Chemistry Regents Review
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
300 Terms
How to convert Celsius to Kelvin
K = C + 273
How to calculate density?
D=m/v
All matter can be classified as
pure substances or mixtures
What type of matter can't be broken down by chemical change?
elements
Where does heat flow from?
High to low
The temperature of a substance is a measure of the
average kinetic energy of its particles
The energy absorbed and the energy released during a chemical reaction are best represented by a
Potential energy diagram
Which physical changes are exothermic?
Combustion, condensation, freezing (the releasing of heat)
What physical changes are endothermic?
Melting, evaporating, boiling (absorption of heat)
How to find the specific heat capacity?
dividing the amount of heat energy added to a substance by the substance's mass and the change in temperature (found on ref table)
What is sublimation?
solid to gas
What is deposition?
gas to solid
Which sample of matter has the greatest distance between molecules at STP?
gases
At standard pressure, during which physical change does the potential energy decrease?
Liquid to solid (cooling)
What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory?
Gas particles are in constant, random and rapid straight - line motion. A gas consists of very tiny particles .Gas particles are very far away from each other. The size of the particles are very small relative to the distances between the particles. All particles are assumed to have zero volume. All collisions between particles are perfectly elastic (that is, no energy is gained or lost during the collision). There are no attractive or repulsive forces between the molecules
What is the motion and attractive forces of ideal gas particles?
random straight-line motion and no attractive forces
What does Boyle's Law state?
as pressure increases, volume decreases
What does Charles' Law state?
volume and temperature are directly proportional
What does Gay-Lussac's Law state?
Pressure and temperature are directly proportional
what is Grahm's law of effusion?
under the same conditions, heavier gases travel slower
Under which conditions of pressure and temperature is a real gas most like an ideal gas?
High temperature and low pressure
What type of question is this? : Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, which gas will di use at the slowest rate?
Grahm's law of effusions
What is BP?
the temperature at which vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to atmospheric pressure (directly proportional)
What happens when there is higher (stronger) intermolecular forces?
Higher BP and lower vapor pressure
What happens when there is lower (weaker) intermolecular forces?
Lower BP and higher vapor pressure
How was the electron discovered?
JJ Thomson completed the cathode ray experiment. Concluded there must be a negative particle. Called it the electron.
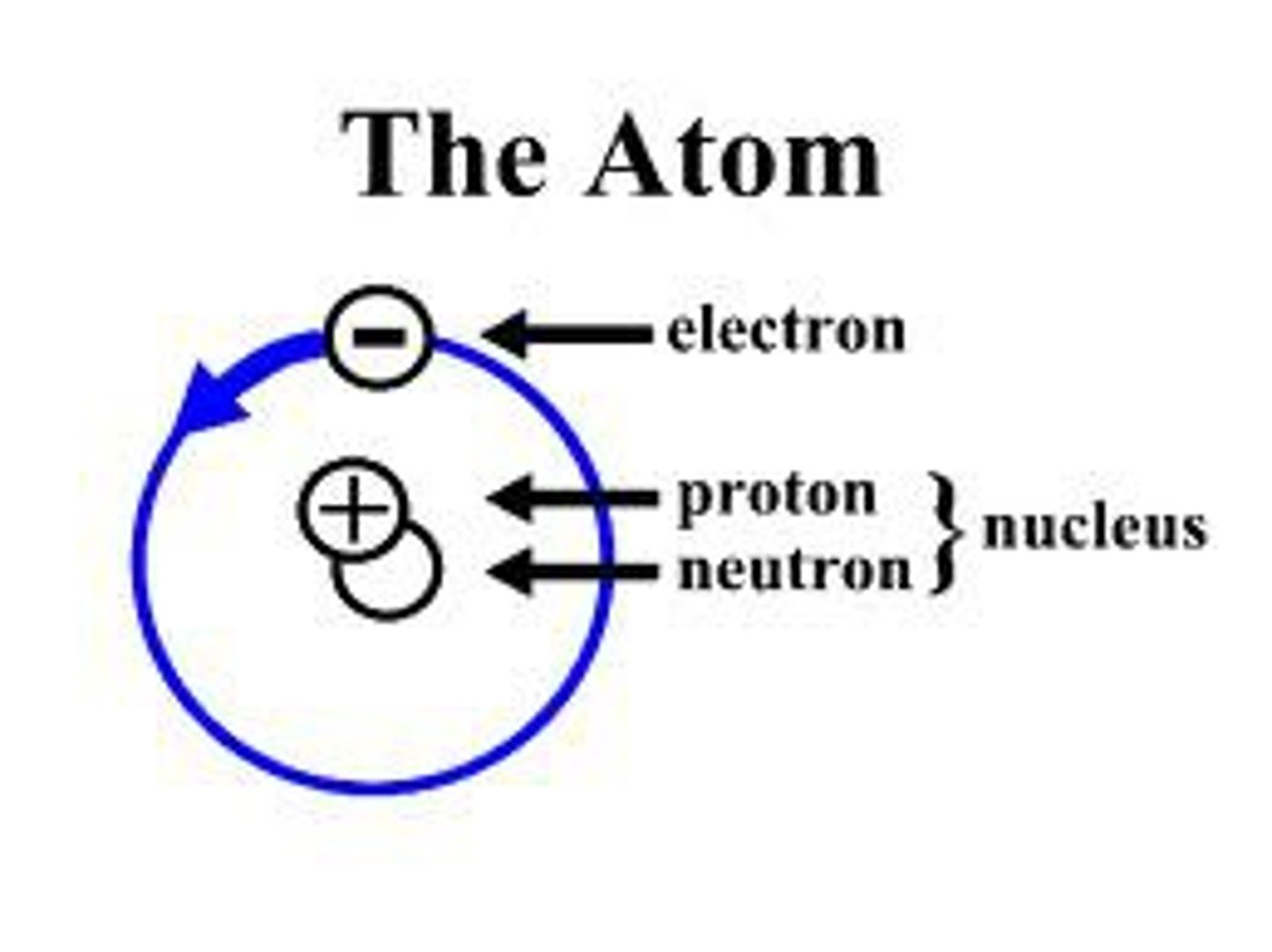
What particles are found in the nucleus of an atom?
protons and neutrons
What charge does the nucleus have and what charge is it surrounded by?
Positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons
When is the bright line spectrum of an element produced?
It is produced when excited state electrons (higher energy) travel back to their more stable ground state (lower energy). Energy is released b/c it is exothermic creating a flash of light
What indicates the number of protons in an element?
Atomic number
What do all atoms of the same element have in common?
Atomic number (number of protons)
How to calculate the mass number of an atom?
number of protons + number of neutrons
How to calculate the number of electrons in an atom?
It is equal to the number of protons so look at the atomic number
Which two particles in an atom have a mass approximately equal to one atom?
protons and neutrons
Which particle remains undetected when passing through an electric field?
Neutrons are electrically neutral particles, meaning they have no charge, so they are not affected by electric fields
What is the charge of protons?
Positive
What is the charge of neutrons?
Neutral
What is the charge of electrons?
Negative
How to find the charge of the nucleus?
Atomic number (Number of protons)
How to find the number of neutrons when given the mass?
Mass number - atomic mass (protons)
A neutron has a charge of
0
What happens when an ion loses 2 electrons?
It becomes positive and the radius becomes smaller
What happens when an atom becomes ion?
The atom gains an electron giving it a negative electric charge
How to find the net charge of an atom
# of Protons minus # of Electrons
What makes something an isotope?
Same number of protons, different number of neutrons
How to calculate atomic mass of an element?
multiply the mass of each isotope by its natural abundance, expressed as a decimal, and then add the products

In the ground state which atoms have a completely filled valence electron shell?
The noble gases
What is the Law of Conservation of Matter?
matter cannot be created or destroyed
What is the law of definite proportions?
types of atoms in a compound exist in a fixed ratio
What did John Dalton state about the atom?
All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are too small to see, indivisible, and indestructible. They cannot be created or destroyed. All atoms of a given element are identical.
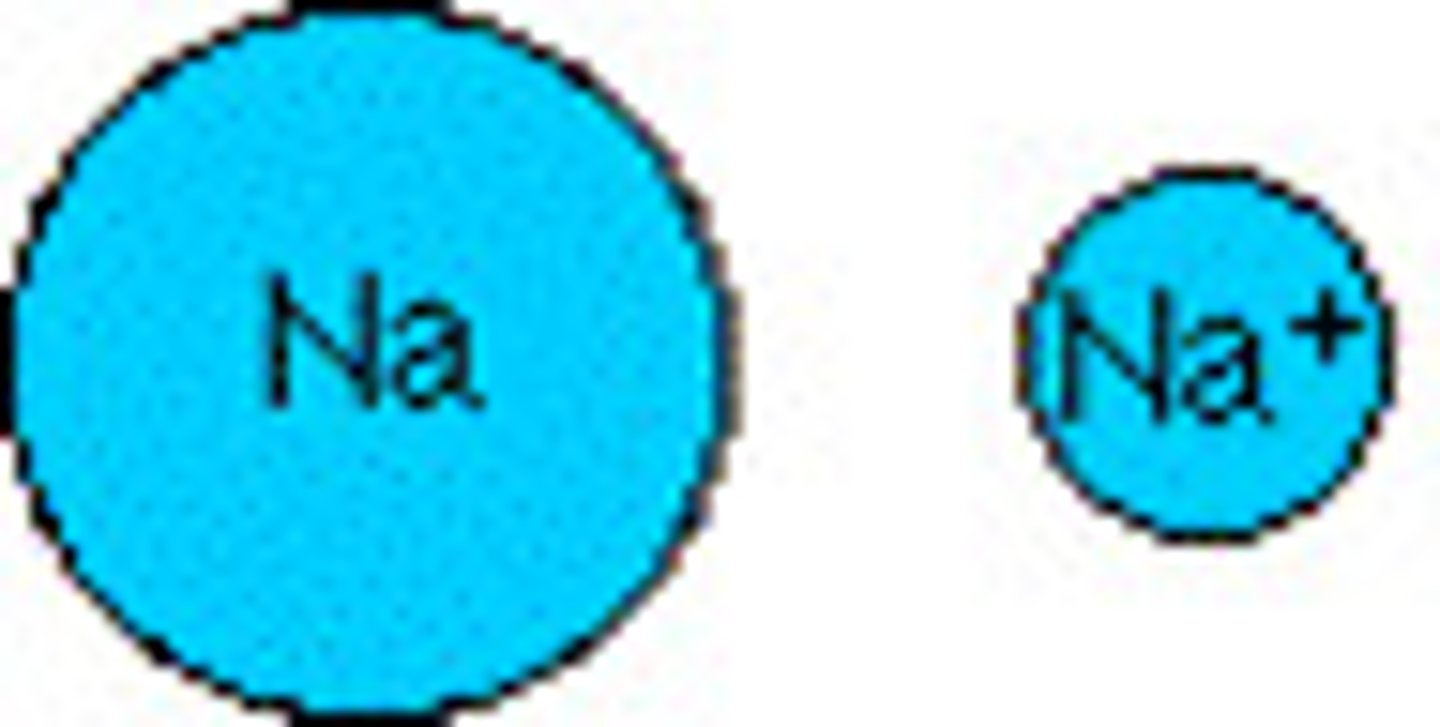
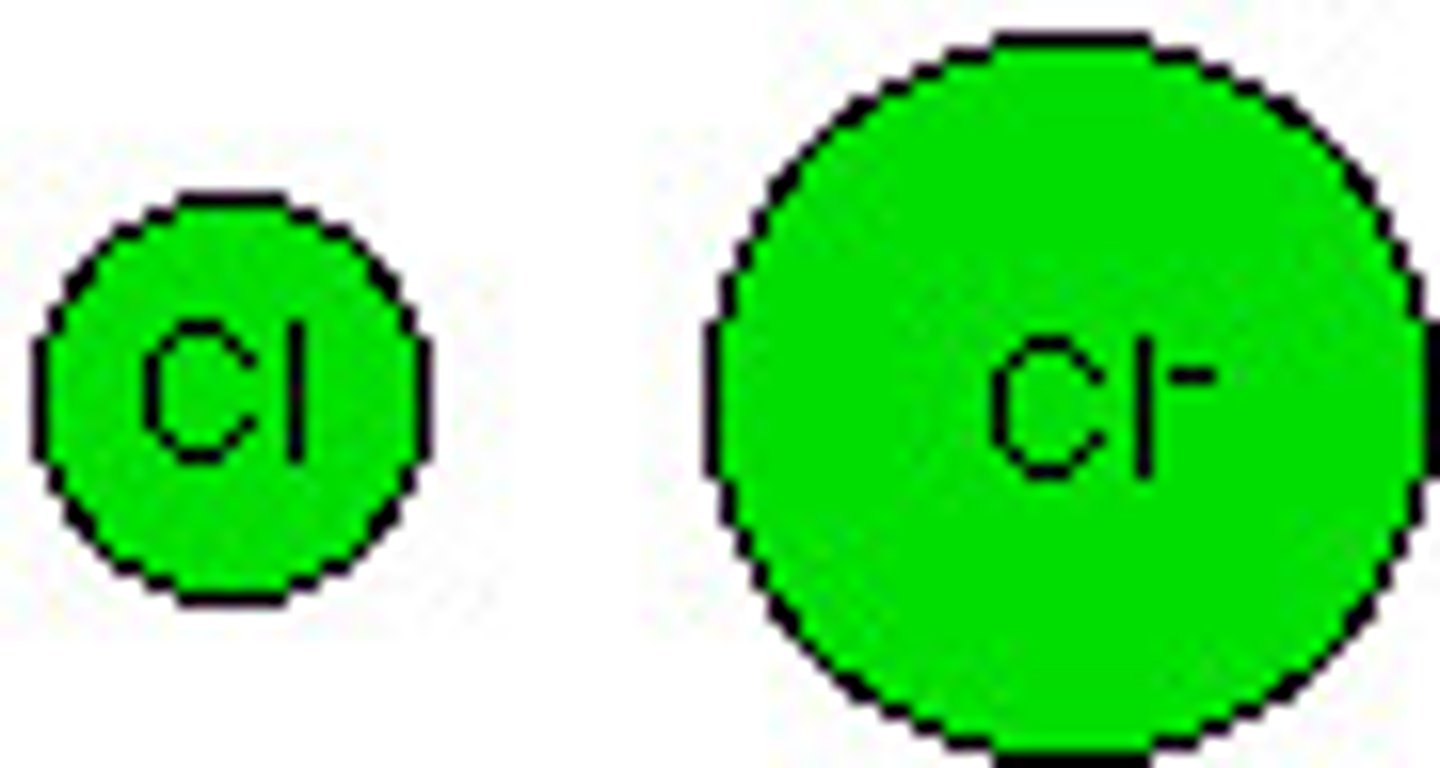
What are cations?
positively charged ions (attracted to negative electrodes). Metals lose electrons (lose the entire energy level, and there are now less negative charges to attract) Ionic radius of metals is LESS THAN their atomic radius.

What are anions?
negatively charged ions (Attracted to positive electrodes). Nonmetals gain electrons (fill their energy level, and there are now more negative charges to attract) Ionic radius of nonmetals is GREATER THAN their atomic radius.
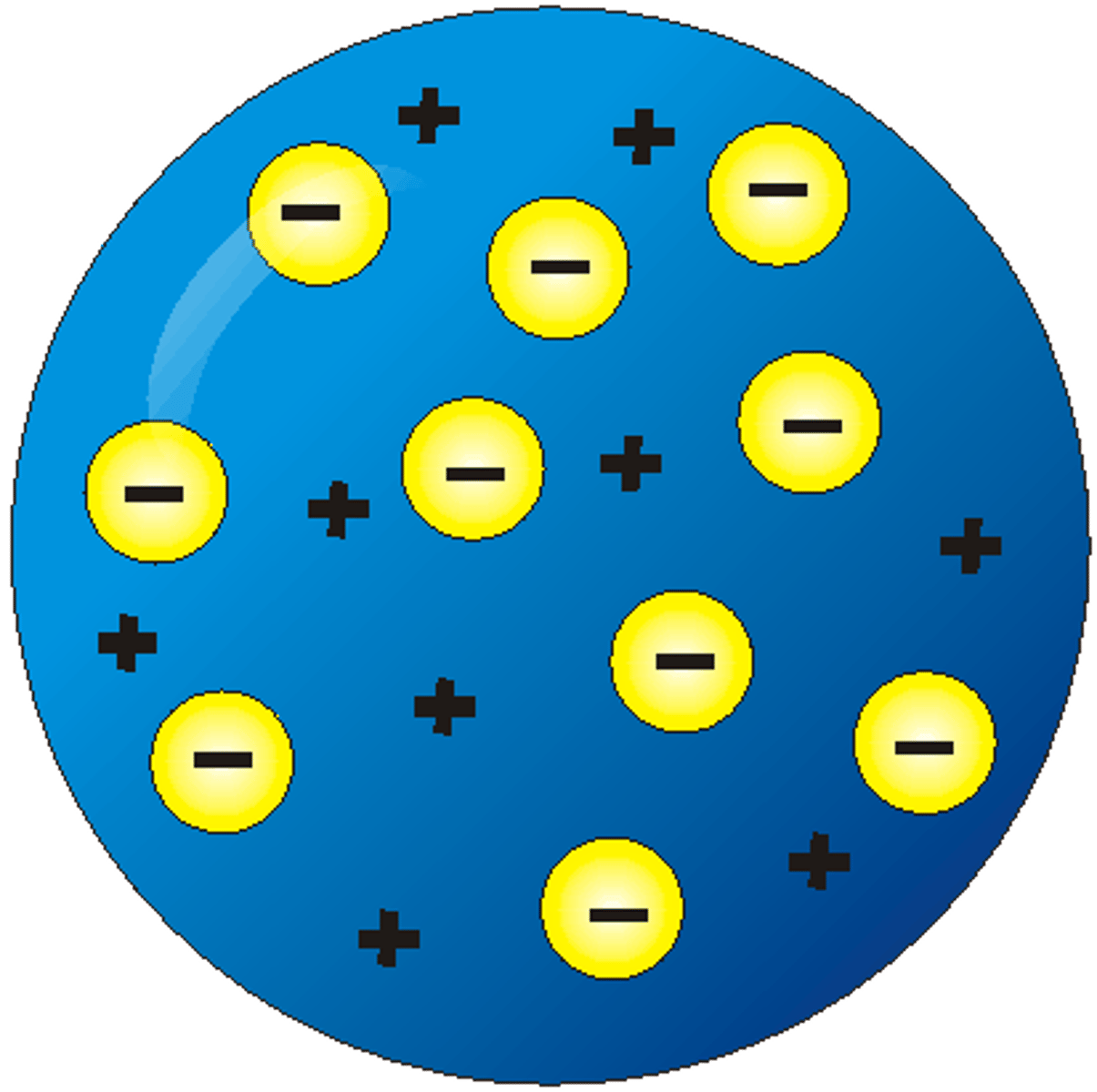
What did J.J. Thompson discover?
Discovered the existence of the negative electrons , and predicted that there are also positive particles to keep electrons in place. It was then discovered that one electron carried one unit of negative charge, and that the electrons had less than 1/ 1000 th the mass of a proton.
What is this model?
Plum pudding model
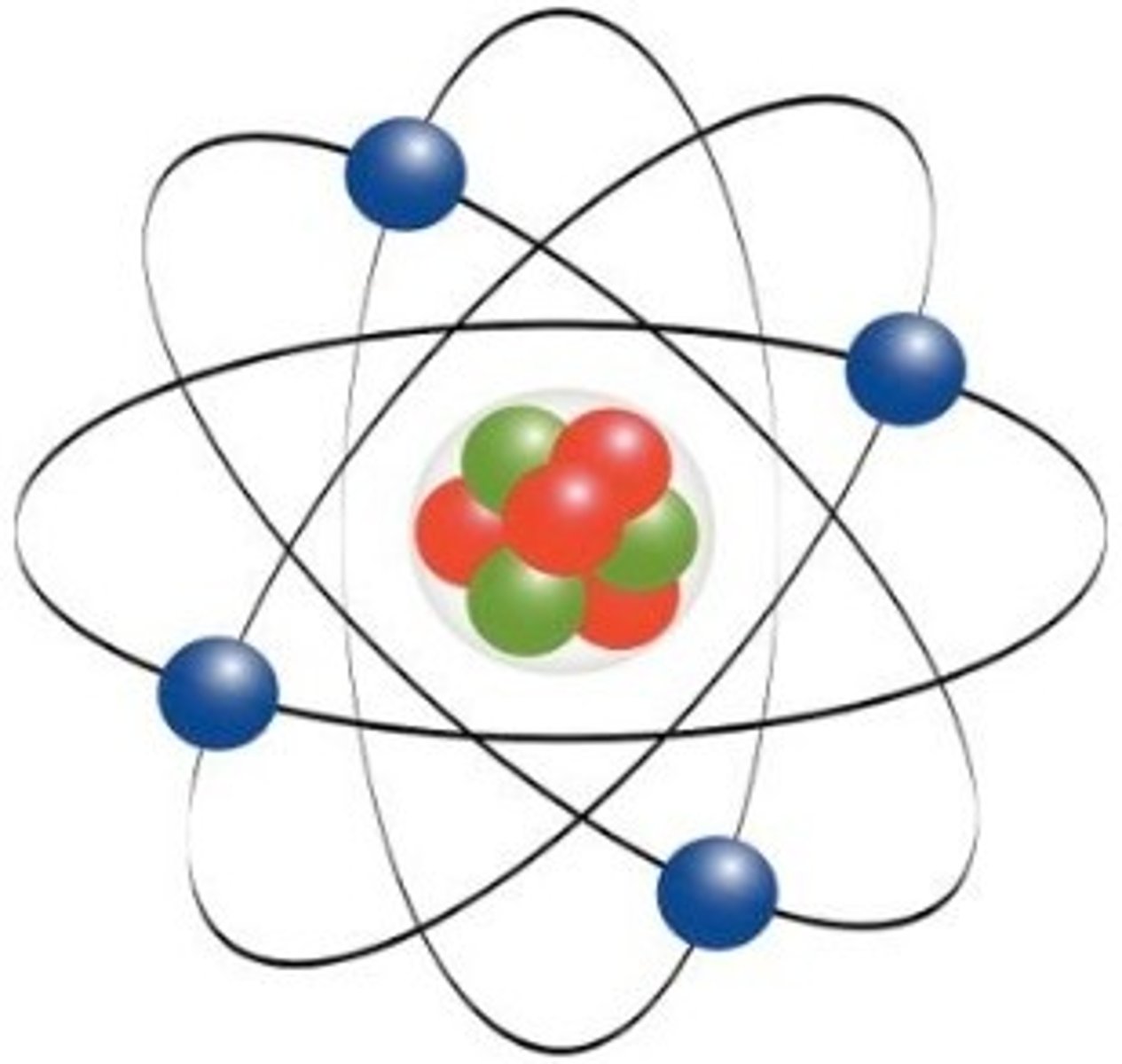
What did Ernest Rutherford state about the atom?
Discovered the nucleus of an atom, and named the positive particles in a nucleus 'protons". His experiment concluded that electrons are scattered in empty space around the nucleus. (Atoms are mostly empty space, and most of the mass in in the center.
What experiment discovered the nucleus of the atom?
Gold foil experiment
What is the mass of a proton compared to that of an electron?
It is greater
What are nucleons?
Subatomic particles in the nucleus (neutrons and protons)
What is a nuclide?
a distinct kind of atom or nucleus characterized by a specific number of protons and neutrons.
Where are electrons located in an atom?
electron cloud
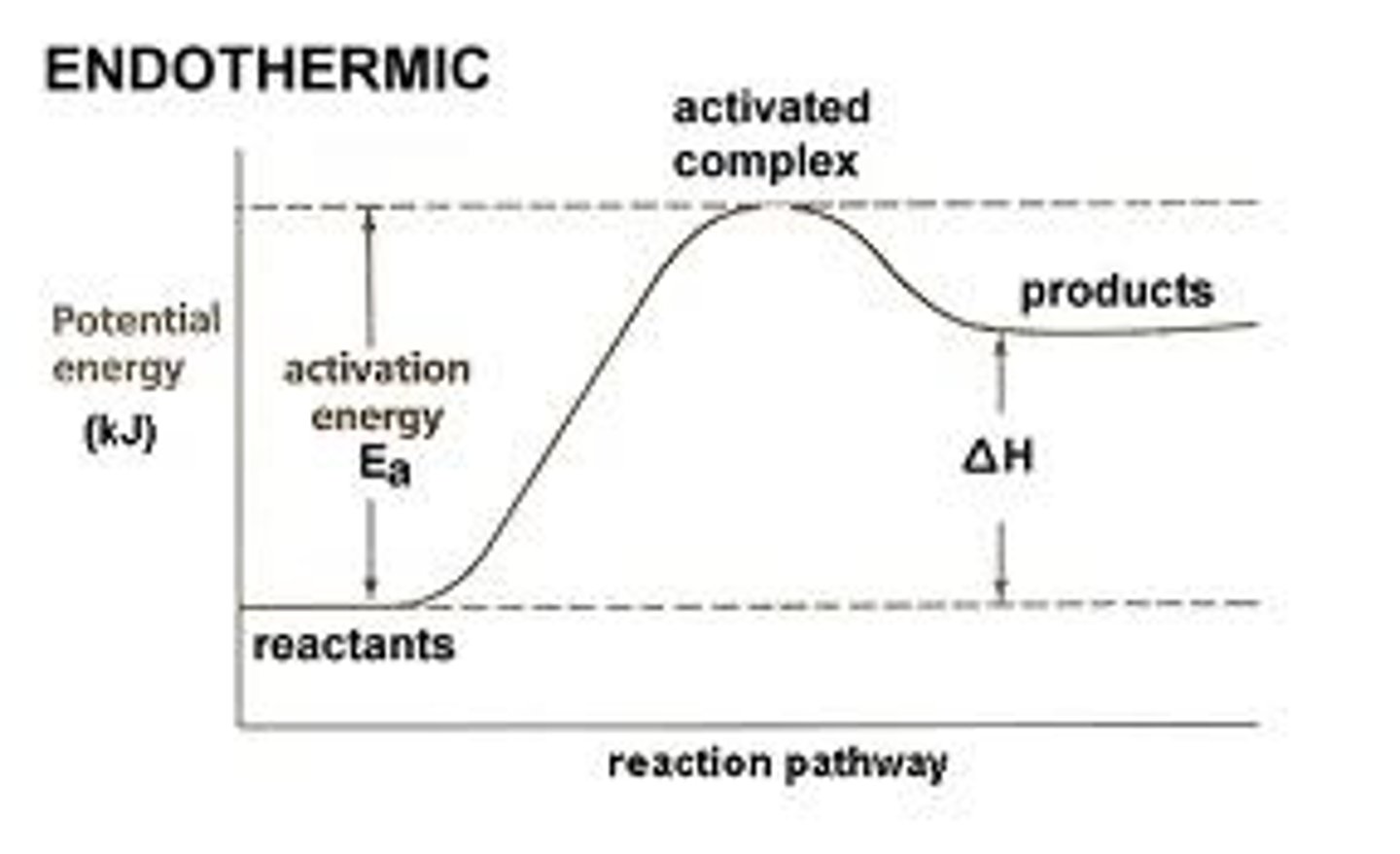
What does it mean for something to be endothermic?
Energy was absorbed so the surrounding temperature decreases
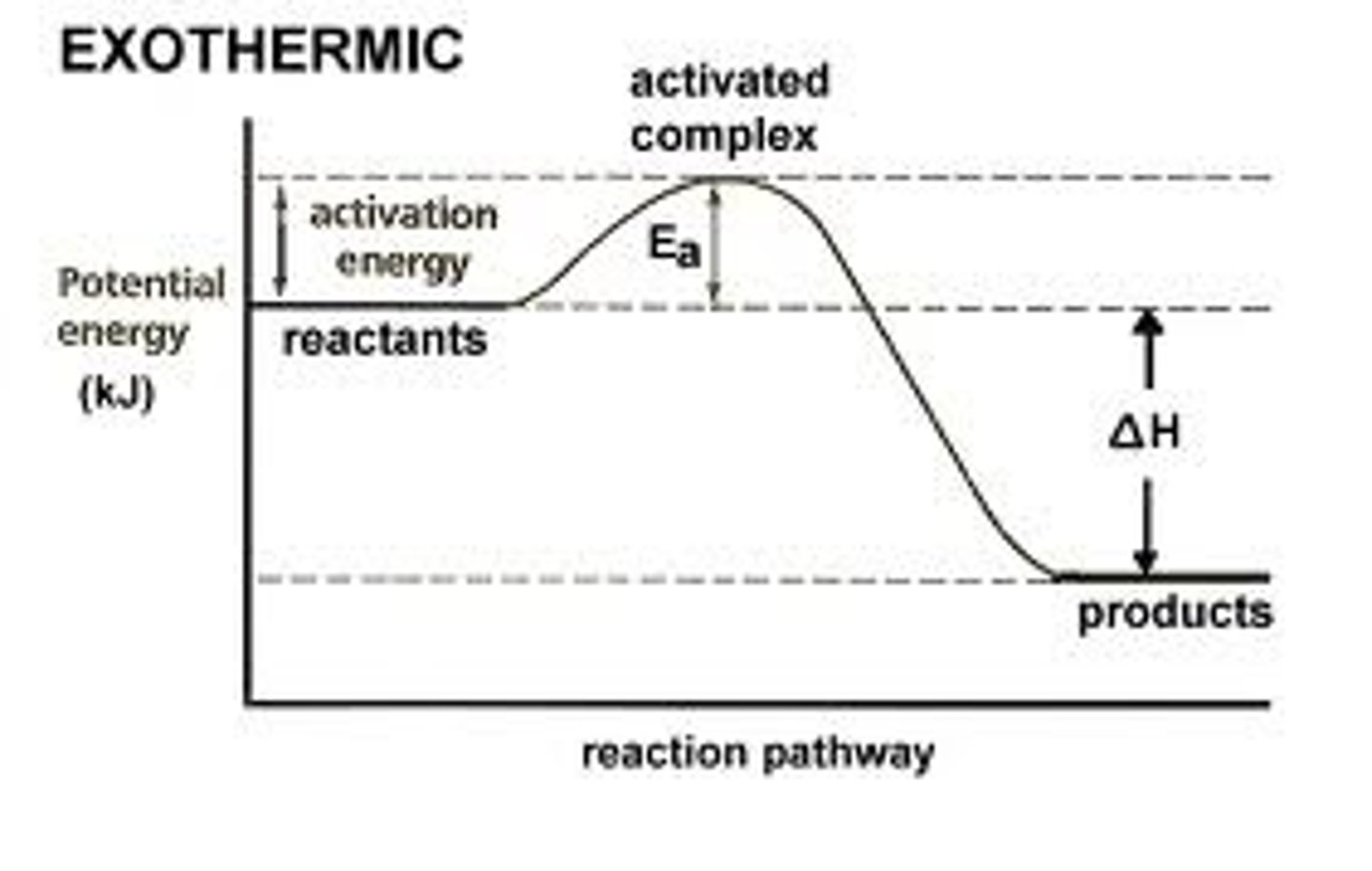
What does it mean for something to be exothermic?
Energy is released so the surrounding temperature increases
What is enthalpy?
The heat content of a system at constant pressure
In an endothermic reaction the products have _____ energy than the reactants
More
In an exothermic reaction the products have _____ energy than the reactants
Less
What is entropy?
a measure of the disorder of a system
What does the law of disorder state?
systems tend to move from a state of
order (low entropy) to a state of disorder or randomness (high
entropy). Entropy is forever increasing!
When does entropy increase?
When a substance is broken up (decomposition)
How to tell if entropy has increased in a reaction?
Entropy increases in a reaction where the total number of product particles/molecules is greater than the total number of reactant particles (coefficients/moles will add up higher)
What do heating and cooling curves show?
Heating and Cooling Curves help to describe the energy changes that accompany phase changes.
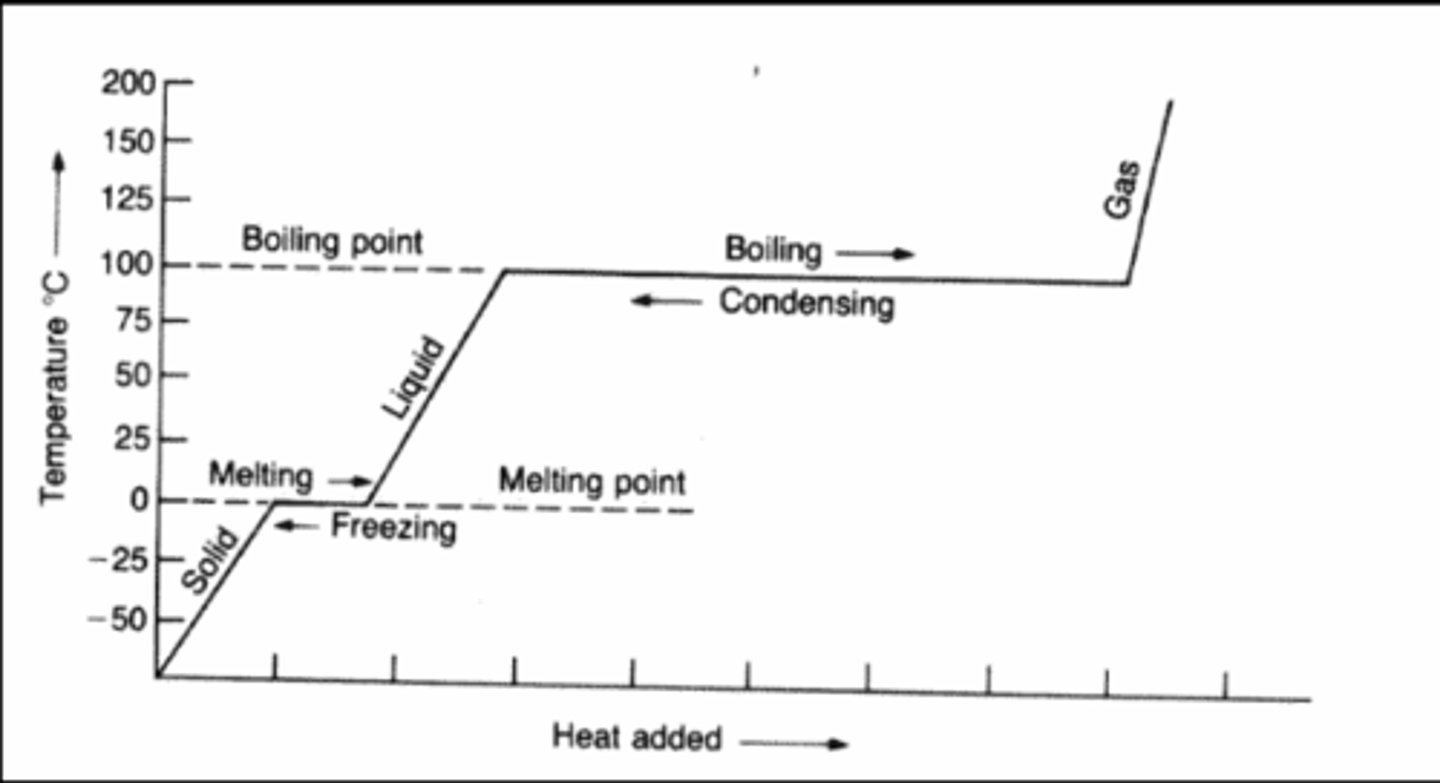
When to use specific heat capacity equation?
When there is a temperature change
When to use heat of fusion of water is 334 equation?
When it is asked how much heat is required to melt or is released when freezing
When to use heat of fusion of water is 2260 equation?
Use when asked how much heat is required to boil or is released when condensing.
How to construct a Lewis Dot Diagram?
Write the element symbol and add in the number of dots that represent the valence electron of the element.
What are valence electrons?
electrons in the outermost shell
How to determine if an electron is in the excited state?
any electron configuration in which the last electron (again, the valence electron) is in a higher energy orbital, this element is said to be in an excited state.
Which electron shell in an atom has the greatest amount of energy?
The outermost shell
The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing___
Atomic number
How to tell if two elements have the same chemical properties?
Elements of the same group have the same valence electron and therefore similar chemical properties.
What are metalloids?
B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te - elements that have the same properties as some metal and some nonmetals
Where are metallic elements located on the periodic table?
On the left side
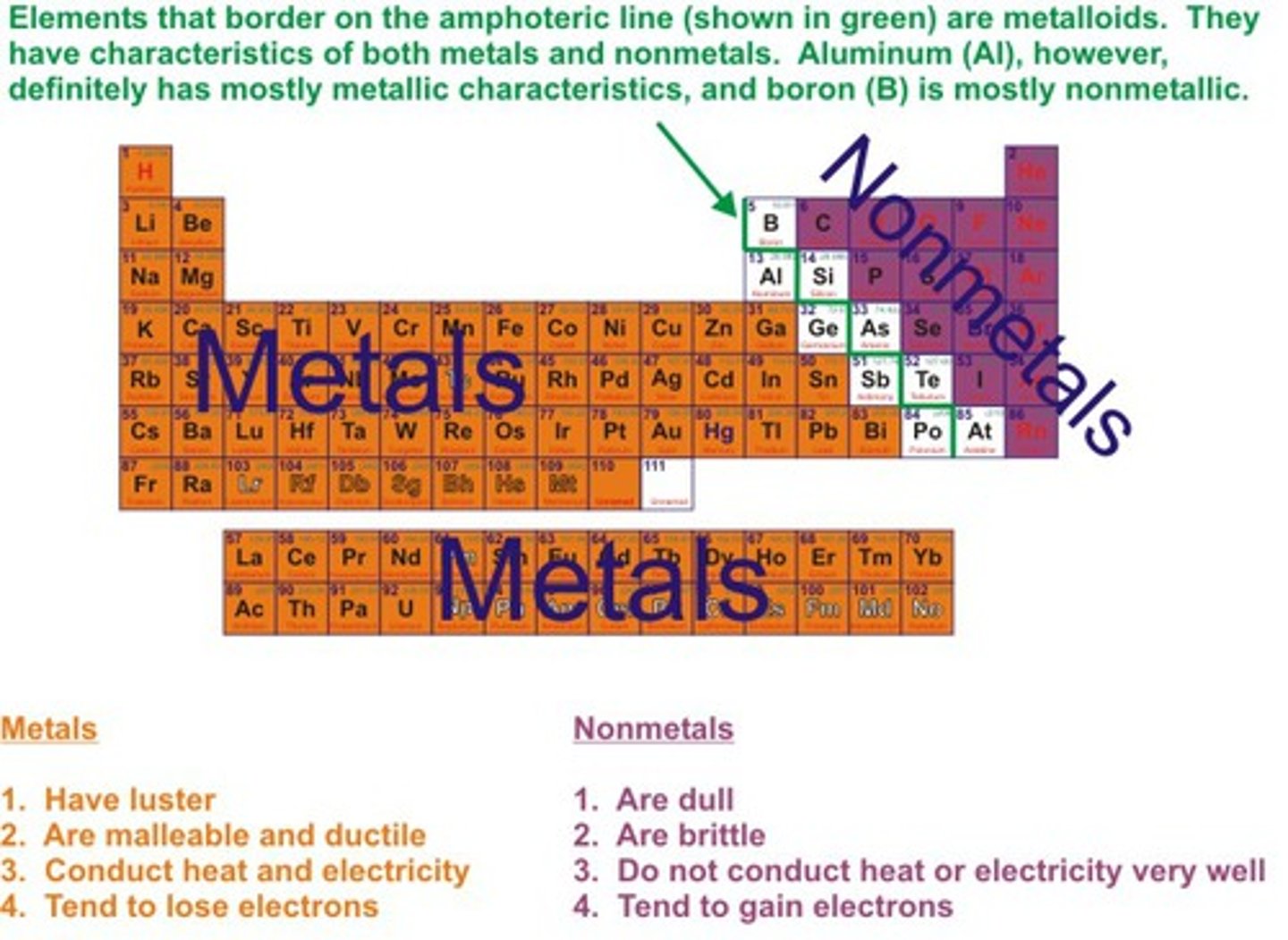
Where are nonmetallic elements located on the periodic table?
On the right side
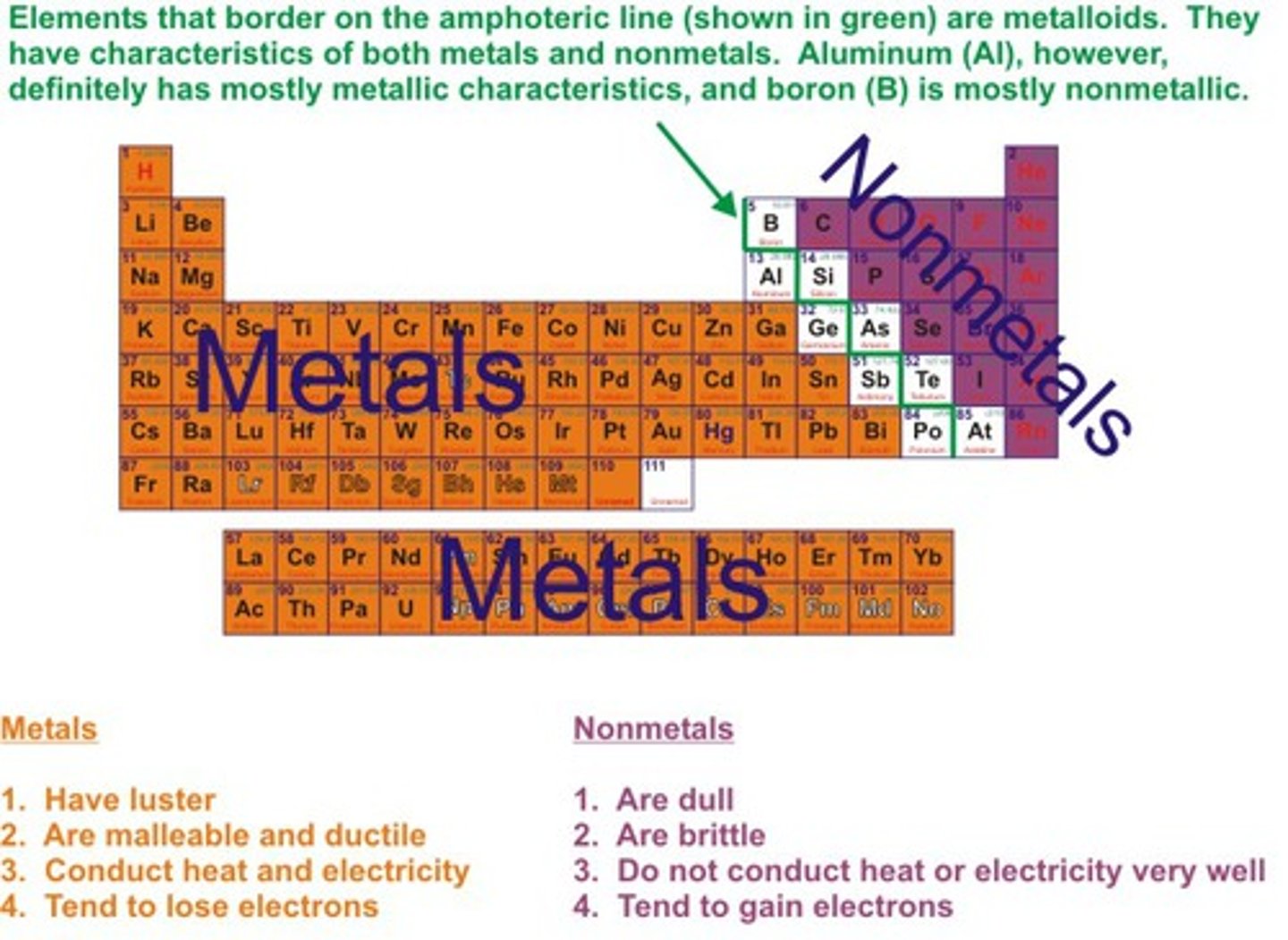
What are properties of metallic elements?
solid at room temp (except Hg), lustrous, conduct heat and electricity, malleable, ductile and melt at very high temps (except Hg)
What are properties of nonmetallic elements?
Non malleable, brittle, poor conductors of heat and electricity, no metallic luster, low melting points
Is hydrogen a metal or a nonmetal?
it is classified as a nonmetal, but can behave like a metal in some ways
Which element tends not to react with other elements?
Noble gases do not react because they do not tend to gain or lose electrons.
What are alkali metals?
Group 1 in the periodic table (excluding hydrogen). the are very reactive metals
What are alkaline earth metals?
Group 2 in the periodic table. The are somewhat reactive metals.
What are halogens?
Most reactive nonmetals. Group 17
What is electronegativty
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
Group A on the periodic table?
Representative elements
Group B on the periodic table?
Transition metals
Group C on the periodic table?
Inner Transition Elements
What are the phases of the elements at STP?
Two liquids: Hg and Br. Gas: Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Florine, Chlorine, and Noble gases. Rest are solids.
What is shielding?
The effect of the kernel electrons pushing outwards of the valence electrons. (Negative electrons repel other negative electrons) As there are more energy levels there is more shielding (the effect gets stronger)
What is atomic radius?
The typical distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost isolated electron
What is the octet rule?
Atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to have a full set of valance electrons.
What is ionization energy?
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
metals have ___ ionization energy
Low. They lose electrons easily.
Nonmetals have ___ ionization energy
High. They don't want to give up electrons