3.5 Demand Management (demand side policies) – monetary policy
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
conducted by the central bank of the country and controls money policy and interest rate. the use of the interest rates (via manipulating the money supply) to influence aggregate demand.
Regulates behaviour of commercial banks to make sure they don't engage in risk lending to increase their profits. Wants to avoid banking crises.
Collects government revenues from taxation and other sources and makes all government payments
What is an interest rate?
cost of borrowing money and the reward for saving money over a period of time (%)
**By increasing supply, central bank can decrease interest rates and vice versa.
The nominal interest rate is the interest rate on a loan or on savings deposits unadjusted for the rate of inflation.
What are goals of monetary policy?
Low and stable rate of inflation - inflation targeting: achieve and maintain price stability (e.g. around 2% for UK, US, eurozone). If economy is in recession (or at risk), monetary policy can be used to increase AD and unemployment will decrease. Conversely, if growth is too fast and risk of rising inflation, monetary policy used to decrease AD to decrease inflationary pressures.
Low unemployment - Quantitative easing (QE); helps economies grow and reduce unemployment while avoiding deflation. Monetary policy would involve cutting interest rates. Lower rates decrease the cost of borrowing and encourage people to spend and invest. This increases AD and should also help to increase GDP and reduce demand deficient unemployment.
Reduce business cycle fluctuations: If economy is in recession (or at risk), monetary policy can be used to increase AD and unemployment will decrease. Conversely, if growth is too fast and risk of rising inflation, monetary policy used to decrease AD to decrease inflationary pressures.
Promote a stable economic environment for long-term growth - It directly lowers banks borrowing costs, which in turn lower lending rates for firms and households, and this supports consumption and investment which are components of real GDP so will enable economic growth.
External balance:country's revenues from exports are balanced by spending on imports over extended period of time. Partially the result of the value of the country's currency or exchange rate. Central bank can influence exchange rates because of the close relationship between interest rates and exchange rates.
* Increase inflation
* Increase growth
* Reduce unemployment
\-Households have greater incentive to save and not to spend.
* Firms borrow less and spend less on capital goods.
* C and I decrease so AD will decrease and the inflationary gap can close.
How do you calculate real interest rate?
nominal interest rate - rate of inflation (expected or actual)
A real interest rate is an interest rate that has been adjusted to remove the effects of inflation. Once adjusted, it reflects the real cost of funds to a borrower and the real yield to a lender or to an investor.
(DEFLATIONARY/ RECESSIONARY GAP) Expansionary (loose) monetary policy = interest rate decreases and money supply increases so cost of borrowing decreases and the inventive to save decreases more is spend increasing AD.
AD increases and real GDP increases, lowering unemployment.
* Reduce inflation
* Prevent asset/ credit bubbles
* Reduce excess debt and promote saving
* Reduce current account deficit
* Incremental: interest rates can be increased or decreased by 0.25% at a time
* Flexible: monetary policy committee meets frequently to set interest rates
* easily reversible short time lags: easy to reverse direction and increase/ decrease interest rates in the next morning.
* Independent of government and politicians: politicians care more about their short-term re-election chances and less about the benefits of long-term stability to the economy.
* Limited scope of reducing interest rates when close to zero
* Low consumer and business confidence
* Consumption/ investment might be interest inelastic (even though interest rates change by large amount, not big response)
* Conflicting government objective - falling growth might require expansionary monetary policy but high inflation could suggest contractionary monetary policy required.
* Limited effectiveness when the economy is in a recession – instead of borrowing, firms and consumers might simply repay the debts
What is the process of money creation by commercial banks
Money creation = the process by which commercial banks create new money when they make loans. This is based on the idea that only a fraction of deposits need to be kept in the bank's vaults (fractional reserve system.)
Banks must legally keep some funds/ deposits called required reserves (legally determined fraction of total deposits called the minimum reserve requirements). The rest of the money is called excess reserves and can be lent out.
The lower the minimum reserve requirement, the greater the excess reserves, the more loans can be made by commercial banks, and the more new money can be created.
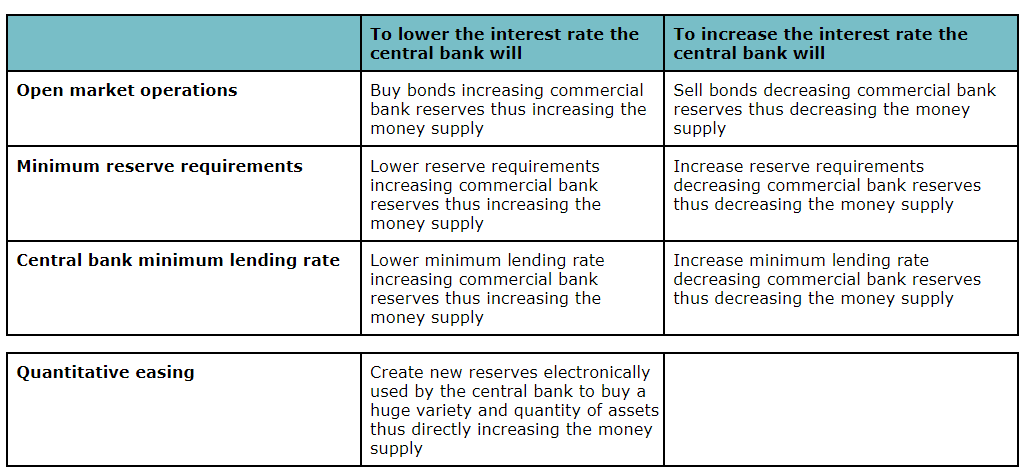
What are the tools of monetary policy?
How is the equilibrium rate of interest determined + definitions of interest and money
Interest = A payment per unit of time, for the use of borrowed money to owners of capital resources (borrowers pay interest, lenders receive interest).
Money = medium of exchange. Anything that is acceptable as payment for goods and services. (consists of currency (coins and paper money) and checking accounts.)
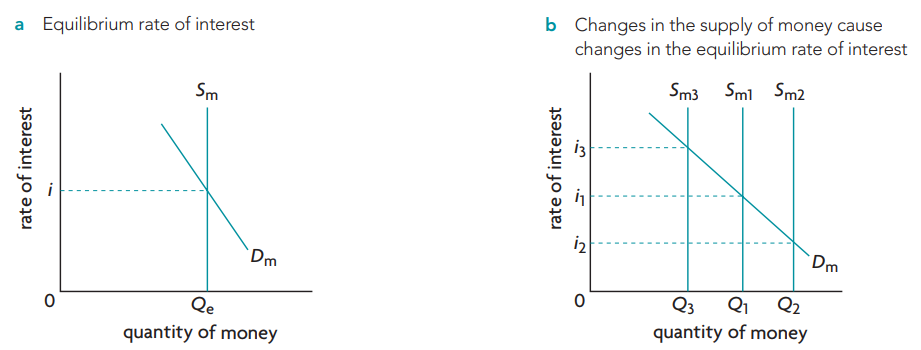
-> The supply of money is fixed at a level decided upon by the central banks. It appears as a vertical line (Sm) because it does not depend on the rate of interest.
-> Demand for money (Dm) has downward-sloping demand curve.
-> As rate of interest falls, the quantity of money demanded by the public increases.
-> Point of intersection between Dm and Sm determines equilibrium rate of interest (i).
(increase in supply of money leads to fall in the rate of interest; decrease in supply leads to increase in the rate of interest.)