Pre-Calc Final
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Rectangular coordinate system
intersecting two perpendicular lines in a plane
Origin
the point of intersection
Horizontal axis
the horizontal line (the x-axis)
Vertical axis
the vertical line (the y-axis)
Quadrants
four divisions created by axes
Ordered pair
a pair of numbers (x, y) that represent a point in a coordinate plane
Midpoint
the point that is exactly halfway between two points in a coordinate plane, calculated as the average of the x-coordinates and y-coordinates.
Graph
a visual representation of data or mathematical functions plotted on a coordinate plane.
Circle
the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point called the center
Center
of a circle, the fixed point from which all points on the circle are equidistant.
Radius
the fixed distance from any point of the circle to the center is called the radius, which is half the diameter of the circle.
Domain
the set of x values in the ordered pairs, that a function can take as input.
Range
the set of y values in the ordered pairs, that a function can produce as output.
Function
a relationship between two quantities, where each input has exactly one output.
Scatter plot
a visual representation of a set of points
Regression line
the curve that models a set of data to show the trend in the data points.
Linear Function/Equation
an equation of the form y = f(x) = mx+b, where m and b are constants
Constant function
a function that always goes to the same value, regardless of the input. modeled by f(x) = b
Secant line
a line drawn through two points on a nonlinear curve
Average rate of change
the slope of the secant line aka the points (change in y / change in x)
Parallel lines
two distinct nonvertical lines when their slopes are equal
Perpendicular lines
two lines that their slopes are negative reciprocals (m and -1/m)
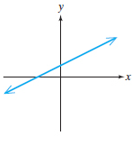
Linear functions
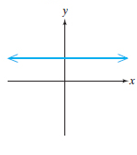
Constant functions
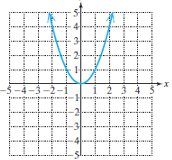
Quadratic function
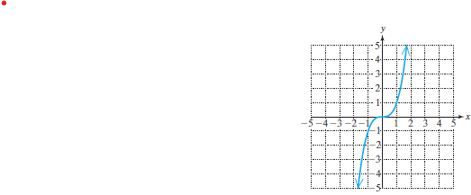
Cube function
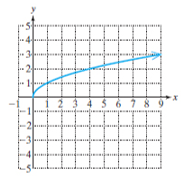
Square root function
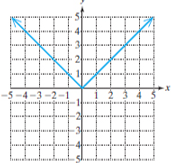
Absolute value function
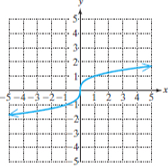
Cube root function
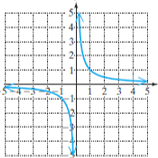
Reciprocal function
Symmetry
remain unchanged under reflections
Even function
if f(-x) = -f(x) for all values of x, and the graph of f is symmetric about the y-axis
Odd function
if f(-x) = -f(x) for all values of x, and the graph of f is symmetric about the origin
Piecewise-defined function
a function in which we define each “piece” on a restricted domain
Continuous
the graph of a function that has no “gaps”
Discontinuous
the graph of a function that has a gap at x=a
Increasing function
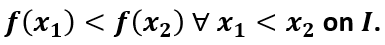
Decreasing function
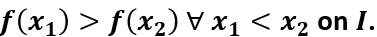
Composition
the function f(g(x)) is the composition of f and g
Quadratic Functions
second degree formulas
Axis of symmetry
graph is symmetric with respect to the vertical line through the vertex
Vertex
key point on a graph or function that represents the maximum or minimum value of the function
Zeros
the values of x for which f(x) = 0, or the x-intercepts
Quadratic formula
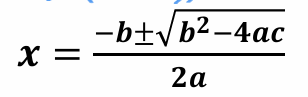
Polynomial function
a sum of power function whose exponents are nonnegative integers
Degree
n, a non-negative integer and it cannot = 0
Coefficients
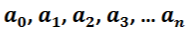
Constant term
the constant coefficient
Leading coefficient
the coefficient of the highest-powered term
Leading term
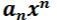
End behavior
a description of what happens as x becomes large in the negative and in the positive direction
Rational functions
a function of the form —— where p and q are polynomial functions
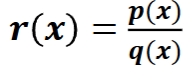
Horizontal asymptote
the line y=k of f if the function values get arbitrarily close to k as x gets large (either + or - or both)
Vertical asymptote
the graph of f has one at x=a if
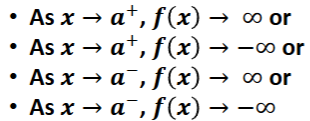
One-to-one function
a function is if for a and b in the domain of f, a doesn’t equal b, and f(a) doesn’t equal f(b)
Horizontal line test
If there is a horizontal line that intersects a functions graph in more than one point, then the function is not one-to-one.
Inverse functions
if y = f(x) is a one-to-one function then it has one, invertible
Invertible
capable of being turned upside down, reversed in position, or subjected to inversion
Exponential function
represent change at a constant percent rate and y = f(x) has the standard form:
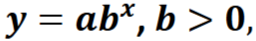
Exponential growth
r > 0 and b > 1
Exponential decay
r < 0 and 0 < b < 1
Natural base
base e
Compound interest
interest on interest
Logarithmic function
for b > 0 and for when b doesn’t equal 1, the log function is
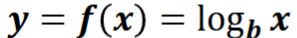
Logarithms
functions for finding exponents, y
Base
b
Argument
x
Angle
formed by rotating a ray about its endpoint
Standard position
its vertex is at the origin in the xy-plane, and its initial side is the positive x-axis
Measure
the direction and the amount of rotation from the initial side to the terminal side
Degree
one unit with which to measure an angle
Radian
another type of angular measure that is better suited for applications in trig and calc
Arc length
s
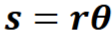
Unit circle
is the circle of radius 1 centered at the origin with the equation x² + y² = 1
Trigonometric Functions
sin, cos, tan, csc, sec, cot
Identities
relationships of trig functions with each other; reciprocal identities, quotient identities, Pythagorean identities
Periodic
if there is a positive number p such that f(t+p) = f(t) for every t
Period
the smallest number p that makes f(t+p) = f(t)
Amplitude
|A|, largest value the function obtains
Phase shift
C/B, shifting cycles to the right