6.2.2 Amino acids, amides and chirality
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what groups do amino acids contain
amine group and carboxylic acid
α-amino acid
both groups are attached to the same carbon atom
general formula of α-amino acid
RCH(NH2)COOH
general strucure of α-amino acid
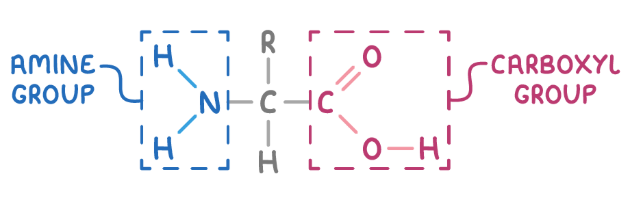
how to name amino acids systematically
Identify the longest carbon chain that includes the carboxyl carbon.
Start numbering the carbons from the carboxyl carbon, assigning it the number 1.
Specify the position and identity of the amine substituent.
why are amin acids bi functional
they have both carboxyl and amine groups so can act as an cid or base and react with an acid or base
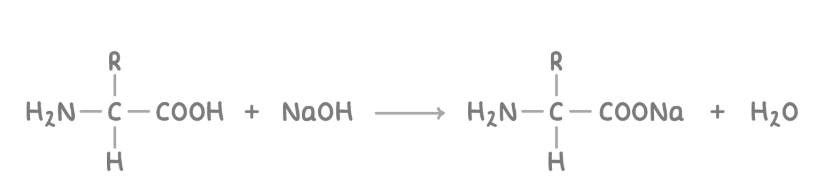
reaction of amino acids with alkalis
The carboxyl group can react with aqueous alkalis such as NaOH(aq) to form carboxylate salts and water.
reaction of amino acids with acids
The amine group can react with acids like HCl to form ammonium salts.
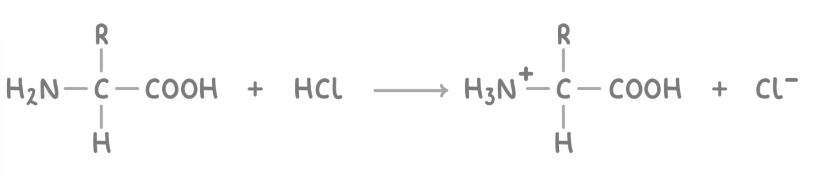
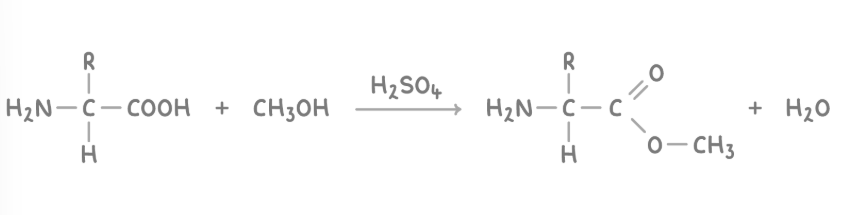
esterification of amino acids
The carboxyl group is capable of reacting with alcohols to form esters and water, in a reaction catalysed by concentrated H2SO4
functional group of amides
CONH2
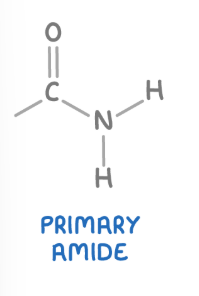
Primary amide
These are amides where the nitrogen atom is bonded to one carbonyl group (C=O) and two hydrogen atoms
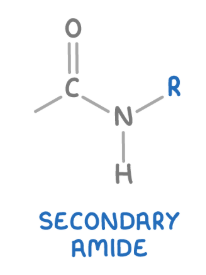
secondary amide
These are amides where the nitrogen atom is bonded to one carbonyl group (C=O), one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group
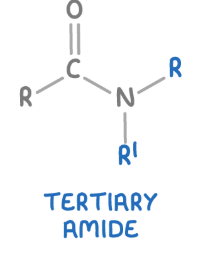
tertiary amide
These are amides where the nitrogen atom is bonded to one carbonyl group (C=O), and two alkyl or aryl groups.
how to name primary amides
stem of the alkane followed by amide
how to name secondary amide
look for the chain containing the carbonyl group and name as if were a primary amide
add prefix to show the other alkyl group on nitrogen
in fornt of everthign add N-
how can primary amides be formed
The reaction between acyl chlorides and ammonia produces primary amides
ehtanoyl chloride reaction with ammonia
ethanoyl chloride reacts with ammonia to give ethanamide and HCl:
CH3COCl + NH3 ➔ CH3CONH2 + HCl
how can seconary amides be formed
The reaction between acyl chlorides and primary amines produces secondary amides, also known as N-substituted amides.
ethanoyl chloride reaction with methylamine
thanoyl chloride reacts with methylamine to give N-methylethanamide and HCl:
CH3COCl + CH3NH2 ➔ CH3CONHCH3 + HCl
optical isomerism
type of stereoisomerism where isomers have the same structural formula but different arrangements of atoms in space
chiral carbon
chiral carbon is a carbon with four different groups attached to it.
when the groups around a chiral centre are arrnaged differently what does it result in
two non-superimposable mirror image structures.
what are the molecules called when the groups are arranged in 2 different ways around chiral carbon atoms
enantiomers or optical isomers
how to identify and draw optical isomers
Identify the chiral carbon - Carefully draw all hydrogen atoms to clearly identify each attachment. Look for the carbon atom connected to four different groups.
Sketch the optical isomers - Illustrate one isomer with its groups arranged tetrahedrally around the chiral carbon. Next, draw its mirror image.
what happens if a molecules has more than one chiral centres
have more than 2 optical isomers