Introduction to Veterinary Science by James B Lawhead
1/603
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
604 Terms
Chapter 1
Basic Cell Biology
Proteins make up ___% of the dry weight in animals
50
How many amino acids are used to make proteins?
22
How do nucleic acids do?
Provide plans for the differing construction of proteins
What are enzymes?
Protein molecules that speed up chemical reactions in the body
What are infection-fighting proteins called?
antibodies
Metabolism
all reactions conducted in cells
Anabolism
reactions in which smaller molecules are combined into larger ones (joining of amino acids to form proteins)
Catabolism
When large molecules are broken down into smaller ones (Glycogen breaking down to release energy)
What fluid surrounds all living cells and supplies the cells with all the products necessary for function?
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
Where is ECF derived from?
bloodW
When transporting molecules across a semi-permeable membrane, what type of transport requires the cell to burn energy and use enzymes to aid the process?
active transport
Endocytosis
When the cell membrane wraps around the particle, pinches off, and moves into the cytoplasm as a vacuole. Lysosomes then join with the vacuole, providing the enzymes necessary to break down the particle. The smaller fragments are then released into the cell.
Exocytosis
A membrane-bound sac containing the protein joins with the cell membrane and releases it into the ECF.
What does uncontrolled mitosis result in?
Cancer
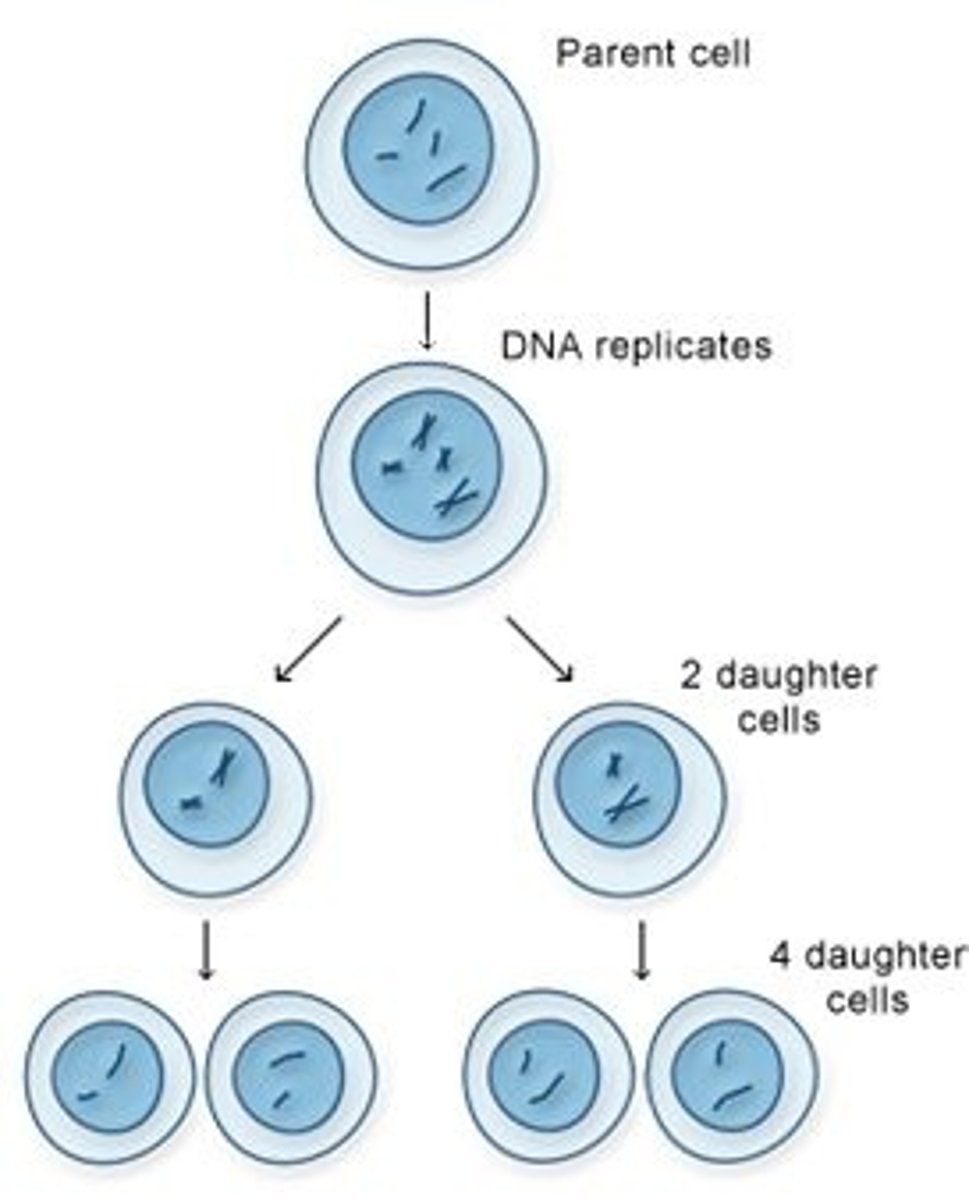
Mitosis
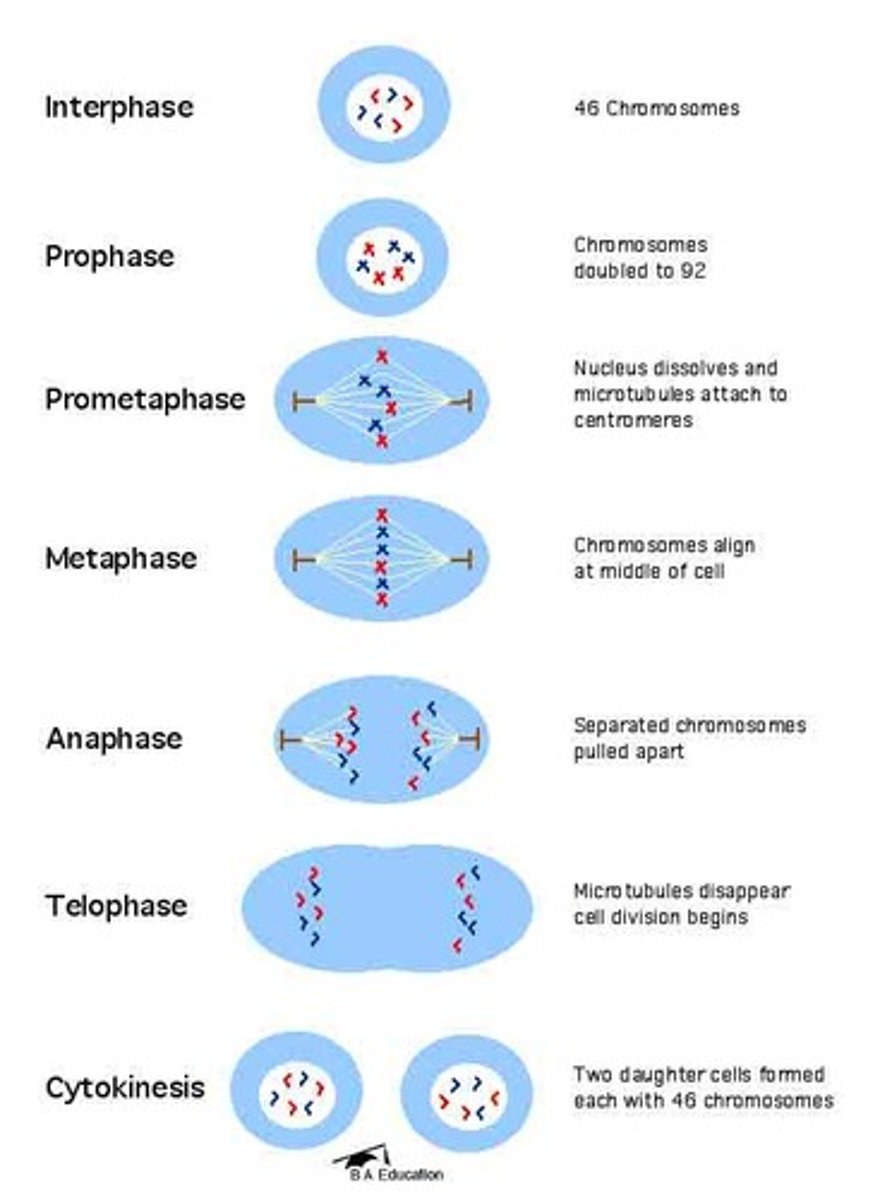
Meiosis
Homologue
Chromosomes come in pairs, and each member of the pair is called this.
What are the two categories of tumors?
benign and malignant
What are the five mechanisms of cellular exchange?
1. Diffusion
2. Osmosis
3. Active Transport
4. Endocytosis
5. Exocytosis
What are the five stages of mitosis in order?
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Chapter 2
Tissue Types and Functions
What are the four basic tissue types?
epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve
Where are epithelial tissues located?
Cells packed together in sheets that line the body's surface and openings, as well as tubes in the body such as blood vessels and the heart. These tissues also cover all openings of the intestinal, reproductive, and urinary tracts
What are the purpose of epithelial tissues?
1. Offers defense against trauma, UV light, bacteria and extreme temperatures (skin)
2. Produce variety of secretions (tears, saliva, mucus, sweat, urine, and milk)
3. Absorb materials
Does the epithelium have a direct blood supply?
No, the connective tissue layer directly below every epithelium provides nutrients and removes wastes for it
Integument
skin
What protects the integument from damaging UV rays and malignant melanoma tumors?
skin pigment
Terms to classify epithelial tissues based on number of layers?
1. Simple (one cell layer)
2. Stratified (multiple layers)
3. Transitional (multiple layers but the shape of the cells can change)
Terms to classify epithelial tissues based on shape?
1. squamous (very flat)
2. cuboidal (cube-shaped)
3. columnar (more tall than wide)
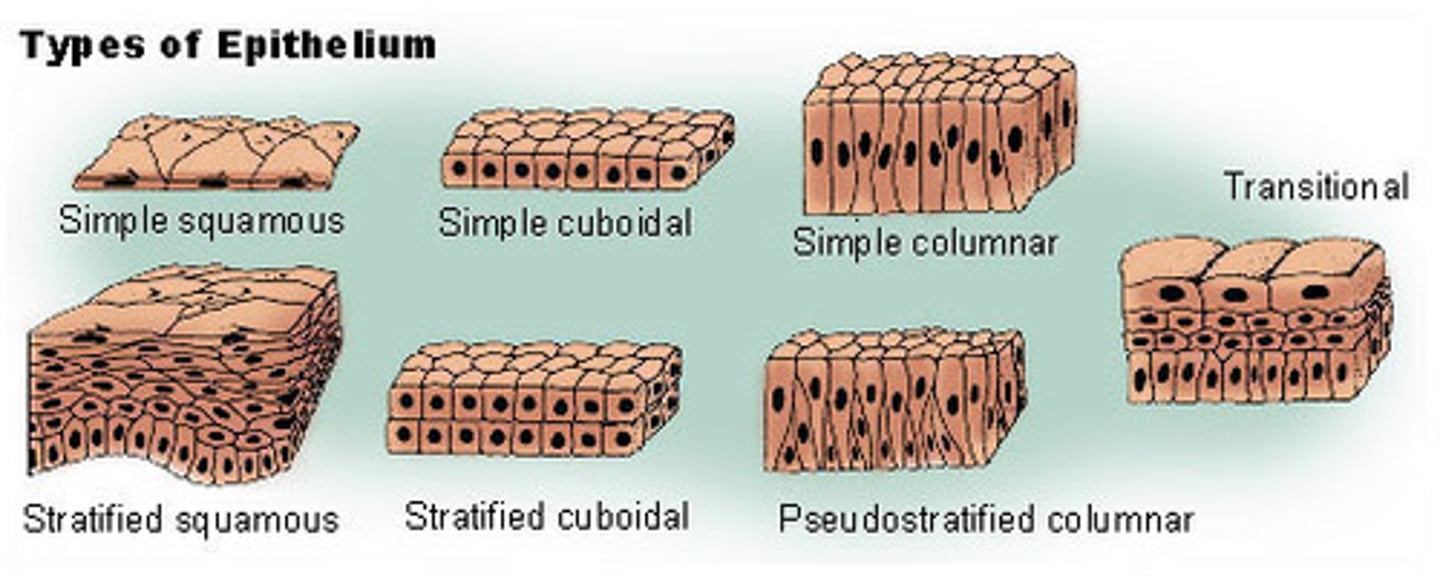
What classification of epithelial tissue lines blood vessels that allows for transfer of fluids, nutrients, gases, and wastes?
simple squamous
Where can you find simple cuboidal epithelial tissue?
Tubules of the kidney (often associated with secretion, absorption, or transport)
Where can you find simple columnar epithelial tissue?
Stomach and intestines (often associated with secretion, absorption)
Where can you find all types of epithelial tissue?
Glands and ducts
What is skin classified as?
Stratified squamous epithelium
What is the basal layer?
Where epithelial cells originate
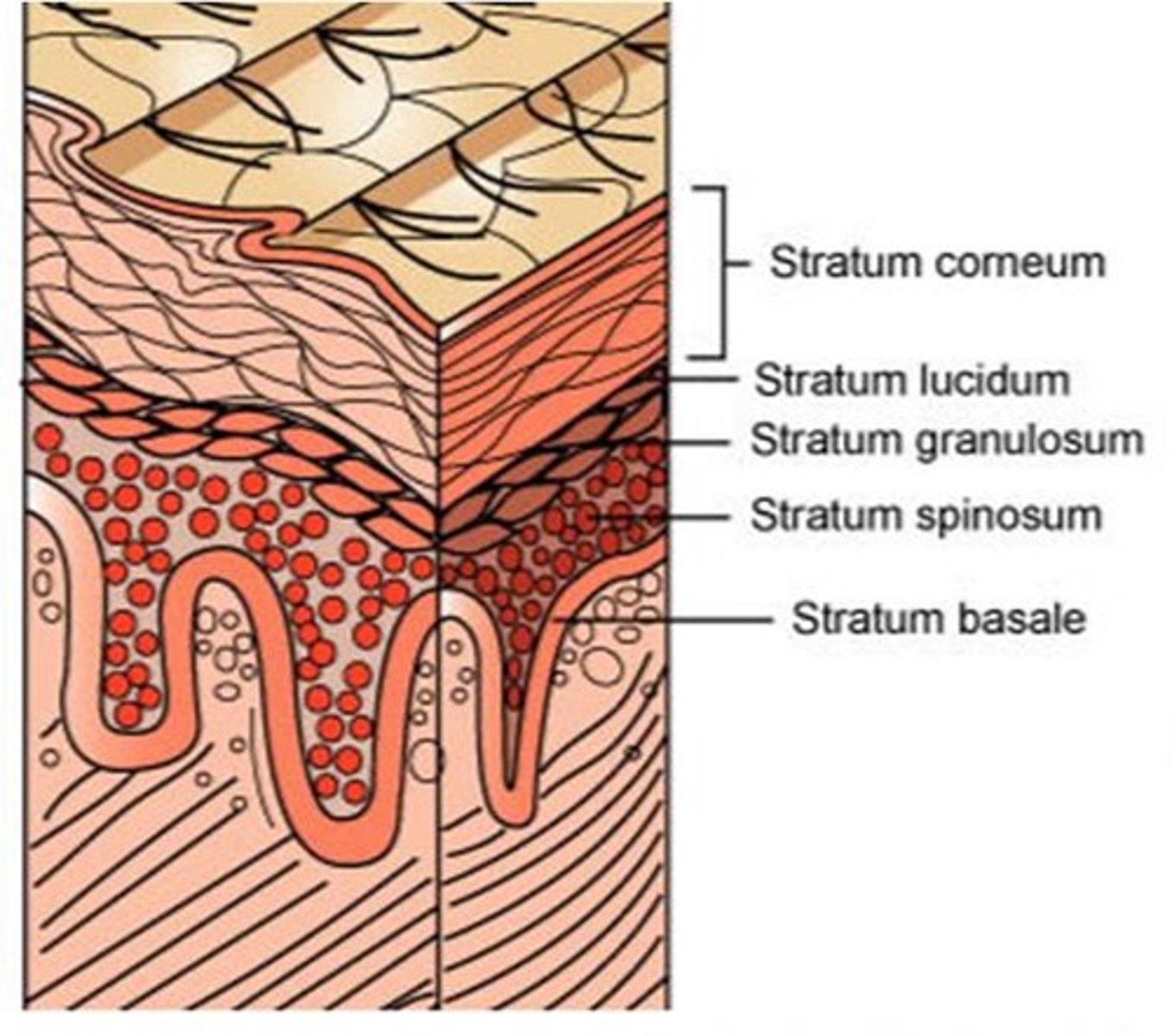
Hypodermis
consists mainly of subcutaneous fat that allows for thermal insulation and binds skin to the rest of the body
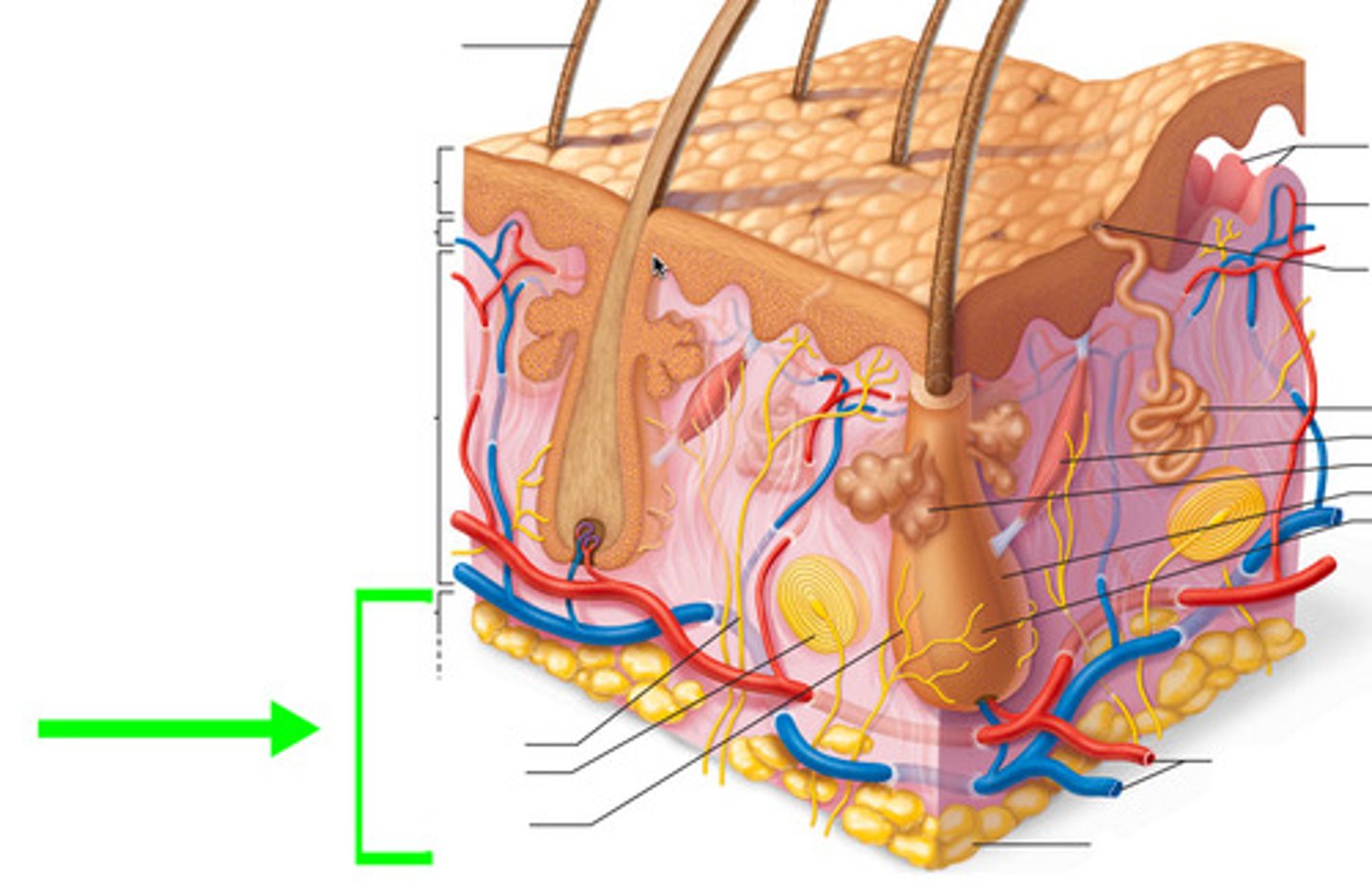
What does the arrector pili muscle do?
When contracted, makes the hair stand upright
Where do hair follicles originate?
dermis layer
What specialized protein is deposited in the cells for claws and hooves to give it the typical hardness and durability?
keratin
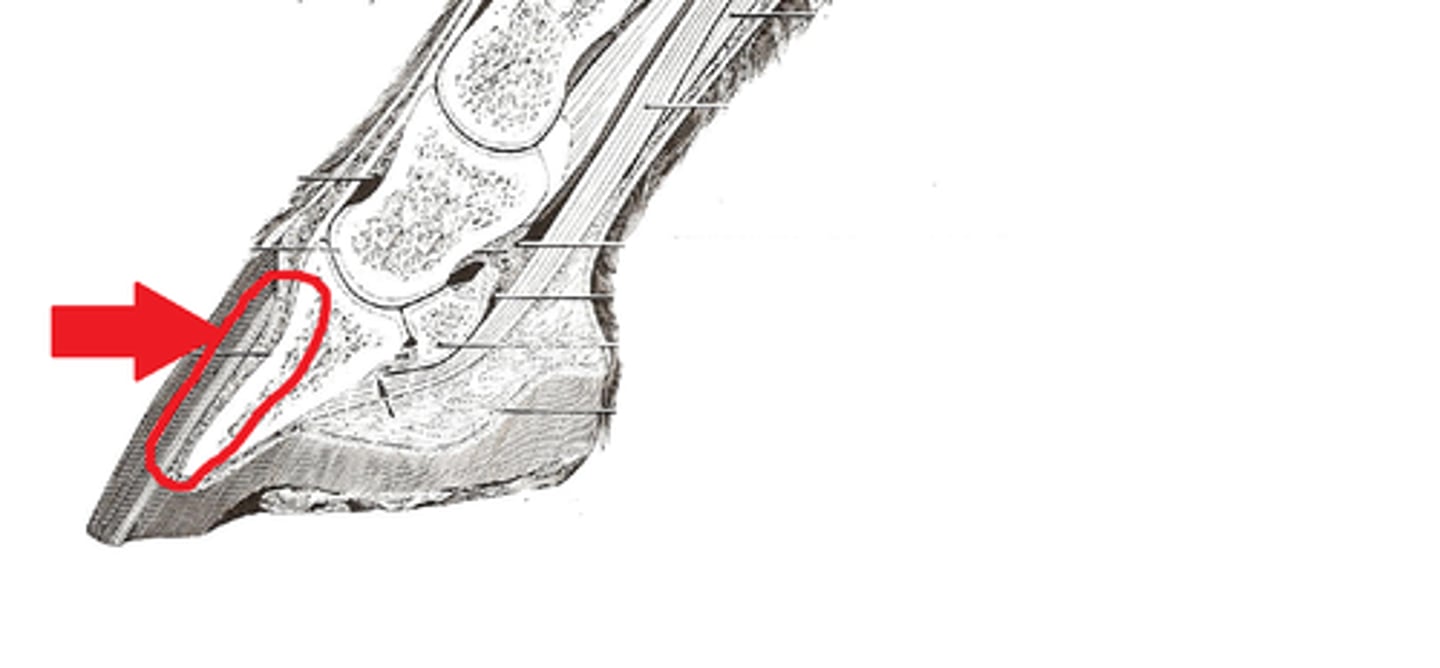
What surrounds the coffin bone that nourishes and supports the hoof with a rich blood supply and connective tissue?
Laminar corium
What is the primary function of connective tissues?
1. Connective tissues connect one organ or tissue to another
2. Provide support and protection
Tendons
connect muscles to bones
Matrix
The material (or tissue) in animal or plant cells, in which more specialized structures are embedded. The internal structure of connective tissues is an extracellular matrix.
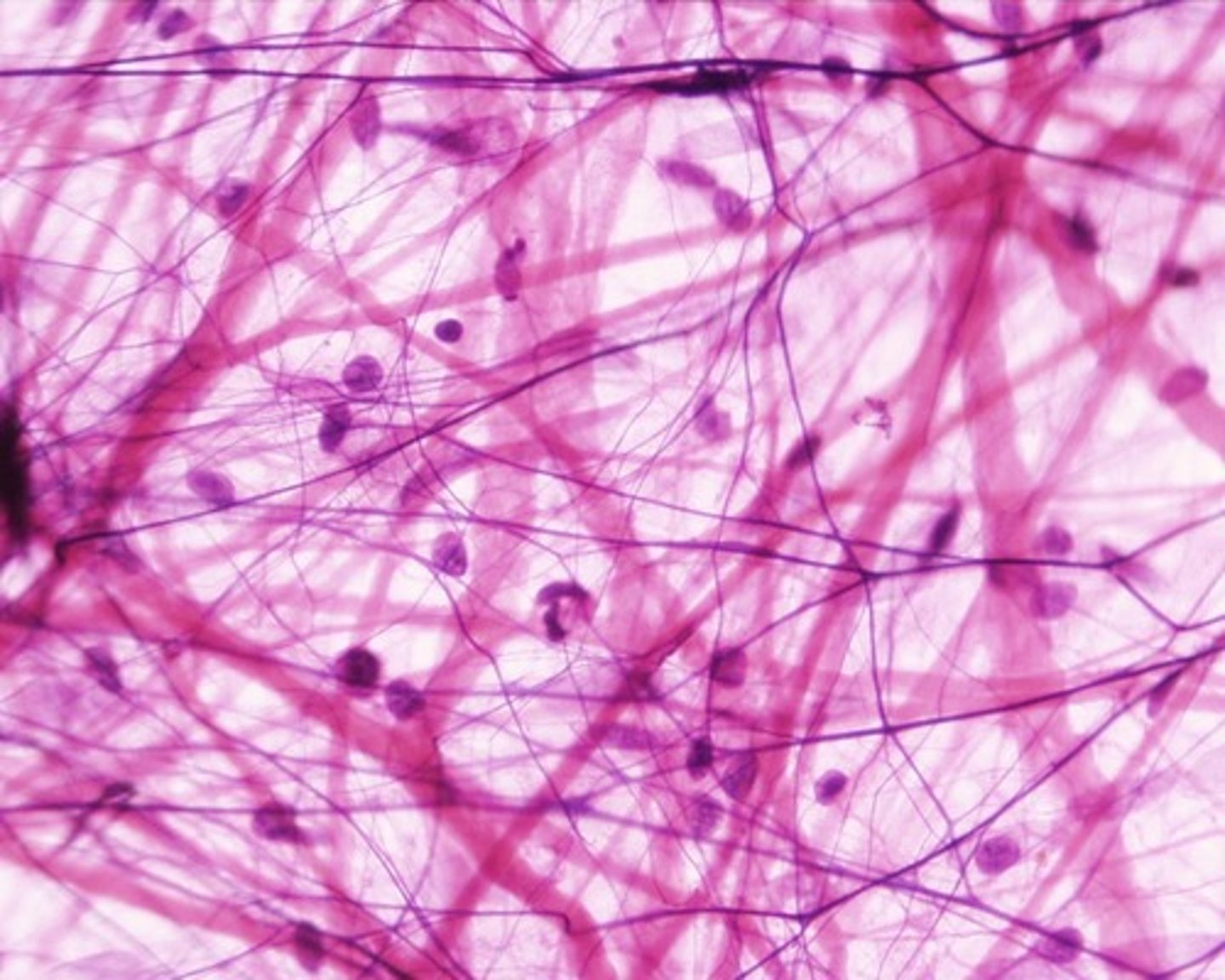
The matrix in tendons is mainly composed of what protein?
collagen
Ligaments
connects bones to bones
In addition to collagen, ligaments is composed of another protein called what?
elastin
What functions do collagen and elastin serve to connective tissues?
Collagen: provides strength
Elastin: ability to stretch and return
Provide five examples of connective tissues
1. Adipose tissue (fat)
2. Bone
3. Cartilage
4. Blood
Myofibers
Muscle cells that organize themselves in parallel rows
What is a striated muscle?
A muscle consists of thousands of muscle fibers
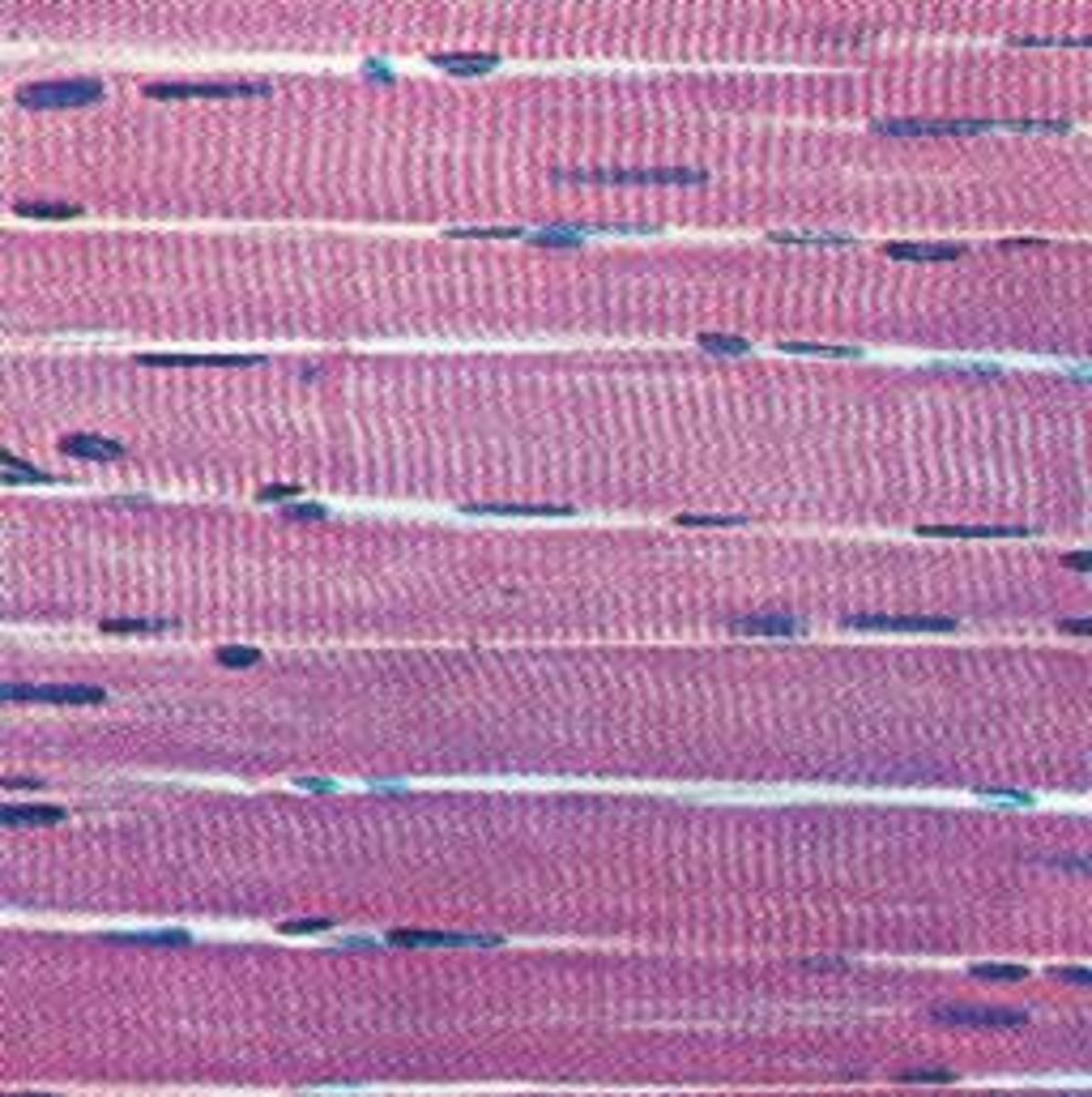
What allows a muscle fiber to contract?
Within the myofibril, there are many myofilaments made up of the proteins actin and myosin. During contraction, the actin and myosin filaments slide against each other. The filaments have small bridges between them that bind and release as they slide
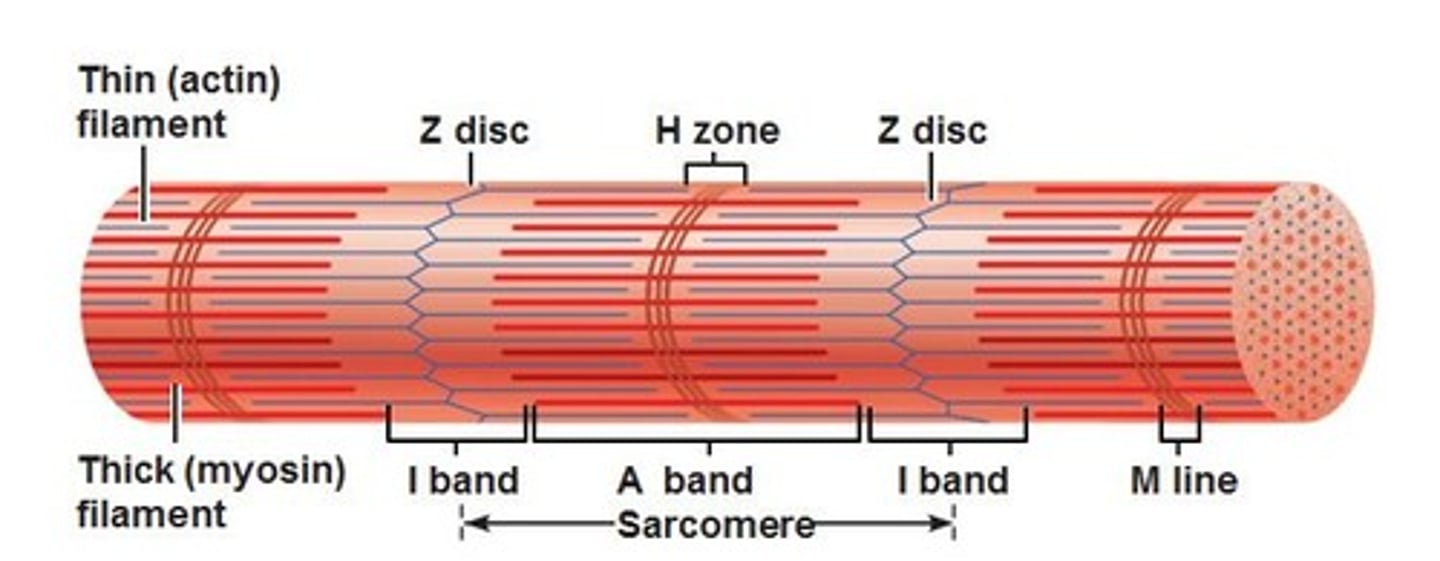
What stimulates the myofilaments to slide against each other?
The stimulation from a nerve cell causes calcium to be released from the endoplasmic reticulum that stimulates the muscle fibers to contract
When muscles are relaxed, what is being actively transported back to the endoplasmic reticulum
Calcium
Porcine stress syndrome (PSS)
Genetically transmitted disease in which calcium does not transport back to the endoplasmic reticulum, causing muscles no to relax normally
Rigor mortis
Muscle stiffness occurs after death because there is no supply of energy to pump calcium back into the endoplasmic reticulum
Hypocalcemia
(also known as milk fever) When calcium levels in the blood and muscles becomes too low. Typically occurs in dairy cows during calving season when calcium use increases dramatically for milk production. Cows become weak and are unable to stand.
Motor unit
Collection of the nerve cell and all the muscle fibers it stimulates
Sweeny
common name for shoulder atrophy (shrinkage or wasting) in the horse. The muscle atrophy is caused by damage to the suprascapular nerve in the shoulder
Does cardiac muscle or skeletal muscle have more mitochondria?
cardiac
What body system controls the action of smooth muscle?
Autonomic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
the part of the nervous system responsible for control of the bodily functions not consciously directed, such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes
Somatic nervous system
the part of the nervous system responsible for control of voluntary actions. Brain interprets sensory info, responds through signals to the voluntary muscles
The nervous system is divided into two parts:
1)Central nervous system - Brain & Spinal cord
2)Peripheral nervous system - Long nerve cells that link these cells to the body's various organs through openings in the spinal column
Neuron
Axon: carries nerve impulse
Synapse: Site of connection between two neurons
Dendrite: receives nerve impulse
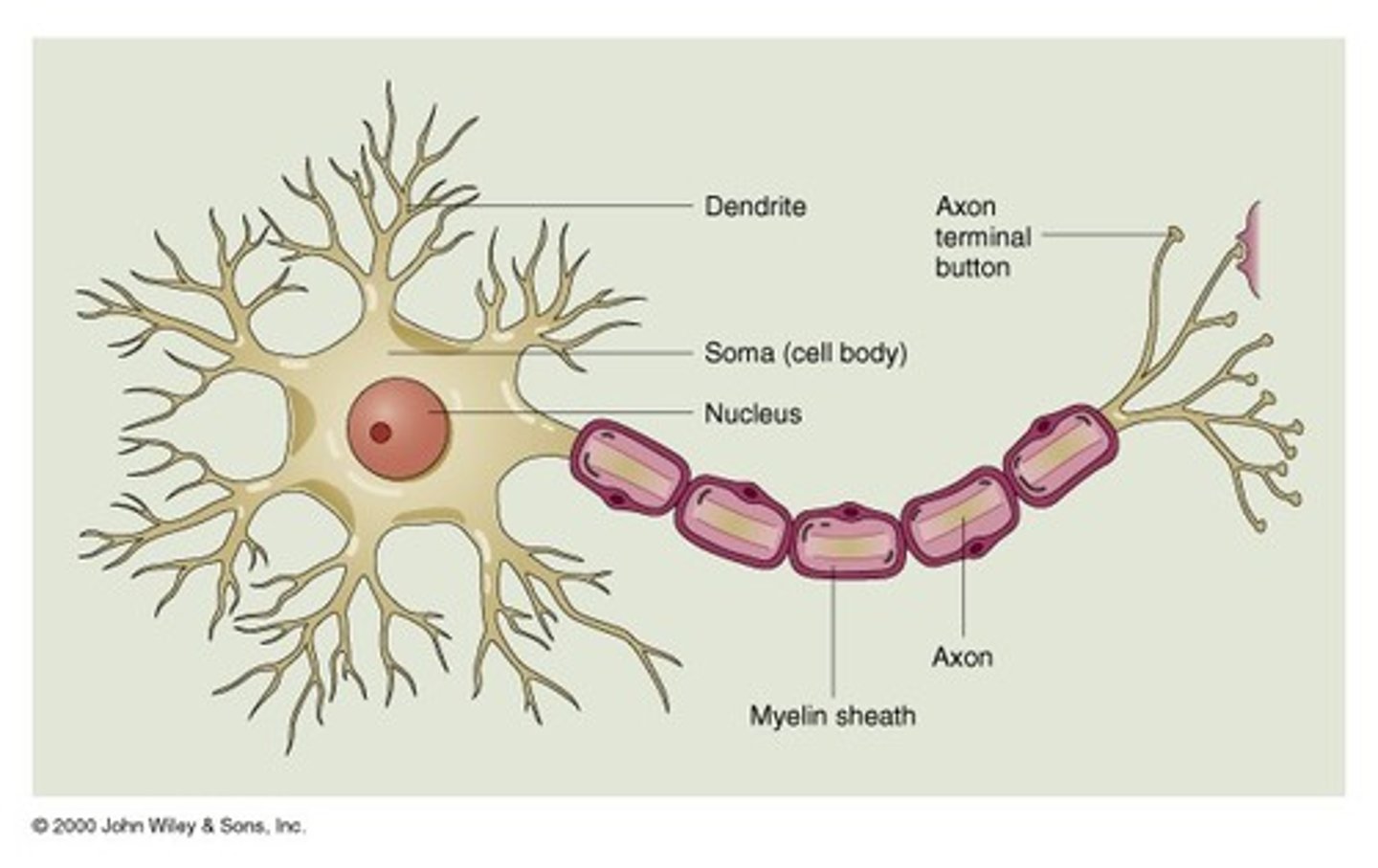
Three basic types of neurons
1. Sensory neurons: Neurons that have receptors that stimulate in response to a change in environment
2. Interneurons: A sensory or other interneuron stimulates an interneuron to communicate with the central nervous system
3. Motor neutrons: These begin in the central nervous system and extend to a muscle or gland. When stimulated, an action occurs
Types of receptors
Light, heat, touch, hearing, balance, smell, taste, internal chemical receptor (thirst/hunger)
Horner's syndrome
Damage to a nerve in the autonomic nervous system. This nerve comes through the neck and base of the skull and controls eye functions.
Signs of nerve damage: 1) constricted pupil 2) upper eyelid droops 3) third eyelid protrudes 4) eye sunken in the socket

Foot and Mouth disease
highly infectious viral disease that selectively attacks epithelial tissue in cloven hoofed animals
Monday morning disease (tying up)
Typically occurs in working horses who begin working after a weekend of resting and consuming a full diet. Sever cramps occur, causing muscle tissue damage. The products from the muscle leak from the cells and are cleared from the blood by the kidneys. These products can damage the kidneys
Displaced abomasum
When the abomasum of a cow fills with gas and is pulled upward

Chapter 3
Musculoskeletal System
Herd checks
Reproductive exams and routine health maintenance work
What is the minimum number of days veterinarians can detect pregnancy in cattle
30 days
Orthopedic surgeon
Veterinarian that specializes in surgery of bones
Four basic functions of bones
structure, protection, minerals, reserve, and blood cell production
Bone structure
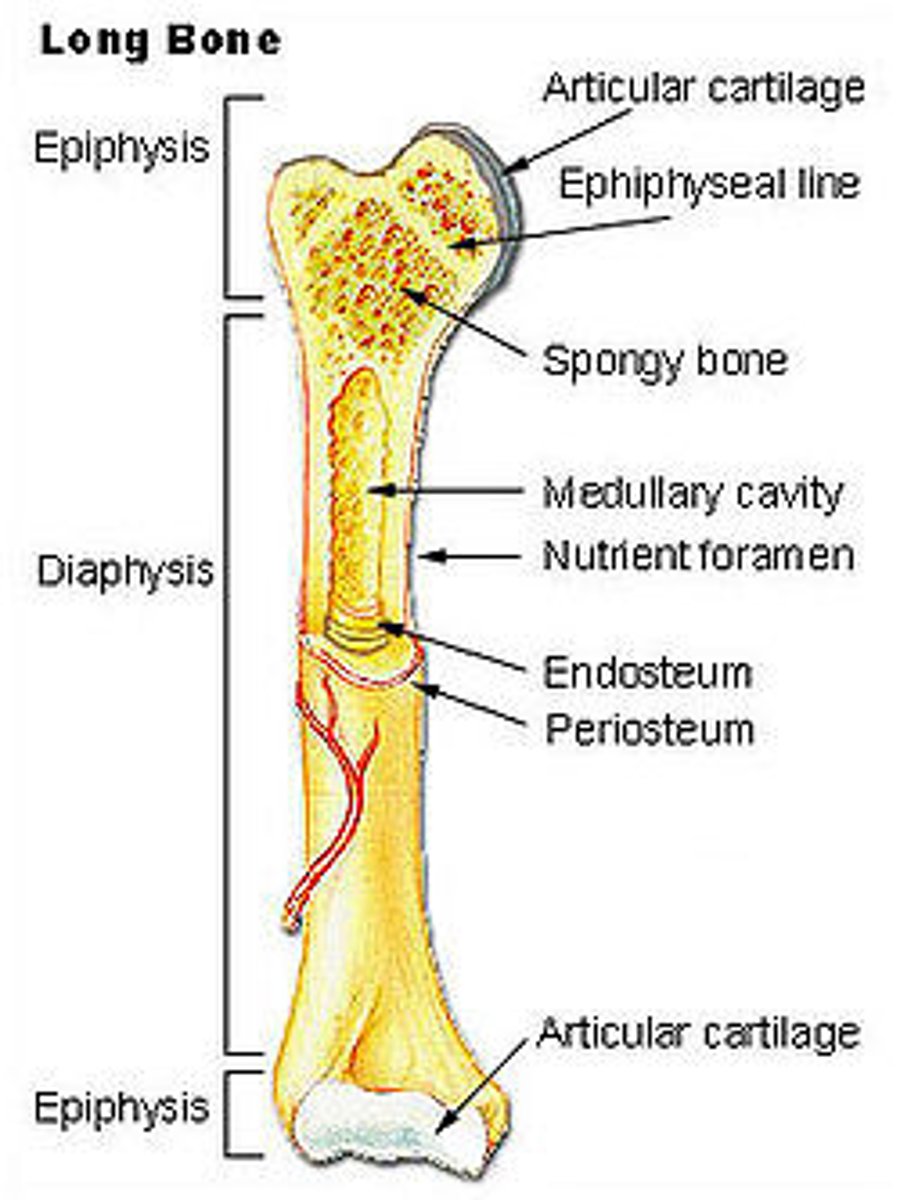
Spongy bone
(also known as cancellous bone) Found within long bones and fills the ends with tiny spicules and plates of bone
Where is bone marrow located?
Within medullary cavity and spaces of the spongy bone
What does bone marrow produce?
red blood cells
Bones are covered in a thin connective tissue called what?
peritoneum- (binds tendons and ligaments to bone)
The cavities within the bone are lined with a similar connective tissue known as what?
endosteum
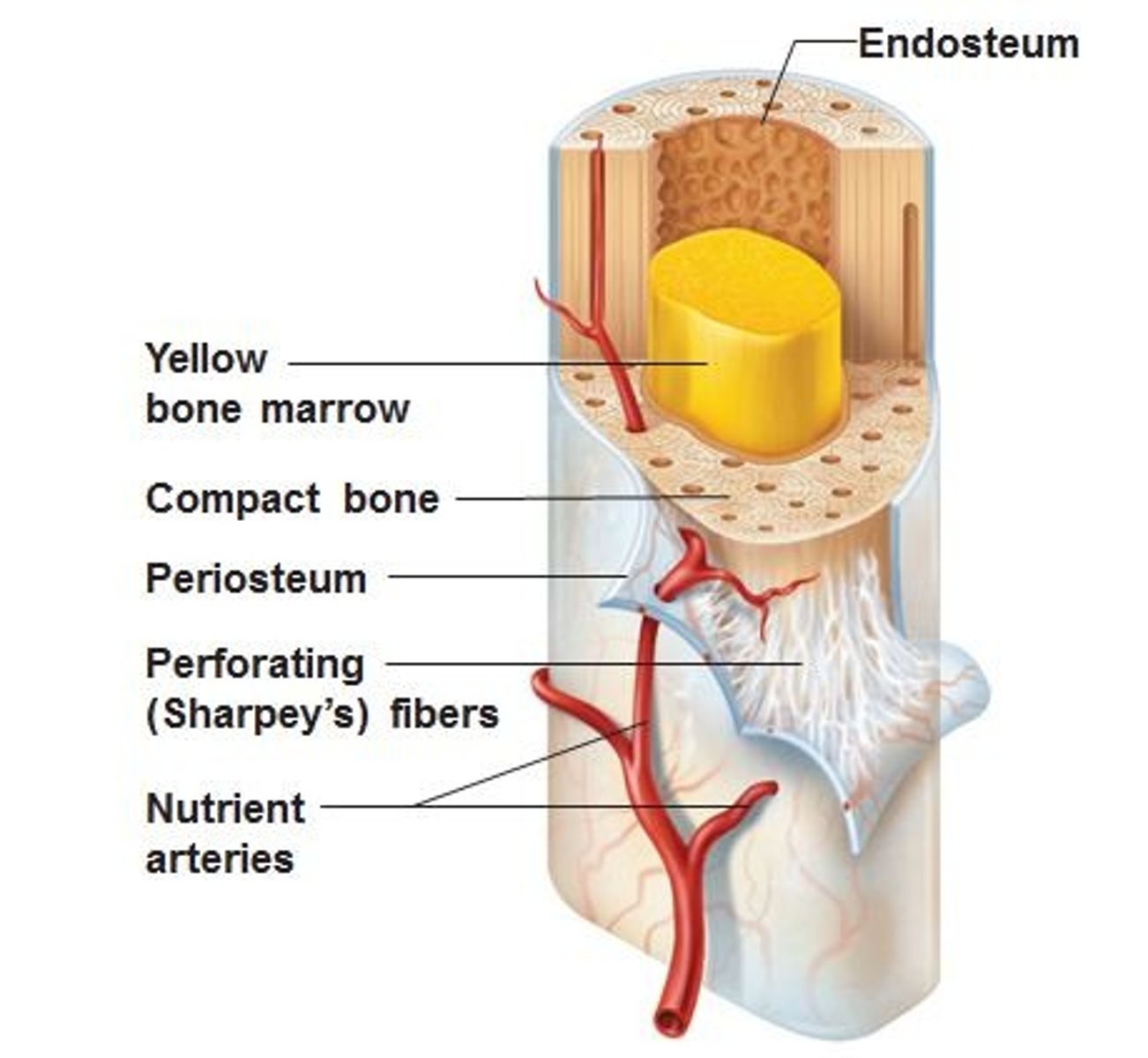
What is the function of the peritoneum and endosteum?
Provide repair
A dry bone is composed of about ___% organic minerals and ___% inorganic minerals
30, 70 respectively
Three types of bone cells
1. osteoblasts
2. osteocytes
3. osteoclasts
Osteoblasts
Lay down collagen matrix, becoming encased in matrix and developing into osteocytes
Osteocytes
maintain bone matrix
Osteoclasts
Multinucleated cells that release minerals from bones
Osteoporosis
Condition in which the bone loses its normal density
Bone is composed of a collection of microscopic units called what?
osteons: that are laid down in ringlets around a canal that allow nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatics to pass through
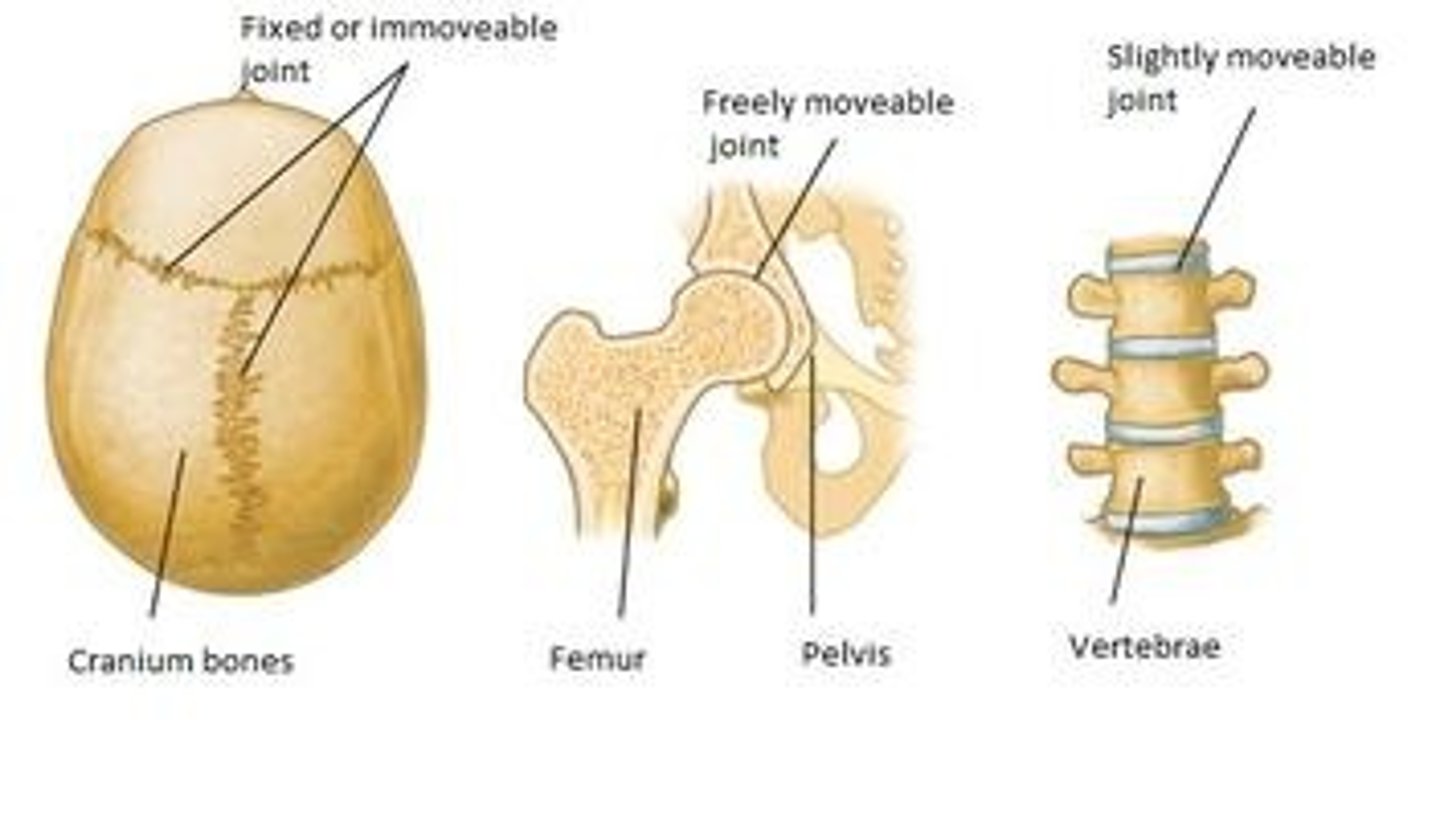
Three main types of joints
1. Fibrous joint: bones joined together by dense connective tissue and allow little movement (skull)
2. Cartilage joint: bones connected by cartilage
3. Synovial joint: True moveable joints where the bones are covered in cartilage and the joint in enclosed by a joint capsule. The outer layer of the joint capsule is strong connective tissue lined with synovial membrane (produces synovial fluid to lubricate the joint)
Meniscus
Hard cartilage pad that acts as a cushion between bone ends
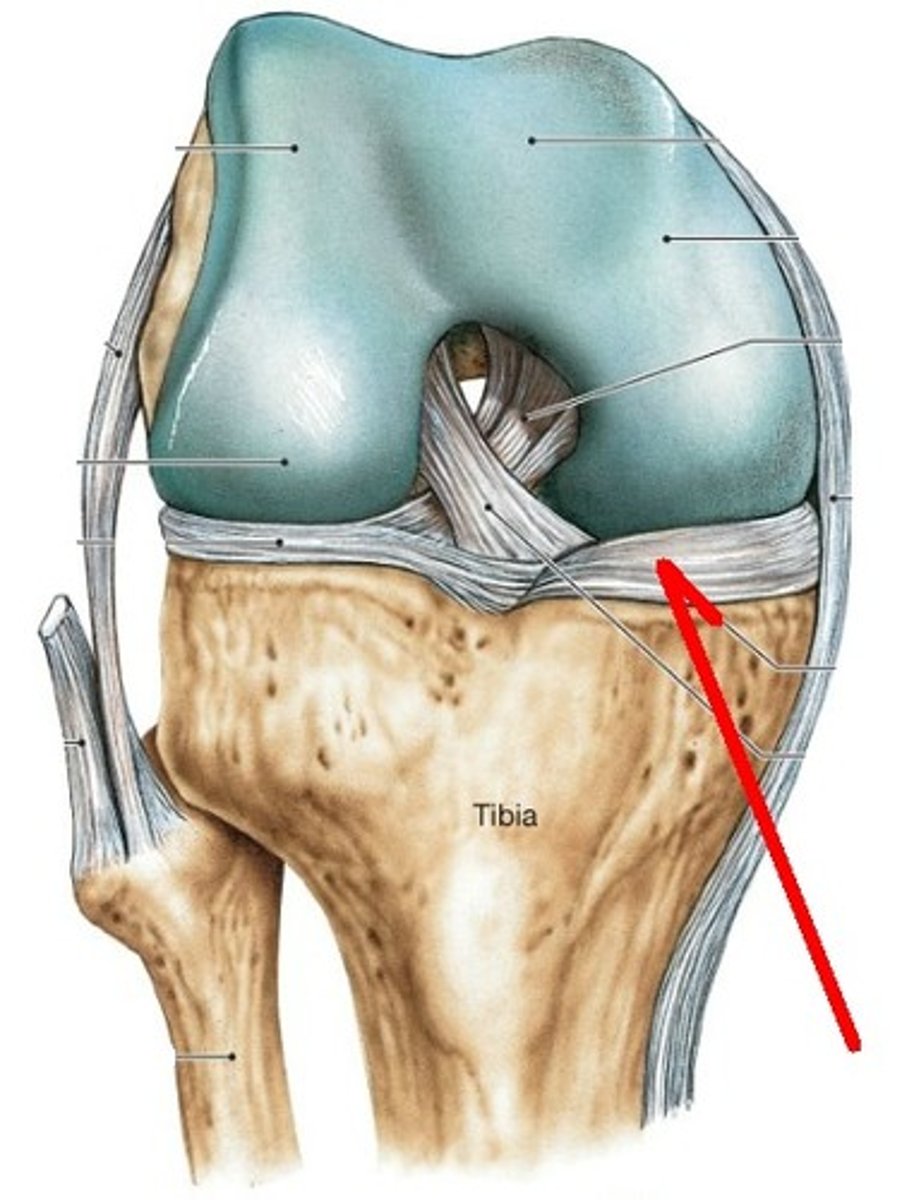
Flexion
angle between two bones decreases
Extension
angle between two bones increases
Abduction
part is moved away from the body
Adduction
part is moved closer to the body
Axial skeleton
Contains skull, vertebrae, ribs, and sternum
Appendicular skeleton
bones of the limbs
How many bones does a "typical" dog have?
320 bones (134 in axial skeleton; 186 in appendicular skeleton)
How many bones does a horse have?
205