Chapter 19: Political Communication
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
political communication mainly focuses on [5]
1. The political content of media
2. The actors and agencies involved in the production ofcontent
3. The effect
4. The impact of the political system on the media system
5. The impact of the media system on the political system
Why is Political Communication Important?
●It influences voter behavior and public opinion formation.
●It determines the effectiveness of political campaigns
and elections.
●It affects democratic accountability and transparency.
●It plays a role in authoritarian regi
Political communication primarily revolves around interactions
between what?
politicians, voters, and the media.
what relies on effective communication between leaders and
the public to function properly?
Representative democracies
what entities continuously interact and influence one another, making
communication a fundamental tool in governance.
Political elites, the media, and citizens
Mass media
powerful instrument that influences our lives, and
in such a way, it could affect our opinions and behavior.
"Natural History”
people tend to have natural history shaped by the specific circumstances of time and place.
"Environmental Factors"
"Environmental Factors" such as government interests,
legislative decisions, rapid technological advancements, and
historical events play a crucial role in influencing this history.
Media Phases
●1st Phase- This ranges from the 19th-20th century until the
1930s wherein the media has a lot of power. The use of
media during the First World War propagandists by having
dictatorial states in the inter-war years.
●2nd Phase- This is from the 1930s to the 1960s. Various
studies have been carried out investigating the effects of
different types of content and media.
●3rd Phase “The return to the concept of Powerful Media”
Media was seen as influential again, with political and
commercial motives shaping content.
●4th phase- This phase changed the attention towards
long-term change to cognitions rather than attitude, towards
also to the collective phenomena such as climates' opinion,
structures of belief, definitions of social reality and
ideologies.
Agenda Setting
The theories of agenda setting suggest that the news drives the
public issues' priorities.
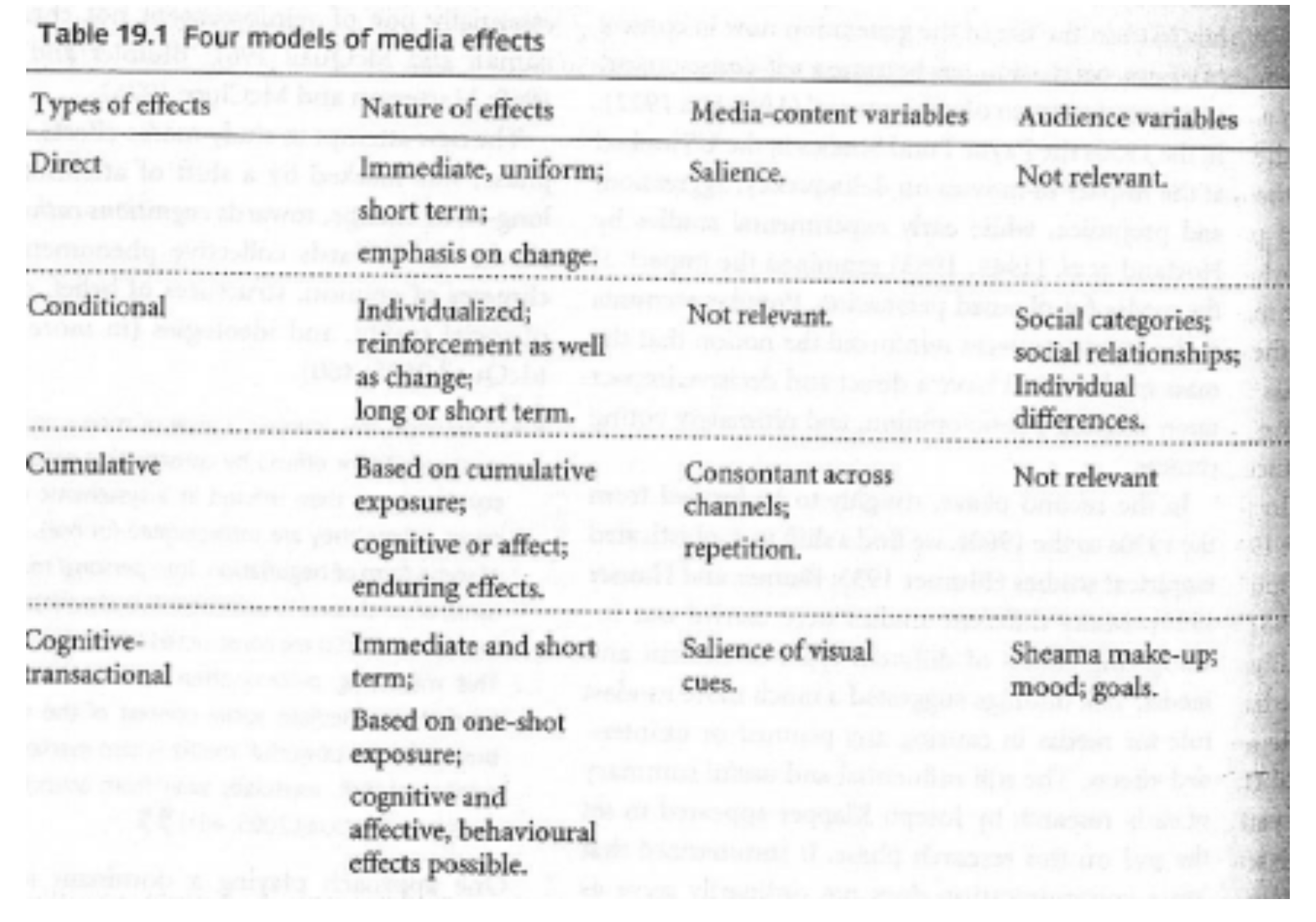
Models of Historical Approach
●Direct effects
●Conditional
●Cumulative effect
●Cognitive transactional
Two Phases of Political Campaigning
Pre-modern Era : Political communication was based on the strength of the local party organization and face-to-face contact.
Second wave of campaigning: Having a mass media party can disseminate to a broader range of audiences since they not only focus on mobilizing the electorate but also target some undecided voters.
Shopping and Adoption Model
Plasser (2002), U.S. election campaigns follow a shopping model, while other countries adopt certain U.S. techniques but maintain unique elements.

different styles of media systems and media logic (3)
Mediterranean or Pluralist Model
Demographic Corporatist Model
North Atlantic or Liberal Model-
The New Political Communication
The rise of new media has transformed election campaigns and political messaging. Political institutions must now adapt to digital communication strategies.
The early days: Web 1.0 Communication
Academic Analysis: Creation and Content- Robert Klotz
(1997)
Potential Impact
Political Communication 2.0