AP BIO unit 4
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Signal Transduction Pathway
converts signals on cells surface into cellular responses
Local regulators
messenger molecules that travel short distances (animal cells)
Long distance signaling
uses hormones (plant and animal cells)
Three stages of cell signaling
Receptions, Transduction, Response
Reception
signal molecule binds to receptor protein, causing it to change shape
Transduction
Amplification of signal through a multistep pathway
Response
causes synthesis of protein or regulation of protein activity
Cell divison is used for
growth, tissue renewal, reproduction
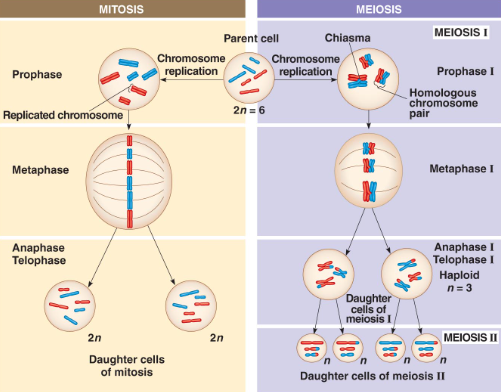
Mitosis
cell division of two indentical daughter cells
Somatic Cells
body cells, non reproductive
Gametes
sex cells, reproductive (half as many chromosomes as somatic)
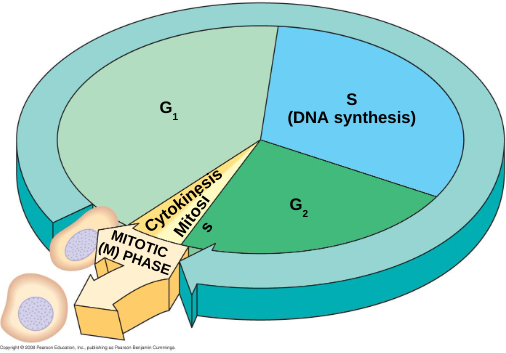
Interphase
preperation for cell divison
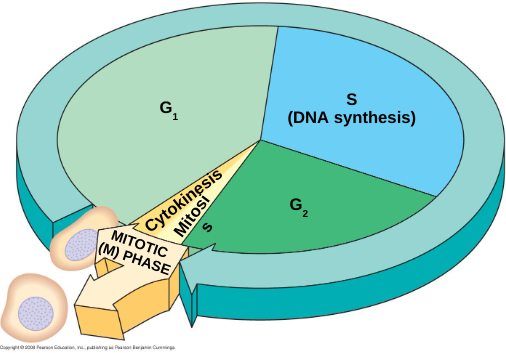
Miotic Phase
divison of nucleus and cytoplasm
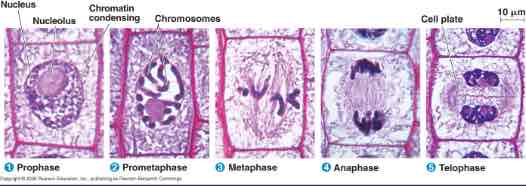
5 phases of Mitosis
Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
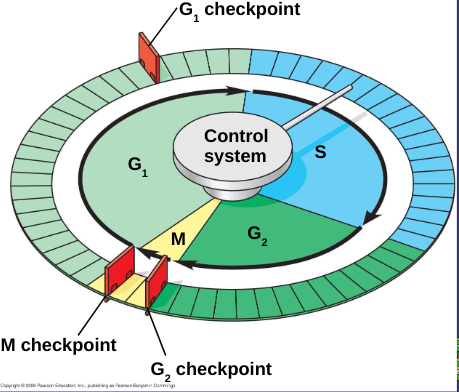
Cell Cycle Control System
directs events of cell cycle
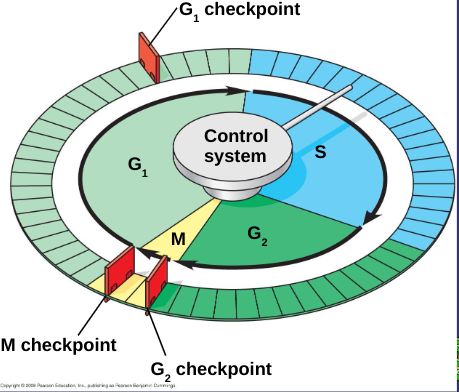
G1 Checkpoint
cells will move on and divide or sent into nondividing stage called G0
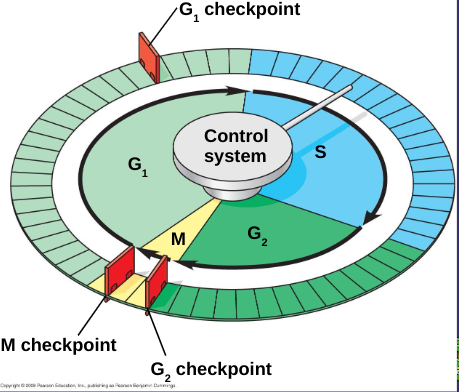
G2 Checkpoint
checks for DNA damage and complete DNA replication
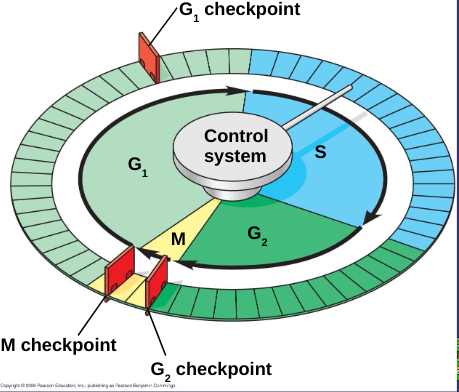
M Checkpoint
checks for completion of DNA replication
Binary Fission
reproductions of Prokaryotes
Internal Signals
non attached kinetochores send signal to delay anaphase
Growth Factors
released proteins from certain cells stimulate other cells to divide
Density-dependent Inhibtion
crowded cells stop dividing
Anchorage Dependence
cells must be attached to substratum to divide