PSIO 201 - Block 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/769
Last updated 3:54 AM on 11/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
770 Terms
1
New cards
Maintains homeostasis
Rapidly transmits information
Responsible for voluntary and involuntary movement, perception, behavior, memory, and more
Rapidly transmits information
Responsible for voluntary and involuntary movement, perception, behavior, memory, and more
What does the nervous system do?
2
New cards
Neural tissue made up of neurons and neuroglia
What is the nervous system composed of?
3
New cards
Sensory information
Integration
Motor function
Integration
Motor function
How does information flow in the nervous system?
4
New cards
Input, information goes into the brain and spinal cord via cranial and spinal nerves
What is sensory information?
5
New cards
Proccessing, integrates sensory information by analyzing and storing it
What is integration?
6
New cards
Output, information from the brain and spinal cord is sent out to effectors (muscles or glands)
What is motor function?
7
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
What are the two parts of the nervous system?
8
New cards
Brain and spinal cord
What does the central nervous system consist of?
9
New cards
Primarily cranial and spinal nerves, essentially all nervous tissue outside of the CNS
What does the peripheral nervous system consist of?
10
New cards
Sensory division and motor division
What are the components of the peripheral nervous system?
11
New cards
Sent to the CNS for processing and interpreting
Where are sensory inputs sent from the PNS and why does this occur?
12
New cards
Somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
What are the components of the motor division of the PNS?
13
New cards
Controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscle
What does the somatic nervous system do?
14
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Enteric nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Enteric nervous system
What are the divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
15
New cards
Fight or flight
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
16
New cards
Rest and digest
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
17
New cards
Controls gastrointestinal functions
What is the role of the enteric nervous system?
18
New cards
Neurons and neuroglia
What are the two cell types of nervous tissue?
19
New cards
Excitable cells that transmit action potentials within nervous tisse
What are neurons?
20
New cards
Have many functions including support, protection, and nourishment of neurons
What are the functions of neuroglia?
21
New cards
Glial cells
What is another name for neuroglia?
22
New cards
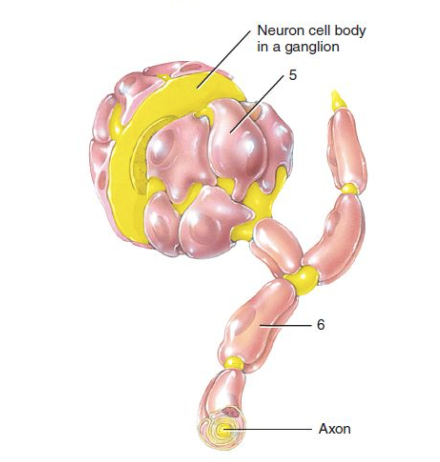
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and receives information
What is the cell body?
23
New cards
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information
What are dendrites?
24
New cards
transmits information to other neurons, muscles, or glands
What does an axon do?
25
New cards
These are the enlarged ends of the axon terminals.
Neurotransmitters are stored and released from here to transmit the impulse from this neuron to the next structure.
Neurotransmitters are stored and released from here to transmit the impulse from this neuron to the next structure.
What is a synaptic end bulb and what does it do?
26
New cards
Branches at the end of the axon
What are axon terminals?
27
New cards
Around 200 billion
How many neurons are found in the adult human body?
28
New cards
Side branches of the axon
What are axon collaterals?
29
New cards
From the dendrites towards the synaptic end bulb
What way do electrical signals flow through a neuron?
30
New cards
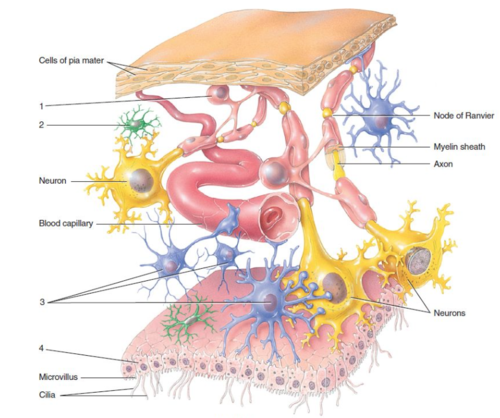
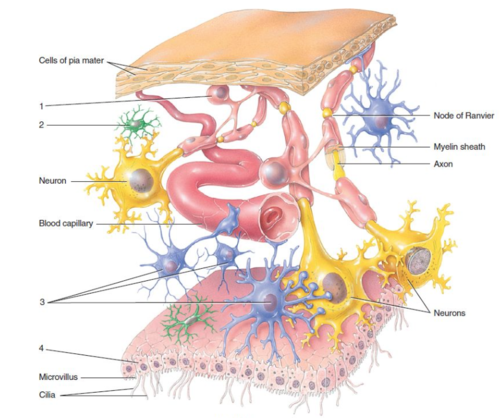
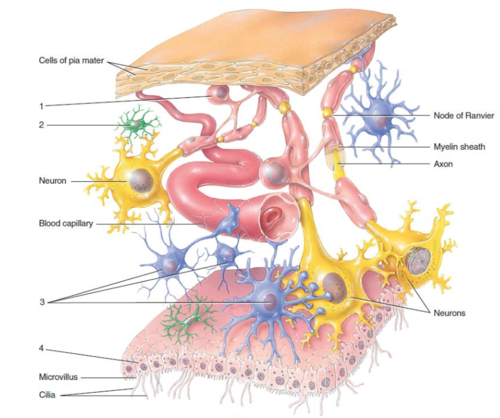
Fatty substance that helps insulate neurons and speeds the transmission of nerve impulses
What is myelin?
31
New cards
Afferent neurons (Sensory neurons)
Interneurons (Integrative neurons )
Efferent neurons (Motor neurons)
Interneurons (Integrative neurons )
Efferent neurons (Motor neurons)
What are the three functional classifications of neurons?
32
New cards
Information goes to the brain and spinal cord via cranial and spinal nerves
What do afferent neurons do?
33
New cards
Mylenated axon
What is an axon surrounded by myelin called?
34
New cards
Integrates sensory information by analyzing and storing it
What do interneurons do?
35
New cards
Peripheral nervous system
Where are afferent neurons located?
36
New cards
Brain and spinal cord
Where are interneurons located?
37
New cards
Information from the brain and spinal cord is sent out to muscles or glands (Effectors)
What are efferent neurons?
38
New cards
Carry signals from CNS to effectors
Where are efferent neurons located?
39
New cards
Afferent neurons
What is label 4?
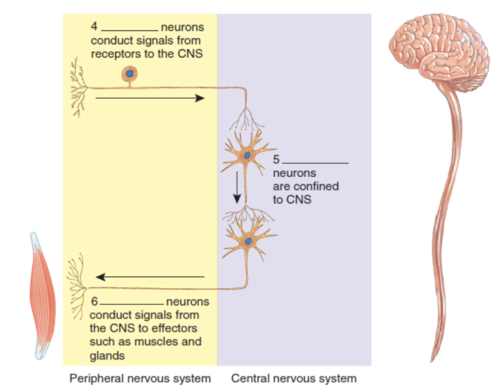
40
New cards
Interneurons
What is label 5?
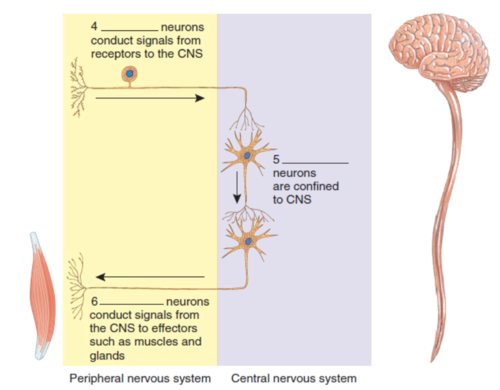
41
New cards
Efferent neurons
What is label 6?
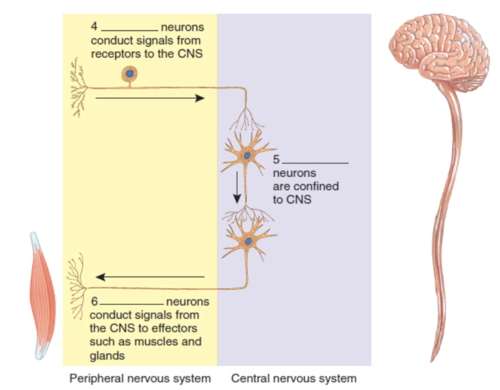
42
New cards
Unipolar
What is the structural classification of this neuron?
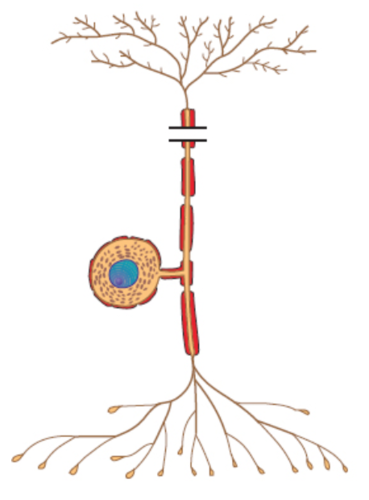
43
New cards
Multipolar
What is the structural classification of this neuron?
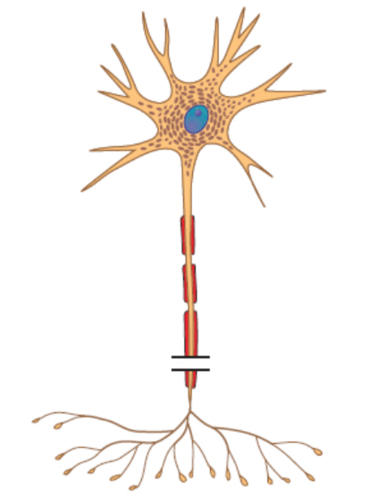
44
New cards
Bipolar
What is the structural classification of this neuron?
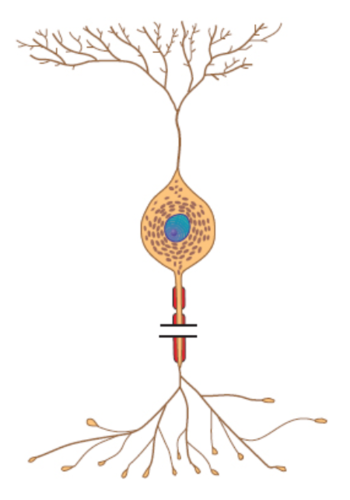
45
New cards
Unipolar or bipolar
What type of structural neurons are sensory neurons in humans?
46
New cards
Multipolar
What type of structural neurons are interneurons and efferent neurons in humans?
47
New cards
Six
How many types of neuroglia are there?
48
New cards
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Ependymal cells
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Ependymal cells
What are the four types of neuroglia found in the CNS?
49
New cards
Maintain environment around neurons
Keep neurons in place
Form the blood-brain barrier
Keep neurons in place
Form the blood-brain barrier
What do astrocytes do?
50
New cards
The project foot processes which wrap around capillaries in the brain to form the blood brain barrier
What do astrocytes project and what do they do?
51
New cards
Cell processes form myelin sheaths around axons in the CNS to increase the speed of transmission of action potentials
What do oligodendrocytes do?
52
New cards
Engulf invading microbes, debris, and necrotic tissue
What do microglia do?
53
New cards
Line ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord
Forms and circulates cerebrospinal fluid from blood plasma
Forms and circulates cerebrospinal fluid from blood plasma
What do ependymal cells do?
54
New cards
Sattelite cells
Schwann cells
Schwann cells
What are the two types of neuroglia found in the PNS?
55
New cards
Cover sensory neuron cell bodies
Maintains neuron environment
Maintains neuron environment
What do satellite cells do?
56
New cards
Entire cell forms myelin sheath around axons in the PNS to increase the speed of transmission of action potentials
What do Schwann cells do?
57
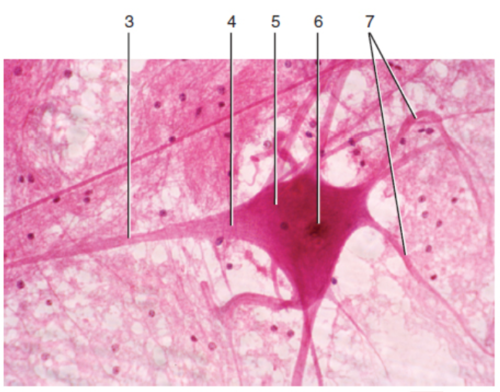
New cards
Axon
What is label 5?
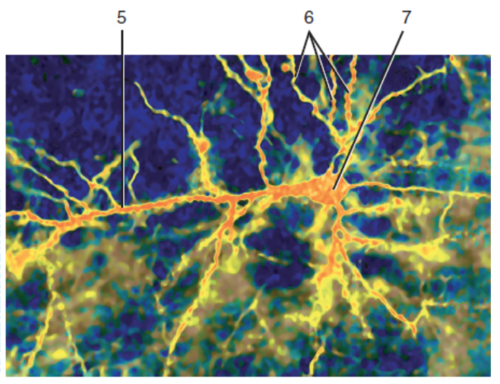
58
New cards
Cell body
What is label 7?
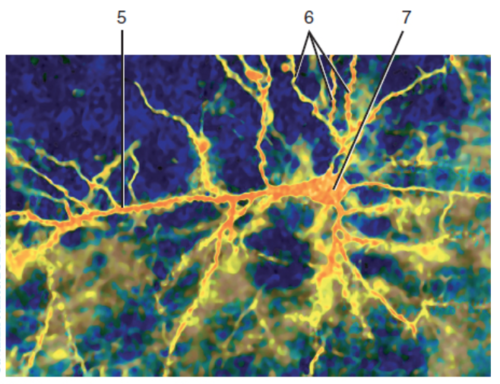
59
New cards
Process
What is label 1?
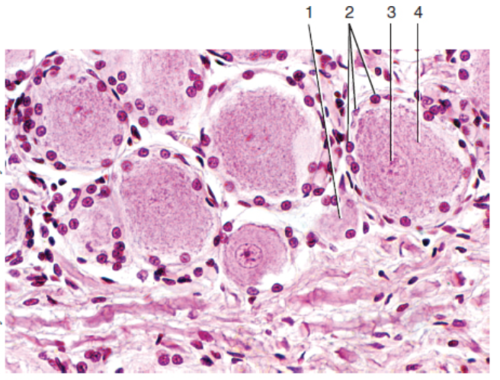
60
New cards
Satellite cells
What is label 2?
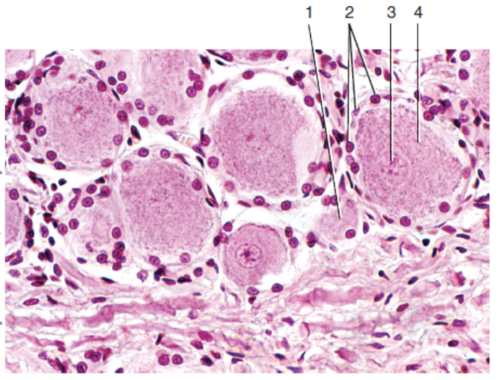
61
New cards
Nucleus
What is label 3?
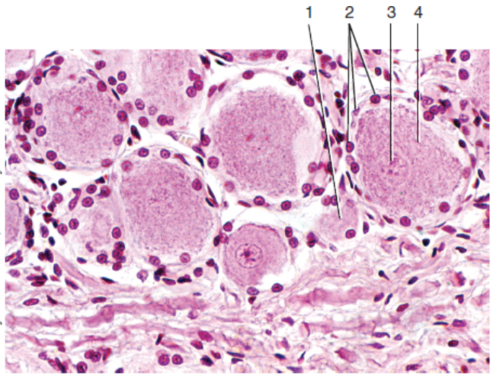
62
New cards
Cell body
What is label 4?
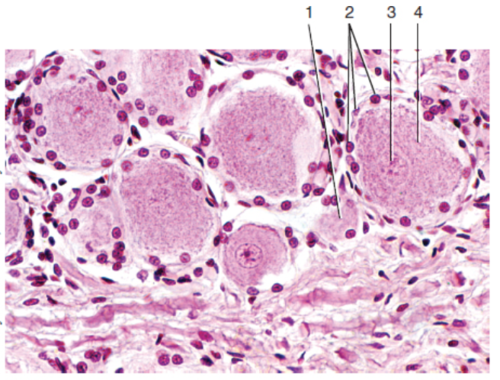
63
New cards
Axon terminal
What is label 1?
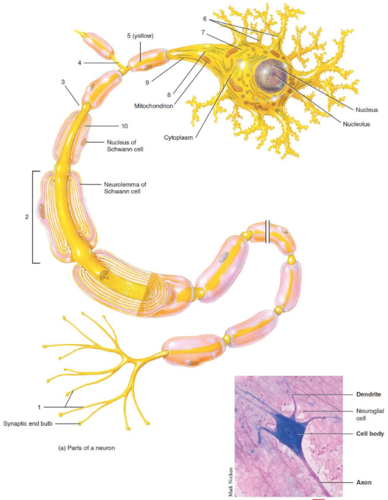
64
New cards
Axon
What is label 5?
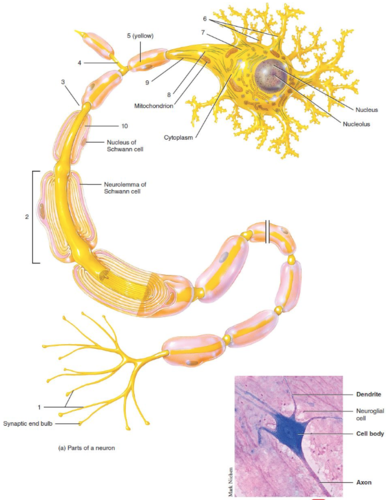
65
New cards
Schwann cell
What is label 2?
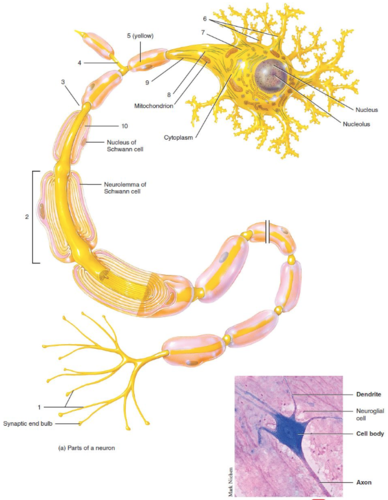
66
New cards
Axon collateral
What is label 4?
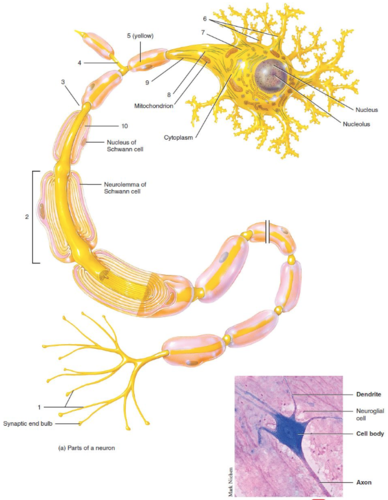
67
New cards
Dendrites
What is label 6?
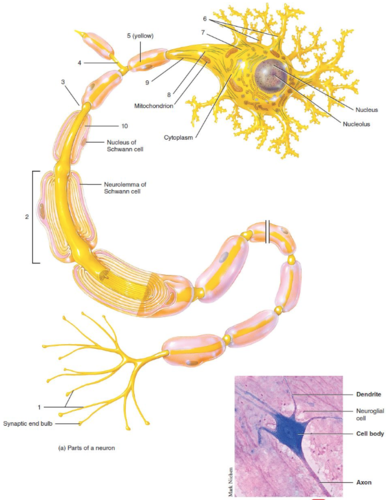
68
New cards
Cell body
What is label 7?
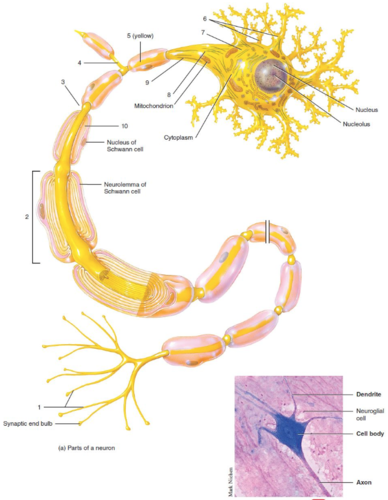
69
New cards
Myelin sheath
What is label 10?
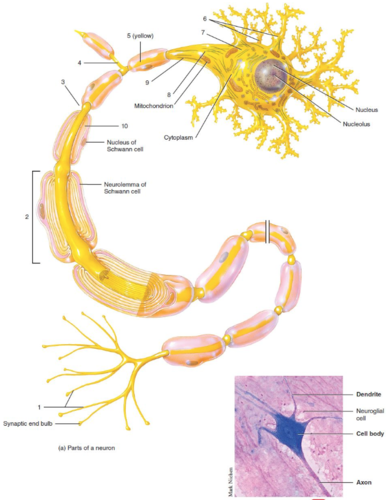
70
New cards
Axon
What is label 3?
71
New cards
Cell body
What is label 5?
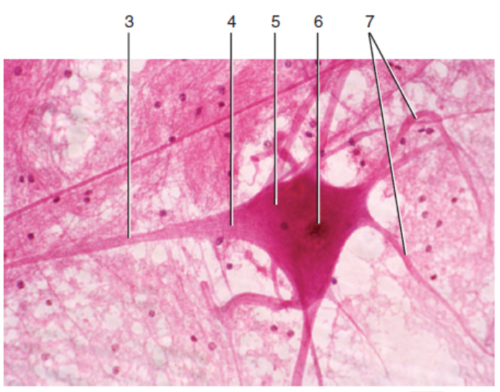
72
New cards
Nucleus
What is label 6?
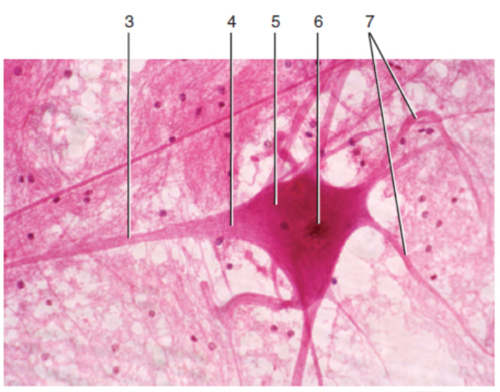
73
New cards
Dendrites
What is label 7?
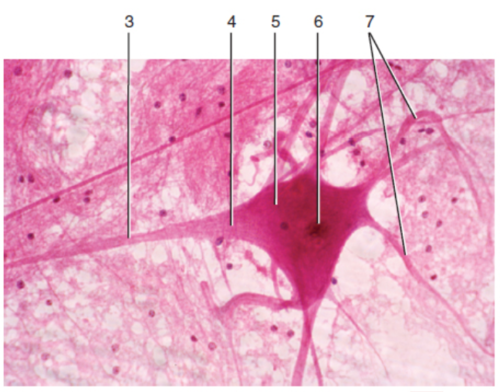
74
New cards
Sattelite cell
What is label 5?
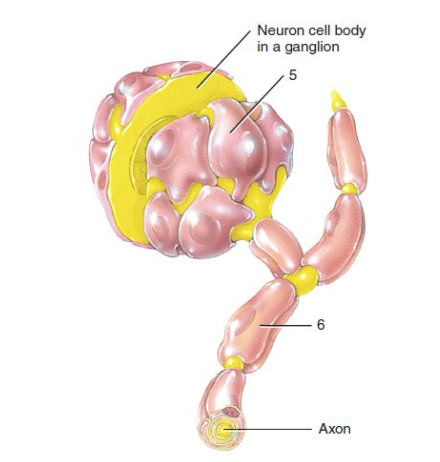
75
New cards
Schwann cell
What is label 6?
76
New cards
Oligodendrocyte
What is label 1?
77
New cards
Microglial cell
What is label 2?
78
New cards
Astrocytes
What is label 3?
79
New cards
Ependymal cell
What is label 4?
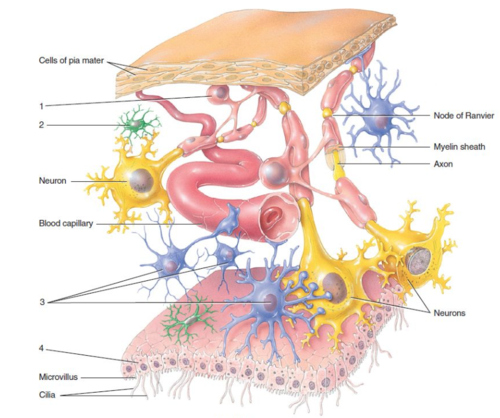
80
New cards
Maintains a stable environment for the brain
What does the blood brain barrier (BBB) do?
81
New cards
Foreign substances in the blood
Hormones and neurontransmitters that are traveling through the blood to the rest of the body
Hormones and neurontransmitters that are traveling through the blood to the rest of the body
What does the blood brain barrier protect the brain from?
82
New cards
Dendrites
What is label 6?
83
New cards
Injecting mice with a blue dye that appeared everywhere but the brain
How was the BBB discovered?
84
New cards
Heroin
Alcohol
Nicotine
THC (Marijuana)
Alcohol
Nicotine
THC (Marijuana)
What are some narcotic/controlled substances that can pass the BBB?
85
New cards
Pituitary gland
Area postrema
Area postrema
What are some areas of the brain with a weaker BBB?
86
New cards
Induces vomiting if toxins are sensed in blood
What is the function of the area postrema?
87
New cards
Least permeable capillaries in the body
What is unique about capilaries in the brain?
88
New cards
Astrocytes extend foot processes around capillary endothelial cells
Why are capillaries in the brain less permeable?
89
New cards
Cells that line the walls around blood capillaries
What are endothelial cells?
90
New cards
Maintain tight junctions between one another
How do endothelial cells make the capillaries in the brain less permeable?
91
New cards
Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and small lipid-soluble molecules
Large lipid-soluble molecules and negatively charged molecules can diffuse slowly
Large lipid-soluble molecules and negatively charged molecules can diffuse slowly
What can cross the BBB?
92
New cards
Transported by channels and carriers
How do glucose and amino acids get across the BBB?
93
New cards
They are small lipid-soluble molecules
Why do antidepressants move across the BBB?
94
New cards
Nanodiamonds
What is a new technique being used to transport things across the BBB in mice?
95
New cards
Connective tissue coverings that surround the brain
What are cranial meninges?
96
New cards
Protect underlying neural tissues
Anchor the brain in the cranial cavity
Anchor the brain in the cranial cavity
What are the functions of meninges?
97
New cards
Inflammation of the meninges due to a bacterial or viral infection
Leads to swelling and stretching which can cause severe headaches, nausau and even death
Leads to swelling and stretching which can cause severe headaches, nausau and even death
What is meningitis?
98
New cards
IV antibiotics
How is bacterial meningitis treated?
99
New cards
Hearing loss and long term brain damage
What are some consequences of meningitis?
100
New cards
Mild cases typically resolve on their own, some antiviral medications can be used, vaccines exist against most common types
How can viral meningitis be treated?