chem 107 tamu nair exam 2
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
kJ = J
1 kJ = 1000 J
cal to kJ
1 kcal = 4.184 kJ
cal to J
4184 cal to 1 J
kg to g
1 kg = 1000 g
Gibbs free energy equation
ΔG = ΔH - T(ΔS)
km/h to m/s
1 km/h = 5/18 m/s
for q (heat)
+ means system gains heat
- means system loses heat
for w (work)
+ means work done on system
- means work done by system
For Delta E
+ means net gain of energy by system
- means net loss of energy by system
unit of q (heat)
kJ
specific heat equation
Cs = q/(m*ΔT)
specific heat for water
4.184 J/gK
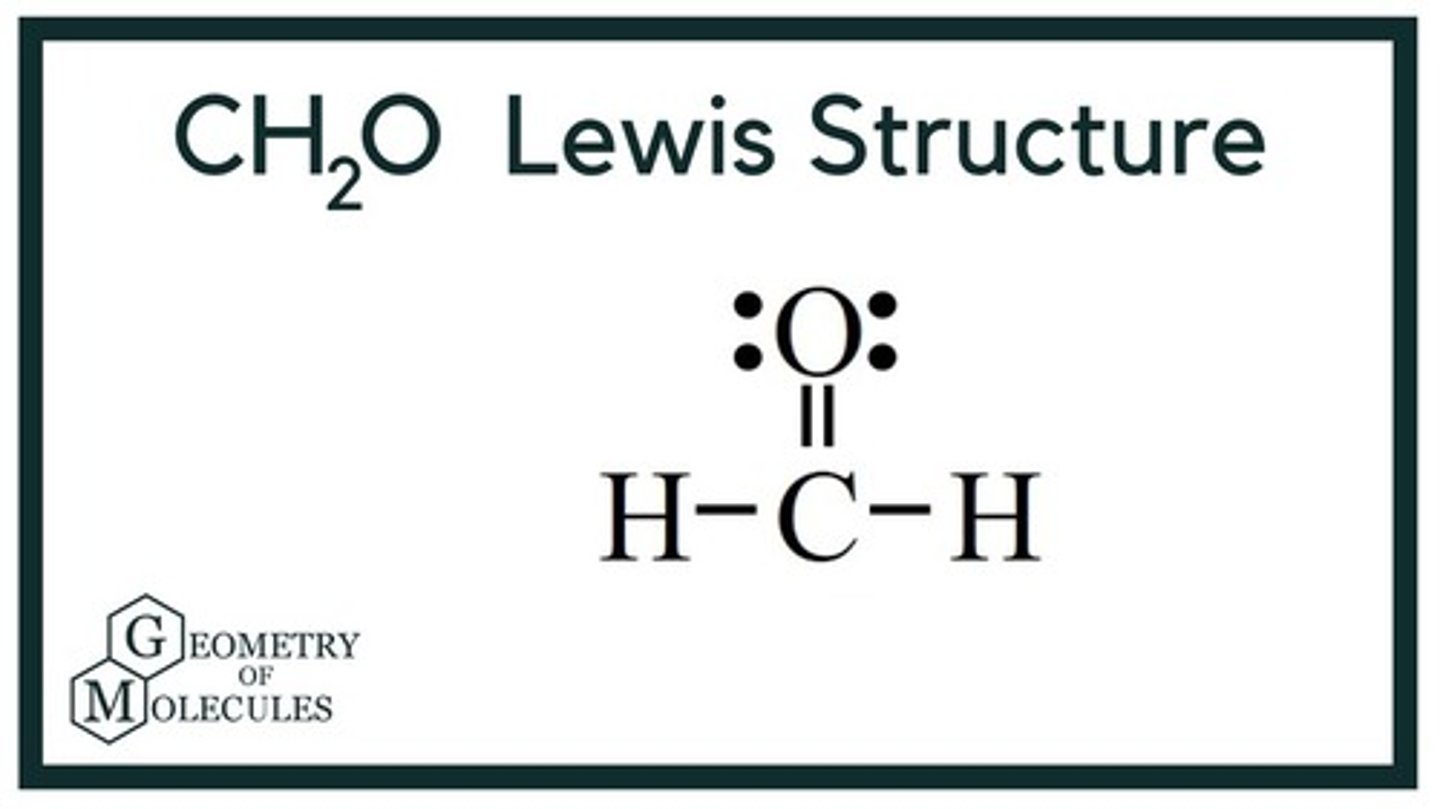
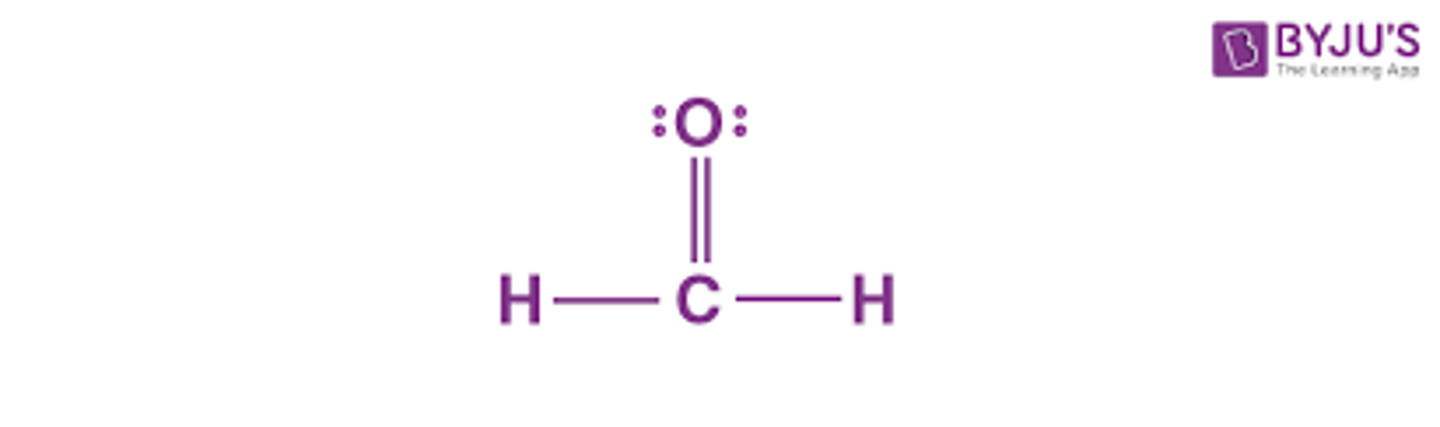
Lewis Structure for CH2O
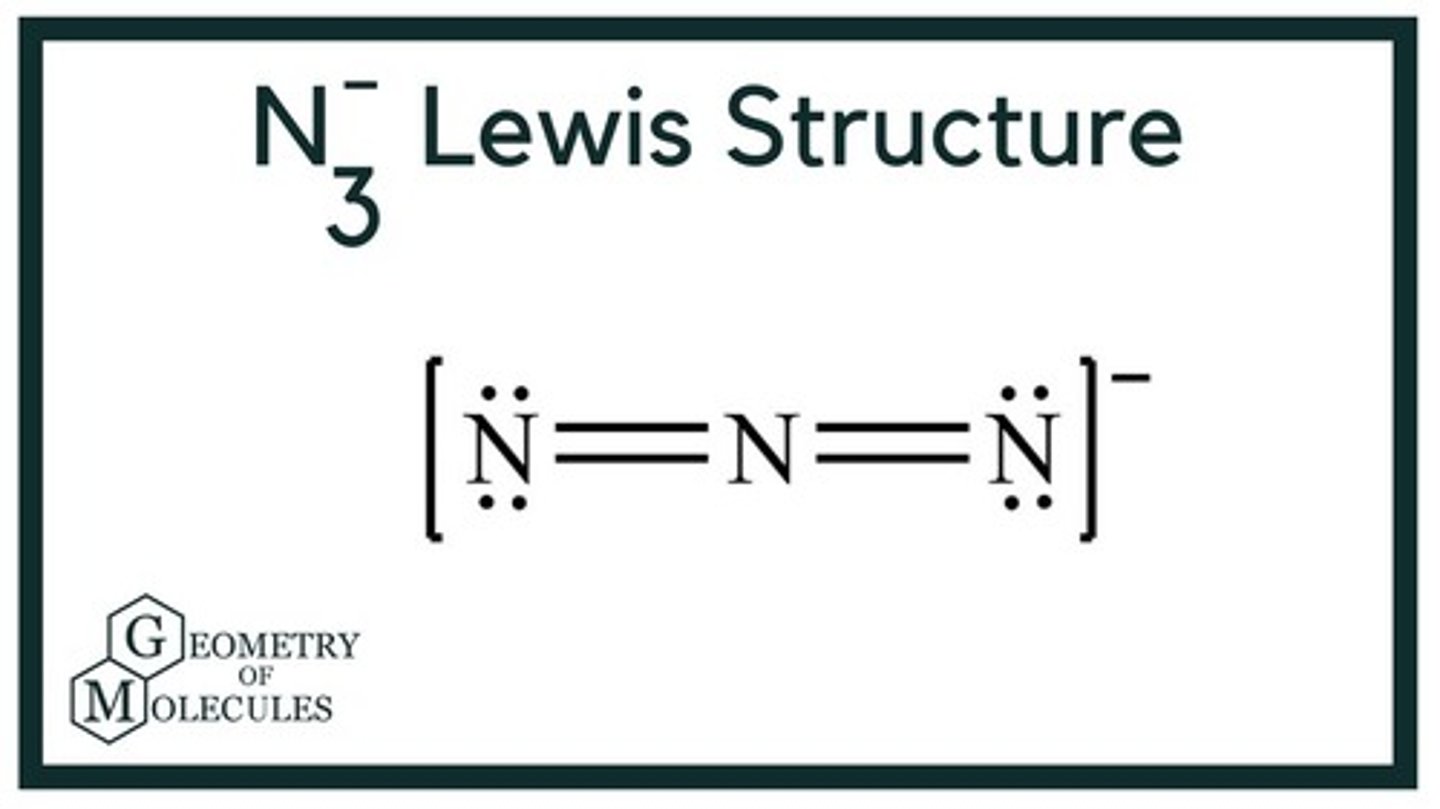
Lewis structure for N3-
carbon: 180°
nitrogen: 107°
Lewis structure for HF
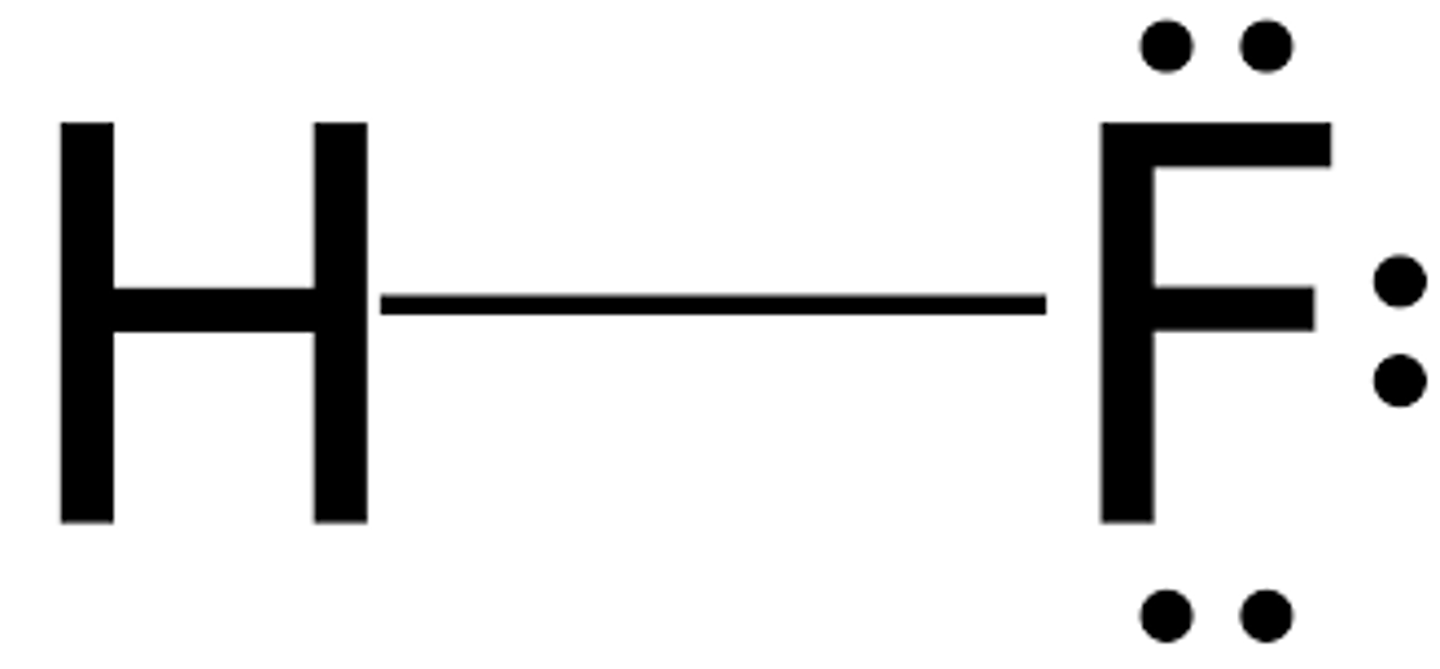
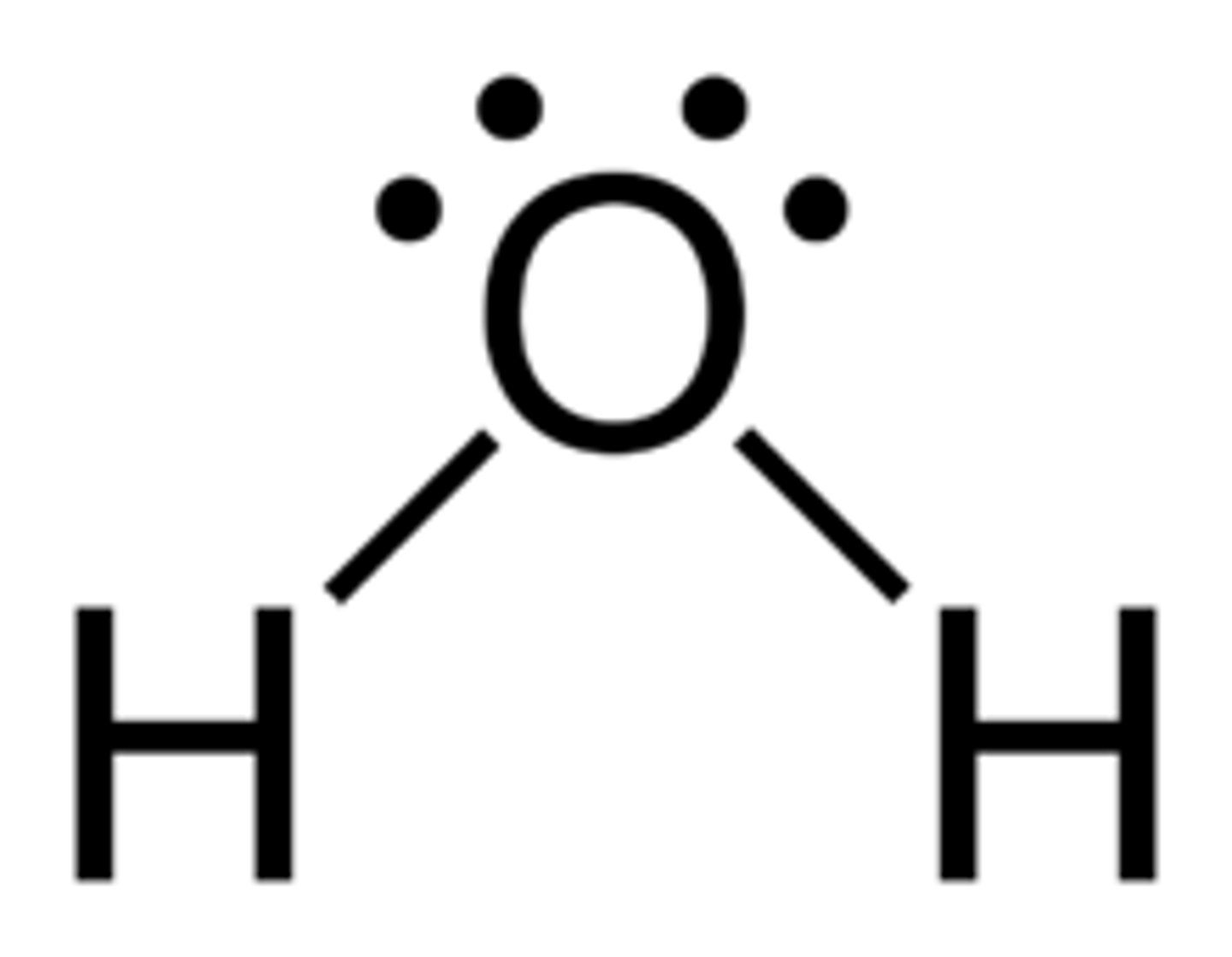
Lewis structure for H2O
Lewis structure for HNO
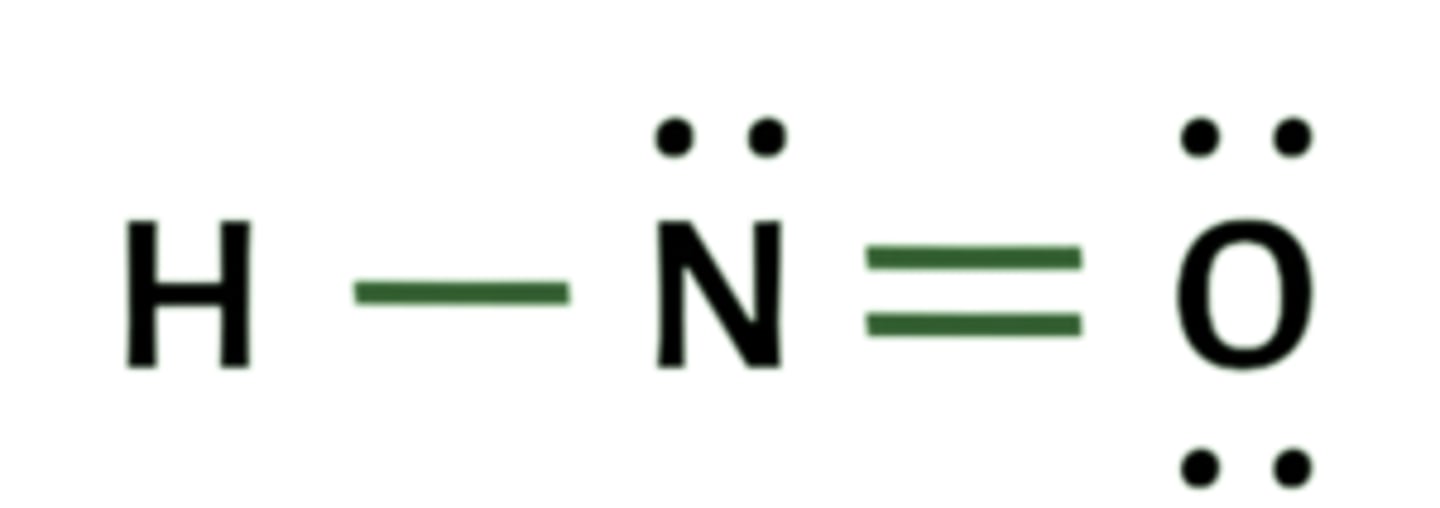
Lewis structure for XeF2
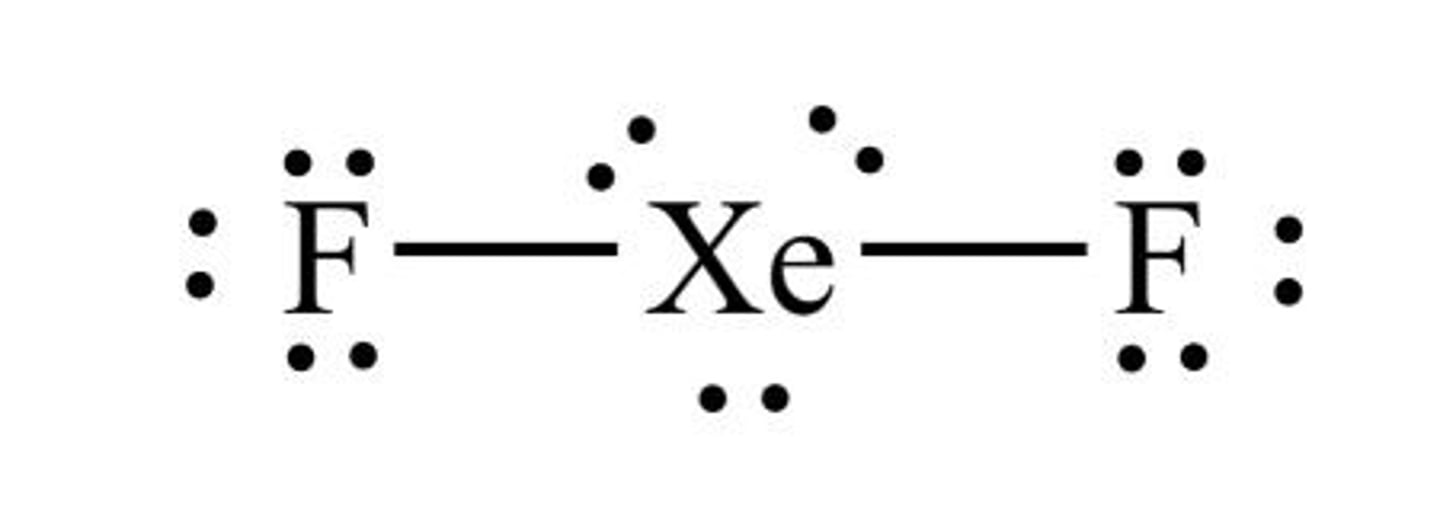
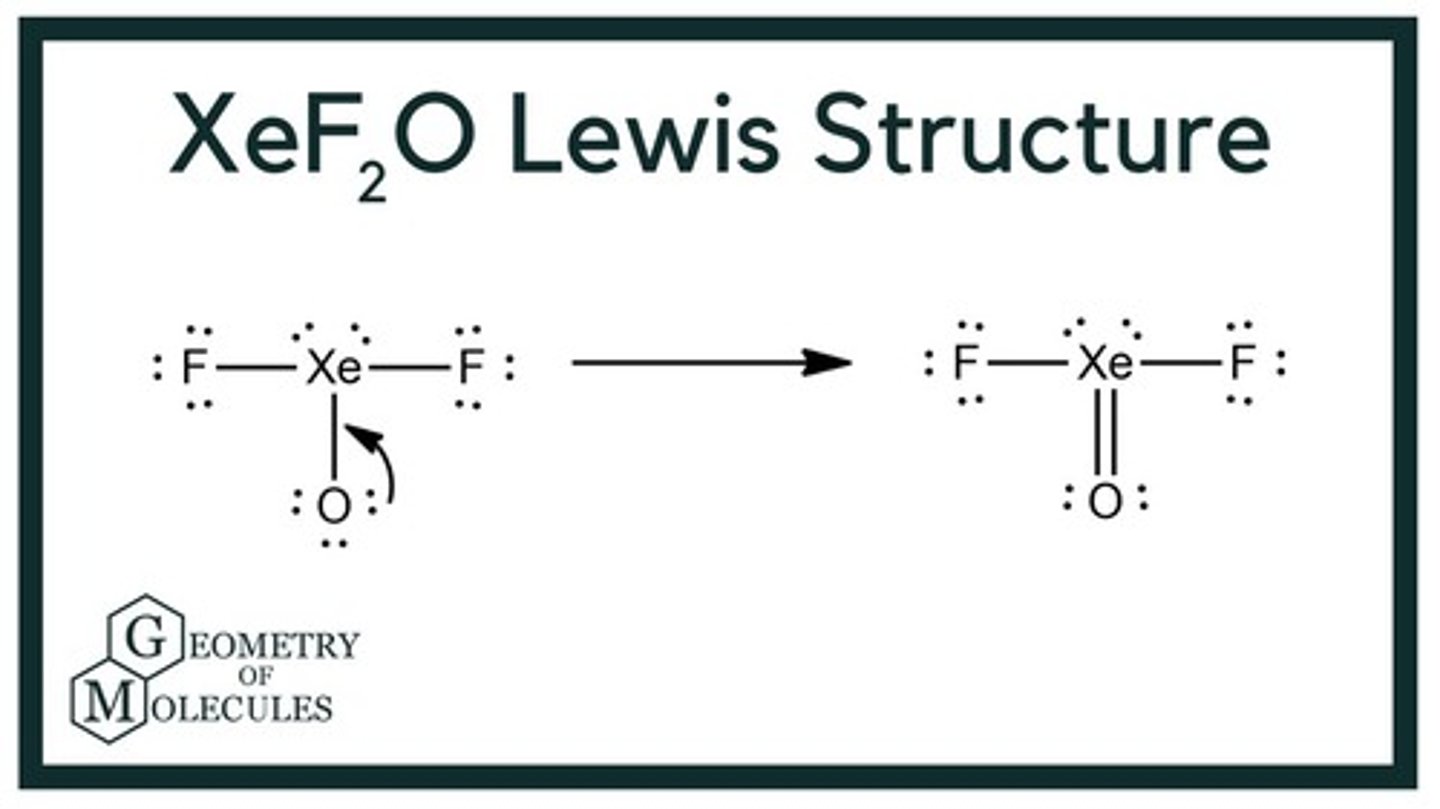
Lewis structure for XeF2O
Longest C-C Bond to shortest
C2H2
C2H4
C2H4
C2H6
C2H4
C2H2
T-shaped
Lewis structure for CH2O
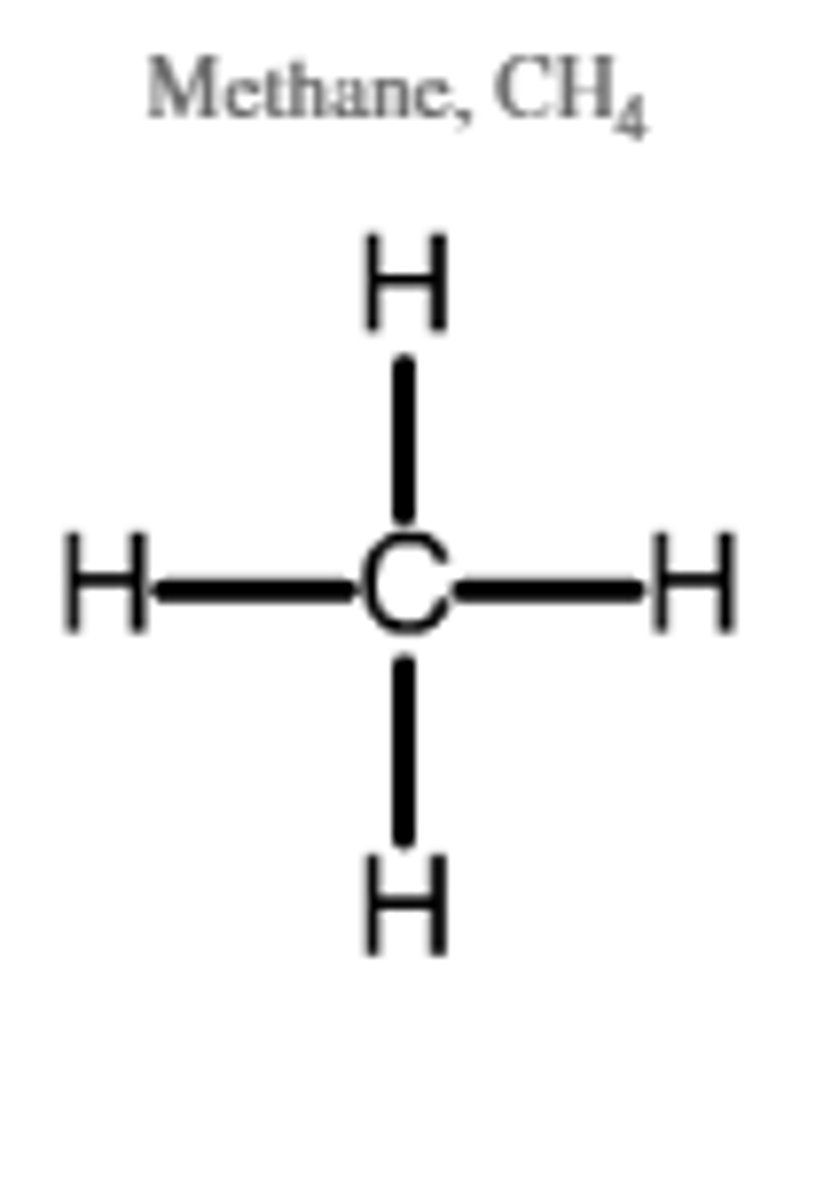
Tetrahedral (109.5°)
4 bonds, 0 lone pairs
trigonal planar (120°)
3 bonds, 0 lone pairs
linear
180, 2 bonds
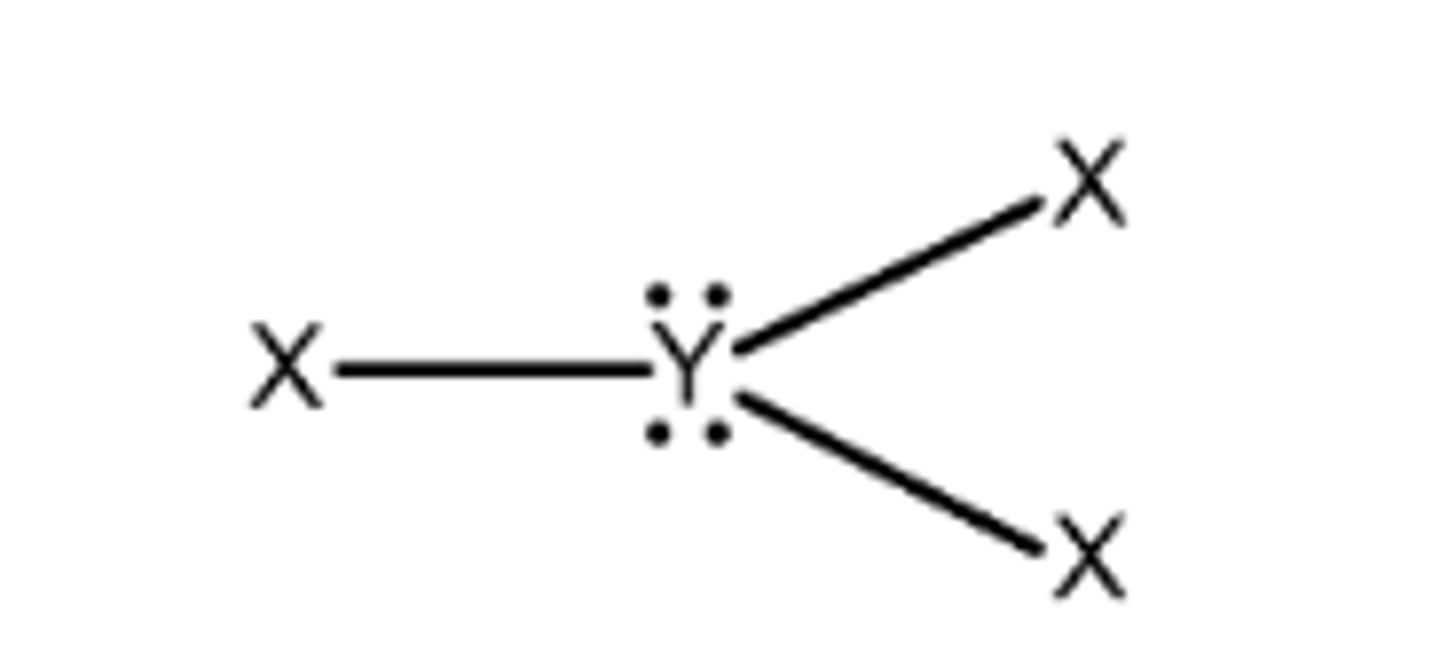
trigonal pyramidal
3 bonds, 1 lone pair
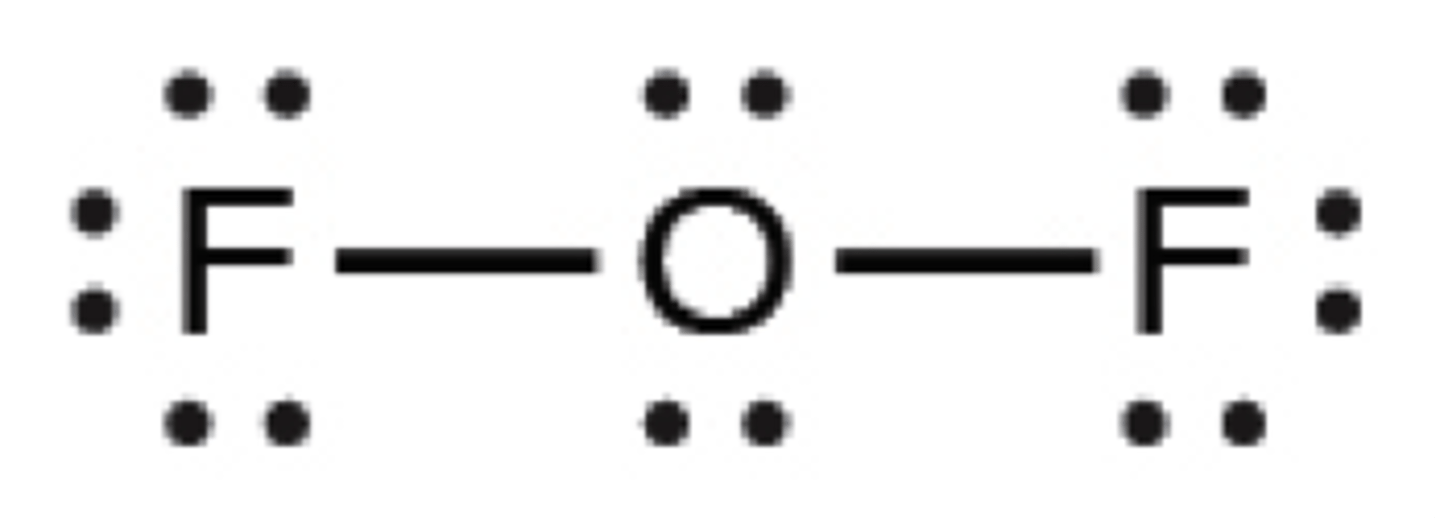
Lewis structure for OF2
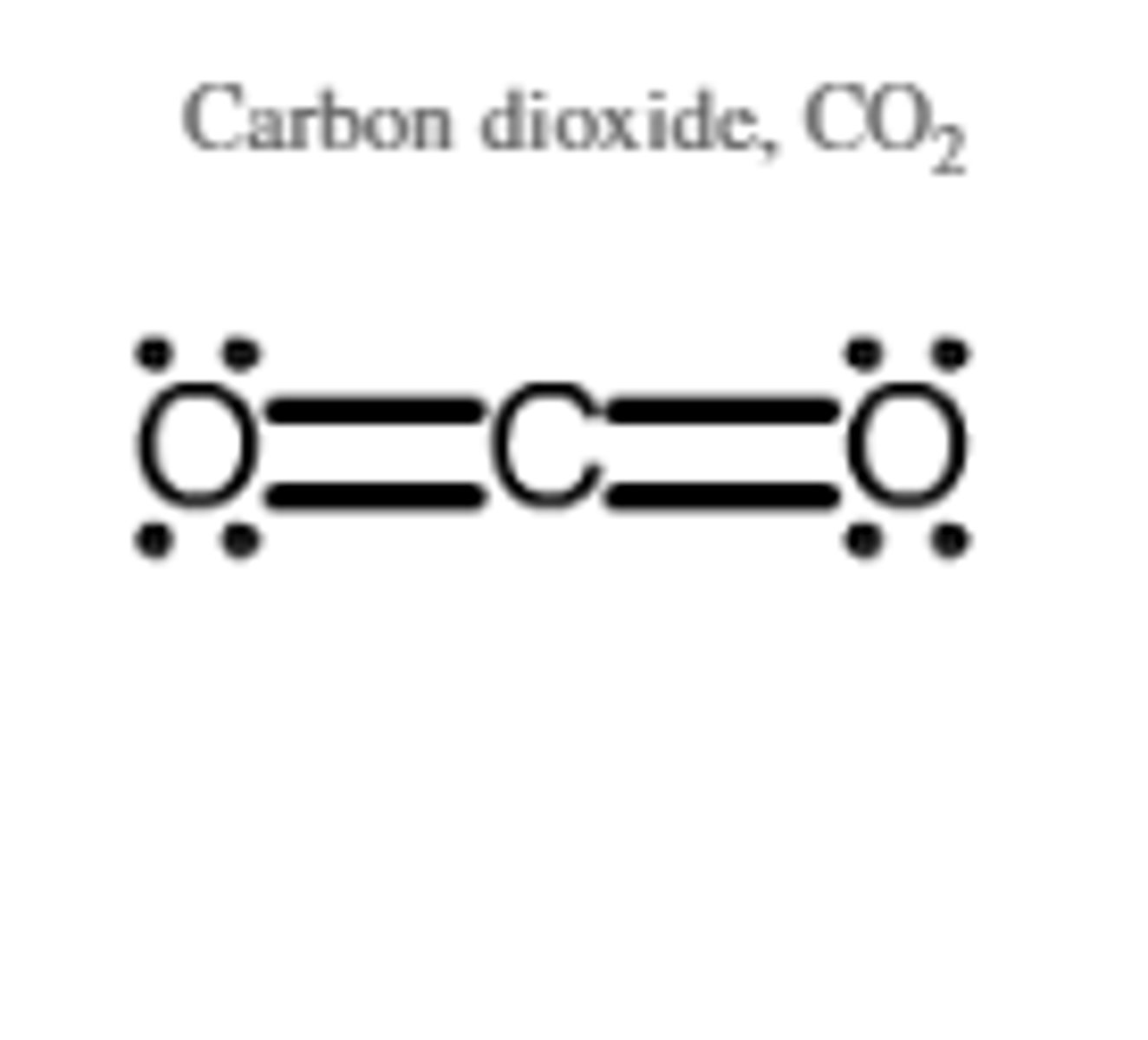
Lewis structure for CO2
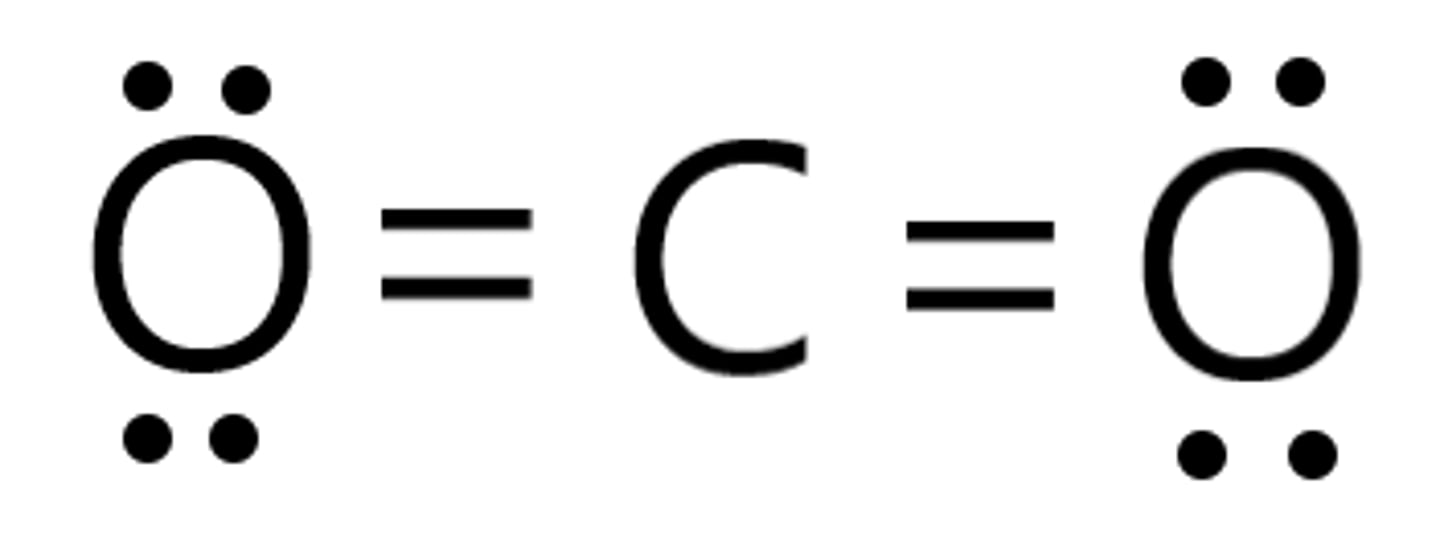
bent
<120
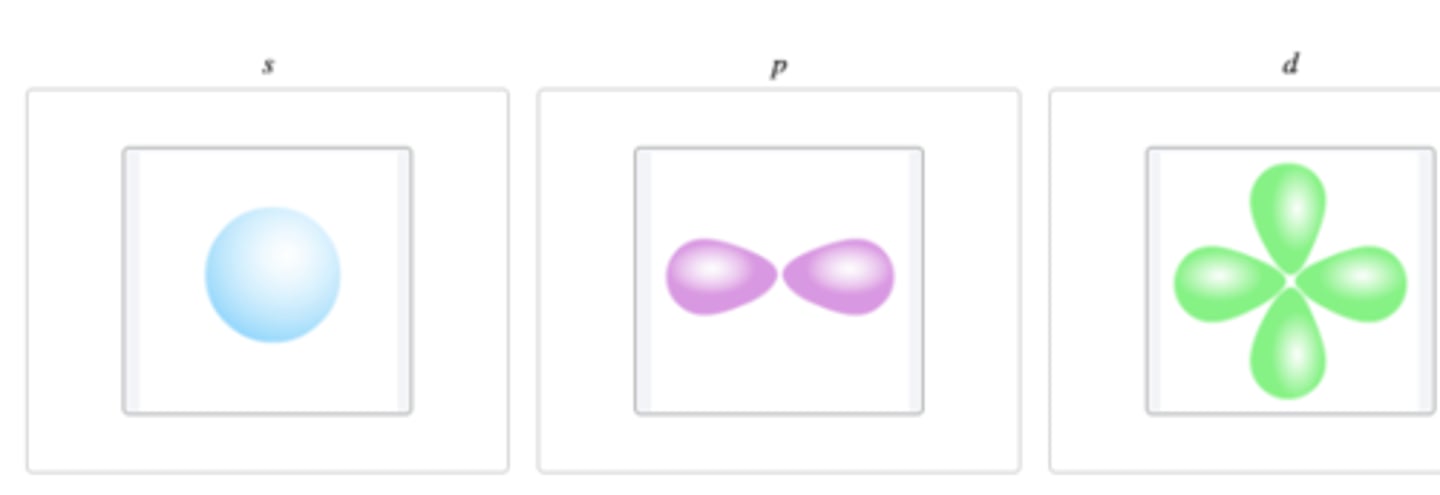
Classify the atomic orbitals as s, p, or d according to their shape.
electron configuration for N
[He]2s^2 2p^3
electron configuration for Sn
[Kr] 5s^2 4d^10 5p^2
electron configuration for Zn
[Ar]4s^2 3d^10
What element forms an ion with an electronic configuration of [Ne] and a −2 charge?
O
Write the full electron configuration for P3−
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
Ar
Cr^2+:
Cu^2+:
Co^3+:
[Ar]3d^4
[Ar]3d^9
[Ar]3d^6
Write the full ground-state electron configuration of O^2+
1s^2 2s^2 2p^2
neutral atom: C
Give the name of the element with the electronic configuration 1𝑠2 2𝑠2 2𝑝1
Boron
Identify the generic outer electron configuration for the alkaline earth metals.
ns^2
direction of increasing atomic radius on the periodic table
increasing on the bottom left
For a hydrogen‑like atom, classify the electron transitions according to whether they result in the absorption or emission of light.
n=1 to n=3
n=2 to n=1
n=3 to n=5
n=3 to n=2
Ignoring sign, which transition is associated with the greatest energy change?
absorption:
n=1 to n=3
n=3 to n=5
emission:
n=2 to n=1
n=3 to n=2
greatest energy change:
n=1 to n=3
direction of increasing ionization energy on the periodic table
increasing on top right
direction of increasing electron affinity on the periodic table
increasing on top right
Largest radius to smallest
Na
Na+
Na-
Na-
Na
Na+
Most reactive to least
K
Li
Ca
Ne
Arrange these elements according to first ionization energy. Highest to lowest ionization energy:
Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F, Ne
Ne
F
N
O
C
Be
B
Li
Arrange these elements according to electron affinity. Most energy released by gaining an electron to Most energy absorbed by gaining an electron
K
Cl
Ne
Cl
K
Ne
Arrange these elements according to electron affinity. Most energy released by gaining an electron to Most energy absorbed by gaining an electron
Mg
Na
Cl
Cl
Mg
Na
Write a chemical equation representing the first ionization energy for lithium. Use e− as the symbol for an electron
Li -> Li+ + e-
Why does ionization energy decrease moving down a group in the periodic table?
because the outer electrons get further from the nucleus
Classify each compound as containing only ionic bonds, only covalent bonds, or containing both types of bonds.
NaCl
ClO2
Ba(ClO4)2
Ionic only: NaCl
Covalent only: ClO2
Both: Ba(ClO4)
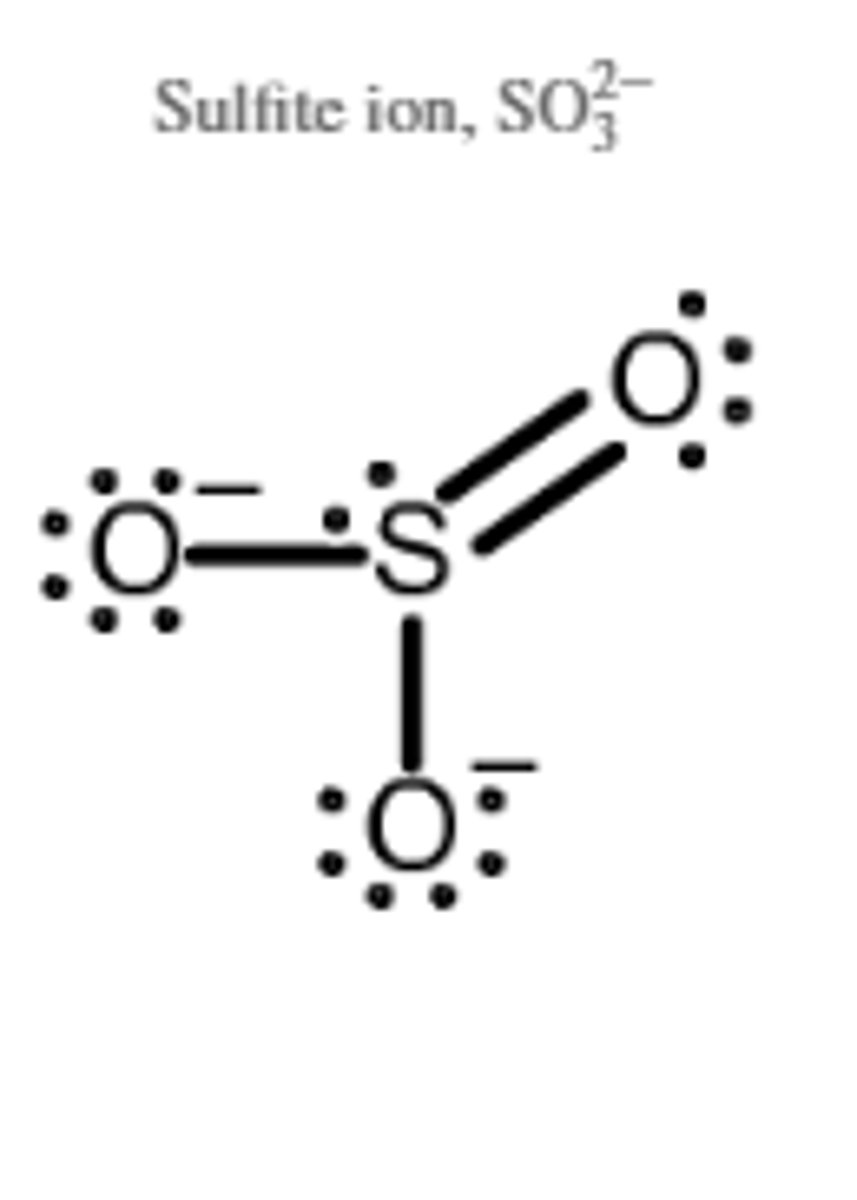
Which of the molecules and polyatomic ions cannot be adequately described using a single Lewis structure?
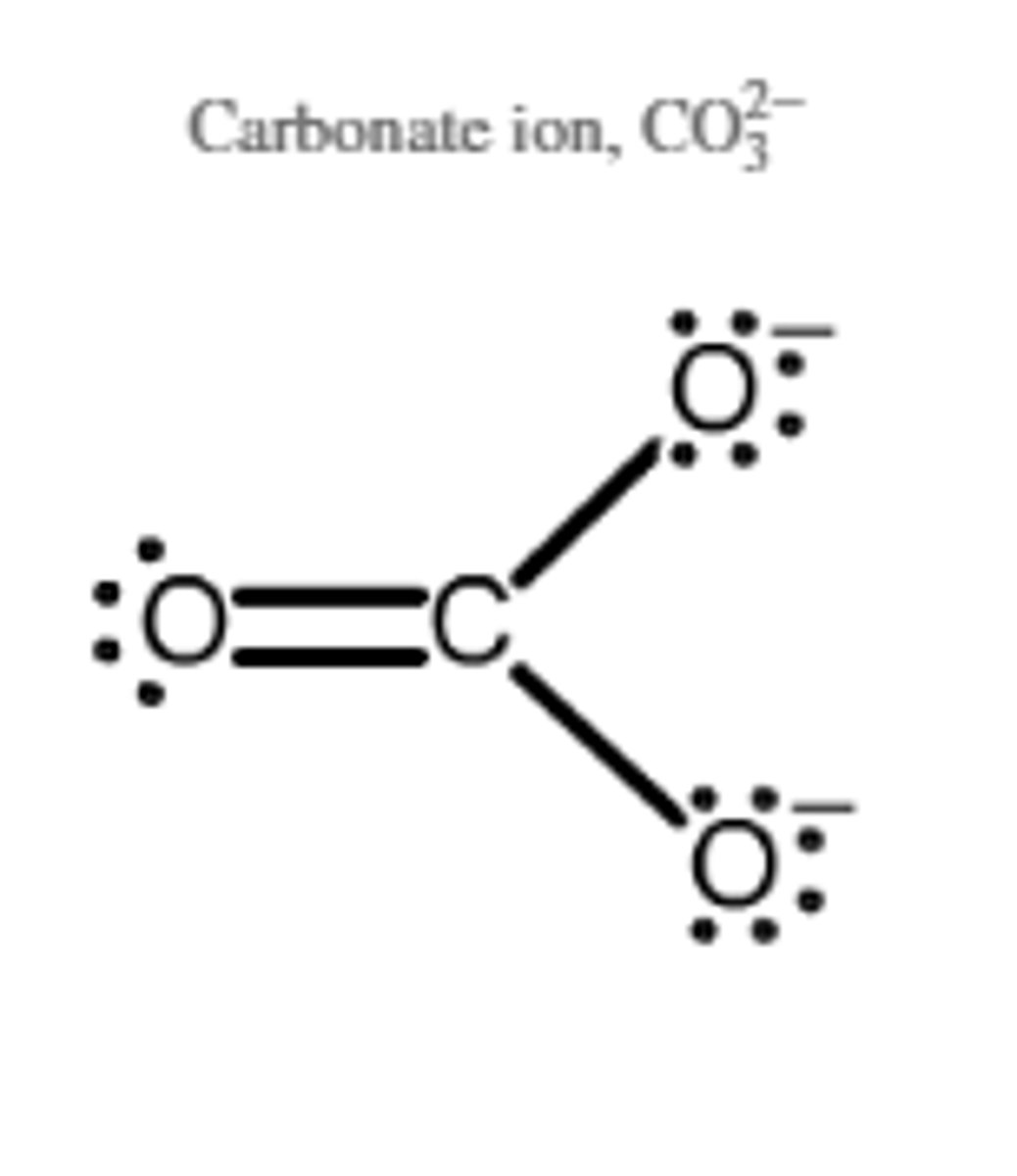
CO3^2-
O3
strongest bond to weakest
I-I
Cl-Cl
Br-Br
Cl-Cl
Br-Br
I-I
strongest bond to weakest
S-Cl
S-I
S-F
S-F
S-Cl
S-I
largest dipole moment to smallest
HF
HCl
HBr
HI
Most polar bond
C-O
lone pair
It is made up of two unshared electrons and is shown as two dots in a lewis struture
single bond
it is made of two shared electrons and is shown as a line between atoms in a lewis struture
double bond
it is made up of four shared electrons and is shown as two lines between atoms in a lewis struture
triple bond
it is made up of six shared electrons and is shown as three lines between atom in a lewis strutures
Most electronegative to least
F
C
Al
Na
Rb
Identify the charge distribution in NF3
N +
F -
top right is most electronegative
- is more electronegative
+ is less electronegative
For each of the three ionic compounds, select which main group X belongs to
X3PO4
group 1A (1)
A 1709 kg car is traveling down the road at 97.8 km/h. While traveling at this rate of speed, what is the kinetic energy of this vehicle in kilojoules?
630.65 kJ
kinetic energy formula
KE = 1/2 m v^2
If a system has 3.50×10^2 kcal of work done to it, and releases 5.00×10^2 kJ of heat into its surroundings, what is the change in internal energy (Δ𝐸 or Δ𝑈) of the system?
964.4 kJ
A 30.58 g sample of a substance is initially at 30.0 °C. After absorbing 1711 J of heat, the temperature of the substance is 189.6 °C. What is the specific heat (𝑐) of the substance?
0.351 J/g*°C
The specific heat of a certain type of cooking oil is 1.75 J/(g⋅°C). How much heat energy is needed to raise the temperature of 2.66 kg of this oil from 23 °C to 191 °C?
782040 J
The specific heat of a certain type of metal is 0.128 J/(g⋅∘C). What is the final temperature if 305 J of heat is added to 91.2 g of this metal, initially at 20.0 ∘C?
T(final) =____∘C
46.127
An 80.0 g sample of a gas was heated from 25 ∘C to 225 ∘C. During this process, 346 J of work was done by the system and its internal energy increased by 7465 J. What is the specific heat of the gas?
c = ___ J/(g*∘C)
.488 J/(g*∘C)
First law of thermodynamics equation
ΔE = Q - W
If you combine 270.0 mL of water at 25.00 ∘C and 100.0 mL of water at 95.00 ∘C, what is the final temperature of the mixture? Use 1.00 g/mL as the density of water.
T(final) = ____ ∘C
43.92 ∘C
When 1933 J of heat energy is added to 39.6 g of ethanol, C2H6O, the temperature increases by 19.9 ∘C.
Calculate the molar heat capacity of C2H6O.
Cp = ____ J/mol*∘C
113.0 J/mol*∘C
endothermic reaction
Absorbs heat, delta H is positive
exothermic reaction
A reaction that releases energy in the form of heat, Delta H is negative
endothermic reaction examples
solid to liquid, liquid to gas, solid to gas
exothermic reaction examples
gas to liquid, liquid to solid, gas to solid
Consider the reaction.
2Fe2O3⟶4Fe+3O2 Δ𝐻∘rxn=+824.2 kJ
The formation of 35.0 g35.0 g of O2 results in
the absorption of 3.00×10^2 kJ of heat
what type of energy does chemical energy have?
potential energy
The balanced combustion reaction for C6H6 is
2C6H6(l)+15O2(g)⟶12CO2(g)+6H2O(l)+6542 kJ2
If 6.000 g C6H6 is burned and the heat produced from the burning is added to 5691 g of water at 21 ∘C, what is the final temperature of the water?
31.6 C
The specific heat of a certain type of cooking oil is 0.418 cal/(g·°C). How much heat energy is needed to raise the temperature of 1.317 kg of this oil from 23.0 °C to 60.0 °C?
20368.72 cal
A 101.6 g sample of a substance is initially at 26.8 °C. After absorbing 153 cal of heat, the temperature of the substance increases to 72.4 °C. What is the specific heat (𝑆𝐻) of the substance?
0.033 cal/g*C
A student places a block of hot metal into a coffee cup calorimeter containing 151.2 g of water. The water temperature rises from 21.1 °C to 37.8 °C.
How much heat (in calories) did the water absorb?
q(water)= ___ cal
How much heat did the metal lose?
q(metal) = ___ cal
q(water) = 2525.04 cal
q(metal) = -2525.04 cal
A 291 g silver figure of a polar bear is dropped into the 247 g aluminum cup of a well‑insulated calorimeter containing 275 g of liquid water at 24.3∘C. The bear's initial temperature is 99.3∘C. What is the final temperature of the water, cup, and bear when they reach thermal equilibrium? The specific heats of silver, aluminum, and liquid water are, respectively, 234 J/(kg·K), 910 J/(kg·K), and 4190 J/(kg·K)
27.8 C
For a particular isomer of C8H18, the combustion reaction produces 5099.5 kJ of heat per mole of C8H18(g) consumed, under standard conditions.
C8H18(g)+252O2(g)⟶8CO2(g)+9H2O(g)
Δ𝐻∘rxn=−5099.5 kJ/mol
What is the standard enthalpy of formation of this isomer of C8H18(g)?
_ kJ/mol
A researcher studying the nutritional value of a new candy places a 4.70 g sample of the candy inside a bomb calorimeter and combusts it in excess oxygen. The observed temperature increase is 2.98 ∘C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter is 47.20 kJ⋅K−1, how many nutritional Calories are there per gram of the candy?
__ cal/g
A 56.59 g sample of a substance is initially at 25.6 °C. After absorbing 2789 J of heat, the temperature of the substance is 101.0 °C. What is the specific heat (𝑐) of the substance?
0.654 J/g*C
(Quiz 9) Calculate the heat energy released when 16.1 g of liquid mercury at 25.00 °C is converted to solid mercury at its melting point.
Constants for mercury at 1 atm
heat capacity of Hg(l): 28.0 J/(mol⋅K)
melting point: 234.32 K
enthalpy of fusion: 2.29 kJ/mol
__ kJ
The heat of vaporization of water is 40.66 kJ/mol. How much heat is absorbed when 1.79 g of water boils at atmospheric pressure?
4.04 kJ
Liquid sodium is being considered as an engine coolant. How many grams of liquid sodium (minimum) are needed to absorb 9.10 MJ of energy in the form of heat if the temperature of the sodium is not to increase by more than 10.0 °C? Use 𝐶P=30.8 J/(K⋅mol) for Na(l) at 500 K.
17.2 g
If you combine 330.0 mL= of water at 25.00 ∘C and 120.0 mL of water at 95.00 ∘C, what is the final temperature of the mixture? Use 1.00 g/mL as the density of water.
43.67 C
P^3- electron configuration
1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^6
atomic symbol: Ar
electron configuration of Ar and a -2 charge
S
Cr^2+ electron configuration
[Ar]3d^4
Cu^2+ electron configuration
[Ar]3d^9
Co^3+ electron configuration
[Ar]3d^6
O^2+ electron configuration
1s^2 2s^2 2p^2
isoelectronic: C
what does more polar mean?
further away