Food tech (condensed)
1/120
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
outline the characteristics of enzymes
Enzymes cause food spoilage
they are catalysts for chemical reactions
they cause browning in certain foods called enzymic browning
enzymes can be destroyed by heat or acid
They cause food to spoil by oxidation
how can you prevent oxidation when cooking?
adding an acid
cooking immediately
protect from light
add antioxidants
refrigeration
outline the characteristics of yeast
they prefer acidic foods
As yeasts ferment the sugars in these foods , they produce alcohol and carbon dioxide
can grow with or without oxygen
Spoil fruit, juices, jam and honey
outline the characteristics of moulds
grow best at 20-30 C
damp air and warm temperature can speed up mould growth
they grow throughout the foods to get all the nutrients
grow easily on bread, cheese, jam, and soft fruits
how are moulds used in food production?
To make cheese: Starter culture is added to change lactose to lactic acid. This gives the correct level of acidity and gives the cheese moisture. The mould gives the cheese a smell, taste and texture.
To make yogurt
how is yeast used in food production?
To produce bread, beer and wine.
Yeast ferments or breaks down glucose into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
how is bacteria used in food production?
Making cheese: Starter culture is added to ripen the cheese and creates curds and whey.
how is mould used in cheese production?
To make blue cheese: creates blue veins within the cheese
To make soft ripened: mould grows on the outside causing the cheese to age from the outside in
how do you use a food thermometer probe?
Clean and disinfect the probe before use
Insert the probe to the centre or thickest part of the food
Wait a few seconds for the display to stabilise before taking a reading
Read the temperature
Check the food has reached 75 C
Clean and disinfect the probe after use
What are the 14 common food allergens?
gluten
celery
tree nuts
fish
soy
sesame
peanuts
crustaceans
eggs
molluscs
milk
mustard
sulphur dioxide and sulphites
lupin
what is sensory evaluation?
Judging the different sensory qualities of food.
why do we carry out sensory evaluation?
ensure food meets a customer’s expectations, so people will enjoy the foods
ensure changes to the product remain acceptable
it guarantees food products remain consistent over time
compare to other products to get ideas for improvements
ensures food products meet the original specification
to monitor the quality and shelf life of products over time.
what is a paired preference test?
A person is given two samples and is asked which they prefer
What is hedonic ranking?
This is a type of preference test that finds out if people like or dislike a product/s.
They rank the samples on how much they like them.
what is the triangle test?
This is used to detect differences in two samples, a person is given three sample, two are the same, and they have to find the odd-one out.
what is the ranking test?
Looks at a particular sensory property in a number of samples.
what is the rating test?
Allows people to rate different sensory properties of a food.
how do you create a fair testing environment?
distractions including smells should be removed
lighting should be controlled and coloured lighting should be used if there are visual differences between samples
seating should isolate testers
water should be provided to allow the sampler to cleanse between samples
What do cholesterol lowering products contain?
Natural extract from plants which stops cholesterol from being absorbed into the bloodstream
What are the disadvantages of a preservative?
some can be linked to a higher risk for developing cancers
What are the disadvantages of flavouring?
Can cause symptoms similar to an allergic reaction
What are the disadvantages of an emulsifier?
Can cause liver disease
some people report flatulence and bloating
What are the disadvantages of stabilisers?
Damage to internal barrier
some people experience flatulence and bloating
Describe the muscle tissue in meat.
It is made up of long thin fibres which are held together by connective tissue. These are either collagen, which holds bundles of fibres together or elastin, which binds the muscle together or the fibres to the bone.
what happens to collagen during slow, moist cooking methods?
it is converted to gelatin which is a soluble protein which is soft and tender and easier to eat and digest.
What nutrients are found in meat?
Protein.
Red meat contains Iron,Zinc and B vitamins.
Describe the muscle tissue in fish.
The muscle fibres are found in short blocks with no elastin and only a thin sheet of connective tissue surrounding them. This ensures it is relatively tender and only requires a short cooking time.
What nutrients are found in fish?
Vitamin D and B2 and Omega 3 and 6
what nutrients are in vegetables?
vegetables which grow above ground are a source of vitamin C
seeds and pods contain protein, dietary fibre and some vitamin C
vegetables that grow below ground contain carbohydrates and fewer vitamins
What is the classifications of cereals?
Wheat
Rye
Rice
Maize
Barley
Oats
what is white flour fortified with?
Calcium, Iron, Vitamin B1 and B3
what is semolina?
a course-ground flour, which comes from wheat
what is durum wheat?
a yellowy, high-protein wheat that is grown especially for pasta-making.
what is the structure of semi-skimmed milk?
88% water
5% carbohydrate
3.5% protein
1.5% vitamins and minerals
1.7% fat
How is milk turned into cheese?
Pasteurise the milk: Destroys bacteria, makes milk ready for starter culture. Milk is cooled
Add the starter culture: starter culture added to ‘ripen’ the milk. Lactic acid bacteria change lactose into lactic acid. Temp is 25-35C for 30 mins.
Add rennet: This helps the milk coagulate. Milk turns into curd and whey. Takes 30 mins
Cut curd and heat: curd is cut with cheese knives into small pieces. Different temps make different types of cheese. Soft cheeses are made from soft curds at lower temps.
Drain whey: Whey is drained and the curds form a mat
Texture curd: Curd mats are cut and piled on top of one another. Cheddaring removes more whey and allows the mats to ‘knit’ together in a tight structure.
Salt: salt is added to produce the right texture and flavour
Form into blocks: Salted curd is placed into cheese hoops and pressed into blocks
Store and age: cheese is stored in coolers until the desired age is reached
Package: cheese cut and placed into blocks. Wax, foil, paper, plastic and cloth can all be used to protect cheeses
How is milk turned into yogurt?
Pasteurise the milk: Pasteurised milk is homogenised so fat droplets are dispersed. Less bacteria so ready for starter culture
Warm the milk: Milk is warmed to 42C
Add the starter cultures: Lactic acid bacteria is used for starter culture. Ripening lets lactose to lactic acid
Hold: Milk is held at 42C. Fermentation creates a soft gel as protein sets
Cool: yogurt is cooled to 7C. fermentation stops
Add flavour: fruits and flavours are added
Package: pumped from fermentation vat to pots. Chilled to below 5C
How is fruit turned into jam?
Select fruit: under-ripe fruit has more natural pectin
Prepare fruit: wash and drain the fruit and remove any bruised fruit or seeds/stones/stalks
Add water and acid: simmer the jam. pectin is released from fruit with the help of the acid
Add sugar: stir gently to dissolve sugar completely
Add pectin: add liquid pectin, if the fruit is low in natural pectin
Boil: a full,rolling boil is required. Stir frequently
Test and pour into jars: setting point for jam is 105C. Use the wrinkle test to ensure this point has been reached. Pour into sterilised jars
what are the effects of canning on food?
Destroys some vitamin C and B groups as they are sensitive to heat.
what are the effects of drying on food?
destroys some vitamin C and B groups but makes vitamin A and E more concentrated in a product
What is the recommended amount of sodium?
A maximum of 6g for an adult daily.
Children under 11 years should eat less.
What is the function of vitamin B12 ?
Maintains nerve cells
Helps make new red blood cells
Releases energy from foods
What is the function of Folic acid ?
Reduces birth defects in unborn babies
Helps form healthy blood cells
What is the function of vitamin C/ Ascorbic acid ?
Needed for healthy connective tissue, production of collagen
Helps wounds heal
Helps in the absorption of iron
Is an antioxidant
What are the sources of vitamin B1/Thiamin ?
wholegrain products
meat
milk and dairy
Nuts
Marmite
Fortified breakfast cereals
Fortified white/brown flour
What are the sources of vitamin B2/Riboflavin ?
Chicken
Eggs
Milk
Fish
Leafy vegetables
What are the sources of vitamin B3/ Niacin ?
Red meat
Poultry
Fish
Brown rice
Nuts and seeds
What are the sources of vitamin B12 ?
Meat
Eggs
Milk
Salmon
Fortified breakfast cereals
Marmite
What are the sources of Folic acid ?
Fortified breakfast cereals
Broccoli
Brussel sprouts, Green leafy vegetables
Chickpeas
Potatoes
What are the sources of vitamin C ?
Citrus foods (lemons,limes,oranges,grapefruit etc)
Blackcurrents
Potatoes
Red/green peppers
Salad and green vegetables
What happens when someone has a deficiency of B1?
They get Beri Beri, a muscle wasting disease
What happens when someone has a deficiency of B3?
They get Pellegra which causes dermatitis,dementia and diarrhoea
What happens when someone has an excess of B3?
Can cause liver damage
What happens when someone has a deficiency of B12?
They get pernicious anaemia.
What happens when someone has a deficiency of Folic acid?
Causes Spina Bifida in unborn babies.
Materials we need in our diets.
Iodine
Iron
Calcium
Sodium
Phosphorus
Fluoride
What is the function of calcium?
Maintains normal bones and teeth
allows normal blood clotting
controls muscle contractions including the heart beating
What are the sources of calcium?
Milk/dairy products
Edible soft bones of fish (canned salmon)
Green leafy vegetables
Fortified soya bean products
Bread (fortified in UK)
What happens when calcium intake is too low?
Calcium is withdrawn from bones.
This leads to low bone density which can cause osteoporosis.
This may be caused by a lack in vitamin D which is common in teenage girls.
What is Iron needed for?
The formation of haemoglobin in red blood cells
Transport of oxygen around the body
Function of the immune system
Normal cognitive function
Reduction of tiredness and fatigue
Cell division
What are the two types of iron?
Haem iron.From animal source.This is readily absorbed into the body.
Non-haem iron.From plant sources,fortified foods and supplements.Vitamin C helps the absorption.
What are the sources of Iron?
Cereals
Nuts
Egg
Fish
Red Meat
Green leafy vegetables
What happens with high intakes of Sodium?
It is linked to high blood pressure (hypertension) which increases the risk of stroke and CHD.
What is Phosphorous needed for?
The maintenance of normal bones and teeth
The production of energy
What are the sources of Phosphorous?
Red meat
Milk/dairy products
Fish
Poultry
Bread
Rice
Oats
What is the function of Iodine?
Making the hormone thyroxin which maintains a healthy metabolic rate.
What are the sources of iodine?
Red meat
Fish/seafood
Cereal
What are the symptoms of Iodine deficiency?
Goitre (swelling of the thyroid gland)
What are the functions of water?
Allows cells to function
Regulates body temperature
Helps us get rid of waste
Allows normal cognitive function
Decreases blood pressure
Stops dehydration
Hydrates skin
Used in respiration
What are the signs of dehydration?
Dark urine
Headaches
Lack of energy
Feeling lightheaded
What are the functions of Vitamin A?
Antioxidant,protects the body
for growth and development of the body
making sure skin is healthy
helping vision in dim light
keeping the skin and the membranes in the body healthy
What are the two types of Vitamin A?
Retinol, animal sources
Beta carotene, vegetable sources
What are the sources of Vitamin A?
ANIMAL
eggs
oily fish
liver
full fat milk
what happens when you have an excess of vitamin A?
Can be toxic, causing liver and bone damage.
Excess retinol can lead to birth defects.
What happens when you have a deficiency of vitamin A?
Can cause night blindness
What is the function vitamin D?
Absorption and use of calcium and phosphorus
Maintenance and strength of bones and teeth
What are the sources of vitamin D?
Oily fish
Meat
Eggs
Fortified breakfast cereals
margarine
Sunlight
what is the function of vitamin E?
Antioxidant that helps protect cell membranes
Maintains healthy skin and eyes
what are the sources of vitamin E?
Polyunsaturated fats, e.g. sunflower oils
Nuts
Seeds
Wheatgerm
what is the function of Vitamin K?
It helps blood clot or coagulate correctly
what are the sources of vitamin K?
green leafy vegetables
cheese
bacon
liver
Adolescents needs
Rapid growth and puberty occur at this time. High demand for energy and most nutrients,high protein intake for boys. Girls need more iron than boys because of menstruation.Recommended that teenage girls and women require 14.8 mg of iron each day, while adolescent boys only need 11.3mg of iron per day. A growth spurt begins around 10 years of age in girls and 12 years in boys. For both boys and girls, an average of 23 cm is added to height and 20-26kg in weight. Before adolescence, both girls and boys have an average of 18% body fat, during, this increases to around 28% in girls and decreases to around 15% in boys.
lacto-vegetarian
Someone who doesn't eat meat and eggs
Lacto-ovo vegetarian
Someone who eats vegetables,eggs and dairy products but not meat.
Iron deficiancy anemia
Iron deficiency anaemia is where your body does not produce enough red blood cells because the level of iron in your blood is too low.
Conduction notes
The direct transfer of heat between adjacent molecules.This is when heat travels through solids like food or metal.
For example cooking with a flat top range.
Convection notes
This is the exchange of heat by the application of a gas or liquid current.The movement of heat in water is called a convection current.
For example boiling potatoes.
Radiation notes
This is energy in the form of rays.Grilling involves the use of infrared heat rays created by gas flames.
Microwaves are electromagnetic radiators of high energy and short wave lengths.They quickly heat anything with water.
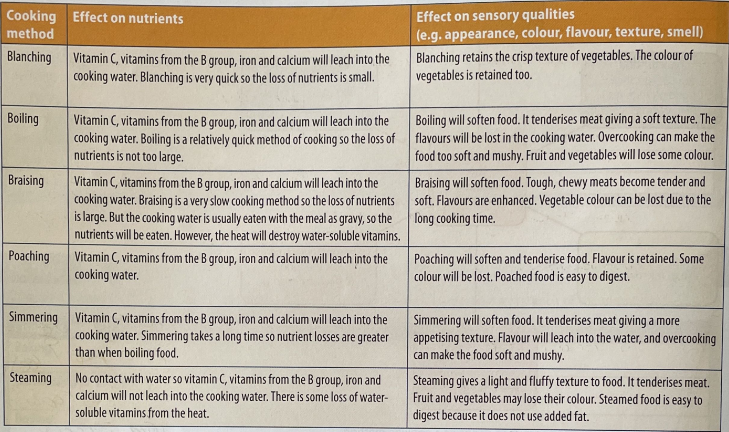
Cooking with water
Heat passes through water very quickly. It is transferred via conduction and convection.
Methods of cooking with water
Blanching
Boiling
Braising
Poaching
Simmering
Steaming
Cooking with dry heat
Heat passes through the air in convection currents as radiation from a grill.
Methods of cooking with dry heat
Baking
Grilling
BBQ
Deep frying

Cooking with fats
Heat will pass through oil or fat by convection currents or conduction
Low fat spreads cannot be used in frying as they contain water
Methods of cooking with fats
Shallow frying
Stir-Frying
Roasting

6 Marker for Carbohydrates
Explain the scientific process that takes place when making roux sauce
Gelatinisation takes place when starch is added to liquid and is heated until boiling point.This process takes place as starch consists of small granules that are suspended in the liquid as they do not dissolve.The sauce must be stirred whilst heating to ensure that the heat is equal throughout as else the granules will clump together.When heated to around 60 celsius,the starch granules begin to absorb the liquid and swell.When it reaches around 80 celsius it starts to thicken and when it finally reaches boiling point the process of gelatinisation is complete.
Dextrinisation (maillard reaction)
This occurs when starch is broken into dextrin by dry heat. Dextrin adds a sweet taste.
This contributes to the colour and flavour of many foods like crossiants.
Parts of amino acid and sugar molecules in food combine, when heated, to form brown compounds (dextrin) which change its colour, odour and flavour. This is also known as non-enzymatic browning or the Maillard reaction.
Caramelization
It is one of the most important types of browning processes.
It is the process of changing the colour of sugar from white to brown when heated.
It leads to a desirable golden brown colour and an attractive flavour in baked goods and drinks. Caramelisation can give a buttery, toasty or even a nutty flavour to food
Shortening
The fat coats the flour particles and prevents them from absorbing water.This reduces the gluten development,which would cause the dough to become elastic.
Used in shortcrust pastry,biscuits and shortbread.
Aeration
This is achieved by creaming a fat with caster sugar.
Small bubbles of air are incorporated and form a stable foam which can be baked to give the springy texture.
Used in creamed cakes.
Plasticity
This describes the ability of a solid fat to soften over a range of temperatures.Fats do not melt at fixed temps but at a range.
This plasticity is due to the mixture of triglycerides,each with its own melting point.
The two types of emulsions
Oil in water emulsion forms when the amount of water is greater than the amount of oil.Tiny droplets of oil are spread throughout the water.E.g milk
Water in oil emulsions forms when the amount of oil is greater than the amount of water.Tiny droplets of water are spread throughout the oil.E.g Butter