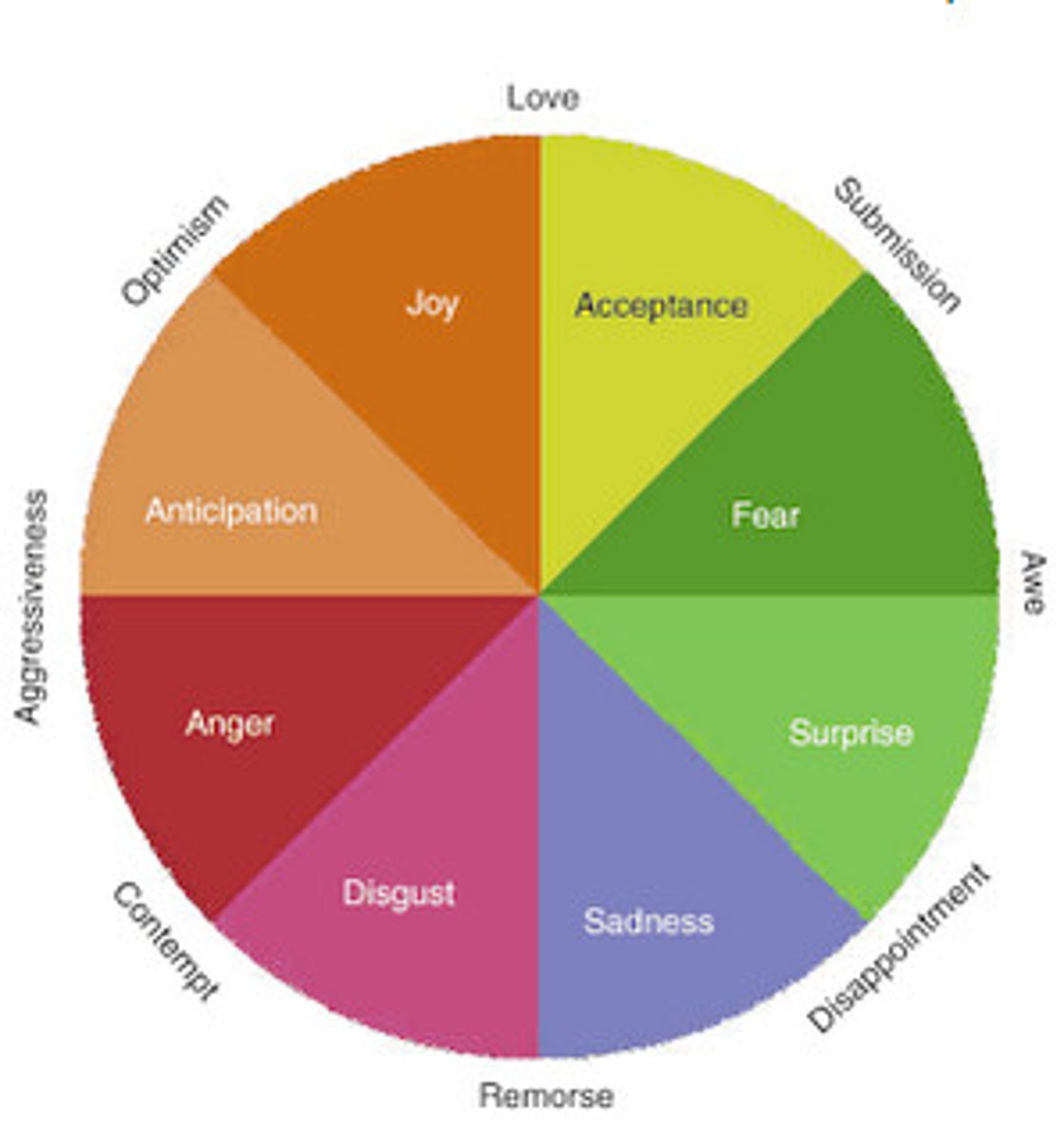
Plutchik's 3D model
1980; 8 basic emotions-fear, surprise, sadness, disgust, anger, anticipation, joy, & acceptance; helps adjust to demands of environment; model illustrates how emotions are more alike to those situated near it than those farther away (circle)_; varies with intensity
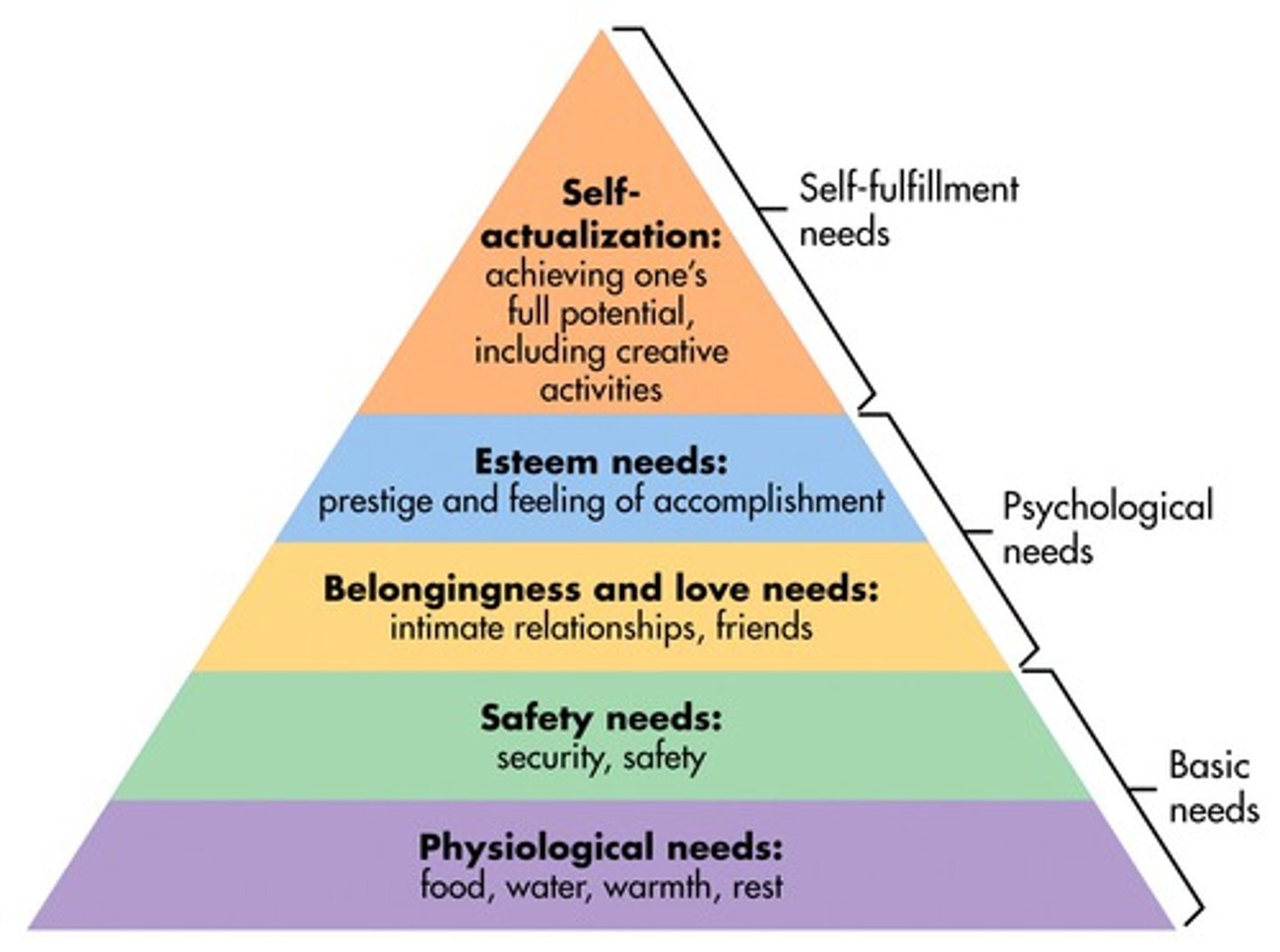
Hierarchy of Needs
humanism; Marlow; graduation of primitive motives to more sophisticated, complex (human needs); higher motives only emerge after basic are fulfilled; Stages-physiological, safety, belonging/love (sometimes a separate stage), esteem, and self-actualization
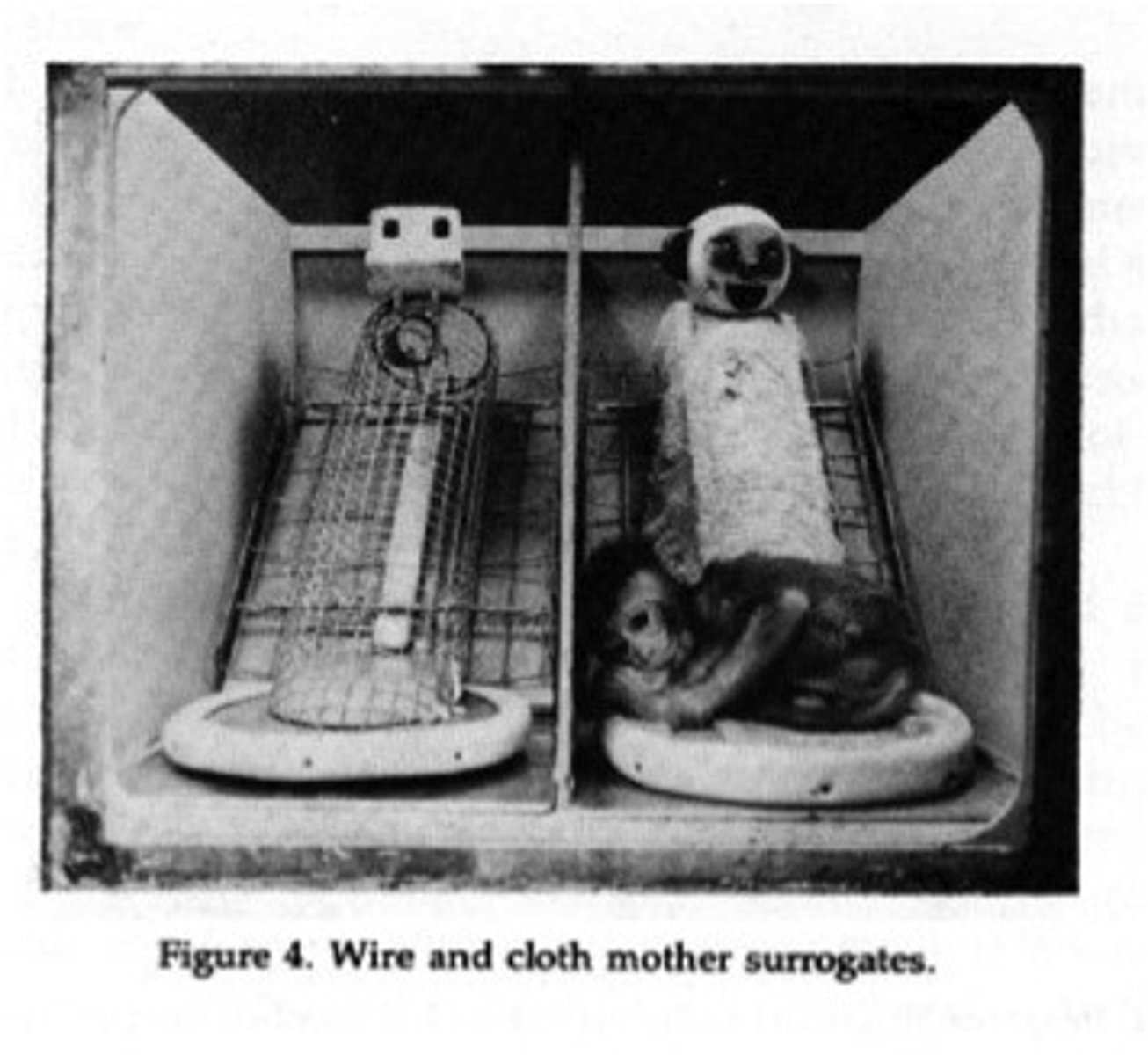
Contact Studies
Harlow; Rhesus monkeys; created surrogate mothers (bare wire and terry cloth); baby monkeys choose cloth 'mothers' over nourishment

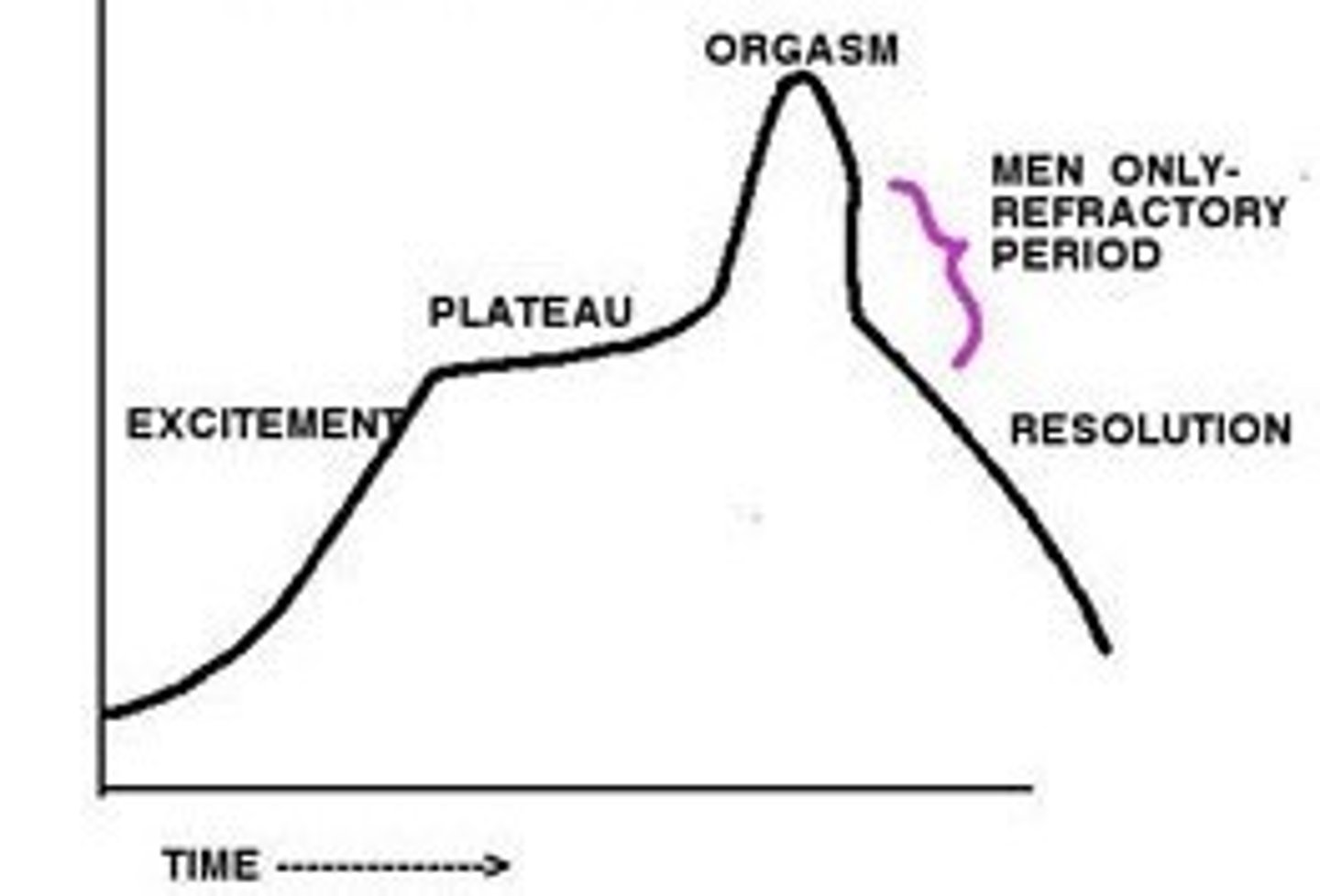
Sexual Response Cycle
explains sexual drive; Masters & Johnson (1966); EXPLORRE: EXcite, PLateau, ORgasm, REsolution (4 phases); describes the sexual response of males and females
Ventromedial Hypothalamus (VMH)
part of the hypothalamus; satiety center; ceases hunger; in rats, works as a "on-off' switch (studies caused obese rats); has been challenged as the on-off switch; L comes before V, therefore you have to start eating before you can stop
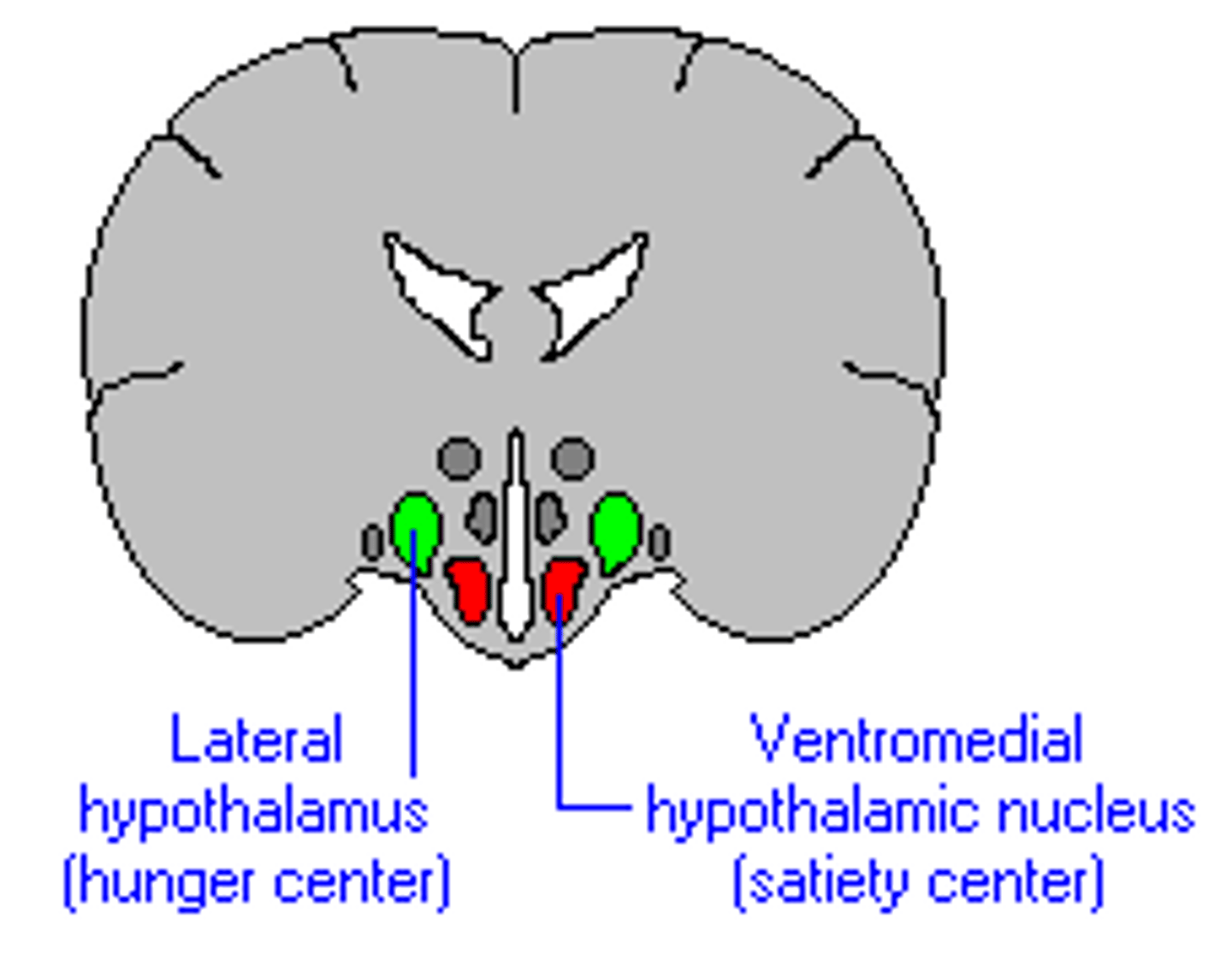
Lateral Hypothalamus (LH)
part of the hypothalamus; feeding center; stimulates hunger; if destroyed, may cause starvation because organism doesn't receive cue to eat; L comes before V, therefore you have to start eating before you can stop
Arousal Theory
theory of motivation; each individual has an optimal level of arousal (alertness, paying attention) that varies from one situation to the next; maintained by desire at that moment; may affect your performance (Yerkes-Dodson Law); Advantages-sensation or thrillseekers
Secondary Drives
acquired through learning; affiliation, social, achievement, aggression, power; Ex. money, grades, friends, intimacy, acceptance, praise, etc.

Affect (as in facial)
facial expression
Positive Psychology
Seligman; field that studies the strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive

Facial Expression
affect; emotions expression on the face
