General/PE Handbook
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
fb (Bending Stress) for typical beam
fb = M/S
NDS 3.3
Applied moment for simply supported beam with uniformly distributed load
M = wl²/8
Handbook 4.1.7
Elastic Section modulus (Sx) for typical beam
S = bd²/6
NDS 3.3
The elastic section modulus is for serviceability design of non-compact members, used to control deflections
Opposite of plastic section modulus which designs for ultimate/collapse
fv (shear stress) for typical beam
fv = VQ/Ib = 3V/2bd
This is just the shear flow divided by the breadth/thickness of the beam
NDS 3.4.2
ASD Design
Uses adjustment factors to decrease nominal strength to design strength
Won’t be used to factor the applied loads
Used for wood and masonry design
Can be used for steel and concrete, HAVE TO FACTOR STRENGTH IF ASKS FOR ALLOWABLE
Most commonly will be dividing strength by 2.0 for steel
LRFD Design
Uses strength reduction factors to decrease nominal strength to design strength AND uses load combinations to increase service loads to ultimate loads
If the question asks to factor the applied load then I should definitely use LRFD
Used for concrete, steel and bridge design
Nominal strength
Calculated strength of a material before being reduced/factored
Letter with subscript n for LRFD
Letter without apostrophe for ASD
Design strength
Reduced/factored strength of a material using strength reduction/adjustment factors
Phi next to letter with subscript n for LRFD
Letter with apostrophe for ASD
Strength Reduction and Adjustment Factors
Factors provided in each codebook to decrease calculated material capacities for factors of safety, used for both ASD and LRFD design
Service Load
The nominal or unfactored calculated applied load on a member
Ultimate Load
The increased/factored applied load on a member
Letter with subscript u for LRFD
Letter with apostrophe for ASD
Load combinations
A series of load factors found in each codebook that are dependent on loading conditions
Resultant Force for multiple PLs on a beam
Rf = sum of all forces in a direction
xR, use sum of moments with only resultant applied force and support reaction forces to find xR
Process to find maximum moment for multiple moving unequal concentrated loads across simply supported beam
First find support reaction forces through sum of moments
Determine the applied resultant force by adding up all the applied forces
Determine the resultant location along the beam through a sum of moments with only the resultant force on the beam and one of the calculated reactions
Then using maximum moment principle from Handbook 4.1.2 align the resultant and the greatest/middle concentrated load to be equidistant from the beam’s centerline. Choose the load and the side of the load based on what would create the maximum moment. May need to check multiple scenarios
Redo the support reaction force calculations
Then find the moment at the location of the applied load close to the centerline by taking a cut/section through the beam at that location and solving
Table with presumptive bearing capacities by soil type
IBC Chapter 18 - Soils and Foundations, 1806 has presumptive values
Abutment
The retaining wall/foundation wall at the ends of a bridge
Culvert
A tunnel that goes below a road/driveway that’s intended for stormwater drainage
Material unit weights
ASCE 7 Commentary C3
AASHTO Table 3.5.1-1 (extremely general)
Ashlar stone
Opposite of rubble stone, this will be very finely cut rectangular stone
Beam under torsion
Torsion is like wringing a towel out, or rotation along the length of the beam
Torsion causes shear stresses in the beam
Circular beams are the strongest against torsion
Torsional Stress Tau (T) = Torque (T) * r / J (Polar moment of inertia)
So the torsional stress increases as the radius/beam size increases
And torsional stress decreases as polar moment of inertia increases
These occurrences are because like a moment arm, the mass far from the object’s centroid will be much more efficient at resisting torsional stress than mass near the object’s centroid
Polar Moment of Inertia
Measure of objects resistance to torsion/twisting, like a shaft being turned
This is the sum of (2) axes of moments of inertia
J = r² * A
r = radius of gyration
Radius of Gyration
Radius of an area from a point where that area highly affects the moment of inertia
rx = sqrt(Ix/A)
Moment of Inertia
Ix = Integral (x²)dA
An object’s resistance to rotation based on its mass
Ix is resistance in rotating about the x axis (deflecting for a beam)
Iy is resistance in rotating about the y axis (buckling for a column)
The x² accounts for the fact that mass further from the centroid has a much higher resistance to rotation than the mass near the centroid
dA is a tiny slice of the overall area
Moment of inertia has distance units to the 4th power
Also known as second moment of area…
Shear Diagram
Should step vertically at concentrated loads, slope linearly at UDL, and slope parabolically at triangular distributed loads.
Mmax is typically where the V diagram crosses the x-axis and the shear is zero
V will have values at start and end of diagram
Unaffected by hinges or internal moment couples
V should jump to opposite side of V diagram at all supports
Capital W = total load on beam, while lowercase w = distributed load per unit length
Moment Diagram
Should slope linearly where V diagram steps rectangularly, slope parabolically where V diagram slopes linearly, and slope cubically where V diagram slopes parabolically
Change in section of M diagram = area under section of V diagram
M will be zero at any hinges
M will start and end at zero except for at fixed supports where it should have a value
Should be similar to a deflection diagram in that Moment should be negative for extreme sagging/deflection like at concentrated loads or UDL, and Moment should be positive for hogging/upwards bending
An isolated CCW moment at the midspan causes a jump in the M diagram since it would be picking up the right side of the beam/relieving the right side from tension (as represented by the bottom side of the M diagram)
Negative Moment Zone
In beams, typically over intermediate supports and in cantilever beams, where the top edge turns into tension (hogging) and the bottom turns into compression.
Unit weight of water
62.4pcf
Effective soil stress at a certain point
Effective stress = Total stress - pore water pressure
Total stress is sum of soil layer unit weights multiplied by the height of each soil layer above the point in question
Pore water pressure is just water unit weight 62.4pcf multiplied by height of water layer about point in question
Diaphragms
Floor and roof systems act as deep beams for lateral line loads, so the moment within a diaphragm M = wl²/8
The structure perimeters that are along the length of the line load are the chords, whose force can be found from taking a cut through the deep beam and using the T/C moment couple along with the beam depth to find the Fc/Ft = M/d
The structure perimeters that are on the edges of the line load are the struts, whose force can be found from a simply supported beam with a UDL, F = wl/2
Extra - Next step in lateral force transfer would be dividing strut reactions by wall length to get unit shear
Zero force members in trusses
All non-collinear members at 2-member and 3-member joints where no external loads are applied
Then do sum of forces in x and y to check for other zero force members
First moment of area
Q = A*ybar
Cross sectional area of the outer member of a composite/built-up member multiplied by ybar (the distance b/t center of entire cross section to center of outer member)
Shear flow
q = VQ/I
Q = first moment of area, see flashcard
Horizontal distribution of shear force per unit length over a composite/built up cross-section like I-beams used to determine fastener spacing for nails/bolts to prevent the different composite section components from sliding apart
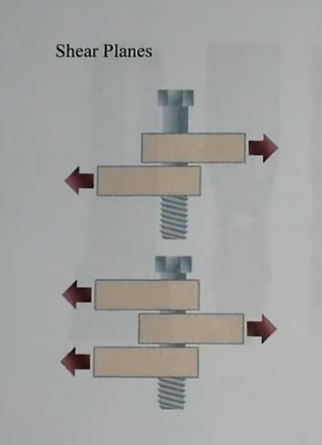
Shear plane
Failure location for a bolt connecting steel plates
For several steel plates, the force on the bolt cross section where it will fail will be reduced by the number of steel plates and the increased number of shear planes
Stress and strain, principal stresses
PE Handbook 1.6.4, Mohr’s circle
Equation for principal stress
Note that tensile stresses are positive and compressive stresses are negative
Eccentricity
e = distance from center
To calculate eccentric stresses, find the moment induced by the eccentricity (M = F*e), and then the eccentric bending stress induced by the moment (fb = M/S)
For the max compressive stress exerted onto a support (typically the foundation), the eccentric bending stress should be added to the normal compressive stress (fc = F/A), just the applied load divided by the area of the transfer member (usually a post or column)
IBC Deflection Limits
Chapter 16 - Structural Design, 1604 - General requirements, 1604.3 - Serviceability
For deflection limits, you get out whatever unit you put into it. Put span in inches then you get allowable deflection in inches, and vice versa with feet
Stress
Force divided by an Area
Strain
epsilon = change in length divided by the original length
Unitless
Strain has a direct relationship with ductility
Modulus of Elasticity
E = stress divided by strain
So E = (F/A) / (change in L/original L)
Elastic longitudinal deformation
Delta = PL/AE or play
Relative Density
Dr is a percentage of how dense/compact the soil is
Multiple graphs in Handbook to determine or huge equation in transpo section, but table with associated N60 values is the quickest
Note that transpo section does have some helpful Geotech stuff
The void ratio e will be max at Dr = 0% and min at Dr = 100%
Linear Interpolation
Set slope of 4 known points equal to slope of 3 known points, then solve for the unknown point
(y2-y1) / (x2-x1) = (y-y1) / (x-x1)
Where blank x and y values are the new data set we’re searching for
Just multiply the left side by (x-x1) and add y1 to solve for y, or solve for x
Process to find total lateral earth force per unit length for retained soil acting on a retaining wall
Multiply unit weights (dry soil, saturated soil, water, etc.) by Ka (coefficient of active pressure) to get triangular pressures
Then multiply by areas to get force per unit length, noting that the soil above the water table will have a triangular pressure above the water table and a rectangular pressure below the water table
Alternatively you can just find the average soil unit weight (unit weight 1 x height 1 + unit weight 2 x height 2) / total wall height
Then use F = .65 * ka * avg unit weight * (total wall height)²
Submerged Soil Density
This is the density of the soil itself that is under water
Gamma prime (submerged density) = Gamma saturated - Gamma water
Lateral earth pressure facts
k coefficients are a ratio of the horizontal stresses divided by the vertical stresses exerted by the soil
The strain required to achieve passive pressure is much larger than the stress required to achieve active pressure
Active pressure is the backfill soil pushing the wall over (0.2<ka<0.4)
Passive pressure is the wall sliding into the soil opposite the backfill and compressing the soil (3<kp<10+)
At rest pressure, used to design for rigid retaining/foundation walls like basements or bridge abutments (0.4<k0<0.6)
Active earth pressure can be negative, typically in cohesive soil where the soil is expanding away from the wall causing soil tension cracks