College Biology - Genetics Unit
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Gregor Mendel (Father of Genetics)
Come in pairs
Retain characteristics through generations
Separate in gamete formation
Pisum Sativum
The perfect species for studying genetics
Control characteristics
7 characters each with 2 traits
Traits either completely dominant or recessive
Self pollinate or cross pollinate
Genotype
Genetic Makeup [RR, Rr, rr]
Phenotype
Physical physiological makeup [example: round or wrinkled]
Mendel’s Experiments
Started with true breeding plants
P and F1
What is “P”
Parent generation
What is “F1”
First filial (generation)
1st born
Mendel learned…
There is no blending of traits!
Alleles
The pair that traits come in
Law of Segregation
Alleles separate during gamete formation
Meiosis - one from each parents
How Mendel’s Experiment Worked
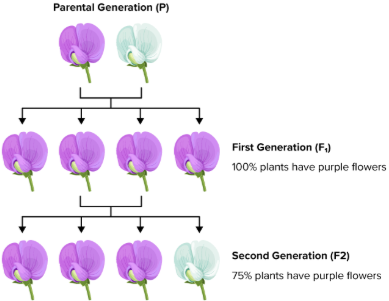
What is a punnett square?
A square diagram that is used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross or breeding experiment
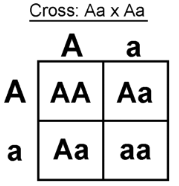
Monohybrid Punnett Square Example
Dihybrid Cross - what did Mendel find out?
Similar ratios when he crossed single traits and double traits: therefore…
One trait DOES NOT affect the other.
Law of Independent Assortment
During gamete formations gene pairs assort independently of one another
Dihybrid Punnett - Steps
Write down genotype of parents
Make two separate monohybrid punnett squares
Jot down ALL phenotypes
Find ratios of all by multiplying
Dihybrid Punnett Square Example - from my notes
Note: it is the same process for Trihybrid crosses and more

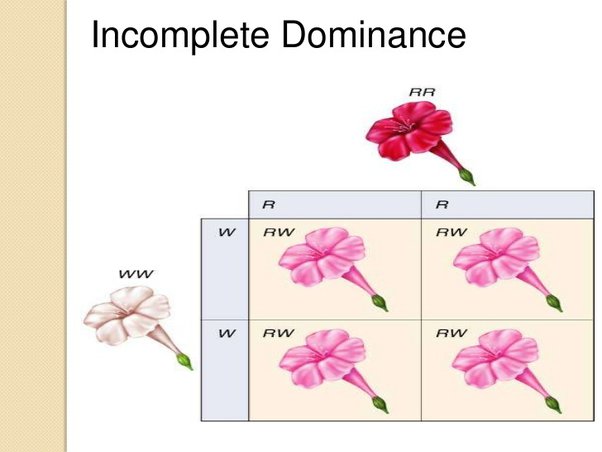
Incomplete Dominance + Example
Heterozygous is intermediate between homozygous phenotypes
Middle
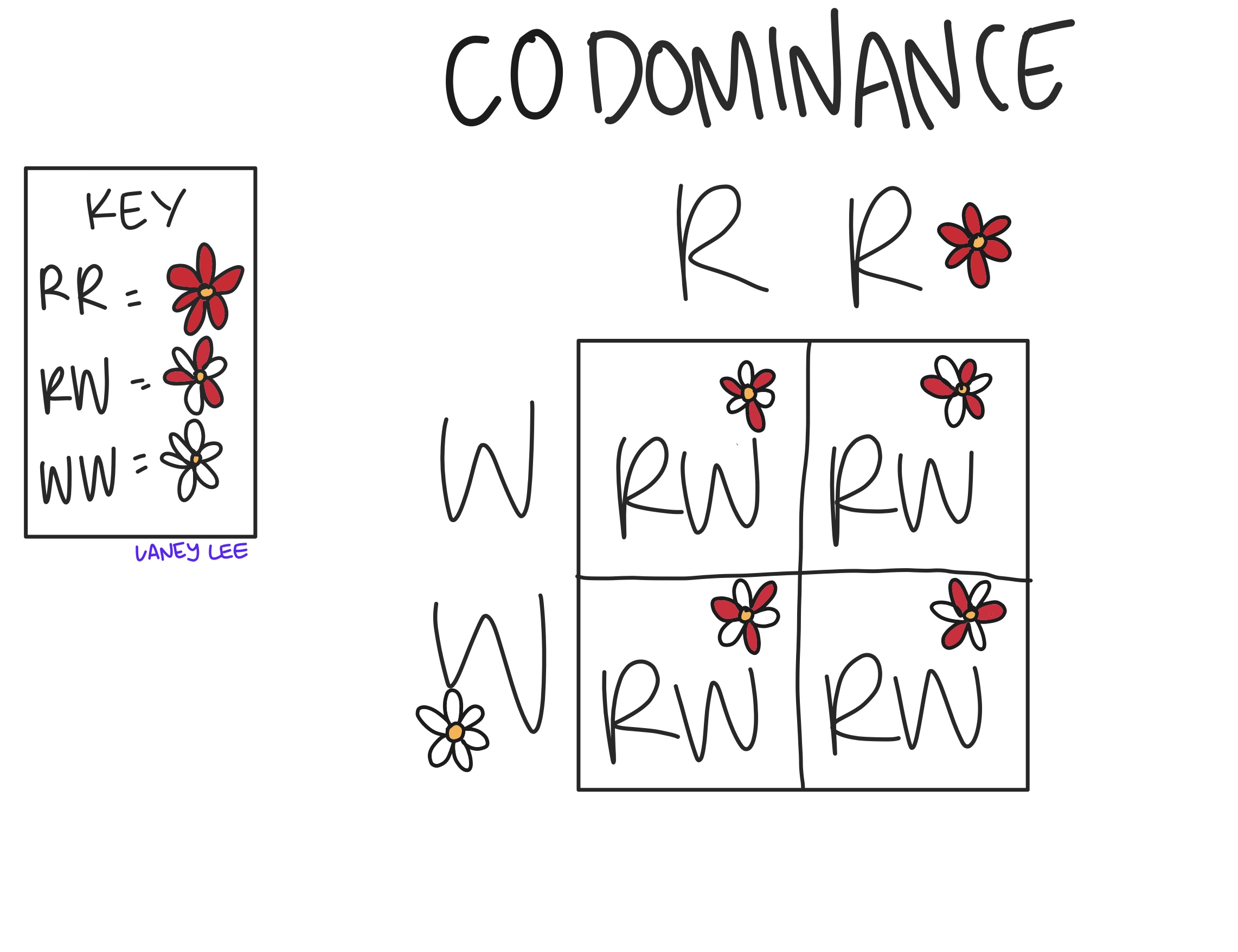
Codominance + Example
Heterozgous shows BOTH phenotypes of different alleles
Co = blended
Multiple Alleles + Example
More than 2 possible alleles for a trait
(One from mom, one from dad)
Think blood types
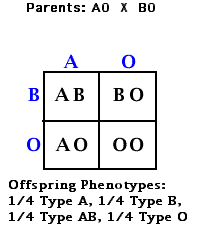
RH Factor - key and what is it?
Positive or negative in a blood type
(+) = dominant
(-) = recessive
Genotype / Phenotype List for Blood
AA - Type A
AO - Type A
BB - Type B
BO - Type B
AB - Type AB
OO - Type O
Male vs Female
Male = XY
Female = XX
Note: In X-linked, Y has no allele attached
X-Linked Recessive - key
X-Linked
A = normal
a = trait
X-Linked Dominant - key
X-Linked
A = trait
a = normal
Y-Linked
XYA or XYT
A = normal
T = trait
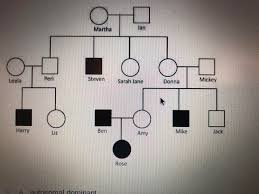
Pedigree - key
Square = male
Circle = female
Colored = trait
Pedigree - Example
Autosomal Dominant
Autosomal
A = trait
a = normal
Autosomal Recessive
Autosomal
A = normal
a = trait
Polygenic Traits
Many genes control 1 trait
Shows continuous variation
Must show a bell curve
Pleiotrophy (opposite of polygenic)
One gene having many effects
Fragile x syndrome
PKU
Marfan syndrome
Epigenetics
External environmental influence that increases or decreases the chances of a gene being expressed
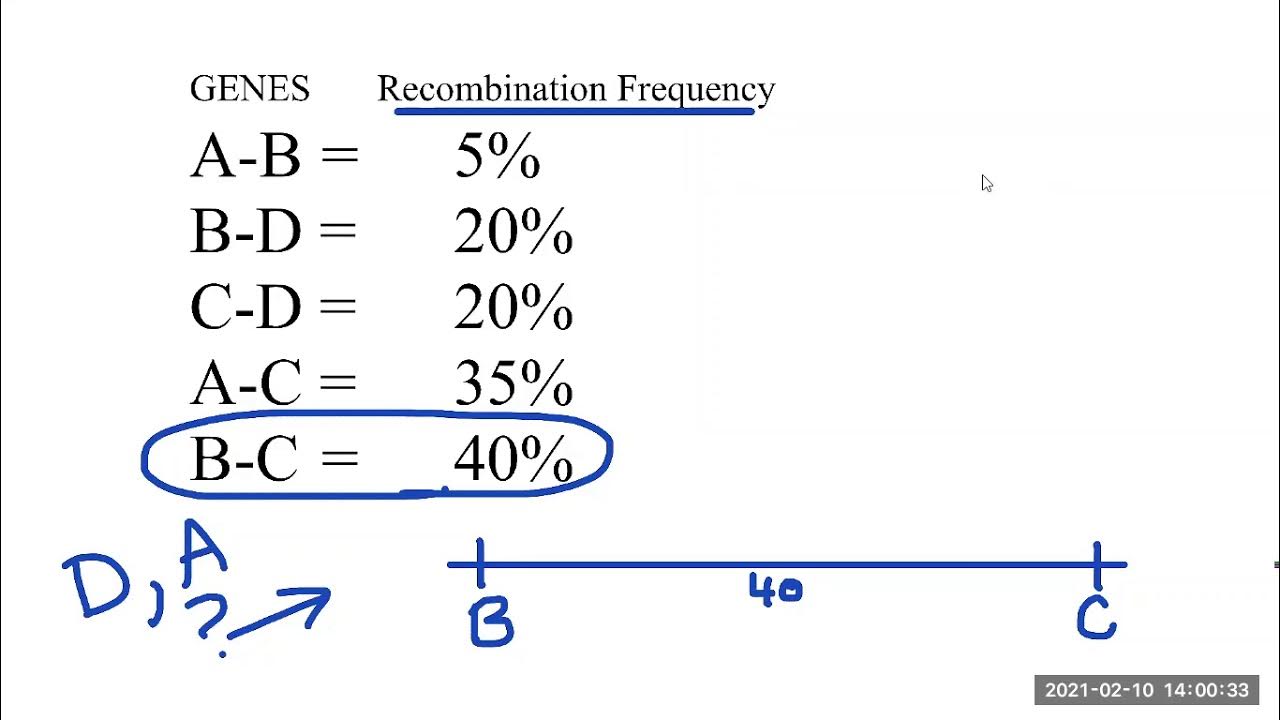
Gene Mapping
The process of determining the location of genes on chromosomes
Gene Mapping - Example