Chapter 11 The Nervous System BIO
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Nerves
Macroscopic structure that contains bundles of neurons. Surrounded by connective tissues.
Cells found in the Nervous System ( Neurons )
Functional units of the nervous system
Specialized cells to conduct electrochemical impulses→ regulates.
Cells found in the Nervous System ( Glial (Support) Cells )
Comes in many forms- each doing specific jobs to help support the function of neurons
Ex: Schwan Cells that make myelin
Cell Body (soma)
Contains the nucleus and most of cytoplasm
carries on the normal metabolic activities of the cell
Integrates signals from dendrites and initiates nerve impulses down to the axon
Dendrites
Projection of the cell body
numerous and highly branched
Receive signals and send them toward the cell body
“The listeners”
Axon
Long single projection of cell body.
Conducts impulses away from cell body towards terminal
Can be anywhere from 1mm to 1m in length
Node of Ranvier
Spaces between myelin sheath
Myelin Sheath
Schwann cells → peripheral nervous system
A layer of fatty protein wrapped around sections of the axon
Synaptic Terminal
AKA axon terminal, synaptic bouton, and synaptic bulbs
Releases neurotransmitters to communicate with other cells
Neurilemma
Thin outermost membrane of Schwann cells; helps to regenerate damaged PNS axons
In the peripheral nervous system (PNS), Schwann cells make myelin
Since there are no Schwann cell ins CNS, the myelin is made by other cells and therefore will not have a neurilemma and cannot regenerate damaged axons.
Sensory Neurons
Bring in sensory information from receptors to the CNS
Interneurons
Link neurons in the body, sensory to motor and interneurons to each other (connects messages and neurons to each other)
Motor Neurons
Relay information from CNS OUT TO the effectors (muscles or glands elsewhere in body )
The Reflex Arc
Simple neural circuits
reflexes keep you out of danger- they are designed to be fast
They are involuntary movement that are initiated without brain control.
Sensory neurons-interneurons-motor neurons- muscle movement
Resting Membrane Potential (around -70mV)
At rest neurons is maintaining
Sodium channels are closed (Na+ cannot get in)
Potassium channels are closed (K+ cannot get out)
Na+/K+ pump is active
Stimulus
Neurons stays the same until there is a stimulus
Stimulus must be strong enough to Depolarize (make more positive) up to about -55mV for an action potential to occur. Known as threshold potential
Nerve impulse
A wave of positive charge traveling along the axon, resulting from the movement of ions across the axon membrane that results in the change of a membrane potential
Depolarization
Pump is deactivated
An influx of sodium ions into the cell
Makes the cell more positive
Na+ in
Repolarization
Potassium K+ in
Pump still deactivated
Potassium channels open making the cell more negative
Does not close until the cell reaches -90 mV
The Refractory Period- Reseting the Neuron
-90 mV to -70 mV
The neuron is NOT receptive to another stimulus until the resting potential of -70 mV and proper ion concentration (lots of Na+ outside and lots of K+ inside) are established
Sodium-potassium pump ACTIVE
Channels are closed
Neurotransmitters (NT’s)
Chemicals released by the presynaptic neuron that influence the activity of the postsynaptic neuron.
Presynaptic Neuron
Action potential reaches synaptic terminals causing Ca+ ions to flow into terminals
This causes synaptic vesicles inside terminals to fuse with the membrane freeing NT’s into synapse (cleft)
NT’s diffuse through synapse, bind to receptors on the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron→ opens ion channels in dendrites
Postsynaptic Neuron
Depending on the type of ion channel opened, the dendrites becomes more positively charged (if Na+ flows into neuron) or more (if K+ flows out of neuron)
NT’s remaining in the synapse are degraded by enzymes, taken back in the presynaptic neuron through reuptake channels - The longer neurotransmitters are in the synapse; the greater the effect on the postsynaptic neuron
Responses in the Postsynaptic Neurons
Depending on the type of neurotransmitter excitatory vs inhibitory NT’s
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Open sodium channels in the postsynaptic neuron
Sodium ions flow into the neuron causing local depolarization.
Promotes nerve impulses by bringing potential closer to threshold
Increase the likelihood of a response
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Open potassium channels in postsynaptic neuron
Potassium flows out of the neuron causing local hyperpolarization (neurons becomes more negative)
Inhibits nerve impulses by bringing the potential further from the threshold
Decreasing the likelihood of a response
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Neurotransmitter opens sodium channels in muscle fibers causing depolarization and muscles contraction.
Dompamine
Found in midbrain; helps control movement and also involved with the “pleasure centre”
Serotonin
Affects sleeps and mood
Endorphins
Natural pain killers in synapses in brain; also affects emotional areas of brain
Epinephrine/Norepinephrine
General excitatory neurotransmitter
Cholinesterase
Enzymes that degrades acetylcholine to end contraction, released by presynaptic neuron.
Skull
“Bony armor”
Meninges
3 layers of tough elastic tissue
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Circulates between meninges and throughout brain and spinal cord
Mainly for cushioning and shock absorption but also transports nutrients, hormones and white blood cells
Blood Brain Barrier
Protective barrier formed by glial cells and blood vessels
controls entrance of substance into the brain from the blood
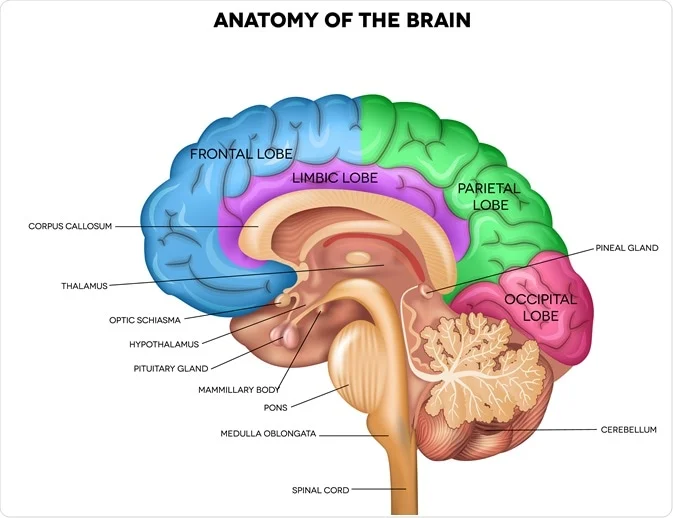
Medulla Oblongata (Hindbrain)
Controls autonomic functions such as breathing, blood pressure, swallowing
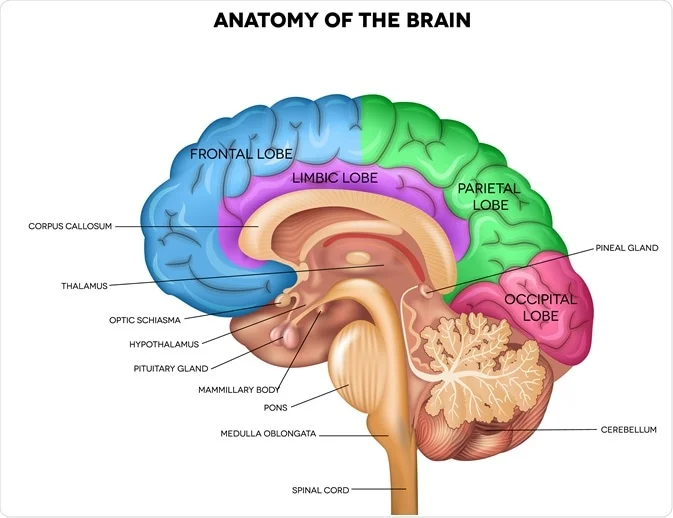
Pons (Hindbrain)
Relay (bridge) between left/right sides of cerebellum and relay to cerebrum
responsible for controlling muscles for biting, chewing, and swallowing
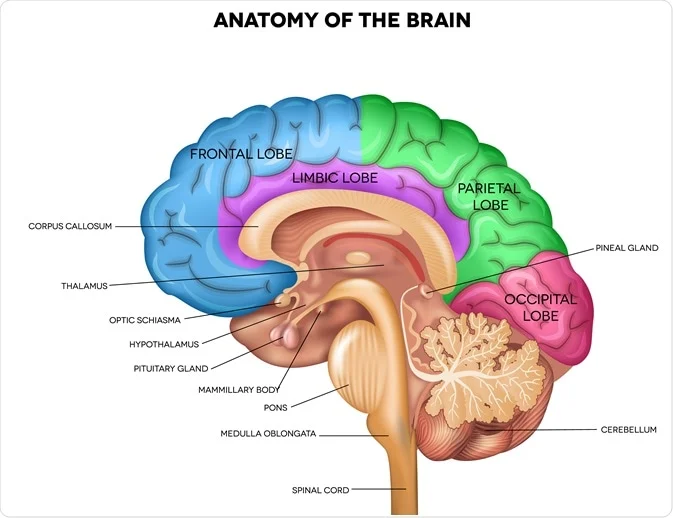
Cerebellum (Hindbrain)
Coordination of unconscious and voluntary movements, balance and posture.
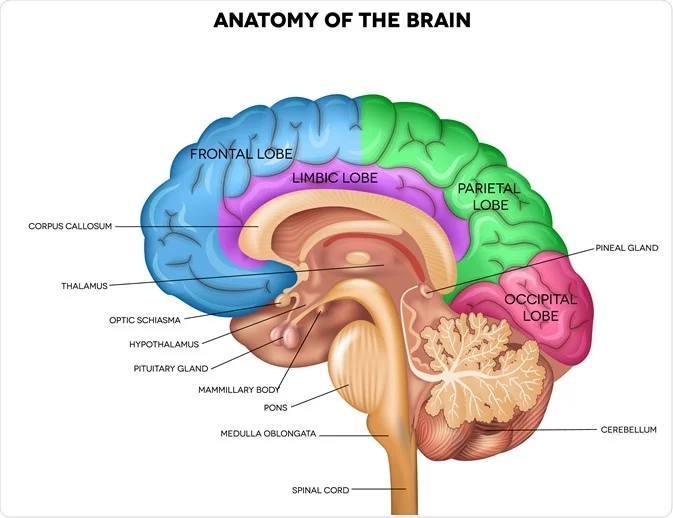
Midbrain
Role in eye movements and control skeletal muscles
processes auditory and visual informations
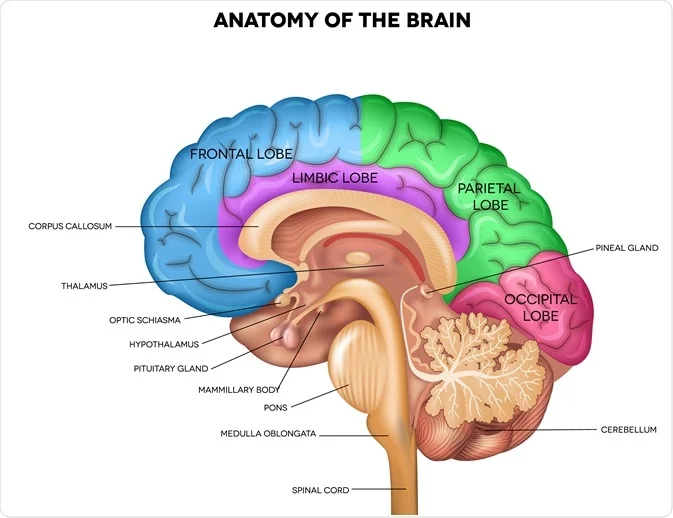
Hypothalamus (Forebrain)
Releases hormones major link between nervous and endocrine systems.
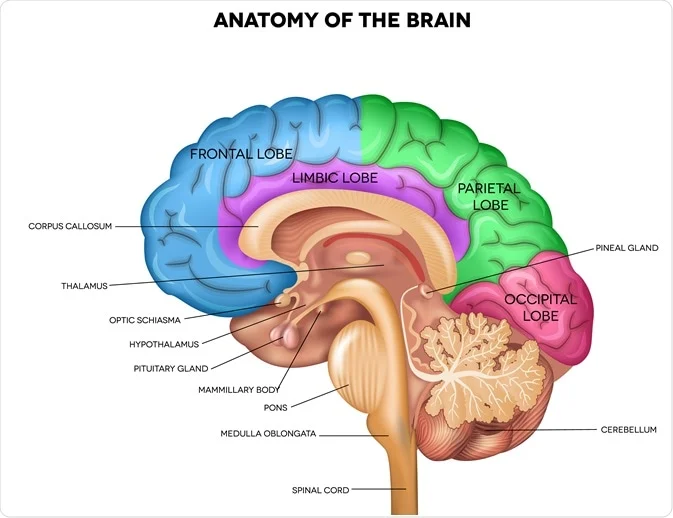
Cerebrum (Forebrain)
Controls higher-level thinking→ Language, interpretation of sensory information, muscle movement.
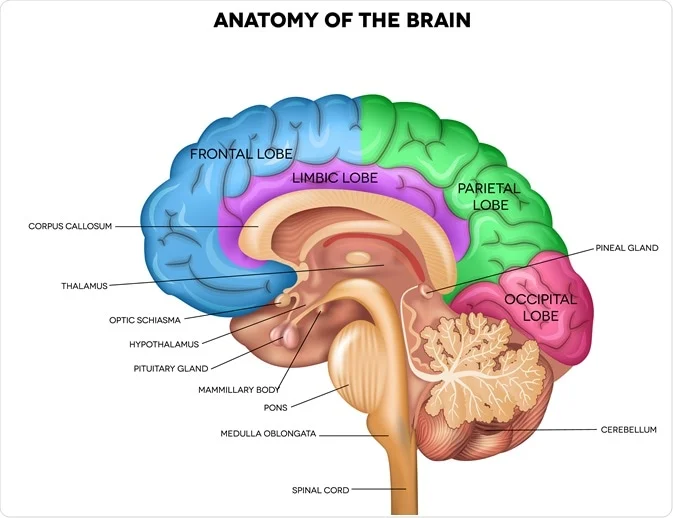
Right of the brain
Controls the left side of the body, often specializes in artistic and spatial awareness
Left of the brain
Often specializes in logic, math, and language skills
Corpus Luteum
A band of myelinated axons that helps both sides of the brain communicate.
Frontal lobe
Integrates info and control higher cognitive functions
Reasoning, critical thinking, memory, and personality
Controls precise, voluntary motor skills, including speech production
Parietal Lobe
Process sensory info from skin
Touch, pain, pressure, temperature
Help process body position info
Temporal Lobe
Process auditory information, stores visual and verbal memory
Occipital Lobe
Process visual information.
Sensory Neurons
Carry information from the receptors to CNS
Motor neurons
carry information from the CNS to the effectors
Somatic Nervous system
Voluntary control
controls mainly skeletal muscles (except vague nerve_> helps to control some organs)
Autonomic Nervous System
Involuntary control
Control organs, glands, smooth muscles
Maintain homeostasis (stable state) by stimulating or inhibiting involuntary process
Controlled mainly by the medulla oblongata and hypothalamus
Sympathetic Nervous System
Fight or flight
Prepares body for stressful or energetic activity
Release epinephrine and norephinephrine
Parasympathetic nervous system
Rest and digest
Dominates during times of relaxation
Release acetylcholine