AP WORLD UNITS 1 AND 2 SUMMATIVE REVIEW
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Meritocracy
Bureaucratic structure where officials earn roles based on merit
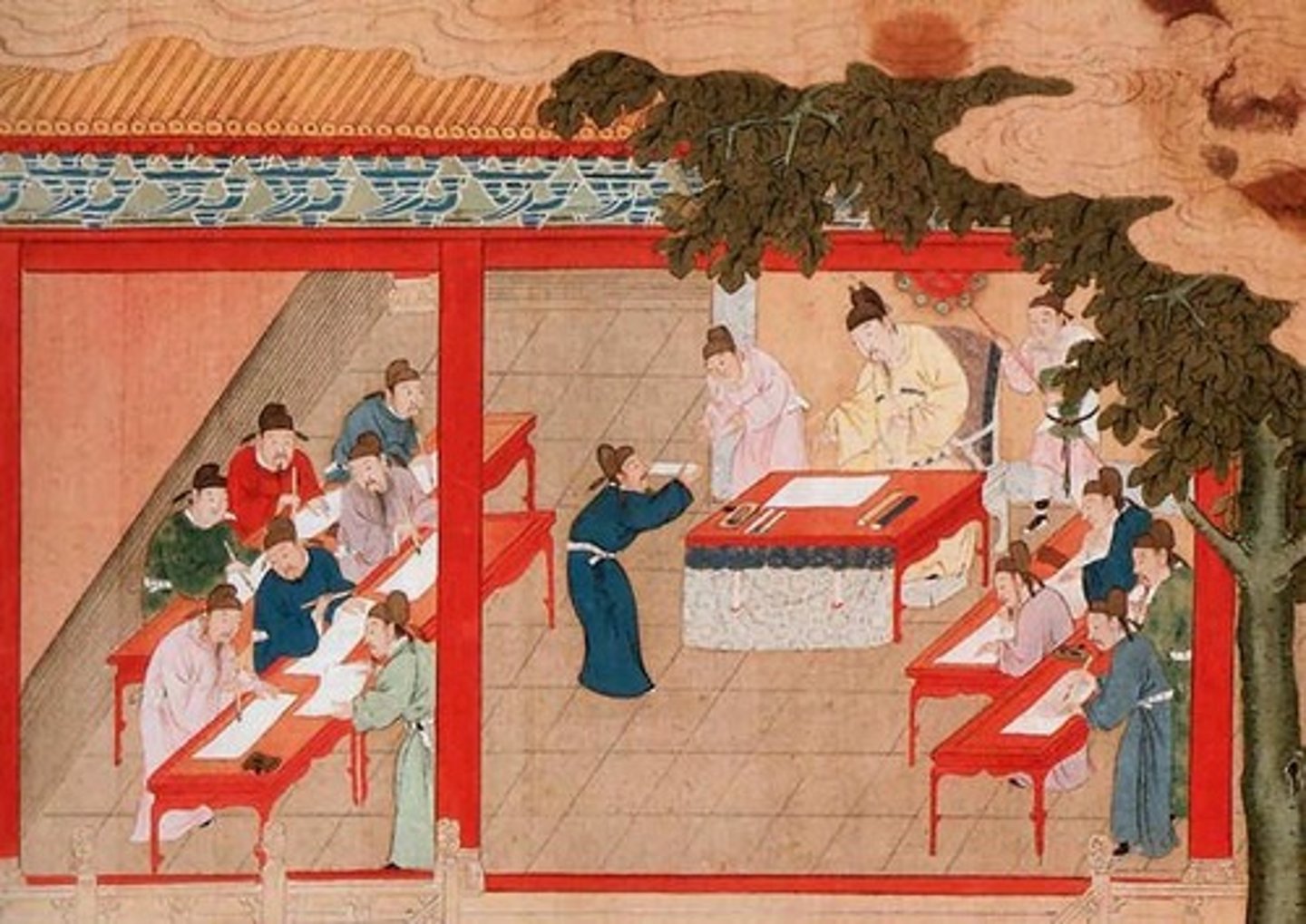

Grand Canal
Over 30,000-mile waterway aiding China's trade dominance

Champa Rice
Fast-growing, drought-resistant, flood resistant rice leading to increased crop yields

Chan Buddhism
Syncretic faith combining Buddhist and Daoist principles
Filial Piety
Loyalty and submission of families to the older generations i.e. parents and grandparents

Neo-Confucianism
Blend of rational thought (Confucianism) with abstract notions (Buddhism)
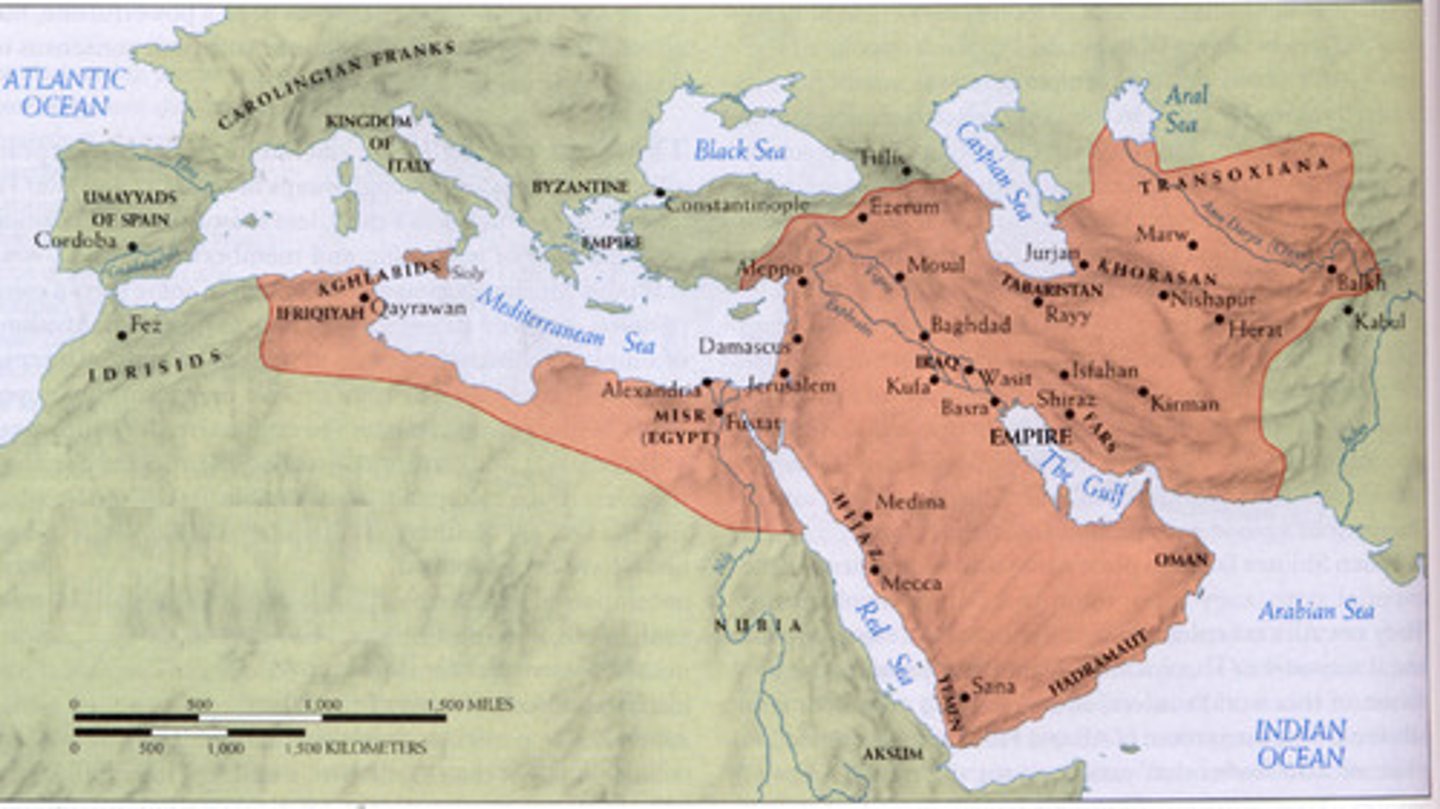
Abbasid Empire
Islamic empire facing challenges from Central Asian nomads and European powers
Mamluks
Enslaved ethnic Turks in Arabic culture, serving as soldiers and bureaucrats

Seljuk Turks
Central Asian group challenging the Abbasid Empire

Baghdad
City at the heart of trade routes, significant in the Abbasid Empire
Sufis
Muslim mystics focusing on introspection and spiritual truths: include Whirling Dervishes

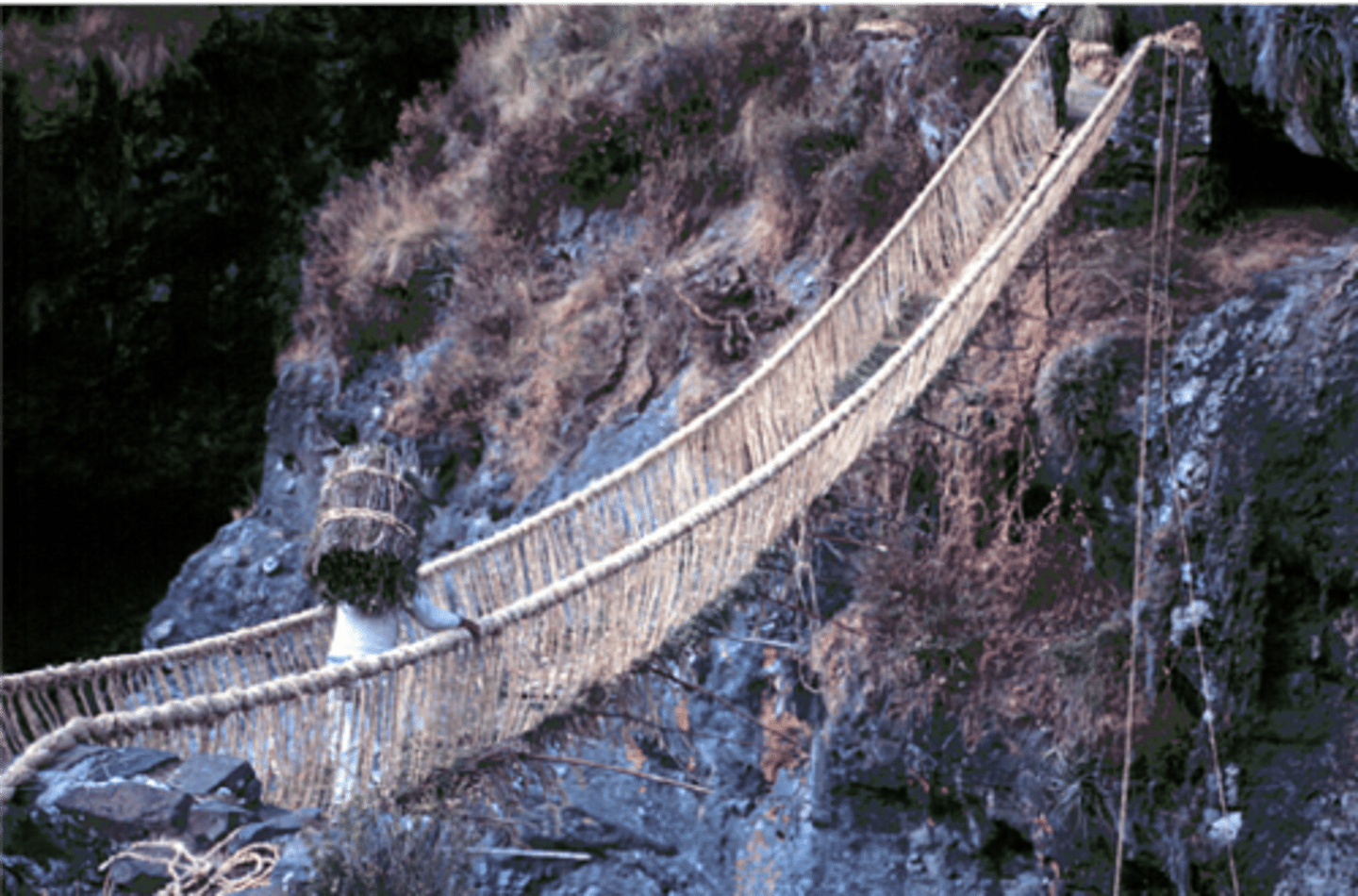
Incan Empire
Massive South American empire known for road building

Carpa Nan
Impressive Incan roadway system spanning about 25,000 miles

Bantu Migration
Spread of Bantu-speaking people in Africa, sharing agricultural knowledge
Kin-based Networks
Dominant society type in Africa, Community leadership system based on familial ties
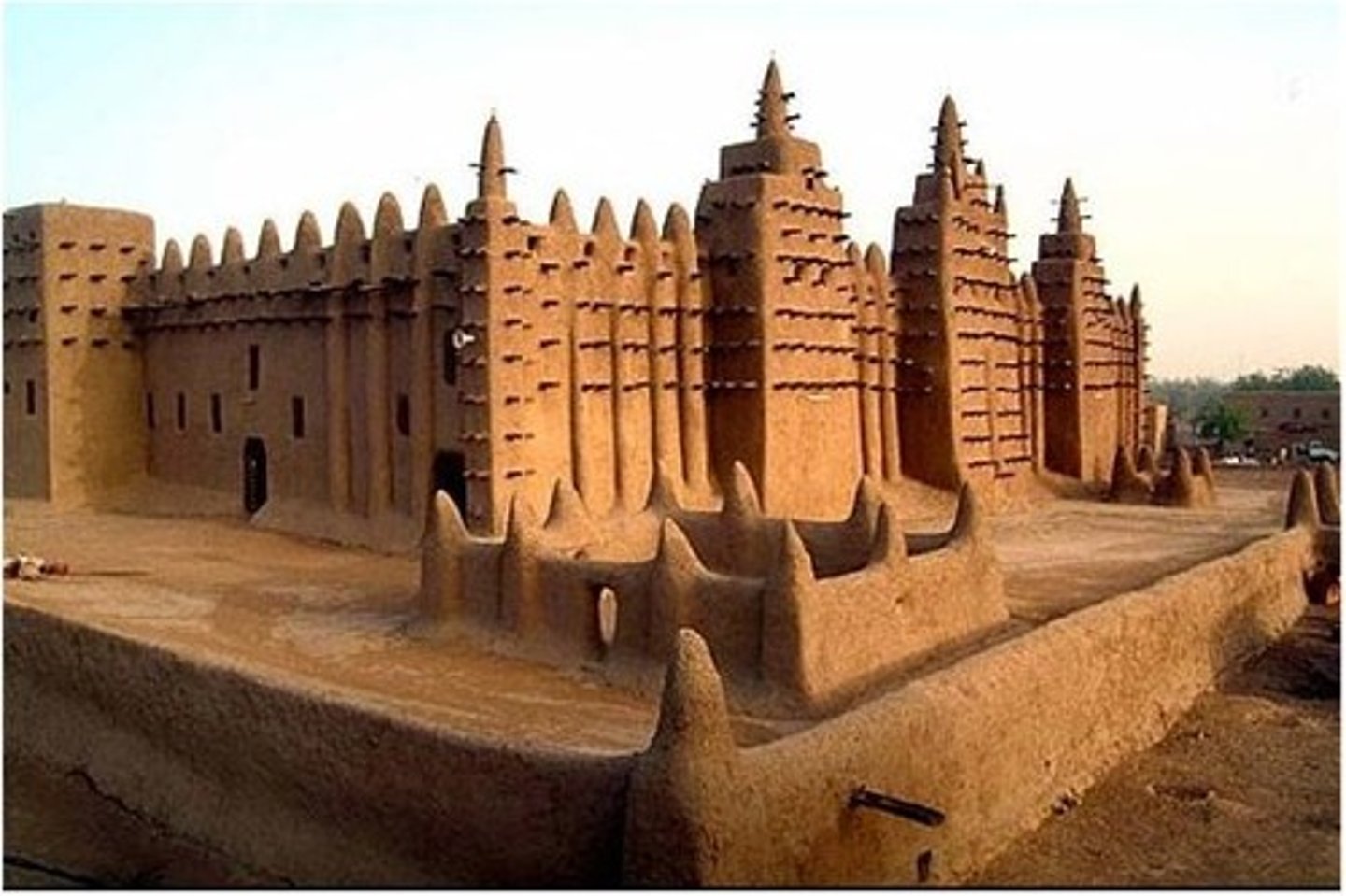
Mali Empire
Powerful trading society known for its gold exports and city of Timbuktu

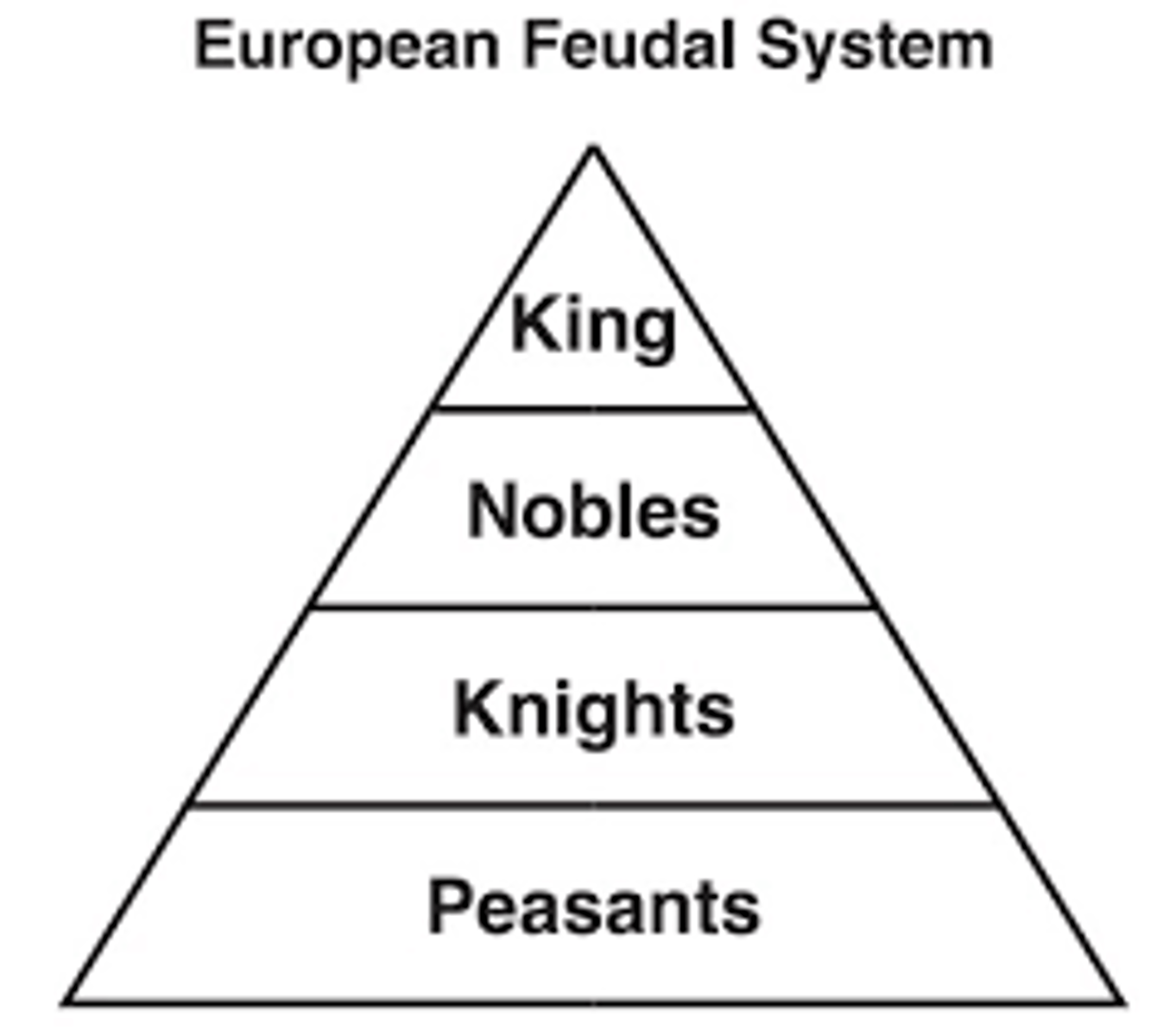
Feudalism
System of land exchanges for loyalty in European civilization
Three-Field System
Agricultural method rotating crops across three fields for soil fertility

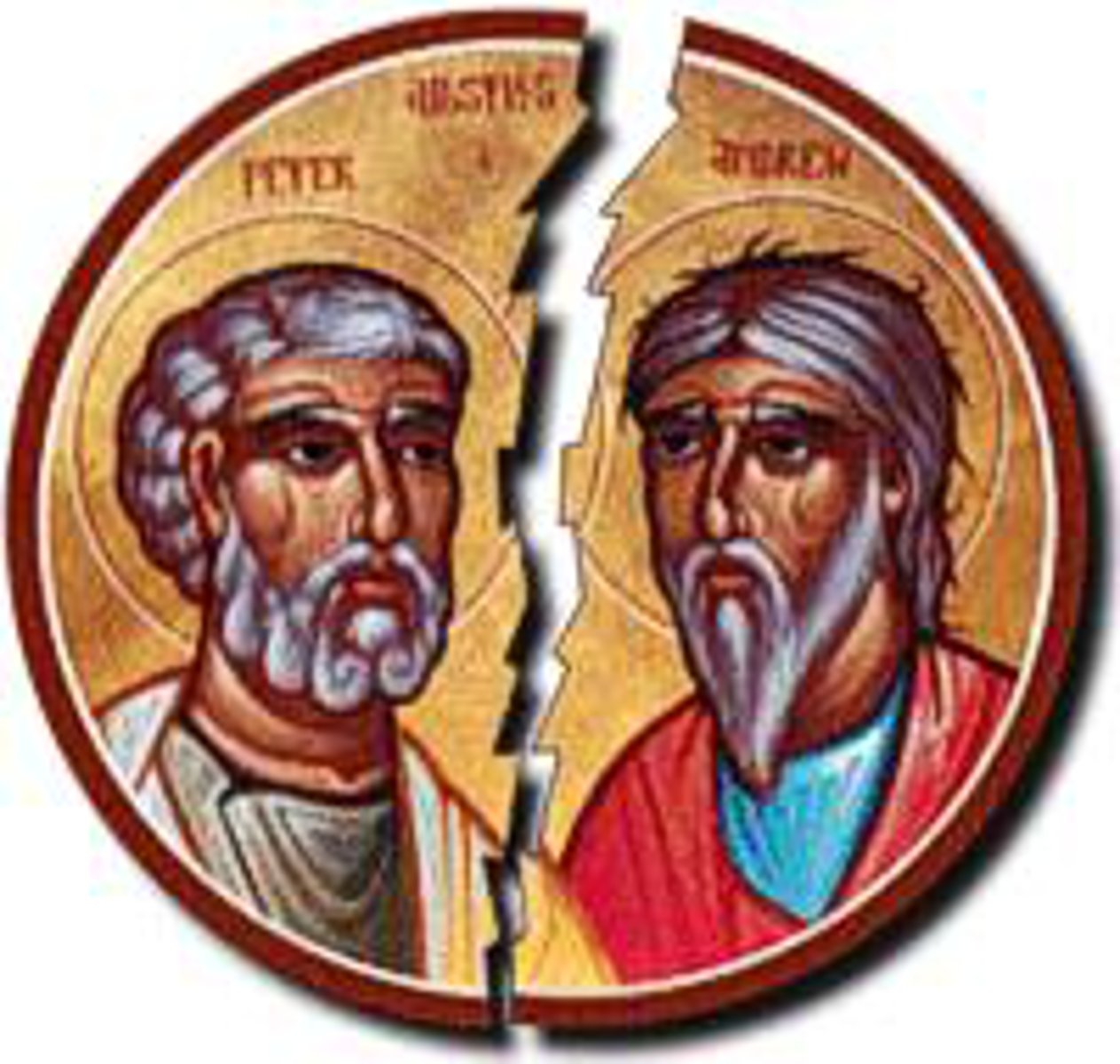
Great Schism
Split in the Christian Church leading to Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox branches

Primogeniture
Inheritance system leaving estate to eldest son, common in medieval Europe, this led to landless aristocrats who fought in the Crusades

Bourgeoisie
Middle class including merchants, shopkeepers, and craftspeople
Cartography
The art and science of mapmaking
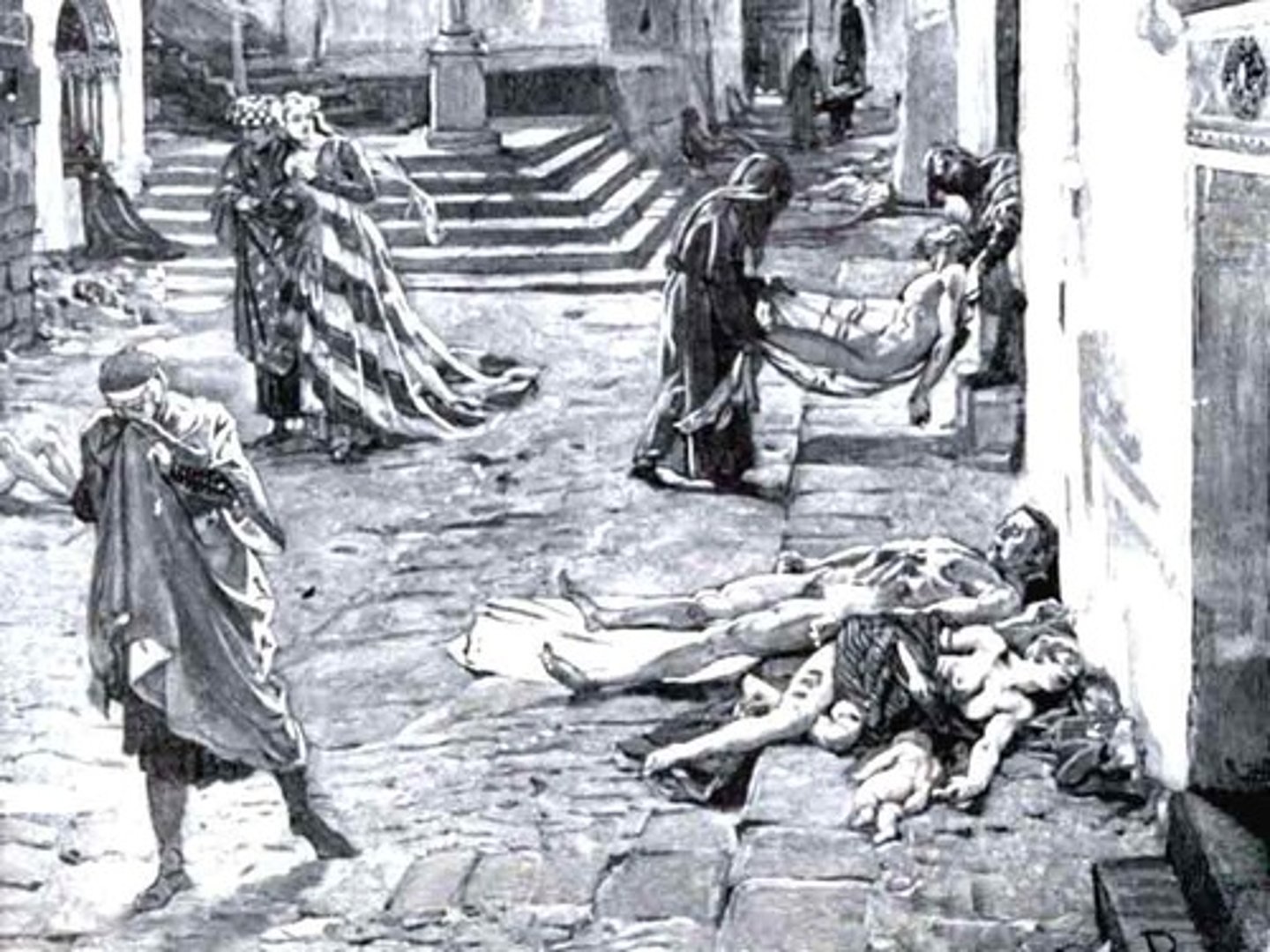
Black Death
Epidemic of bubonic plague in the 14th century

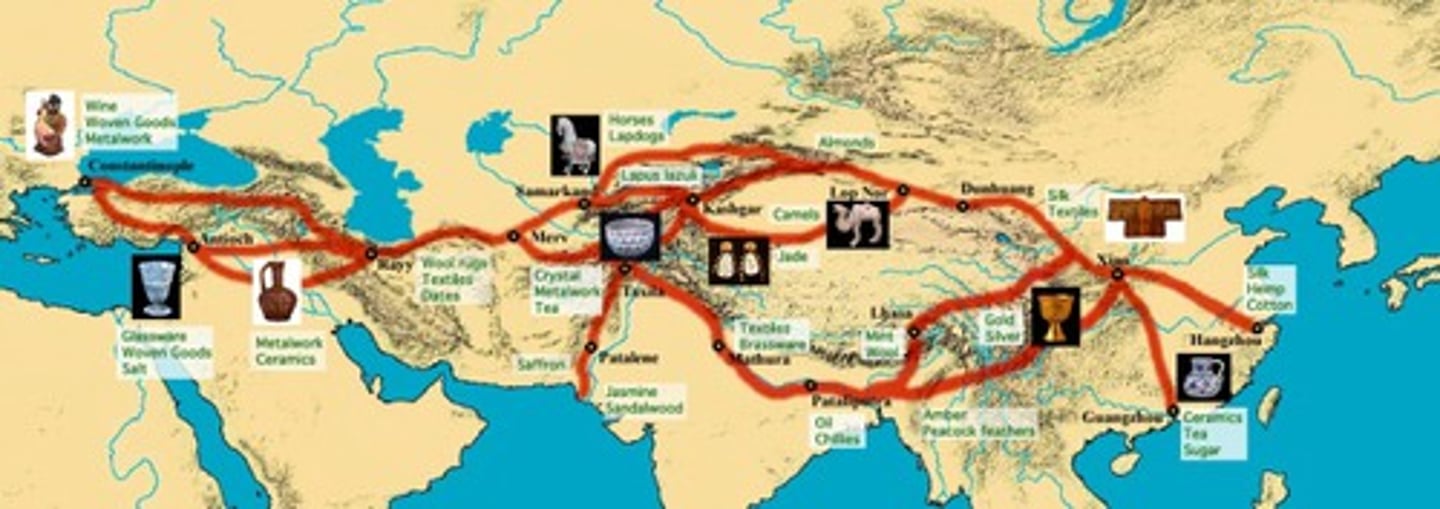
Silk Roads
Ancient trade routes connecting Asia and Europe
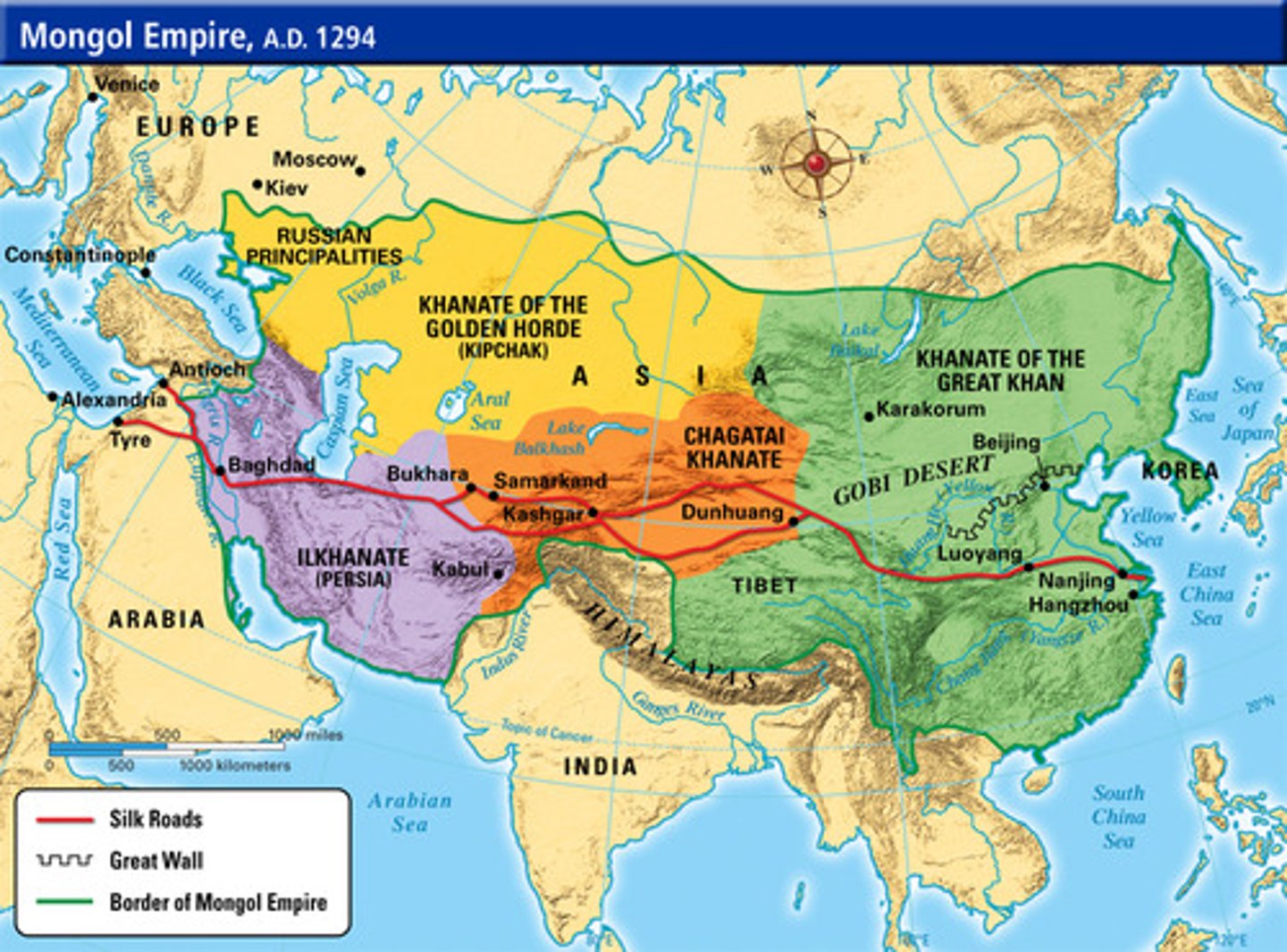
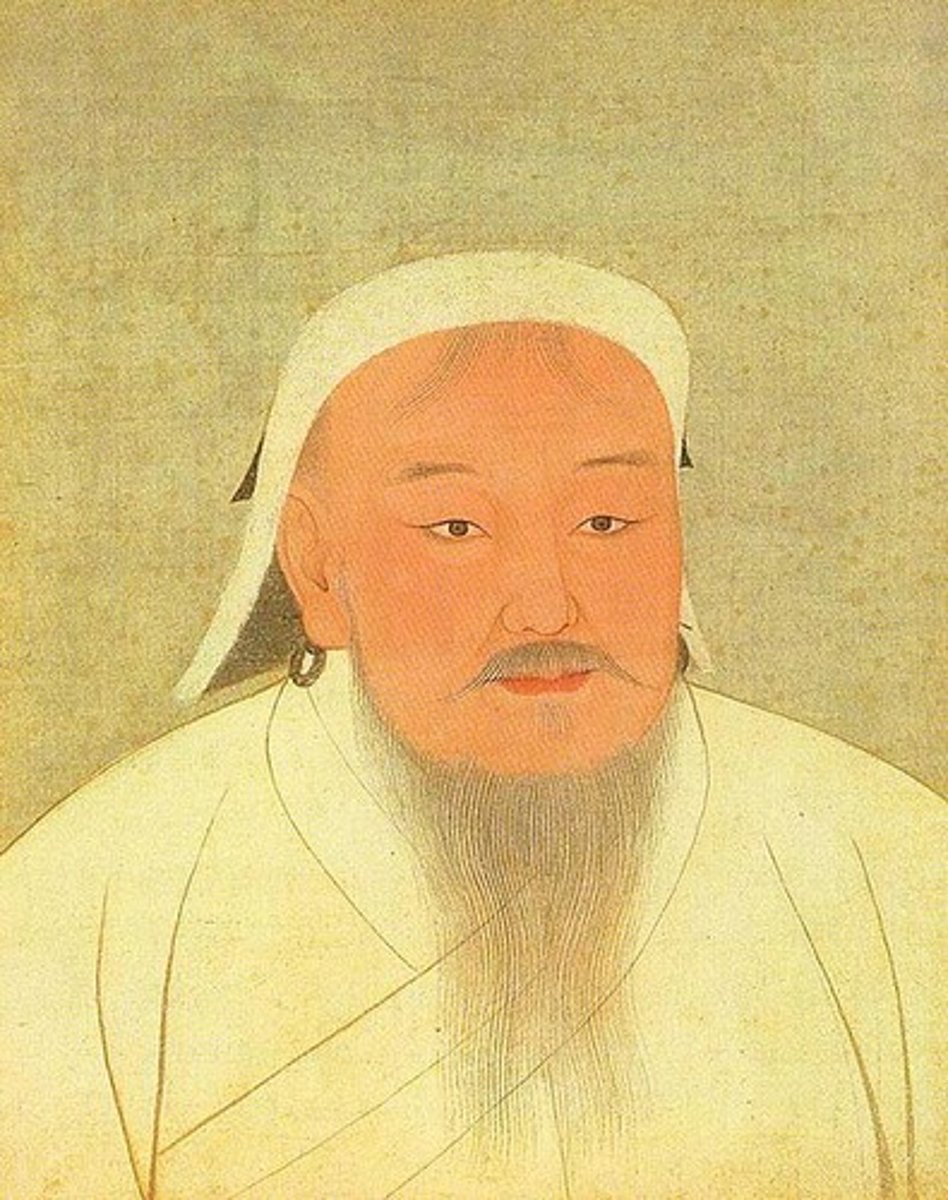
Mongol Empire
Vast empire in Asia led by Genghis Khan

Pax Mongolica
Era of peace in Eurasia under Mongol rule
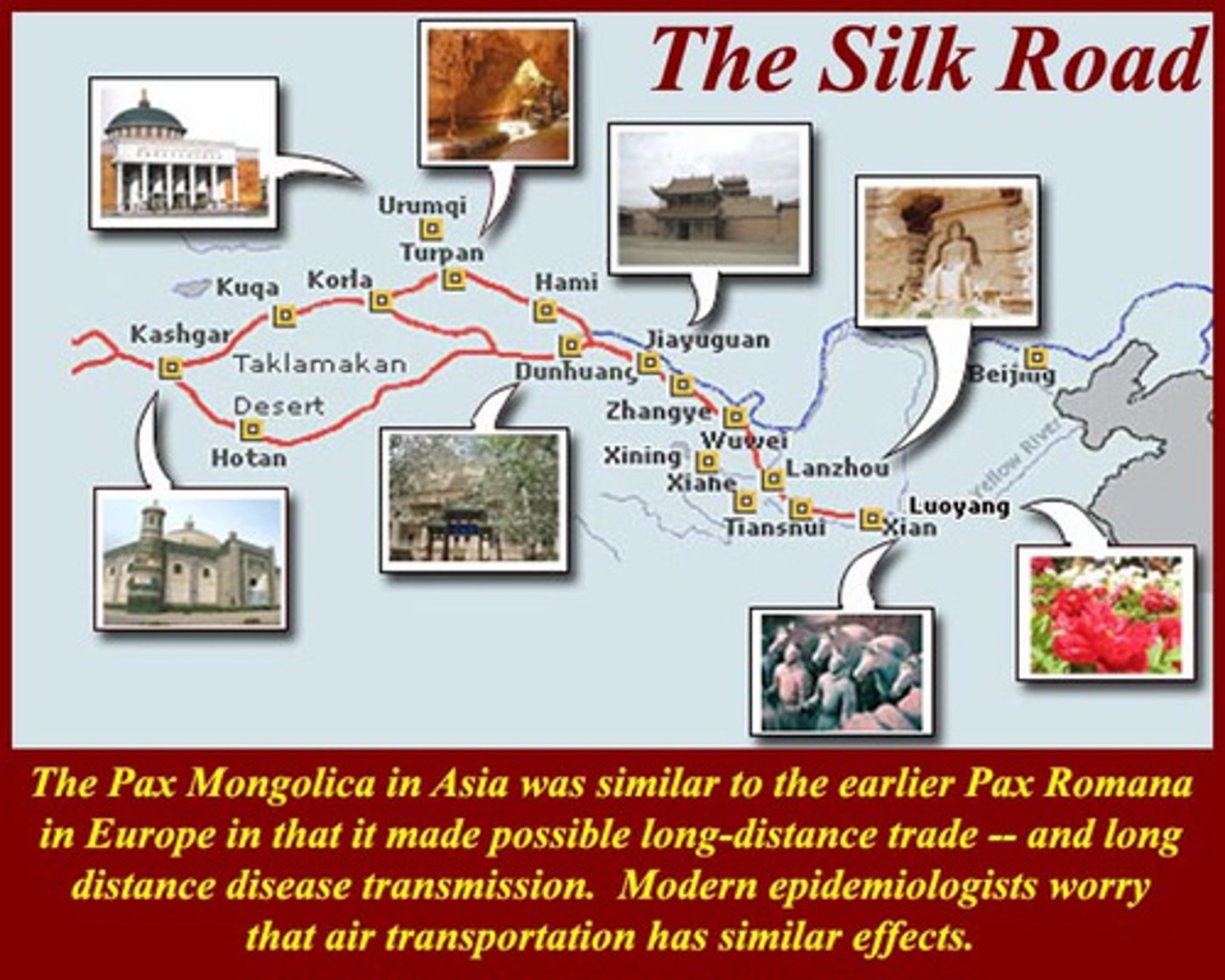
Hanseatic League
Alliance of northern European cities for trade defense, that monopolized trade on certain goods

Genghis Khan
Mongol leader who founded the Mongol Empire

Islamic Slavery
While Islamic empires were tolerant of other religions, only other monotheistic religions like Christians and Jews were exempt from slavery.
Caravanserai
Roadside Inns along the Silk Roads that led to increased efficiancy and trade as well as the development of cities along the routes like Samarkind and Kashgar

Flying Cash
System of paper money deposits for merchants, like today's wireless bank transfers
Lateen Sails
Triangular sails invented by Arab sailors that led to an increase in the Indian Ocean Exchange

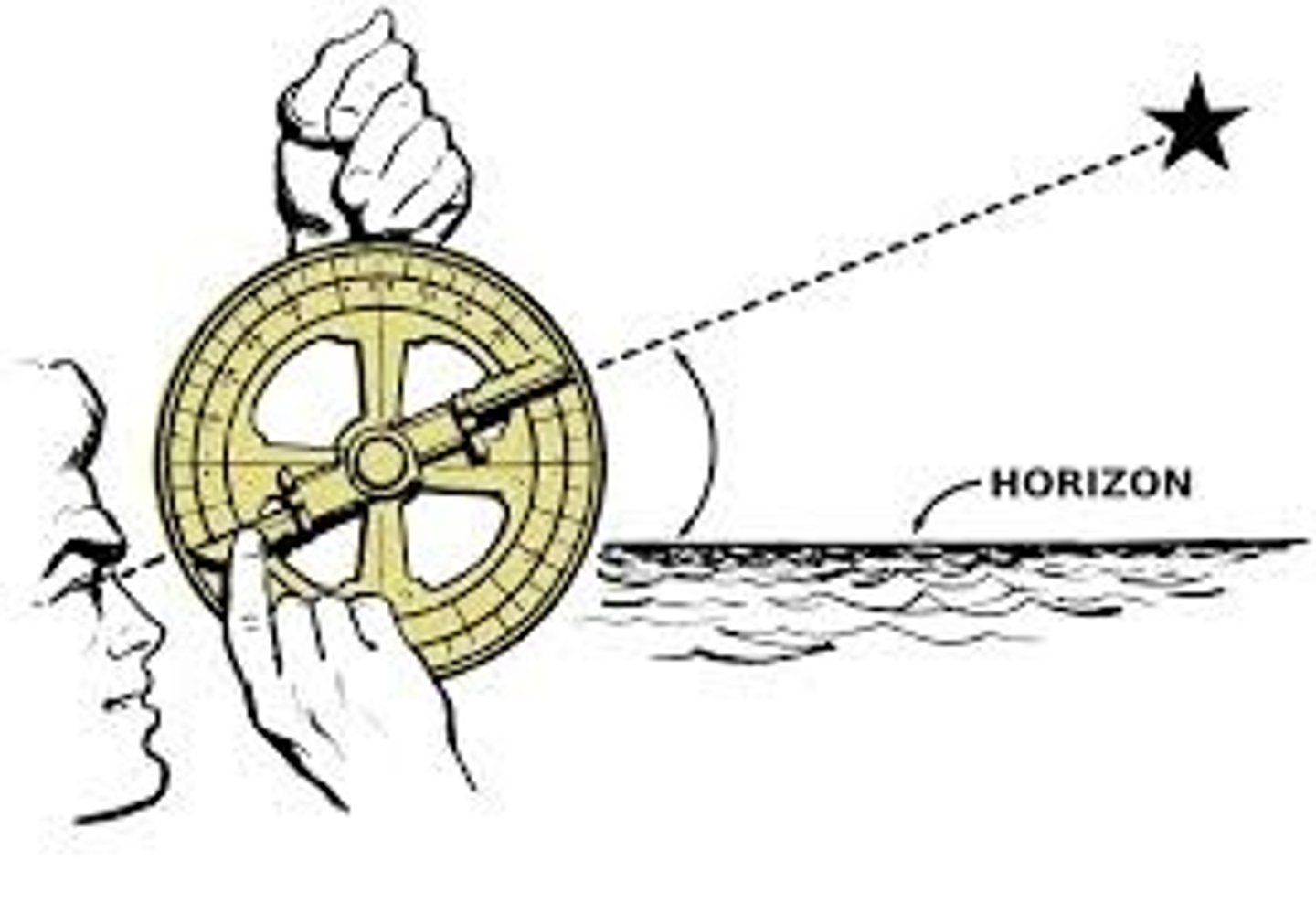
Astrolabe
Navigational tool for determining latitude, led to increased trade in the Indian Ocean
Zheng He
Chinese seafarer known for voyages and trade interactions who brought the first giraffe to China from Africa

Trans-Saharan Trade Routes
Trade routes crossing the Sahara Desert, linking West Africa to the Mediterranean
Camels
Preferred desert transport due to efficiency and water conservation

Somali Camel Saddle
Saddle enabling camels to carry up to 600lbs of cargo

Timbuktu
Trade and Islamic learning hub in Mali

Mansa Musa
Malian ruler known for wealth display and Islamic commitment (not subtle)

Hulagu Khan
Grandson of Ghengis Kahn known for destruction of Baghdad and the fall of the Abbasid Caliphate
Islam
Religion with vast influence across Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia

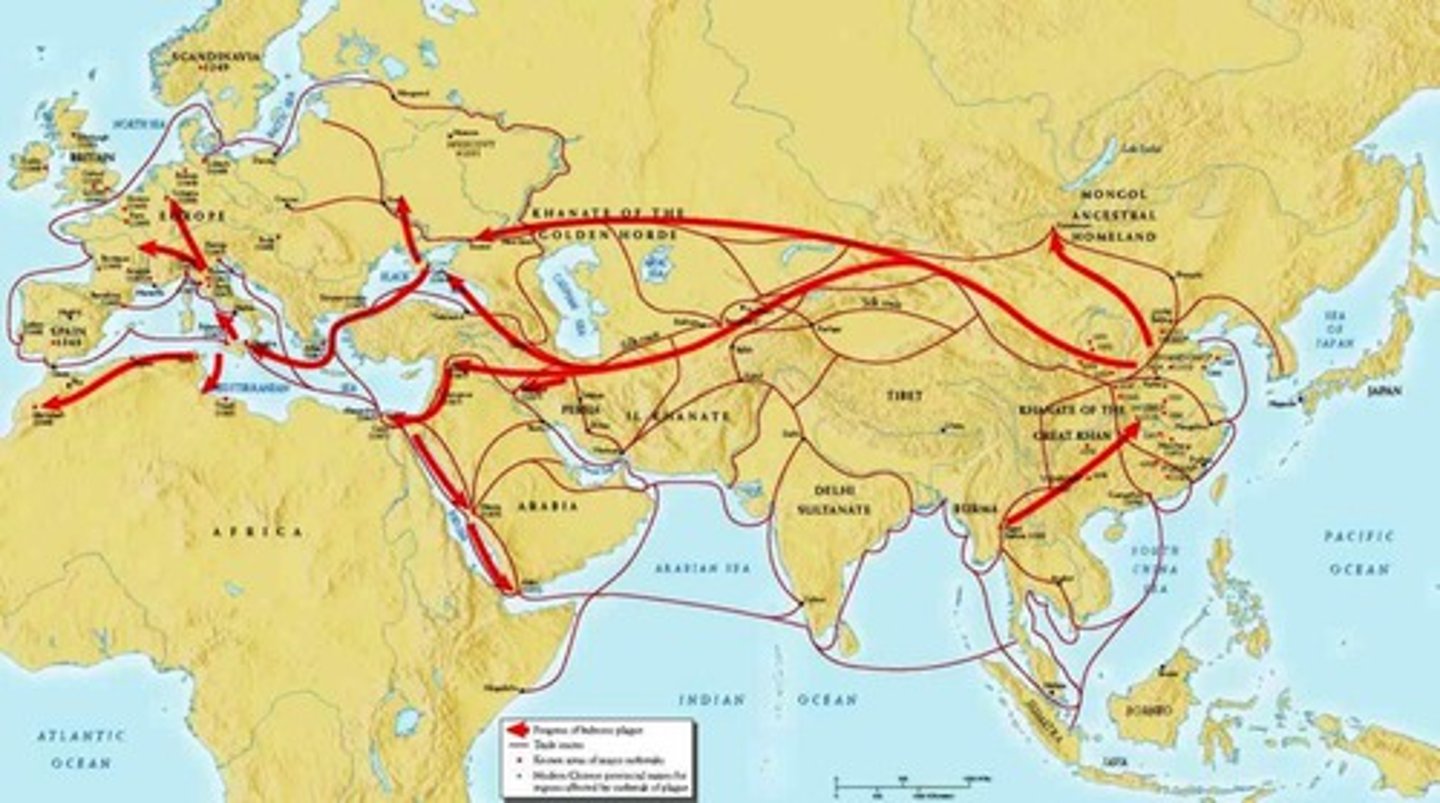
Mongols and the Black Death
The Mongols revitalization of the Silk Roads led to a spread of the Bubonic plague via fleas on animals traveling in close proximity of people.
Bubonic Plague / Black Death
Epidemic causing massive death toll in Europe during the 14th century, roughlt 1/3 of the population
Marco Polo
Venetian explorer and writer whose accounts of China were initially doubted, but ultimatley generated massive curiosity in Europe about the far east

Ibn Battuta
Muslim traveler documenting observations of the farthest reaches of Dar-al-Islam, specifically Africa

Overgrazing
Excessive grazing leading to land degradation and resource depletion ex: Camels outside Zimbabwe
Deforestation
Clearing of forests leading to soil erosion and reduced goods production
Diasporic Communities
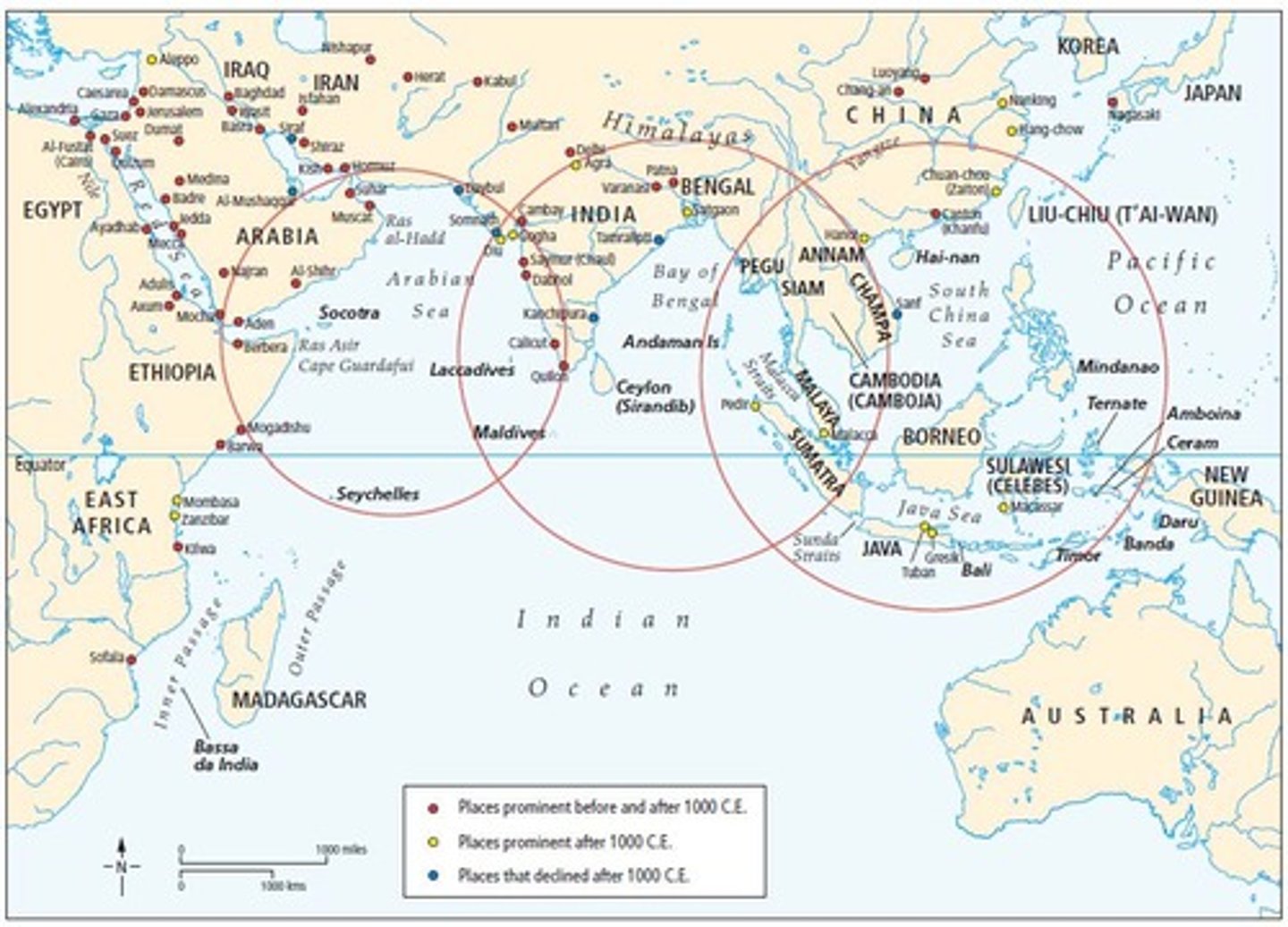
When people live in a land outside of the land of their birth but retain some of their cultural traditions and practices: example Muslim seafaring merchants who settled in port cities around the Indian Ocean expanding the cultural footprint of Islam.
Most valuable commodity traded on the Trans-Saharan Trade Route
Gold (From Mali)
Dar al-Islam
Territories, nations and empires where Islam was the dominant religion practiced
Mongols and the Silk Roads
A conquering people, led by Ghengis Kahn, who revitalized the Silk Roads by adding security and safety measures (After the Abbasid Merchants had paved the way centuries before)