Exam 2 PA
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
How do you perform assessment of mental status?
By observing and asking questions; collecting subjective then objective data
What is level of consciousness?
Is the person alert and awake with eyes open?
Is the patient looking at the examiner?
Is the client responding appropriately?
Response to stating patient's name
Alert/awake
eyes open, looking at nurse, responds appropriately
Lethargic (abnormal)
opens eyes, answer questions, and falls back asleep
Obtunded (abnormal)
Opens eyes to loud voice, responds slowly with confusion, unaware of environment
Stuporous (abnormal)
awakens to vigorous shake or painful stimuli, then returns to unresponsive sleep
Comatose
remains unresponsive to all stimuli; eyes remains closed
What is the order of best to worst LOC?
lethargic -> obtunded -> stupor -> comatose
Glasgow Coma Scale
eye opening, verbal response, motor response
Decorticate
flexion, rigidity, abnormal flexion
rigid posture of flexed arms, clenched wrists/fists, and extended legs
sign of severe brain damage (brain tumor/stroke/drug abuse/ brain bleed)
PULLING IN CORE (CORETICATE)
Decerebrate
extension away from body, abnormal extension
rigid posture of stiff, extended arms, pronated forearms, extended legs
sign of deeper brain tissue
Flaccidity
Relaxed; flabby; having defective or absent muscular tone
No movement response
Posture normal & abnormal
Normal: relax, shoulders back, both feet stable
Abnormal: tense, rigid, slumped, asymmetrical
Gait normal & abnormal
Normal: smooth, coordinated, fluid movements; client alters position occasionally
Abnormal: uncoordinated, staggering, shuffling, stumbling
Movement normal & abnormal (schizophrenia or anxious)
Normal: smooth, coordinated, fluid; alters position occasionally
Abnormal: jerky, uncoordinated; tremors, tics, fast or slow movement. Bizarre movements with schizophrenia; tense, fidgety, and restless behavior in anxious clients
Dress normal & abnormal
Normal: clothes fit in our appropriate for occasion and weather
Abnormal: clothes are XL or small/ inappropriate for occasion.
Hygiene normal & abnormal
Normal: skin clean, nails clean and trimmed
Abnormal: dirty, unshaven; dirty nails; foul odors
Facial expression normal & abnormal
Normal: good eye contact, matches mood. smiles/frowns appropriately
Abnormal: poor eye contact, mask like expression, extreme anger/happiness. Facial expression does not match mood
Speech normal & abnormal
Normal: speech is in a moderate tone, clear, with moderate paste and culturally appropriate
Abnormal: slow repetitive, loud, rapid, disorganized, slurred, garbled dysarthria- distorted speech sounds
dysphasia- having trouble getting the words out
Mood questions
How are you feeling?
What are your plans for the future?
Normal vs abnormal mood
Normal: responds appropriately expressing feels appropriate to situation, expresses god feelings about self, others, and life; verbalizes positive coping mechanisms
Abnormal: Expressing feelings inappropriate to the situation like extreme anger or euphoria. Dissatisfaction with self, others, and life in general; verbalizes negative coping mechanisms; prolonged negative feelings- depression
elation and high energy scene- manic phases
excessive worry- OCD
eccentric mood not to relevant to situation- schizphrenia
How do you assess orientation?
Person: What is your name?
Place: Where are you?
Time: What time is it? What month are we in? What is today's date?
Event: Do you know why you are here? What brought you in today?
normal orientation
client is able to answer all questions; Alert and orientated x_
abnormal orientation
client is unable to answer some or all of questions. Alert and orientated x_, confused to_
(5-1) Dementia (duration, onset, attention, attention, memory, alertness, thinking/judgement)
Duration: Chronic condition that does not resolve over time
Onset: Chronic onset
Attention: generally normal attention
Memory: recent and remote memory impaired
Alertness: generally normal alertness
Thinking/judgement: may have word finding difficulties, judgement may be poor
Delirium (duration, onset, attention, attention, memory, alertness, thinking/judgement)
Duration: hours-weeks in duration
Onset: acute onset
Attention: impaired/fluctuating attention
Memory: recent and immediate memory impaired
Alertness: fluctuates between lethargic and hypervigilant
Thinking/ judgement: disorganized thinking, slow or accelerated
Depression (duration, onset, attention, attention, memory, alertness, thinking/judgement)
Duration: can last weeks to months or years
Onset: often abrupt onset
Attention: distractible but minimal impairment of attention
Memory: islands of intact memory
Alertness: Alert
Thinking/judgement: thinking intact though with themes of helplessness or self-depreciation
Geriatric variations in mental status
-confused in new or acute setting causing slow thought/responses to ANO questions (person/place/time)
-decreased ability to recall directional
-slight decline in short- term memory
-likes to reminisce and tends to wander from topic being discussed
-may have hesitation with short -term memory
-clients >80 should be able to recall 2-4 words after 5 minutes
Subjective vs objective data for SHN
Subjective: reason for visit
hx of present illness
past medical hx
family hx
lifestyle and health practices: specifically hygiene habits, sun/tanning exposure, chemical exposure
Objective:
inspection
palpation
Epidermis function and layers
superficial, thinner layer of skin
composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Function: waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone
Layers (bottom to top):
stratum basale -> stratum spinosum ->stratum granulosum -> stratum lucidum -> strum corneum
Dermis function and components
a layer of dense irregular connective tissue lying deep to the dermis.
Function: support the epidermis and enable the skin to thrive
Components: hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, apocrine glands, lymphatic vessels, nerves, blood vessels
sebaceous glands
attached to hair follicles over most of the body, except soles and palms
they secrete an oily sebum that waterproofs the hair and skin
Sweat (sebum glands)
Eccrine glands: located over the entire skin
secrete sweat and affect thermoregulation by evaporation of sweat from the skin surface
Apocrine glands; associated w/ hair follicles in the axillae, perineum, and arolae of breasts
small and nonfunctional until puberty when they secrete milky sweat
Subcutaneous layers
continuous sheet of areolar connective tissue and adipose tissue between the dermis of the skin and the deep fascia of the muscles
Vellus (peach fuzz)
short, pale, and fine over much of the body
provides thermoregulation by wicking swear away from the body
Terminal (scalp and eyebrows)
longer, darker, and coarser than vellus hair
provides insulation and allows for self-expression
Nail body
extends over the entire nail bed and has a pink tinge as a result of blood vessels underneath
Lunula
The crescent-shaped area at the base of the human fingernail.
In what order will the nurse use assessment techniques to assess skin, hair, and nails?
Interview
Inspection (looking and smelling)
Palpation
What is the nurse looking, smelling, and feeling for?
1) inspect for generalized color, color variation
2) note odors/strong odors of perspiration of foul odor may indicate sweat gland disorder
3) odor may indicate infections
4) body odor may signify need for education
How does the nurse assess for skin color?
Using inspection
Normal: lightskin- light to dark pink; dark skin- light to dark brown
Abnormal: pallor, flushed, cyanosis
How does the nurse assess for skin texture?
palpate
normal: smooth and soft
abnormal: rough, thick, dry-hypothyroidism
How does the nurse assess for skin temperature?
feel with back of hand
normal: warm & dry
abnormal: cool-shock, hypotension, arterial insufficiency, very warm-fever, hyperthyroidism
How will the nurse assess for skin turgor?
pinched up skin on sternum or under clavicle
normal: returns immediately to normal position
abnormal: 30s or longer to return to normal can indicate dehydration
How will the nurse assess for skin edema?
pressing firmly for 5-10s over tibia and ankle
normal: no swelling or edema
abnormal: swollen,
shallow to deep pitting,
ascites generalized edema in CHF,
kidney disease,
unilateral,
localized edema is seen in peripheral vascular problems such as venous stasis, obstruction, or lymphedema
How will the nurse assess for skin integrity?
pay attention to pressure point areas
normal: intact, no reddened areas
abnormal: skin breakdown
primary or secondary lesions
vascular lesions
skin cancer
How will the nurse assess for skin lesions?
detected, inspect and palpate for size, location, mobility, consistency, and pattern (circular, clustered, or straight-lined)
normal: silver-pink stretch marks (striae), moles (nevi), freckles, birthmarks
abnormal:
primary- arise from normal skin owing to disease or irritation
secondary- arise from changes in primary lesions
vascular- seen w increased venous pressure, aging, liver disease, or pregnancy
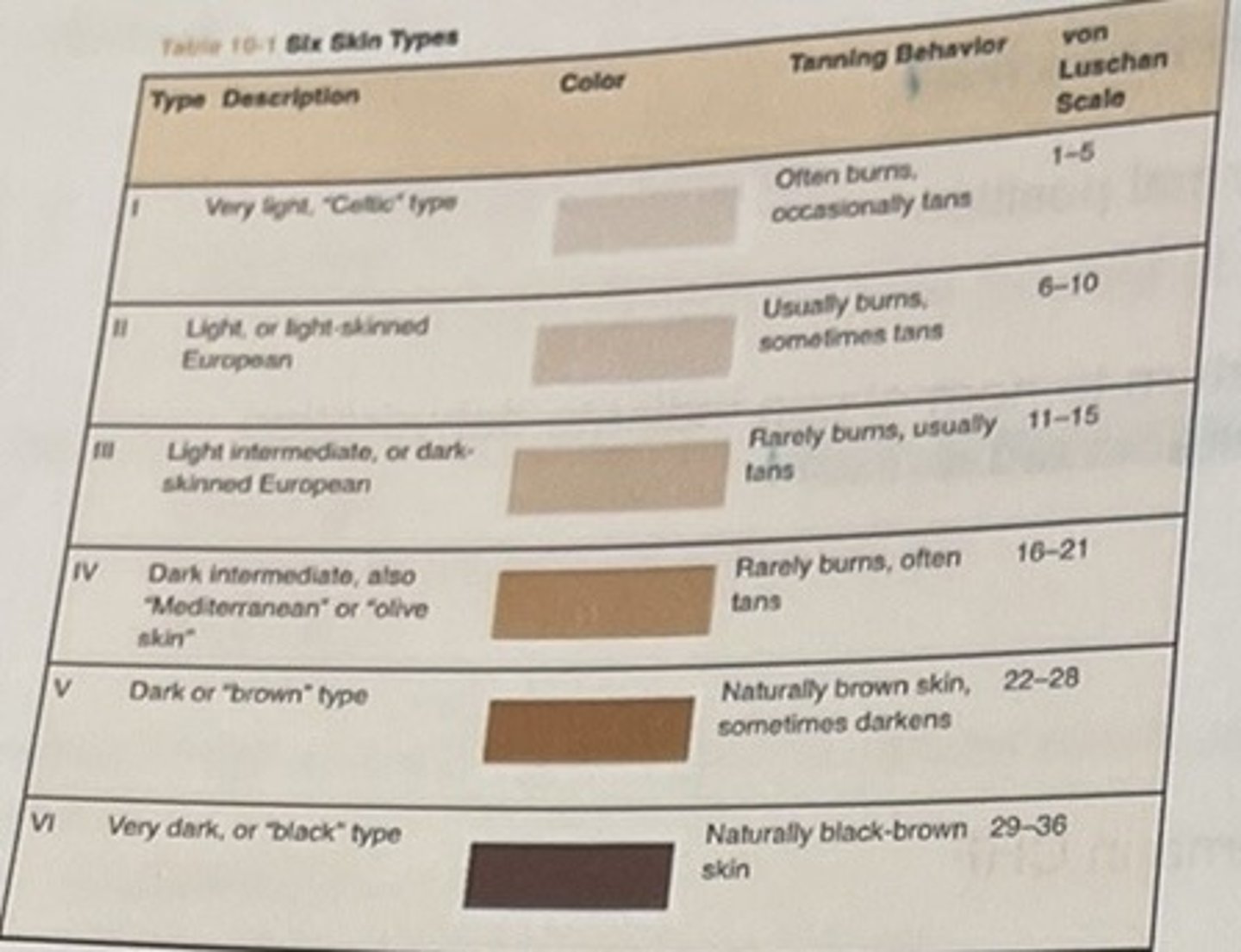
Table 10-1/ skin types
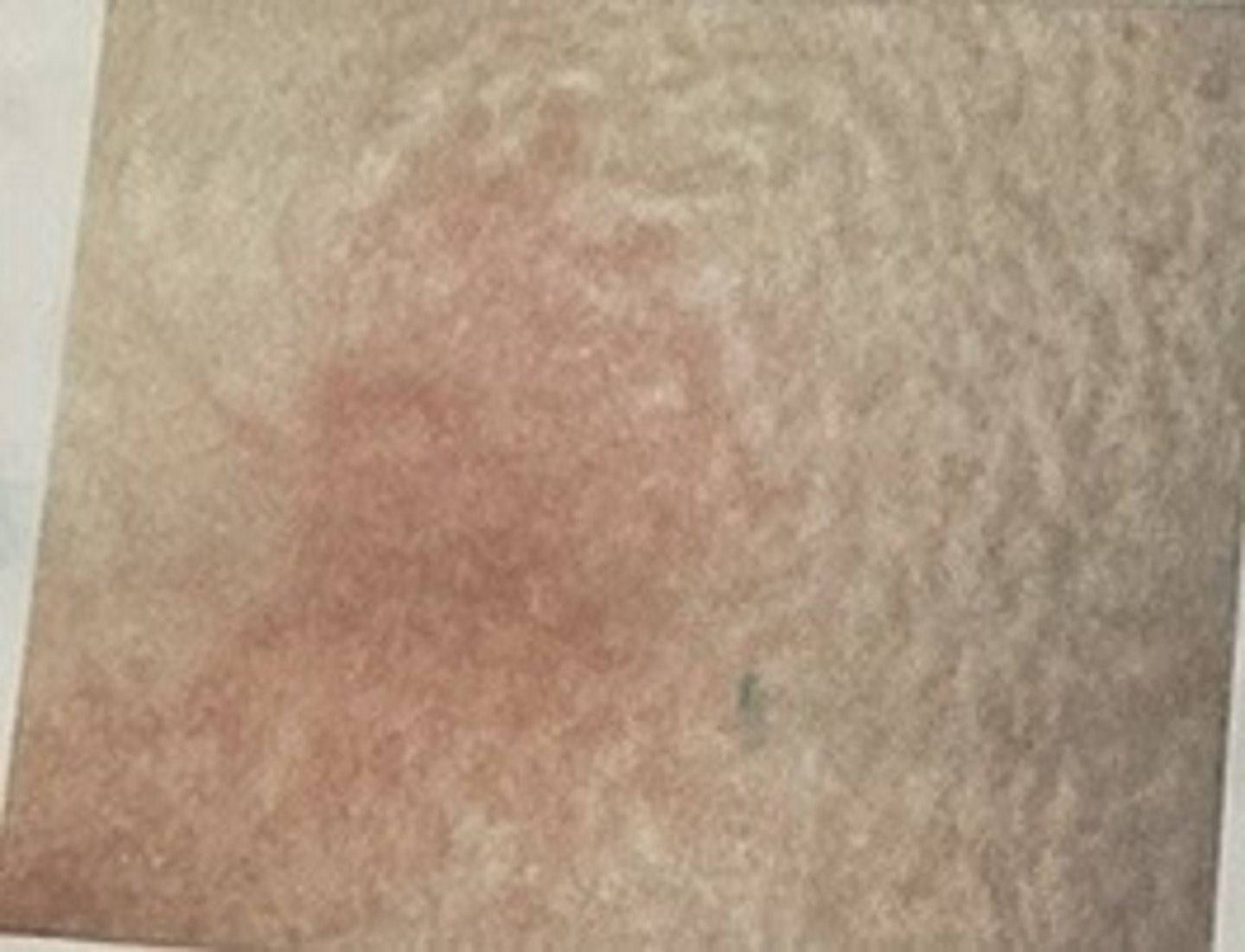
stage 1 pressure injury
non-blanchable erythema of intact skin
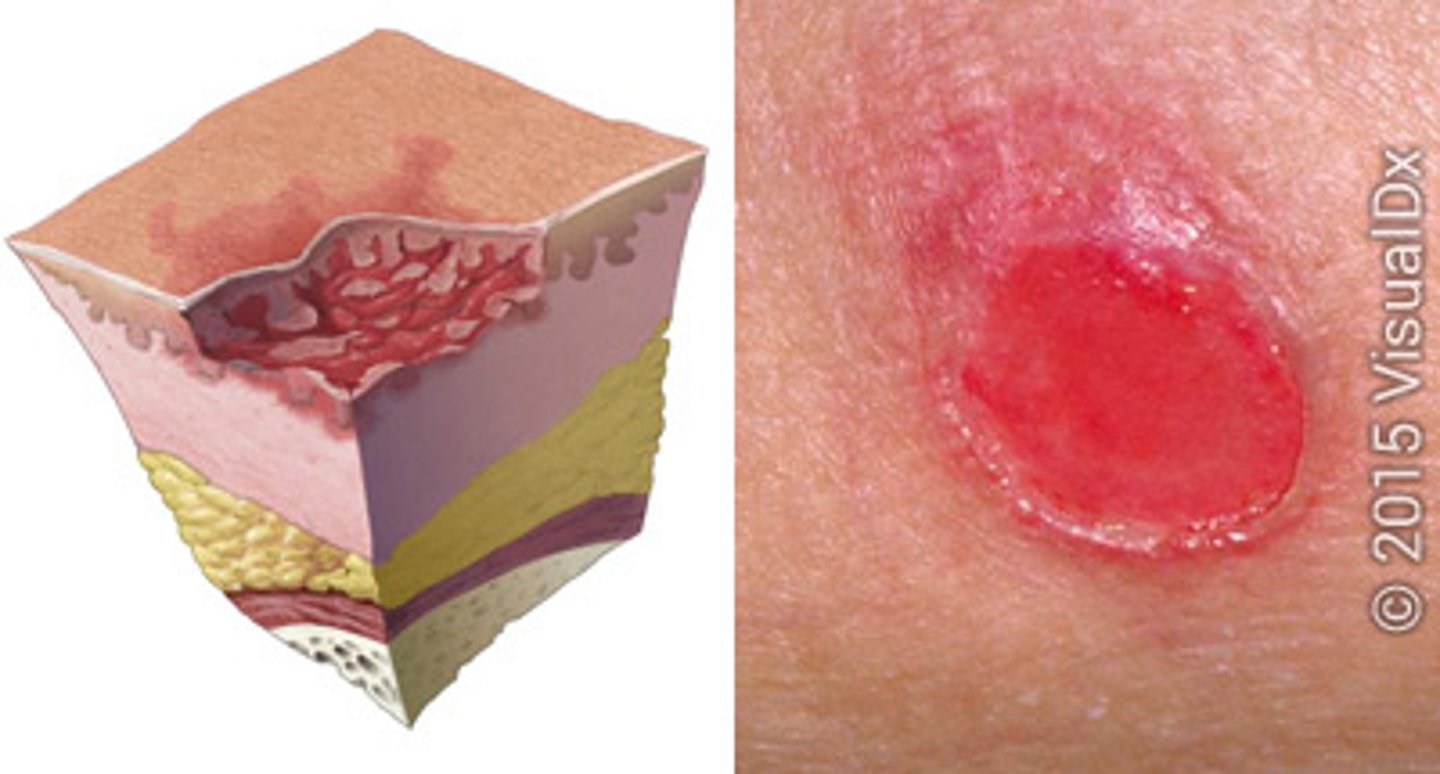
stage 2 pressure injury
partial thickness skin loss with exposed dermis
stage 3 pressure injury
fulll thickness skin loss with adipose tissue, granulation tissue, undermining, and tunneling
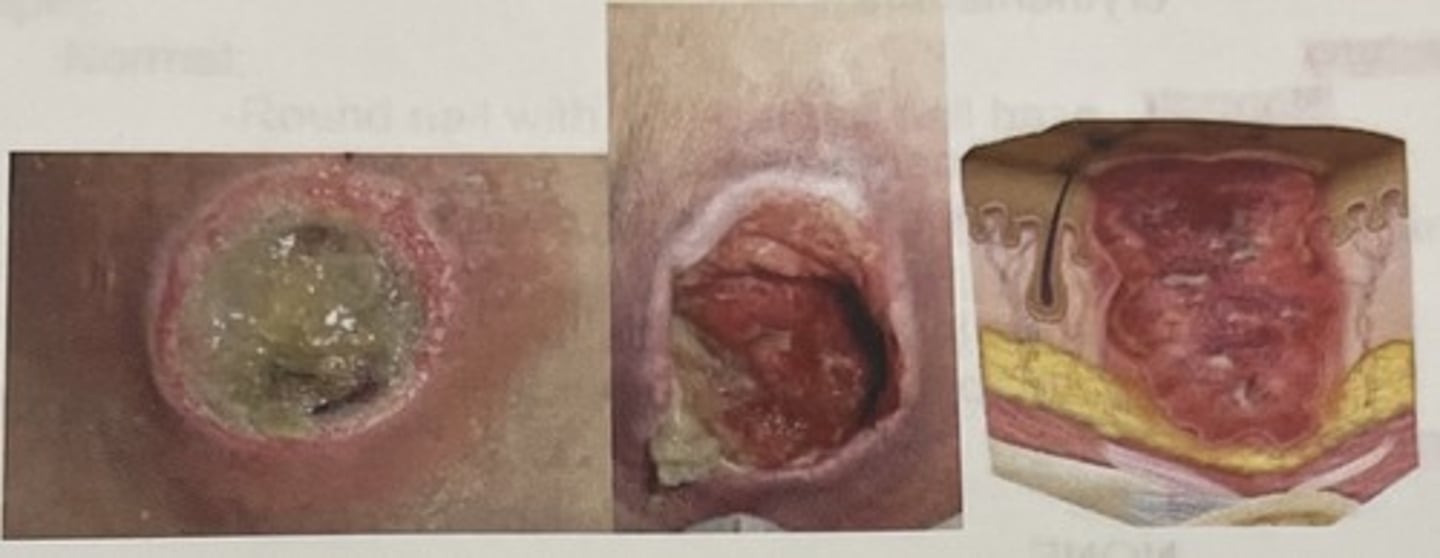
stage 4 pressure injury
full thickness loss of skin with extensive destruction, tissue necrosis, and damage to bone, muscle, or other supporting structures that are exposed
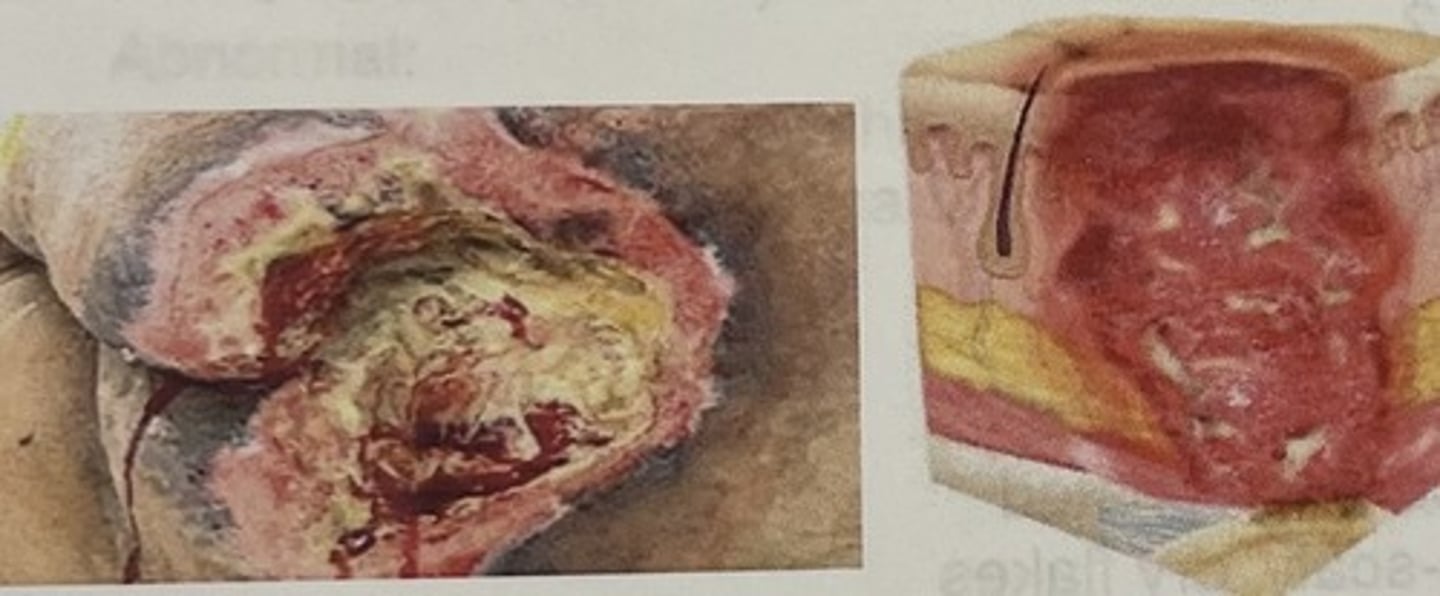
How does the nurse assess for hair color?
normal: ask about a change in color yielding to more inform
abnormal: patchy gray areas seen in nutritional deficiences
copper-red hair (AA)- severe malnutrition
How does the nurse asses for amount and distribution in hair?
normal: observing a head of hair on patient
abnormal:
alopecia- loss of hair suddenly
hirsutism- increase in facial hair in females as seen in Cushing syndrome
seen infections, nutritional deficiencies, hormonal disorders, some types of chemo, or radiation therapy; patchy loss w scale infection and lupus erythematous
How des the nurse assess for hair texture?
normal: fine to coarse, pliant
ask about a change in texture
abnormal: change in texture, brittle. dull/dry hair in hypothyroidism and malnutrition
How does the nurse assess for parasites?
normal: none
abnormal: lice, eggs attached to hair shaft severe itching
How does the nurse inspect for scalp texture?
symmetry: smooth and form
asymmetrical: bumpy, scaly, excoriated
dermatits- scaly, dry flakes
fungal infection- gray scaly patches
dandruff psoriasis
How does the nurse assess for scalp lesions?
normal: NONE
abnormal: open or closed lesions
How does the nurse assess for nail color?
normal: pink nail bed
dark skin- may have small or large pigmented streaks/freckles
abnormal: hypoxia-cyanosis
anemia- pale
fungal infection- yellow discoloration
trauma- splinter hemorrhages (vertical)
acute trauma-beau's lines (horizontal)
psoriasis- yellow or pitting
How does the nurse assess for nail shape?
normal: round nail with 160 degree nail base
abnormal: hypoxia-clubbing (enlargement of ends of fingers and downward sloping, 180 degree or more nail beds)
iron deficiency anemia- spoon shape
How does the nurse assess for nail texture?
normal: hard and immobile
abnormal: decreased ciculation-thickened
How does the nurse assess for nail condition?
normal: smooth pink firm
dark skin- may be thick
abnormal:
infection- paronychia (inflamed)
infection or trauma- oncholysis (detached nail plate
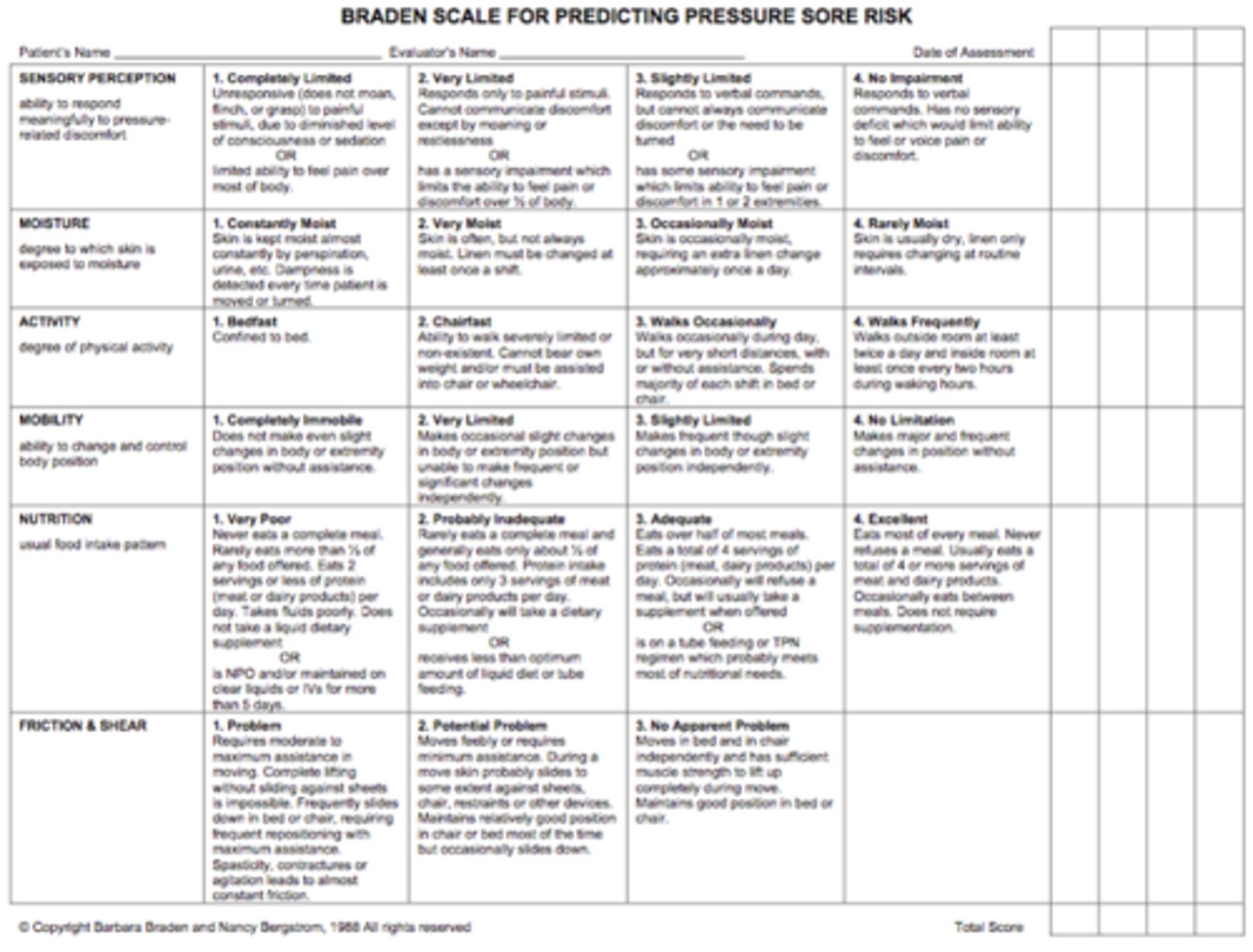
Braden Scale
Pressure ulcers
lower the number, higher the risk
4-23
less than 17 = risk for pressure ulcers
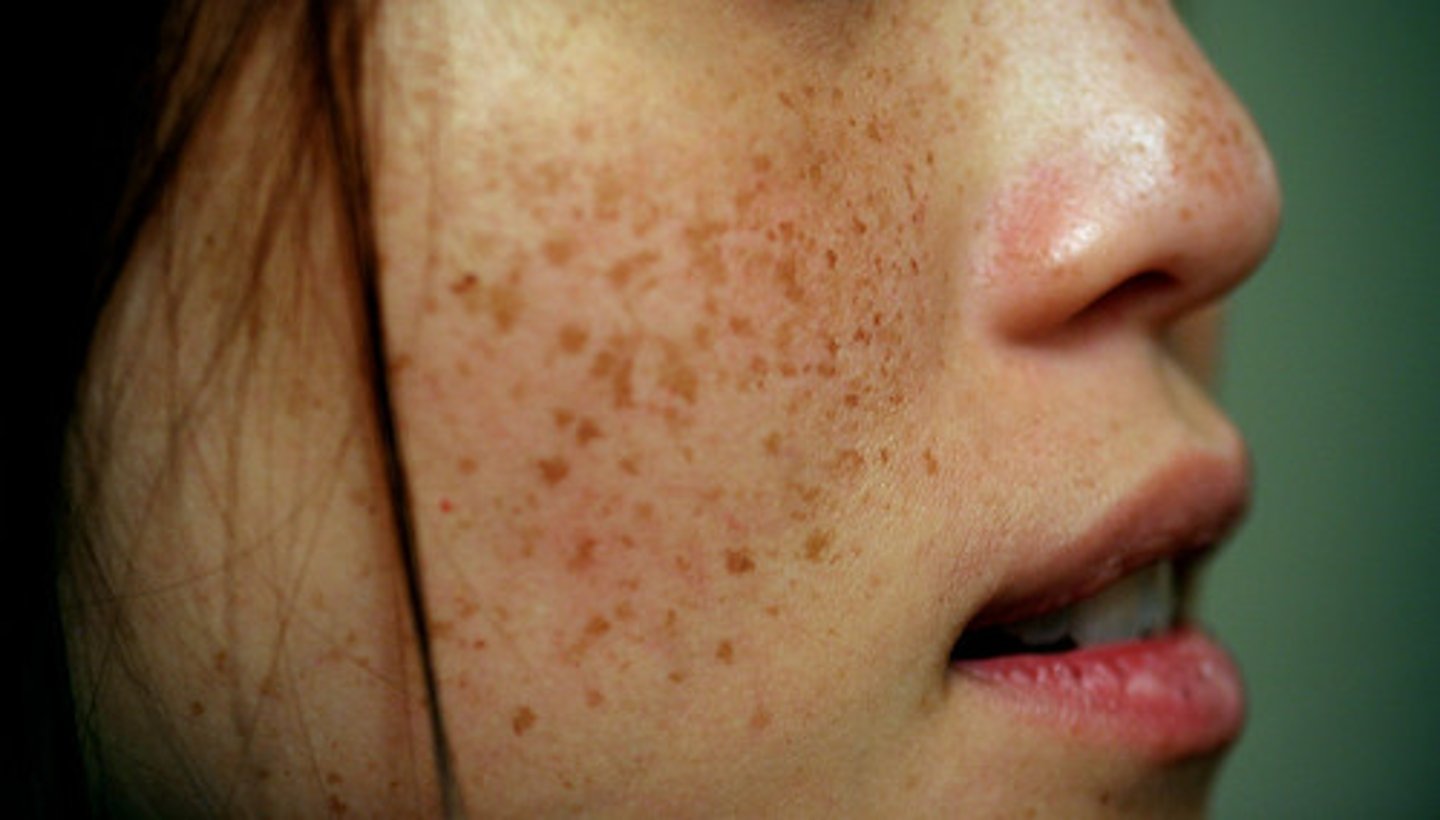
non-palpable lesion (macule)
flat and colored (freckle, petechiae, ecchymosis)
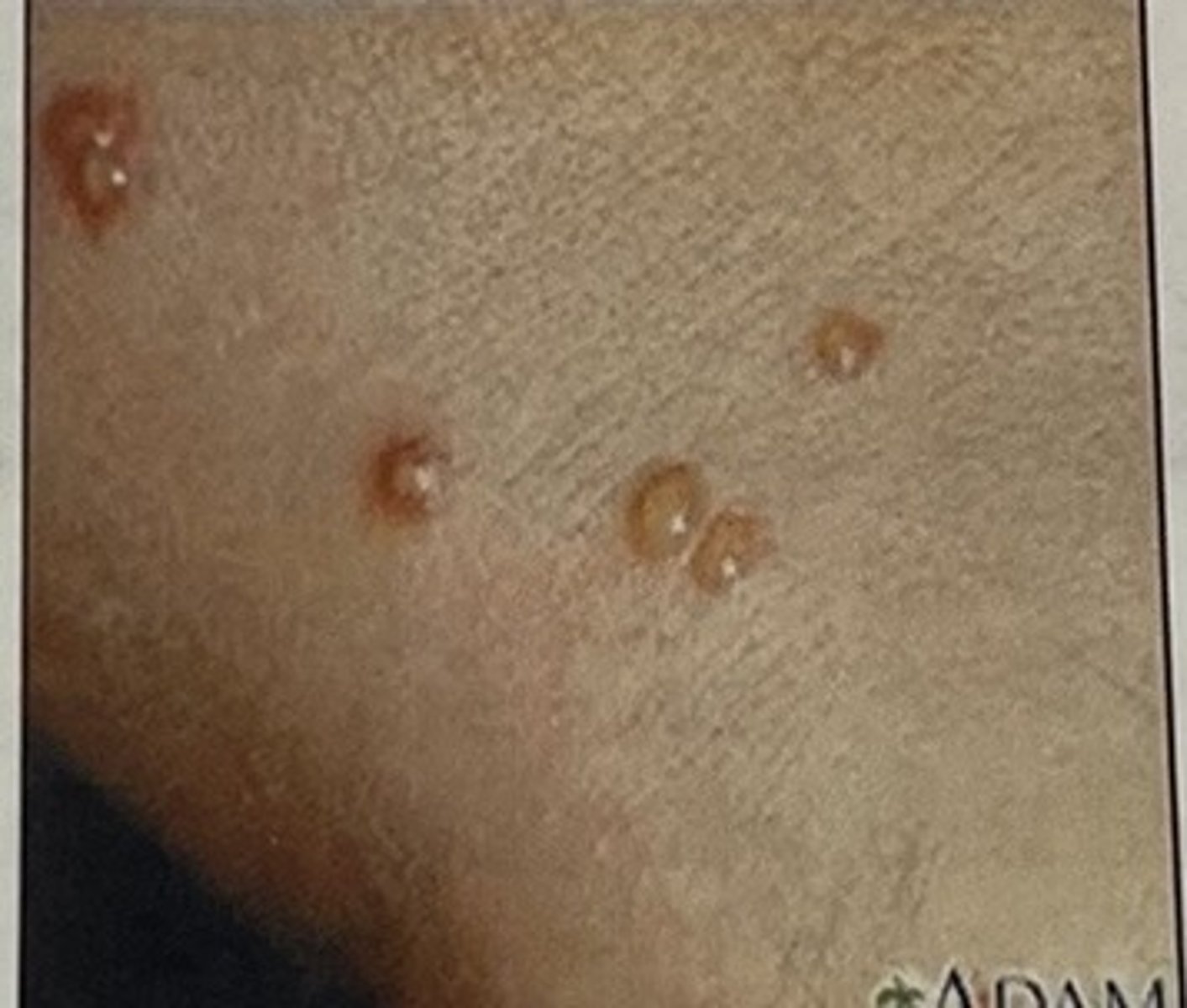
Palpable lesions with fluid (bulla/vesicle)
elevated and filled with fluid (blister)
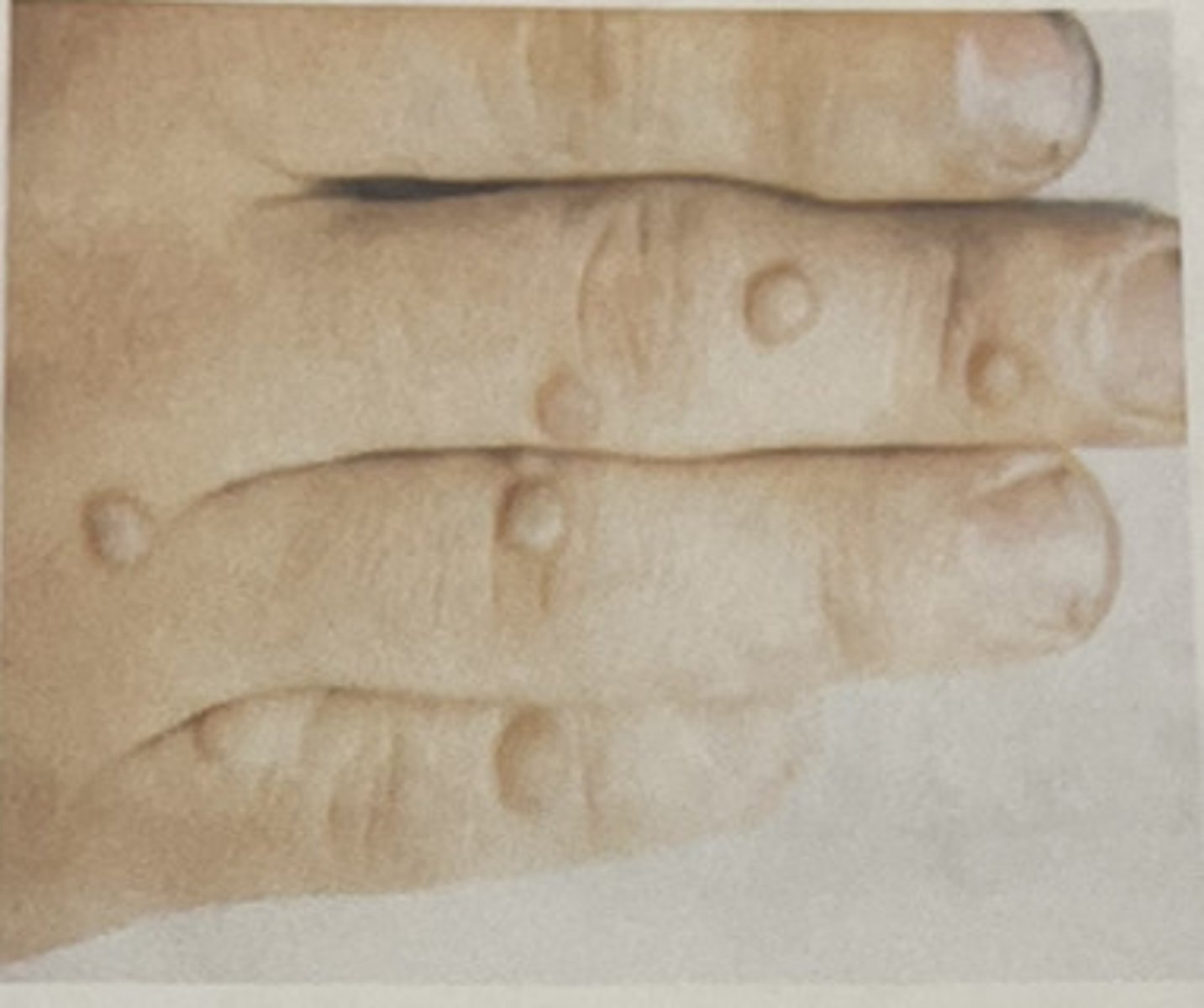
palpable lesions (papule)
elevated and superficial (wart)
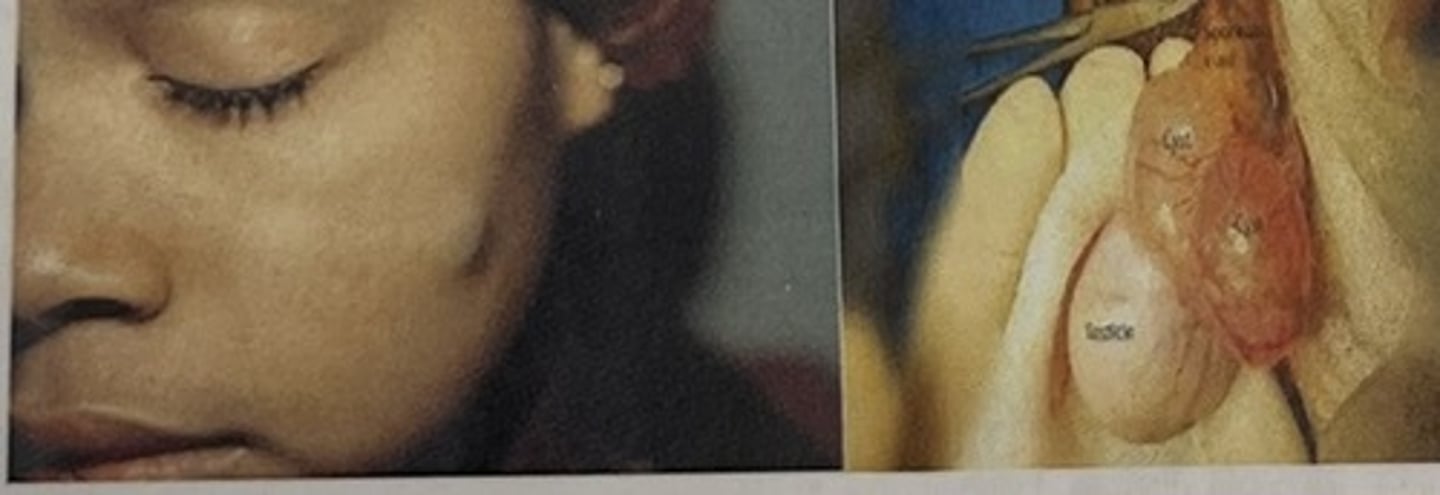
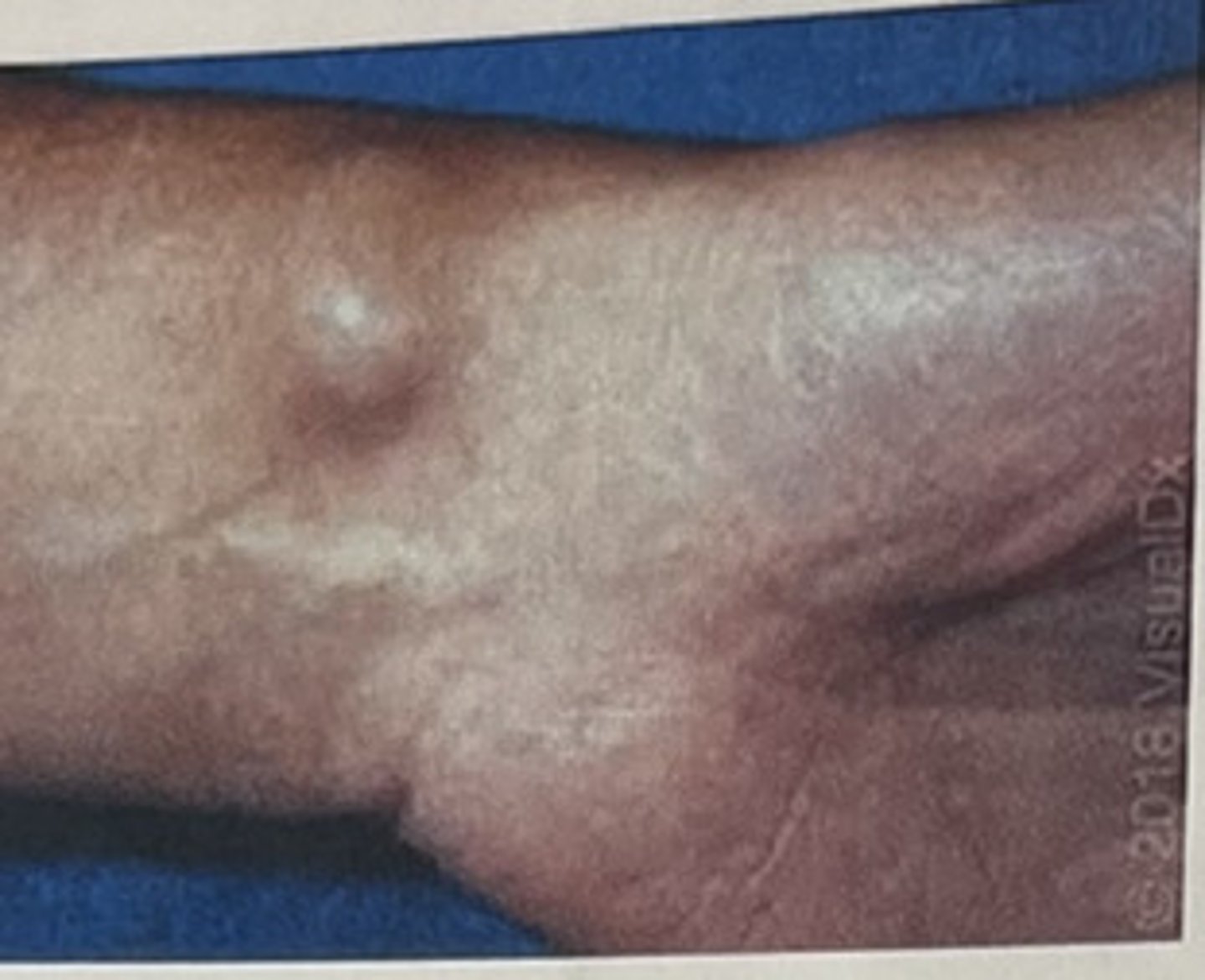
cyst
Encapsulated fluid-filled or semi-solid mass (epidermoid cyst)

tumor (nodule)
elevated and firm, has the dimension of depth (lipoma)
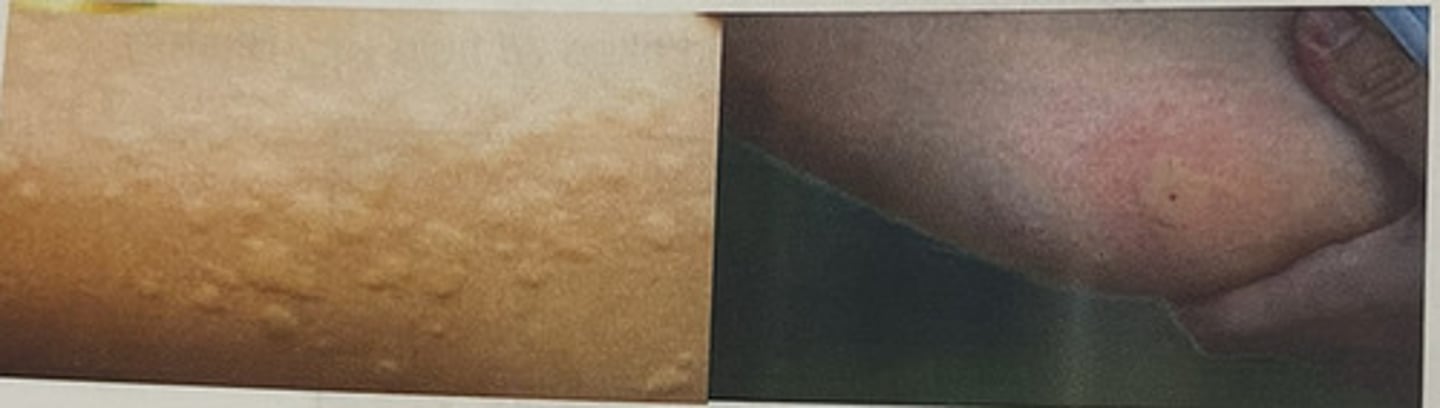
wheal
A localized area of edema (insect bite/hives)

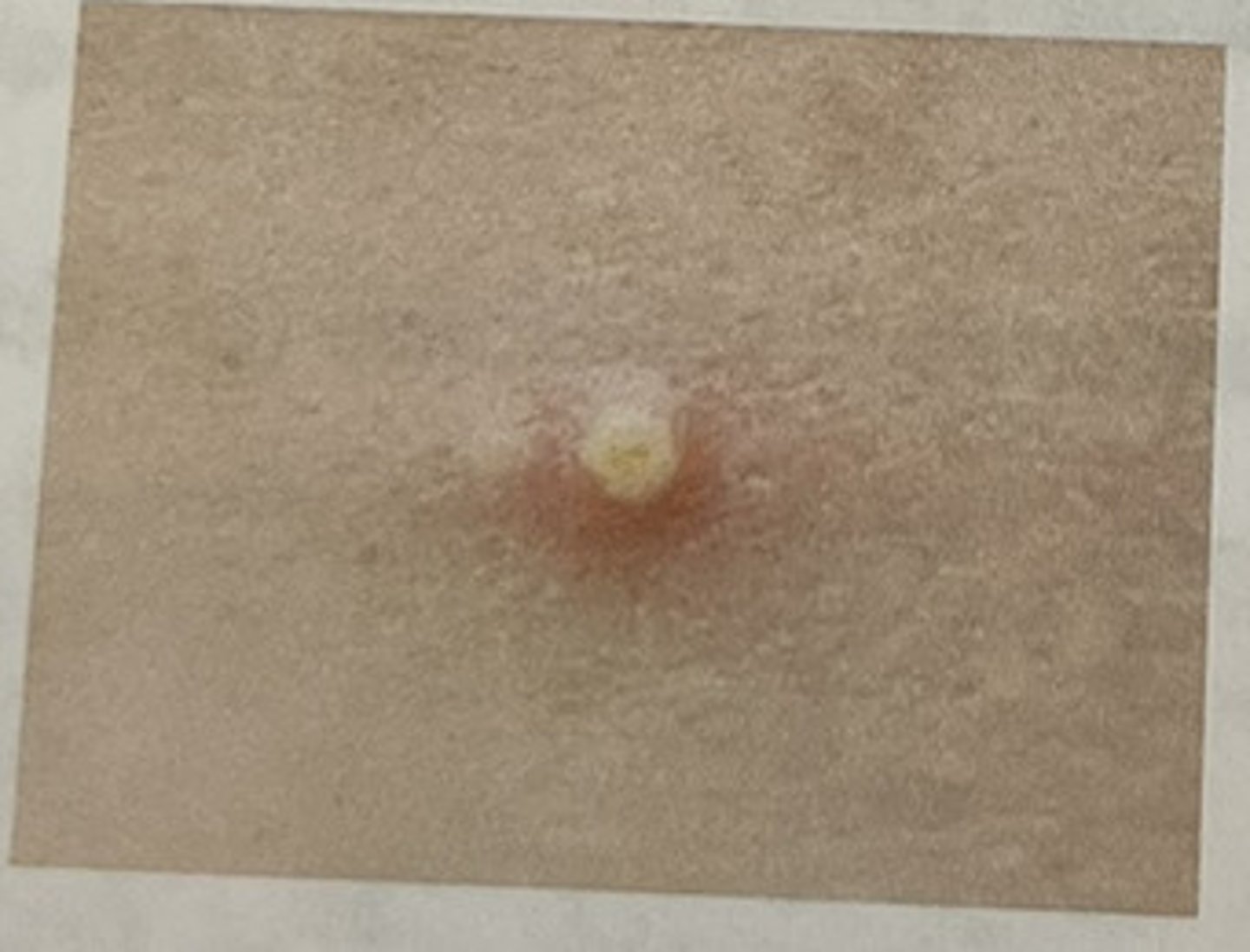
pustule
elevated and filled with pus (acne)
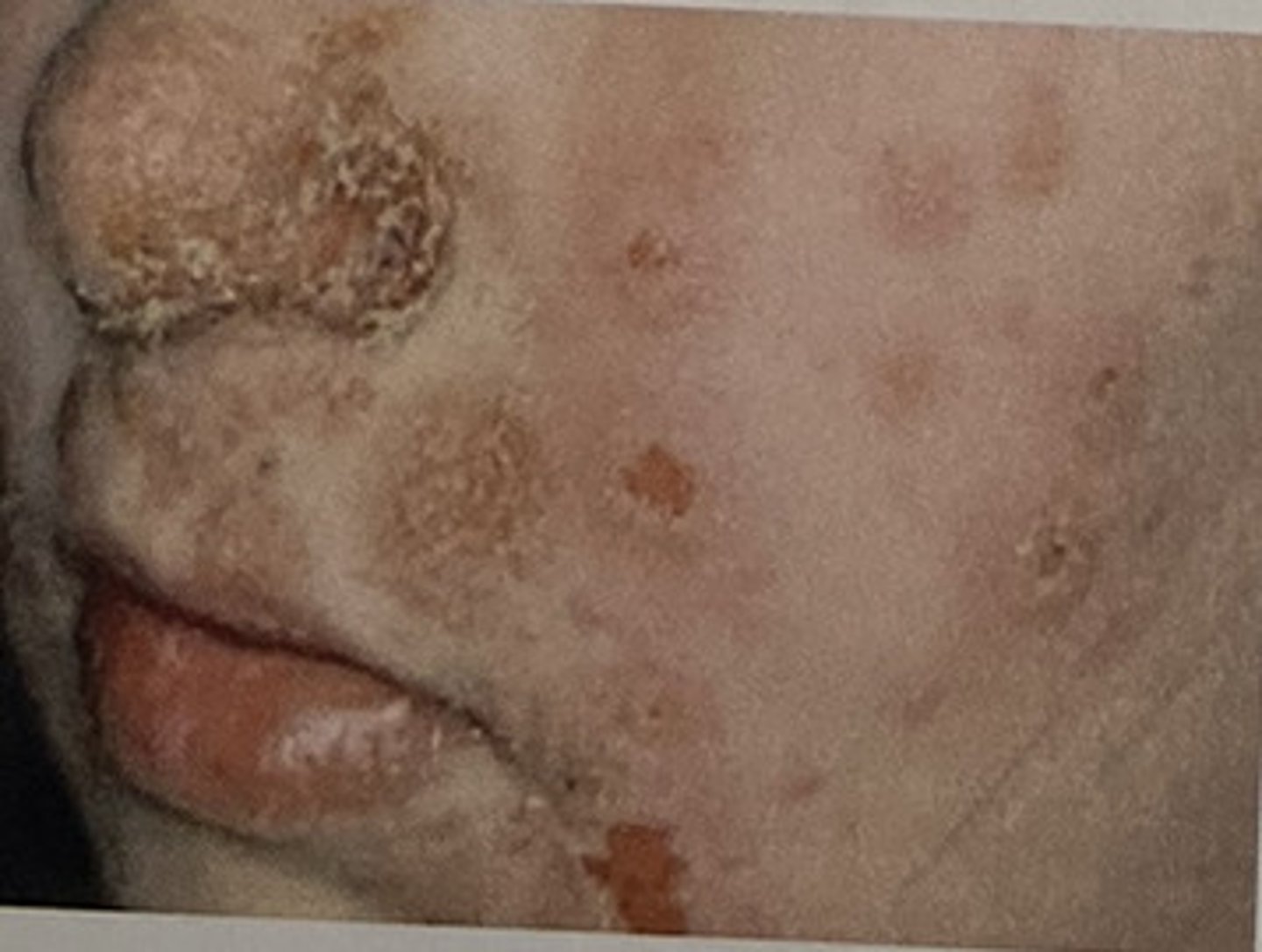
crust
dried pus or blood
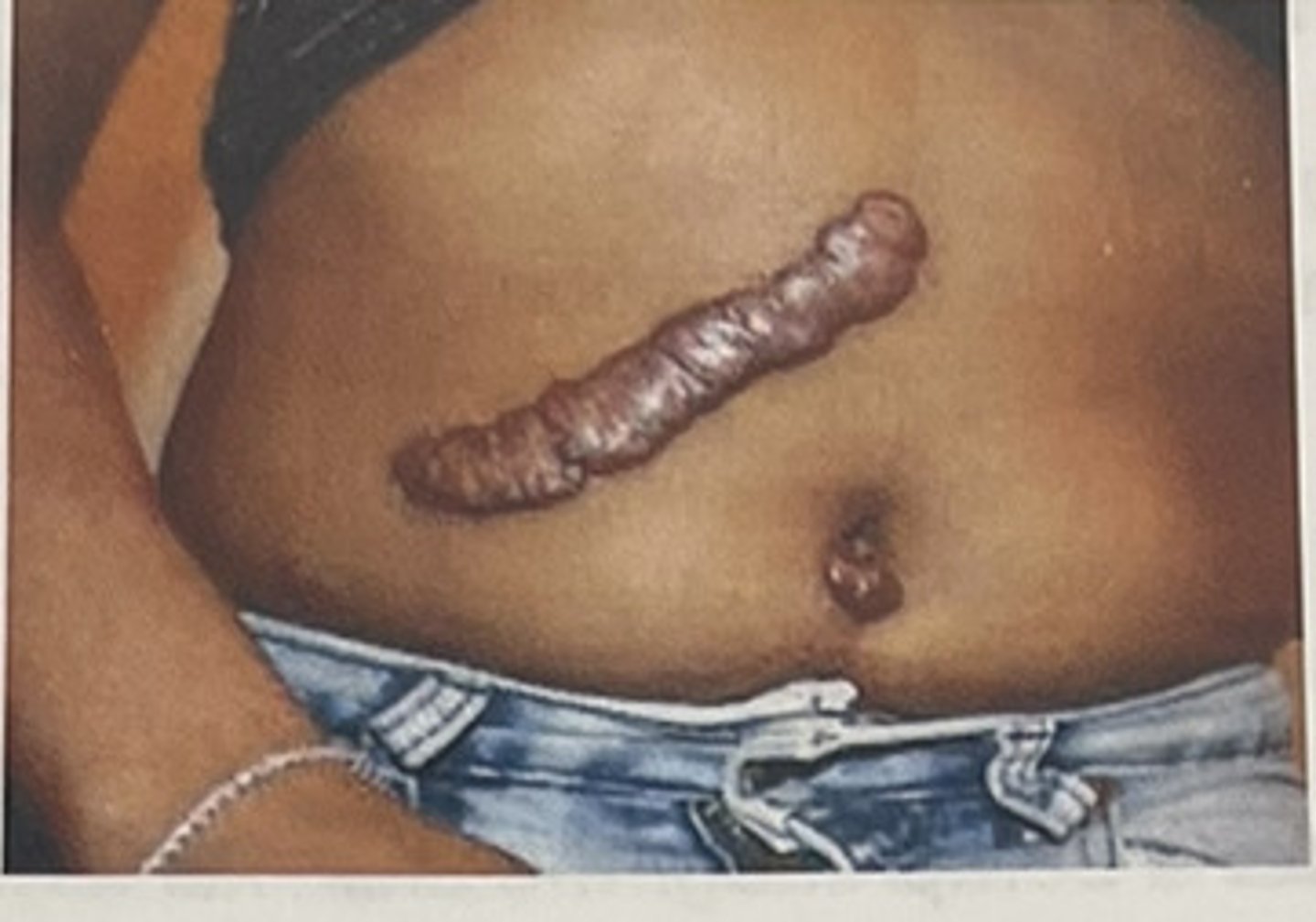
keloid
hypertrophied scar
geriatric variations in the skin
thinning epithelium
wrinkles, decreased turgor, and elasticity
dry, itchy skin due to decrease in elasticity of eccrine and sebaceous glands
prominent veins due to thinning epithelium
Seborrheic (Senile) Keratosis
tan or black macular papular-lesions on neck, chest or back)
senile lentigines
liver spots/ age spots: flat brown maculae on hands, arms, neck, and face
cherry angiomas
small, round, red elevated spots
senile purpura
vivid purple patches
acrochordons
soft, light pink to brown skin tags
geriatric variations in the hair
- Loss of pigment; fine, brittle texture
- Alopecia, especially in men; sparse body hair
- Coarse facial hair, especially in women
- Decreased axillary, pubic, and extremity hair
geriatric variations in the nails
-thickened, yellow, brittle nails
-ingrown toenails
pallor (cultural variations)
-dark skin: loss of underlying red tones
-brown skin: appears yellow brown
-black skin: appears ashen grey
-light skin: absence of underlying tones, skin turns white
erythema (cultural variations)
-dark skin: increased temp to palpation
-light skin: redness
ecchymosis (cultural variations)
-dark skin: red to purple, dark brown, or black bruise and area may be tender to touch. Look for a bump under the skin As it heals may turn yellow, brown, green.
-light skin: black and blue bruise. As it heals may turn yellow, brown, green.
cyanosis (cultural variations)
-dark skin: lips and tongue ashen gray
-light skin: bluish tone
jaundice (cultural variations)
-dark skin: yellow color in sclera, oral mucus membranes hard and soft palates, palms and soles
-light skin: pale yellow to pumpkin generalize color
What are some risk factors related to pressure injuries?
-prolonged pressure due to immobility and decreased activity
-moisture on skin which could be related to diaphoresis or incontinence
-Risks: malnutrition, EtOH, tobacco use, dehydration, lack of sensory perception
-medical history of diabetes melitus (DM), peripheral vascular disease (PVD), cerebral vascular accident (CVA), spinal cord injury (SCI), and corticosteroid use.
What are some signs and symptoms of pressure injuries?
-an area of breakdown or lesions on the skin
-4 stages that reflect the amount of tissue injury and the degree of underlying structural damage
Medical treatment for pressure injuries?
-diagnosis (nursing assessment)
-possible culture of wound to determine presence of type of organisms present in wound
-supporting tests: hemoglobin/hematocrit levels, WBC, transferring levels, albumin and total protein levels, skin biopsy, blood culture
-may need surgical interventions to mechanically debride, may need skin/muscle flaps if very deep (may need drains)
-wound care
What are risk factors for skin cancer?
Repeated, intermittent sun exposure with sunburn beginning at early age; tanning booths; radiation;
genetics-fair skin, light eyes; immunosuppression; HPV; chemicals; actinic keratosis
change in mole/ long term skin irritation
What is primary prevention for skin cancer?
-avoid sun
-use sunscreen
-avoid radiation
What is secondary prevention for skin cancer?
-self assessment
-screen for skin cancer
-chemo prevention
What are example outcomes for impaired skin integrity?
-patient will participate in prevention measures throughout hospitalization
-patient will display wound healing by discharge
-patient will have no complications of wound healing throughout stay
-patient will return demonstrate the prescribed wound care by tomorrow
What are some interventions to assess for impaired skin integrity?
-inspect skin, particularly over bony prominences
-palpate areas on skin that show signs of breakdown
-assess location, size, depth, color of wound bed (pink, red, yellow, brown, black)
-determine location, size, depth, color of wound bed (pink, red, yellow, brown, black)
-determine drainage type, color, odor, consistency, amt
-assess peri-wound for redness, edema, indurations, tenderness, and breakdown of healed tissues to identify signs and symptoms of infection
-determine alterations in mobility, continence, self care
-review history of past skin problems
-evaluate skin care regimen/hygiene
-review lab results (H&H, BG albumin) and collect and send wound culture
What are some interventions to promote healthy/intact skin?
-handle gently
-clean/hygiene, peri care
-keep sheets dry and without wrinkles
-turn q2h
-pressure reducing devices (eggcrate, air mattress, special bed, gel pads, heel rolls)
-be careful w tape/no hot or cold; encourage mobilization
-provide optimum nutrition, protein to provide positive nitrogen balance, and vitamins ACDE
-wound care
What are some intervention for health promotion/wellness?
-prevention
-encourage regular exercise
-smoking abstinence or cessation
-keep nails short
-avoid sun
-proper fit of clothes and shoes
What are the mechanics of breathing?
Respiration
Ventilation
Inspiration
Expiration
What happens during inhalation and exhalation?
-the diaphragm presses the abdominal organs downward an forward (inhalation)
-the diaphragm rises an recoils to the resting position (exhalation)
What assessment techniques will the nurse use to assess the respiratory system?
1- Interview
2- Inspection
3- Palpation
4- Auscultation
What subjective data specific to the respiratory system should the nurse collect?
Reason for visit: what brought you in today?
History of Present Health Concern: difficulty breathing, shortness of breath (SOB), snoring
chest pain (COLDSPA)
cough (productive or not), sputum (color, amount, thick/thin)
Personal Health: allergies, asthma, bronchitis, emphysema, TB, lung cancer
Family History: allergies, asthma, lung cancer
Lifestyle and Health Practices: smoking (calculate pack year), travel to high risk areas for SARS or COVID-19, environmental exposure to asbestos or inhalants (chemicals, spray paint), sedentary lifestyle
How does the nurse calculate pack year?
# of packs per day x # of years smoked