(1, 2) Cable types, terminations, cords, cables, plugs
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
How is most of NSW’s power generated?
gas, hydro, bioenergy, wind, solar. Traditionally coal, reduced in recent years
Why are zone substations interconnected via high voltage distribution network?
Reduces sizes of cabling + support systems required (higher voltage w/ lower current)
Difference between phase voltage and line voltage + values in 3-phase system?
Phase: between one phase and neutral, 230V
Line: between two phases of multi-phase supply, 400V
What is the connection point of a low voltage electrical installation?
NSW Service and Installation Rules states junction between distribution system and consumers installation
What is the earthing system used for low voltage electrical installations in Australia? Where does the name come from?
MEN (Multiple Earthed Neutral). Installations individually earthed, earths bonded to neutral in multiple locations
How do circuit earthing conductors connect to the installation earth electrode?
Circuits to earth link then main earth to earth electrode
What is the flow of energy from the consumer mains to the final subcircuit?
Consumer mains > main switchboard (through circuit protective device) > submains > distribution board > final subcircuit. A final subcircuit is any final circuit supplying an appliance instead of distributing it.
What is the main difference between isolation and protection device?
Isolation: isolates circuits manually when required
Protection: protects circuits automatically
Can a protection device be used as an isolation device? And what precautions to take if isolation device is a fuse?
Circuit breakers can be opened and locked out. Removal of fuse links also isolates circuit but danger tag is required.
What equipment is suitable for testing if circuit is dead?
Voltage tester, test lamps, inductive voltage tester
What should be checked on circuit testing equipment prior to use?
Device tests for VOLTAGE not CURRENT
Suitably within testing range (AC, DC)
Check class (CAT III, CAT IV etc.)
Check lead conditions
What is accomplished by proving test equipment works on circuit before isolating it?
Verifies tester works, proves supply available before isolation
What is the purpose of technical standards and how are they developed?
Usually developed by ISO or Australian Standards, standards are voluntary documents setting out specs, procedures + guidelines to ensure everything’s safe, consistent, reliable
What parts of AS/NZS3000 are performance- or prescriptive-based and what does this mean?
Part 1 is performance-based, desired end result.
Part 2 is prescriptive based, detailed, specific requirments e.g. smoke detector spacing, fire rating for occupancy separation
What’s the advantages and disadvantages comparing copper and aluminium cables?
Copper: High conductivity, tensile strength, slow oxidise (easier to terminate), more expensive.
Aluminium: High conductivity/weight ratio, flexibility (softer), cheaper for same current. Oxidises quickly, harder to terminate.
Name 3 types of cable insulation, one dis/advantage for each
PVC: flexible, easily damaged
MIMS: Very high temp rating, specialised fittings/equipment/processes to terminate
XLPE: X-90 (90C) temp rating, relatively inflexible
What is building wire called in the AS/NZS 3000?
Thermoplastic Insulated (TPI) is cable with only one layer of insulation (single insulated)
What information should be on a personal danger tag?
Name, Date/time, Mobile, Company/department
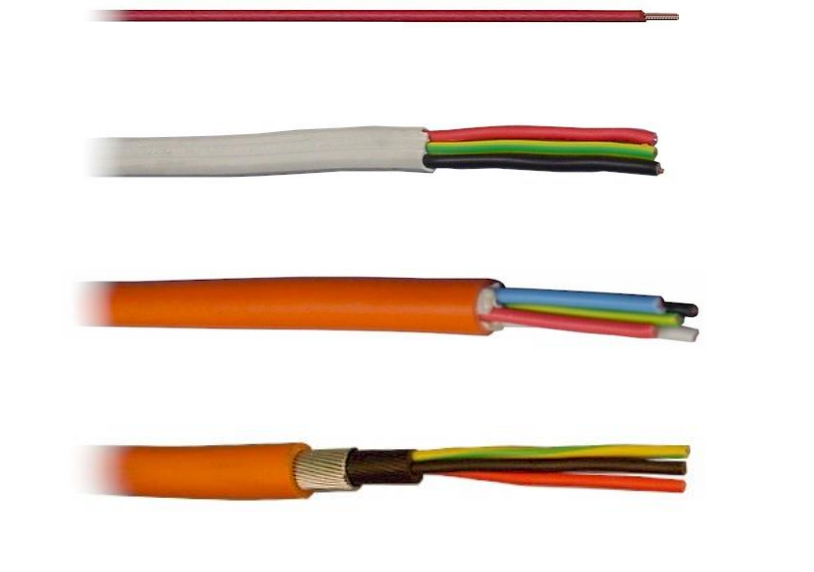
What are these cables called based on their design? What are they used for?
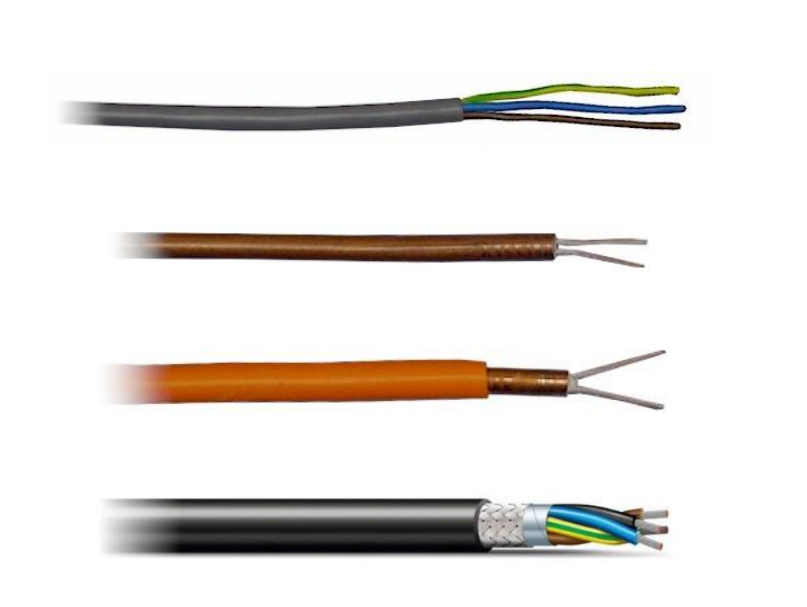
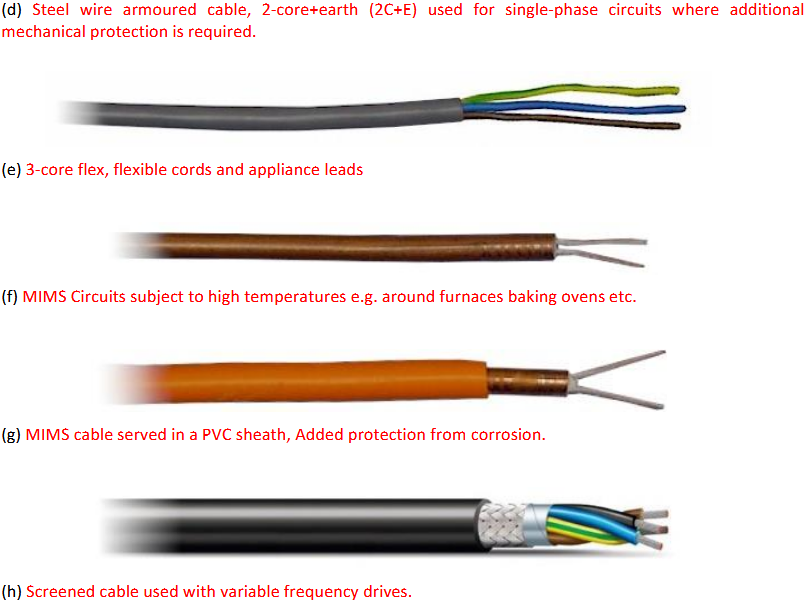
What are these cables called based on their design? What are they used for?
What eight cable sizes (up to 25mm) are most standard?
1mm, 1.5mm, 2.5mm, 4mm, 6mm, 10mm, 16mm, 25mm are referred to in the AS/NZS 3000
Why are electrical conductors used for fixed wiring available in stranded configuration over 2.5mm2 CSA (Cross Sectional Area)?
Stranding enhances flexibility
What information can be gathered from this cable drum label?
7/0.67 (2.5²)) 2C+E FL 0.6/1kV 75C COPPER/PVC/PVC
7 .67mm strands, 2.5mm conductor size, 2C+E core config, FLat shape, 1kV voltage rating, 75C temp rating, Copper conductor, PVC insulation, PVC sheath
What is a luminaire?
A completed lighting assembly
What is an appliance?
A consuming device other than a lamp, in which electricity is converted to heat, motion or other type of energy.
What are some examples of fixed appliances, hand-held appliances, portable appliances, stationary appliances?
Over/cooktop/water heater, hairdryer/mixer, toaster/blender, microwave/fridge
Where would a “switched socket with additional switch” be used?
e.g. Bathroom beside sink with switch controlling mirror light, kitchen with switch supplying cooktop
When referring to switch plates, what does “gang” mean and what is the maximum for a standard pattern switch plate and architrave switch plate?
“gang” means number of switches on plate, SPSP is max.6, architrave is max.4
What are the three general requirements for a good electrical connection?
Must provide electrical continuity, appropriate level of insulation, adequate mechanical strength
What factors must be considered when selecting appropriate method of connection for electrical conductors and equipment?
Material of conductor + insulation, number + shape of wires forming conductors, cross-sectional area of conductor, number of conductors connected together, temps gained in normal service, prevention of water+moisture entry through enclosures
How are tunnel type electrical connections made and how many should they hold max?
Up to 4 conductors twisted together + inserted in tunnel, hand screwdriver used to tighten screw/s. On single screw tunnels, screw should fill 80% of tunnel
What colour code do pre-insulated crimp lugs follow?
Red 1.5mm², Blue 2.5mm², Yellow 4/6mm²
What is the purpose of soldering flux while soldering?
Remove and protect joint against oxygen
What is the main problem when joining flexible cord conductor to fixed wring conductor? How to fix?
Twisting 7 strand conductor with 30+ strand conductor results in finer strands wrapped around heavier ones, fixed by twisting the 7 together and THEN twisting onto the 30+

What are these items called?
1-gang Architrave Switch, 1-gang Standard Switch, Socket-outlet Double
Why are 15A plugs longer than 10A?
So 10A can fit into 15A, but 15A is too long to fit in 15A

What are these items called?
Batten Holder, TPS Junction Box, Light Dimmer/Fan Speed Controller

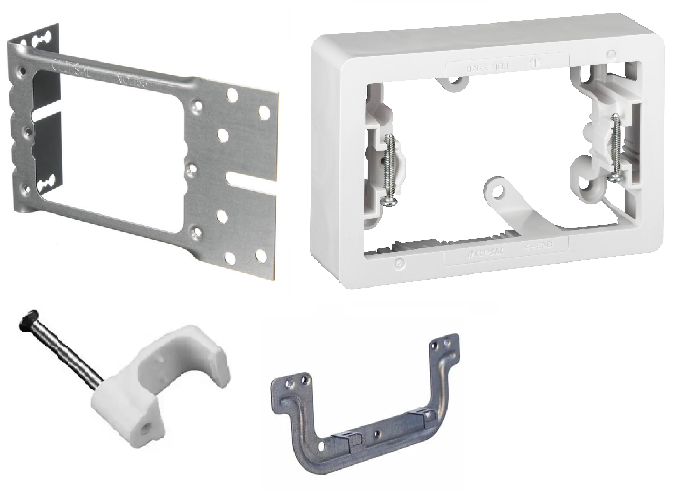
What are these items called?
Mounting Bracket, Mounting Block, Cable Clip, Mounting Clip (“C clip”)