A & P review
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
Define anatomy and physiology and relate them to each other.
Anatomy is the study of shape and structure of the body and body parts while physiology is the study of function. When it relates to each other you study the shape (anatomy) of the heart and the function (physiology) of the heart
List and define the non-invasive methods for studying anatomy.
Inspection: Looking for abnormalities
Auscultation: listening to the area
Percussion: Tapping on an area and listening to the sound
Palpation: Touching, pressing or kneading the area
What is comparative anatomy?
study of multiple species to learn about form, function, and evolution
What is medical imaging
viewing the inside of the body without surgery
Define radiology
branch of medicine concerned with imaging
What is true about x-rays?
They are over half of all medical imaging
What are digital subtraction angiography useful for?
Showing blockages and blood flow and good for dentistry, visualizing bones, mammography, etc
What kind of images do CT scans make and what are they useful for?
Produces a slice-type image and has an increased sharpness and are useful for identifying tumors, aneurysms etc.
What are MRI’s and why are they the best?
Uses electromagnets to make images and have a superior quality to CT scan and no X-Ray
What do fMRIs show?
They show real time of changes in the brain
What do PET scans asses? And how do damaged tissues appear in a PET scan
metabolic state of tissue and they appear dark
What are sonography’s?
Uses sound waves to make images, but the images are not sharp and second oldest and second most widely used
List and briefly describe each characteristic of life.
Metabolism
Homeostasis
Reproduction
Development
Organization
Responsiveness
Cellular composition
Movement
Evolution
List the levels of human structure from most complex to simplest.
Organism
Organ system
Organ
Tissue
Cell
Organelle
Macromolecule
Molecule
Atom
What do anatomy books show?
They show most common organization of structure
What is homeostasis
the tendency of the body to maintain internal stability
When is the body functioning properly?
When it is in a homeostatic balance
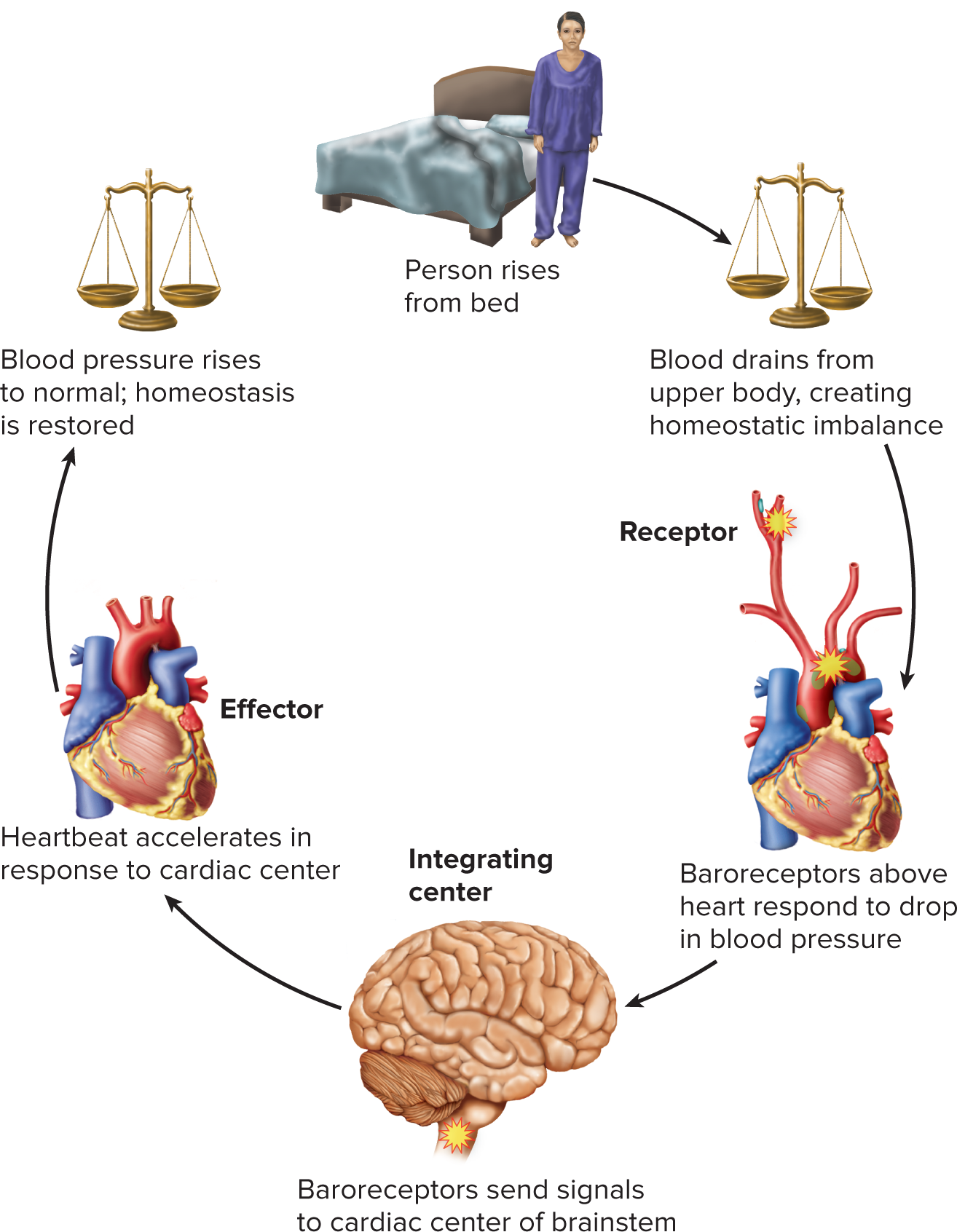
What are the components of a feedback loop?
Stimulus
Receptor
Control center
Effector
Define receptor
Structure that senses change in the body
Define control ( intergrating) center
Processes sensory information, “makes a decision,” and directs the response
Define effector
Cell or organ that carries out the final corrective action to restore homeostasis
Define negative feedback, give an example of it, and explain its importance in homeostasis.
Negative feedback loops oppose changes that are being made and goes in the opposite direction of the imbalance
An example of it would be temperature regulation meaning that when temperature goes up outside of the body a response is to sweat to cool down the body
Homeostasis is usually controlled by negative feedback
Define positive feedback and give examples.
Positive feedback accepts changes being made and will allow body to continue the change and example would be contractions during birth
Understand and be able to identify each component of the feedback loop in the image
Define biochemistry
The study of the molecule that compose living organisms
What is an element?
Simplest form of matter to have unique chemical properties
What elements make up the human body?
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium and phosphorus
How much body weight do minerals take up?
4% of body weight
What purpose do valence electrons serve?
They orbit in the outermost shell and determine chemical bonding properties of an atom
What is an ion?
Charges particle( atom or molecule) with unequal number of protons and electrons
Discuss the importance of valence electrons.
It is important because it determines the chemical bonding properties of an atom
Define Anion
Particle that has a net negative charge (due to gain of electrons)
Define cation
Particle that has a net positive charge (due to loss of electrons)
What is the process of how cations and anions are formed?
ionization which is the transfer of electrons from one atom to another
Ions with different charges are ?
Attracted to each other
Define electrolytes
Substances that ionize in water and form solutions capable of conducting electric current
What is the most important considerations in patient care
electrolyte balance
Define free radicals
Short-lived particles with an unusual number of electrons
How are free radicals created?
Produced by normal metabolic reactions, radiation, certain chemicals
Define antioxidants
Chemicals that neutralize free radicals
Give examples of antioxidants
Selenium, vitamins E & C, and carotenoids
Define ionic bonds
Transfer of electrons
Define covalent bonds
Sharing electrons and are bonded together cannot be broken easily
Which are easier to separate ionic or covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds
What are the two types of covalent bonds
Non-polar covalent bonds and polar covalent bonds
Define non-polar covalent bonds and characteristics
Electrons are shared equally and the electrons are equally attracted to all elements / Also they are strongest type of bond
Define polar covalent bonds and characteristics
Electrons are shared unequally and the electrons in a bond are more attracted to one element
Is water a polar or non-polar molecule
Polar molecule
How much of body weight is water
50-75%
Define mixture
substances that are physically blended but not chemically combined
What type of mixture is body fluid?
Complex mixture of chemicals
Define solution
Substances that are chemically combined and cannot be unmixed
What two things do a solution consist of
Solvent and solute
Define solvent
a substance that dissolves “stuff”
What is a common solvent and is called the universal solvent
water
Define solute
the substance being dissolved (usually a solid)
List the properties of water
Solvency
Cohesion
Adhesion
Chemical reactivity
Thermal stability
Define solvency
Ability to dissolve other chemicals
Define cohesion
Like molecules cling to each other
Why is water cohesive?
Because of its hydrogen bonds
How does surface film happen on water
Happens because of molecules being held together by surface tension
Define adhesion
Different molecules cling to each other
Define chemical reactivity
Ability to participate in chemical reactions
Define thermal stability
stabilization of the internal temperature of the body
Define acid
Releases H+ ions (protons) in water
The stronger the acid , the more H^+ ions there will be in solution
Define base
Accepts H+ ions
The stronger the the base, the less H^+ ions there will be in a solution
What does the pH scale range from
0 being most acidic to 14 being most basic
What is a neutral pH?
7.0
As pH increases –) hydrogen ion concentration ____
decrease
As pH decrease –) hydrogen ion concentration ____
increases
Define pH
measurement of molarity of h^+
What happens to H+ concentration as pH moves up and down
A change of one number on the pH scale represents a 10- cold change in H+ concentration
Are disturbances in pH are very disruptive to physiology?
yes very!
How are acid base homeostasis maintained?
Buffers
Define buffers
chemical solutions that resist changes in pH
Define chemical reaction
Process in which a covalent or ionic bond is formed or broken
What are the 3 types of chemical reactions
Synthesis
Decomposition
Exchange reaction
What is the ABCD for synthesis reaction
A + B = AB
What is the ABCD for decomposition reaction
AB= A + B
What is the ABCD for exchange reaction
AB + CD = AC + BD
Define decomposition reaction
large molecule broken down into two or more smaller molecules
Define synthesis reaction
two or more reactants are combined to form a larger reactant
Define exchange reaction
two molecules exchange atoms or groups of atoms
Explain dehydration synthesis
During dehydration synthesis monomers join to form polymers and water is released as a by product
Explain hydrolysis
The use of water to break polymers into monomers
Define metabolism
all chemical reactions of the body
Define catabolism
Breaks bonds = energy release (exergonic)
Define anabolism
forms bonds = energy required (endergonic)
____ is driven by energy released by ____
Anabolism, catabolism
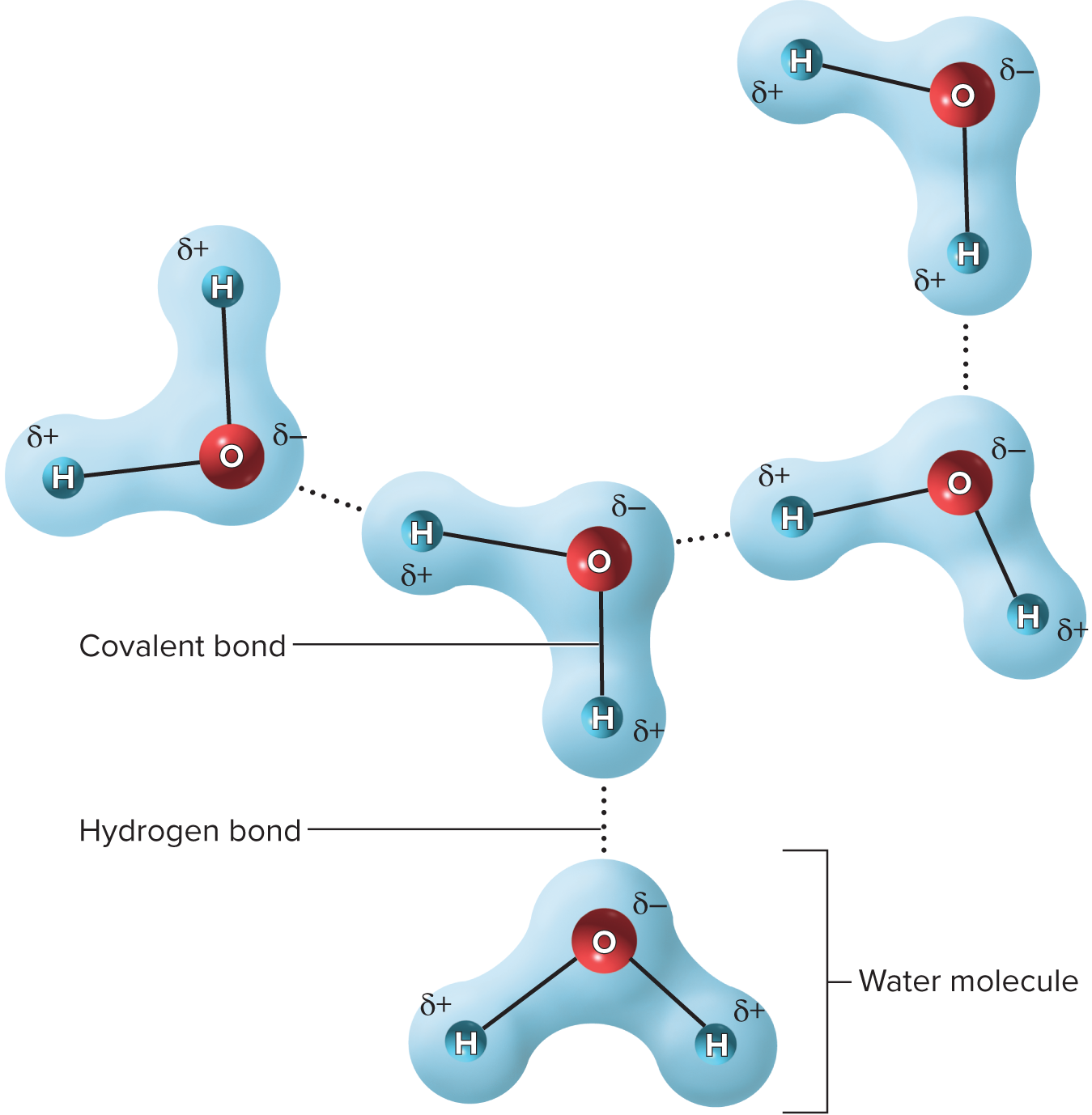
What specific type of bond is found between the atoms of a water molecule?
covalent bond and hydrogen bonds is what does this
Define organic chemistry
The study of compounds containing carbon
What are the four categories of organic carbon compounds
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Define carbohydrates
hyrdrophillic organinc molecules
Why are carbohydrates good for energy
Because they act as quickly mobilized sources of energy
What do oxidized carbohydrates make?
ATP
What are the different carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides
Oligosaccharides
Polysaccharides
Define monosaccharides and function
Simplest carbohydrates and act as monomers which are building blocks for larger molecules
What are the three important monosaccharides?
Glucose, galactose, fructose
Glucose, galactose and fructose are all what of each other?
Isomers
Define disaccharides
Sugars made of two covalently bonded monosaccharides