L17 Ca2+ and NO
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Vascular tissue vs cardiac cells Ca2+ function
Ca2+ works on SR and Myosin LCK in vascular tissue
Cardiac cell is much faster, just bind to troponin C and myosin for contraction
Heart rate change of verapamil, diltiazem and dihydropyridines
Decrease/no effect for V and D
Increase for dihydro though cause of compensation for Bp decrease
Peripheral vasodilation of verapamil, diltiazem and dihydropyridines
Increase both
Blood pressure change of verapamil, diltiazem and dihydropyridines
Decrease both
Av node conduction of verapamil, diltiazem and dihydropyridines
Decrease for V and D
Dihydro has no effect
Cardiac contractility of verapamil, diltiazem and dihydropyridines
Decrease for V and D
Dihydro has no effect/slight increase
Verapamil vs diltiazem vs dihydros binding and abilities
Bind different sites within a1 subunit of L type Ca2+ channel
Differ in ability to modulate channel states
Dihydropyridine for Angina
Dilate peripheral blood vessels to decrease HR and contractility
Reflex stimulation due to BP can increase heart rate though
Antianginal effect can follow from afterload reduction
PRIMARILY FOR HYPERTENSION THOUGH (NOT FOR ANGINA)
Verapamil and diltiazem for angina
Verapamil is NON SELECTIVE, decrease Hr and contractility at similar concentrations
Reflex stim due to lower BP is offset by cardiac suppression (NICE)
Antianginal from reduced peripheral resitstance, lower BP (All with minimal change to heart rate nice)
Lead to reduced myocardial O2 demand
diltiazem is similar
Verapamil therapeutic use and warnings (2+4)
For managing chronic and prinzmetal angina
Also for cardiac arrhythmia and hypertension
CI for CHF, and ventricular dysfunction
Can worsen AFib and cardiomyopathy
CAN INDUCE BRADYCARDIA/hypotension
acute liver injury but rare
Phenylalkylamine
Verapamil ade and DDIs
ADE: Monitor liver dysfunction patients for overdosage
DDIs: MORE IMPORTANT THAN DILTIAZEM
Caution with bblockers, antihypertensive and anti arrhythmia drugs
Verapamil exposure can be increased if given with CYP3A4 inhib
Verapamil is strong inhibitor of CYP3A, can lead to increased plasma level of drugs metabolized by CYp3A4
Verapamil structure and ADME and brand names
Bad bioavailability and t1/2 but got a SR version for longer
Depend on CYp3A4 oxidation to norverapamil (active metab)
Calan is brand name
To metabolize turn the CH3 on the middle plain nitrogen to just a H
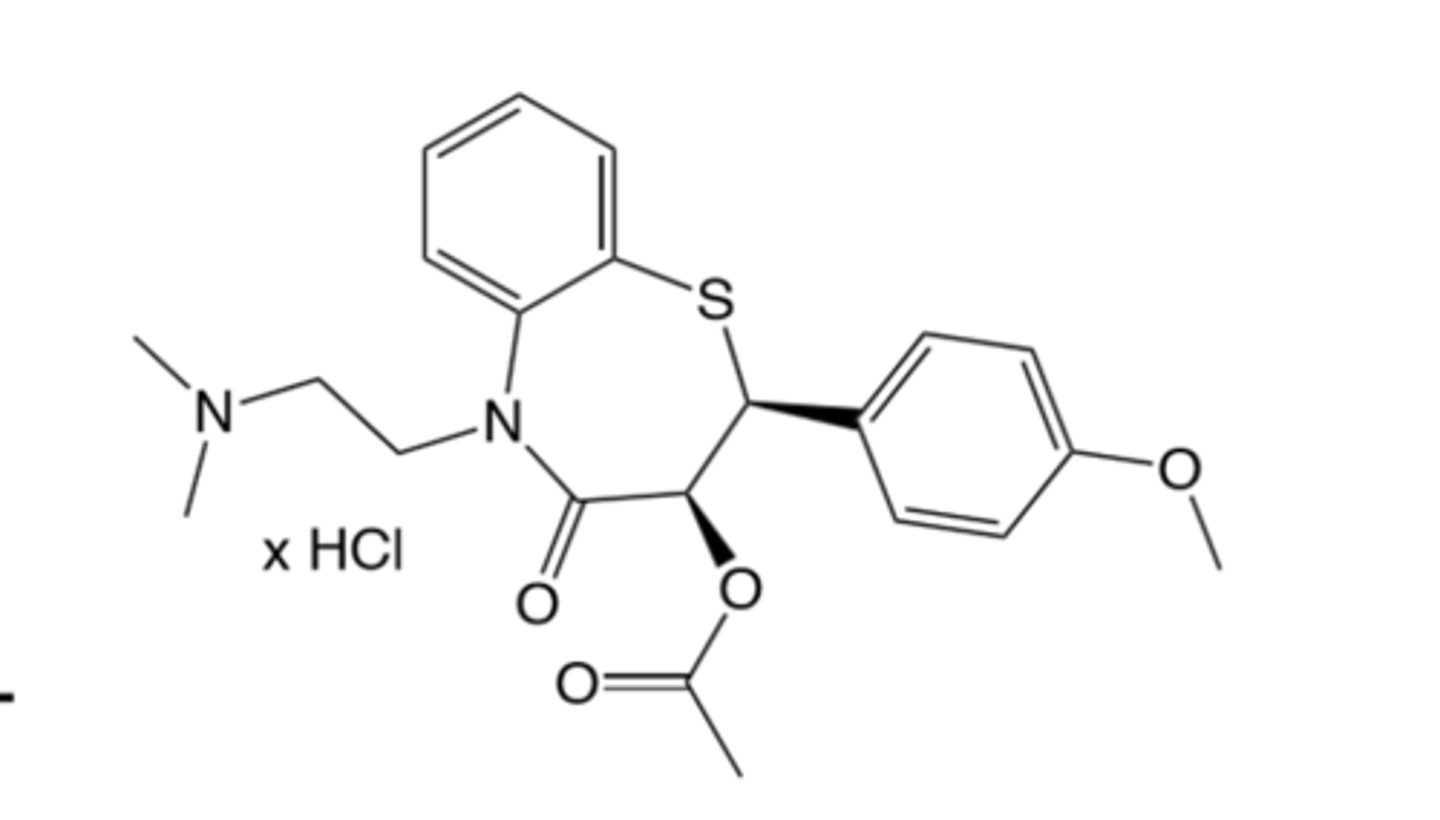
Diltiazem Therapeutic use and Warnings (2+3)
For managing chronic and prinzmetal angina
Also for cardiac arrhythmia and hypertension
CI with other agents that slow cardiac conduction and for use in patients with CHF
can cause hypotension and very rare liver injury
Is a benzothiazepine
Diltiazem HCl ADE and DDIS
ADE: well tolerated but can cause edema, headache, nausea, dizziness, rash
DDIs: MODERATE CYP3A4 inhibitor (not that bad compared to verapamil)
Diltiazem ADME and brand name and structure
Benzothiazepine
Ok F, bad t1/2 but have a LA formulation
Metabolized in liver by CYp3A4 into active metabolite (2 METABOLITES)
Metabolites are des methyl and des acetyl
Has S+N
Is metabolized on the plain nitrogen or remove the ester underneath the bunny ear Os.
Brand name is Cardizem
Endogenous NO production
Produced by vascular endothelium, works on platelets, immune, GI and CNS
Productio of NO is important for blood flow (increase it)
Formed by NOS(nitric oxide synthase) and L-arginine
NOS is ca2+ and calmodulin dependent (Up increase NOS)
NO produced by cutting l arginine into L citruline and NO
NO effects and transport
Can bind to hemoglobin in blood to deactivate as NO3
Also deactivated by intracellular oxidants like O2
Diffuses to smooth muscle cells where it binds to guanlyl cyclase, which then turns GTP to cGMP that causes vascular relaxation (inhibits Ca2+ entry)
Half life of NO is only 5 seconds or less
cGMP metabolism
Metabolized by phosphodiesterase enzymes
GMP just has a lot more phosphate groups (that are not ring fashioned)
Vascular relaxation enhancement in relation to NO and cGMP (3 things)
Increase NO F
Directly work on GC
Inhibit cGMP breakdown by phosphodiesterase
Organic nitrate vasodilators, and GC activators and PDE5
Increase NO F, used to treat angina
GC activators more for hypertension and PDE5 more for hypertension and erectile dysfunction
Organic nitrate vasodilators CI with GC and PDe5 inhib cause too much hypotension
Organic nitrate vasodilators 3 effects
Vasodilation decrease pressure (Venous>arterial) in systemic vasculature
Decrease O2 demand and wall stress from less preload/afterload
Increase O2 supply and prevent vasospasms and vasodilate/improvement of perfusion
How to directly deliver NO? (2 drugs)
Nitroprusside
NO gas
Nitroglycerin brand name, metabolism and ADME and structure
Is GTN/nitrostat
Reduced to 1,2 glycerl dinitrate and Nitrite in mitochondria by ALDH-2 and then No2 to NO through respiratory chain or acidic disproportionation
reduced to dinitro and monitro in liver, RBC and vascular wall (ER but only at high doses)
Ok F, but VERY SHORT t1/2,
3NO3s around a carbon
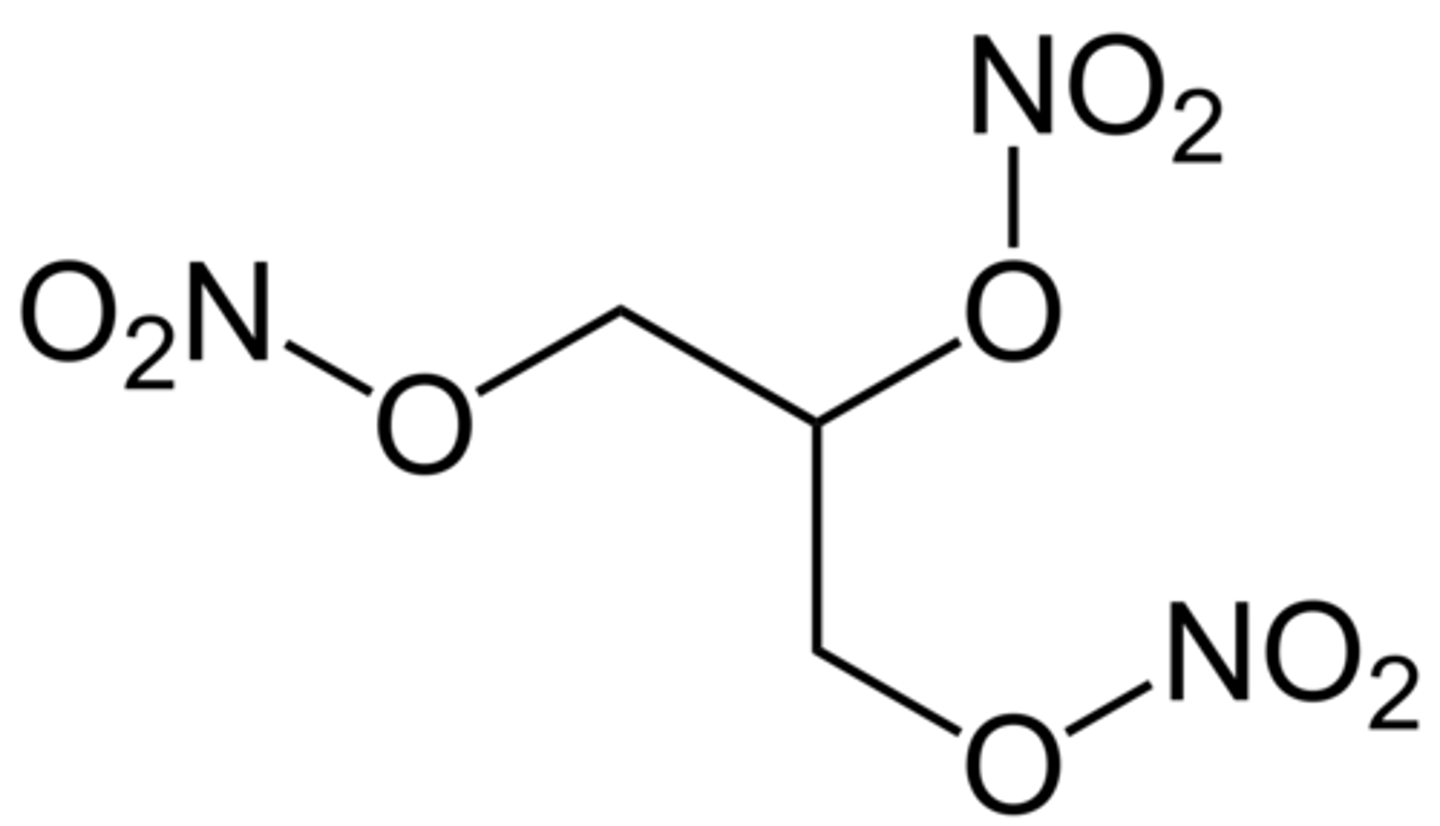
Isosorbide mononitrate metabolism, brand name and ADME and structure
Activated by P450 in ER to make NO
Is ISMN/monoket
100%F, long t1/2, and excrete in kidney only
Has only one No3, has 2 hydrofuran rings

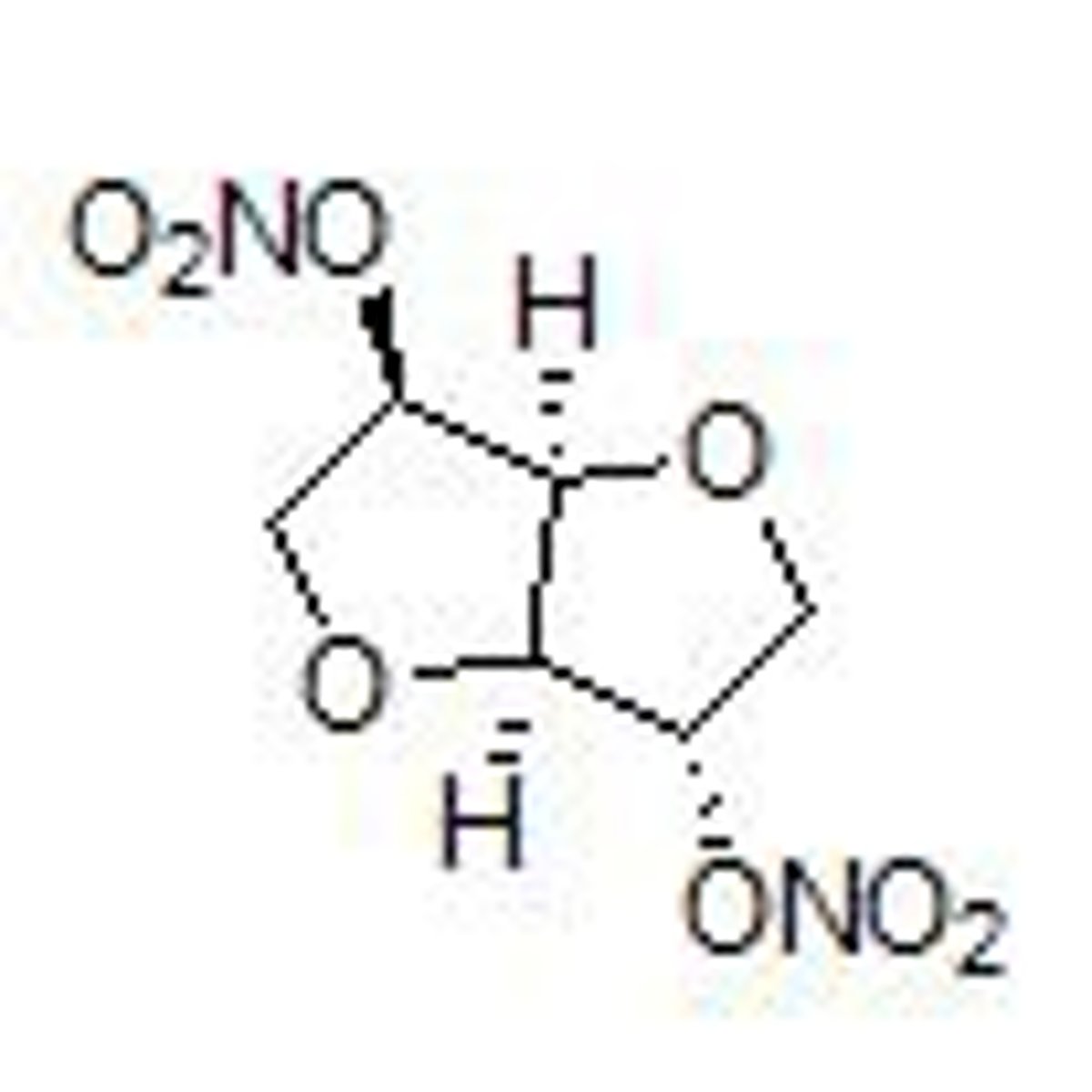
Isosorbide dinitrate metabolism, brand name and ADME and structure
Activated by P450 in ER to make NO
Is ISDN/Isordil titradose or dilatrate SR
Is only 25%F, and short t1/2 of 1h, metabolized and excreted through mononitro metabolites
Is 2 NO3s with 2 hydrofuran rings
GTN Dosage forms (4)
Oral given 2-4x a day
Spray and subliginual Prn and then buccal/3-5 hours
Transdermal for 12-16h/day
IV also
ISMN and ISDN dosage forms
ISMN given every 2-3 hours or 2x/day for ER
ISDN 2x/day or once daily with ER form
BOth are oral only
Chronic stable angina and organic nitrate vasodilators
GTN for rapid treatment or acute prophylaxis before exertion
ISMN, ER GTN and ISDN are for prophylaxis in patients with more occasional episodes
Variant angina and organic nitrate vasodilators
Long acting nitrates only and used in combo with other agnets
Organic nitrate vasodilators ADRs?
Very rare, come from vasodilators MoA
Headache, hypotension, syncope, rash, less common
Organic nitrate vasodilators tolerance description
Anginal effect decreases quickly if given continuously due to tolerance from reduced capacity of vascular cells to make NO (have increase in superoxide and other metabolizers, so decrease NOS, GC and ALDH2)
Also have neurohormonal activation of vasoconstrictors in response to increase in IV volume
How to prevent tolerance in organic nitrates (3)
Avoid high doses and interrupt therapy for 8-12 hr daily
GTN: no night doses for stable angina, use patches to treat nocturnal angina instead
ISD ISMN: manage tolerance through dose schedule
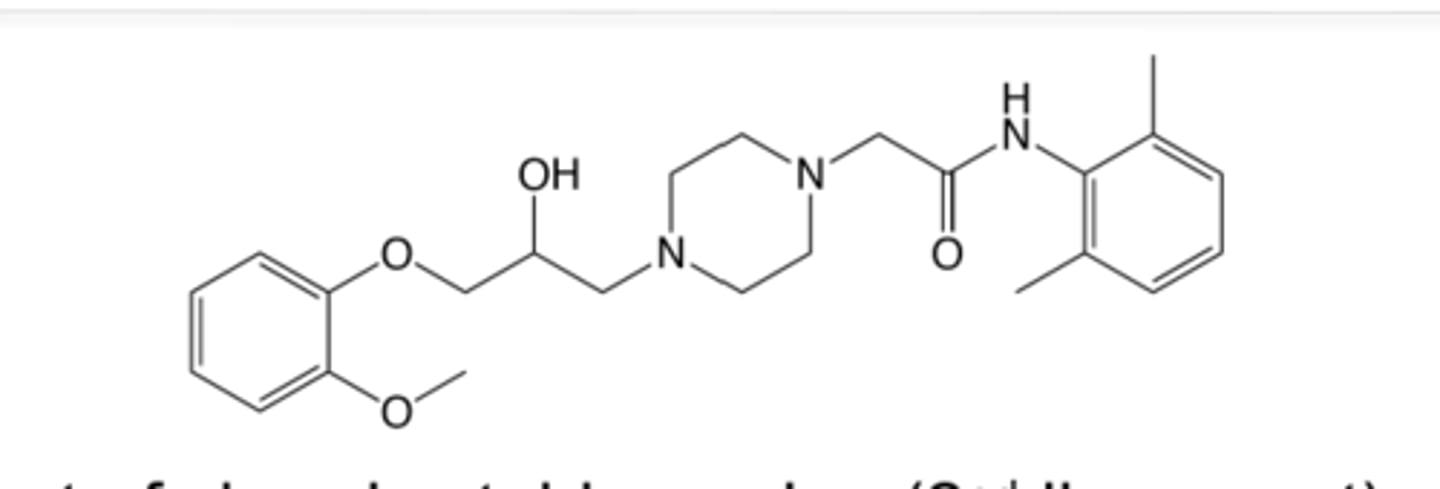
Ivabradine use and MOA
Used for stable angina in which b blockers are not tolerated, is a 2nd line agent FOR ANGINA
Oral and solution formulations reduce risk of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction(So is a 2nd line agent), no benefit in reducing all cause morbidity
MOA: block cardiac Na+ channels (hyperpolarization activated cyclic nucleotide gated) to reduce heart rate, BUT NOT CARDIAC CONTRACTILITY (lead to decreased O2 demand)
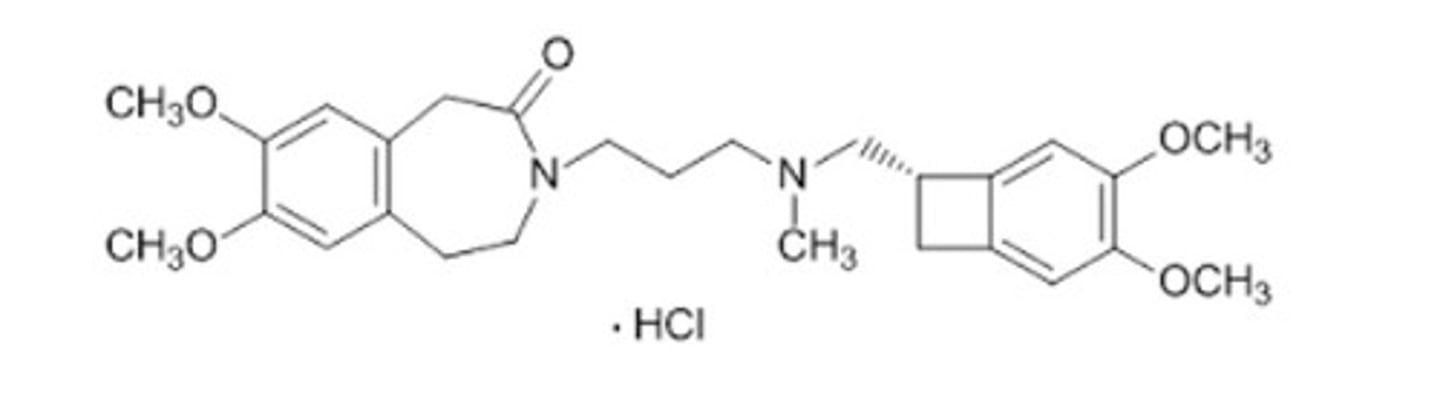
Ivabradine Structure and brand name and ADME
Looks like geometry dash with a block, and metabolized on the plain nitrogen (CH3 to simple hydrogen) into des methyl version that contributes to efficacy
Good F, and need to dose 2x a day cause 6 hrs t1/2
metabolized in kidney and liver
Is Corlanor
Ivabradine Warnings and CIs (3)
Visual changes from effecting Nucleotide channels in the eye
CI for cardiac conduction syndrome, bradycardia, pregnancy and HYPOTENSION
Can cause and/or be victom of CYp3A4 DDIs
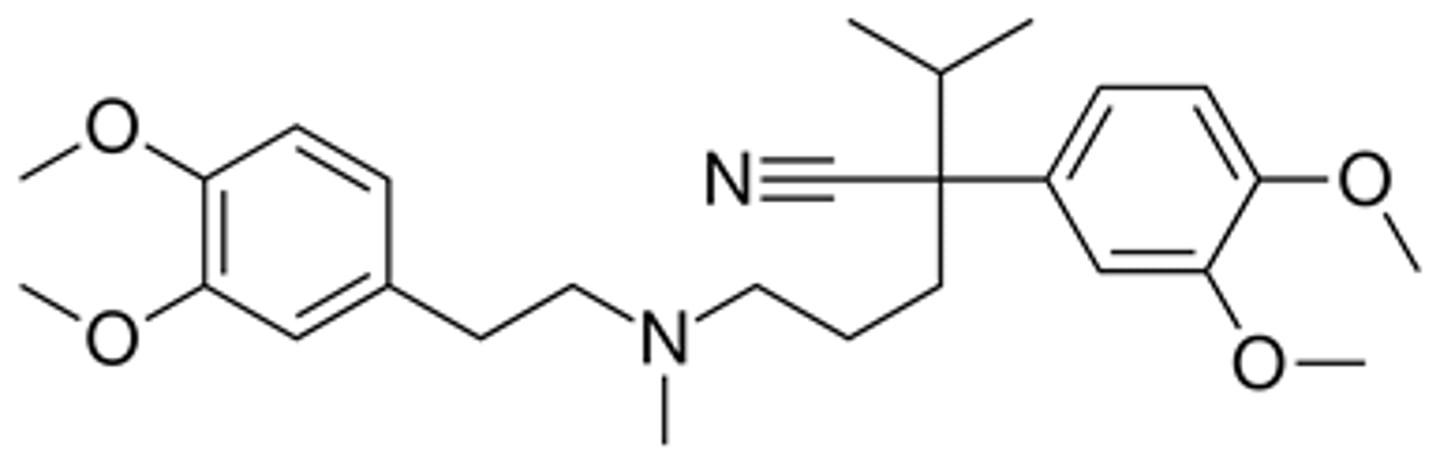
Ranolazine use and MOA
2nd line agent for chronic angina
Can combine with lots of other cardiovascular drugs
MOA not rly understood, but know have reduction of heart rate and BP and change in coronary blood flow
Maybe from inhibition o=f cardiac anion fluxes to maintain Na and Ca homeostasis
Ranolazine Warnings and CIs (3)
Can cause and/or be victim of CYp3a4 DDIs
Most frequent ADE are dizziness, headache, nausea, constipation (CNS and GI effects), but pretty well tolerated
Ranolazine Structure and brand name and ADME
Looks like a beta blocker, but is not cause of the double rings ong
Is ranexa
Good F, 2x a day though cause 7 hr t1/2
Excreted changed and unchanged in liver and kidney
S and R enantiomers have the same ADME