NURS 403 - Pediatrics Unit 2
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
2nd
from birth to 24 months, below the _____ percentile is considered underweight
98th
from birth to 24 months, above the _____ percentile is considered overweight
5th
after 24 months, below the _____ percentile is considered underweight
85th and 95th
after 24 months, between the _____ percentile are at risk for overweight
95th
after 24 months, above the _____ percentile is considered overweight
corrected gestational age
when documenting growth, use a _____ for infants that were born prematurely until they are 3 years old
3
when documenting growth, use a corrected gestational age for infants that were born prematurely until they are _____ years old
3
head circumference is measured on infants until age _____ at each well visit
fever
crying
medications
activity
factors that can increase a child's heart rate
> 20
apnea in infants is no respirations for _____ seconds
lanugo
fine downy hair of an infant
lanugo
this picture indicates:
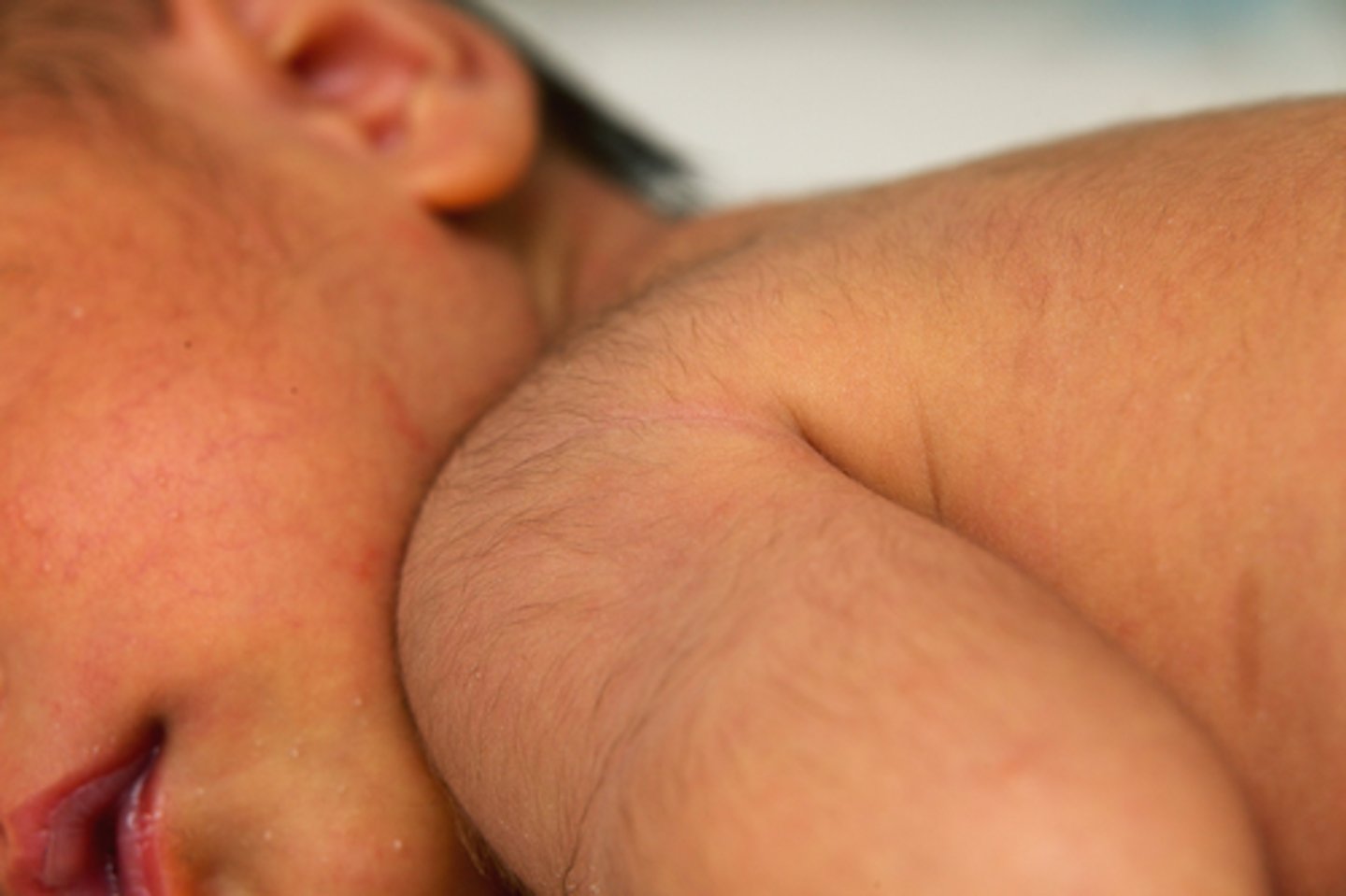
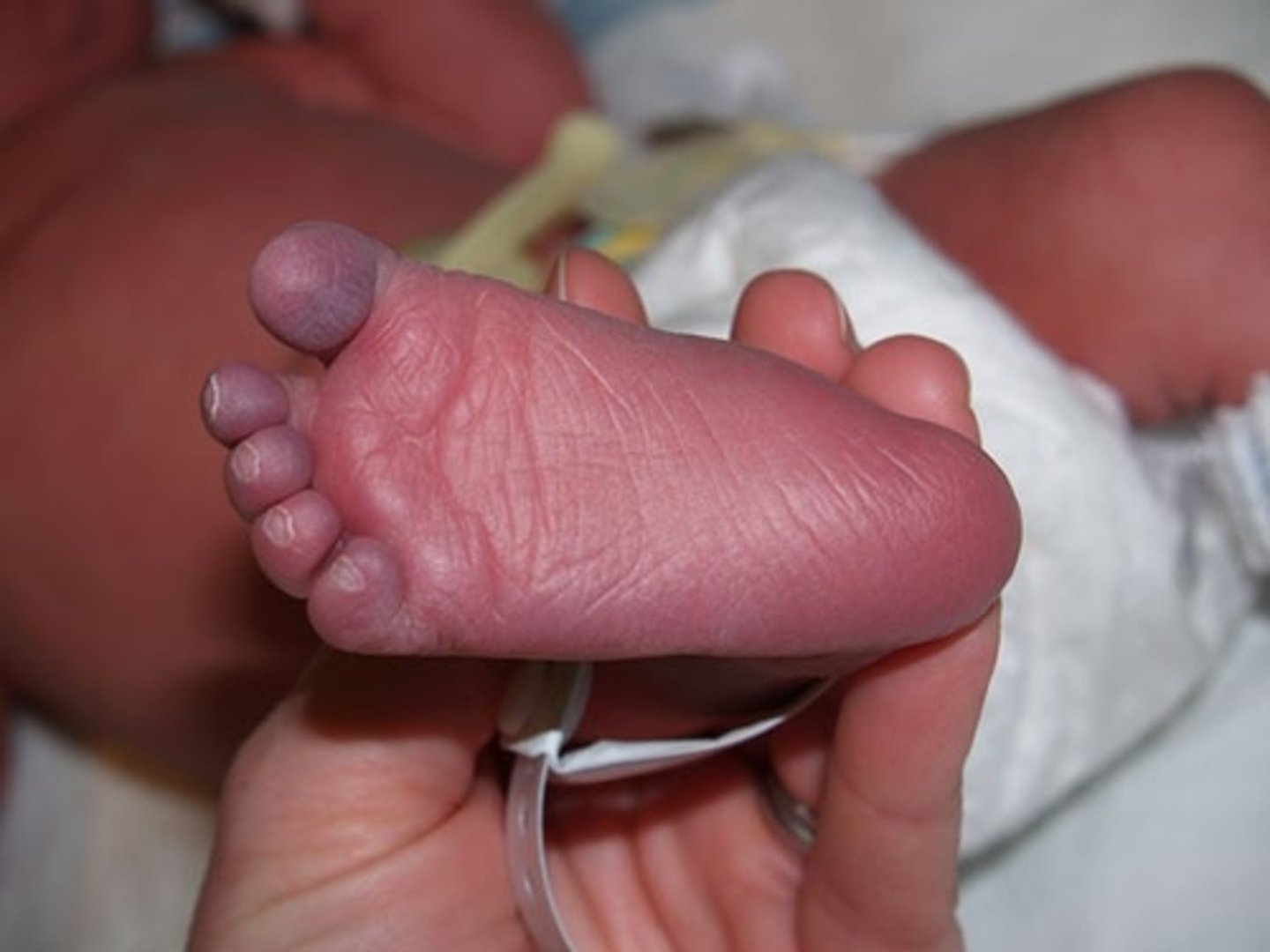
acrocyanosis
blueness of the extremities
acrocyanosis
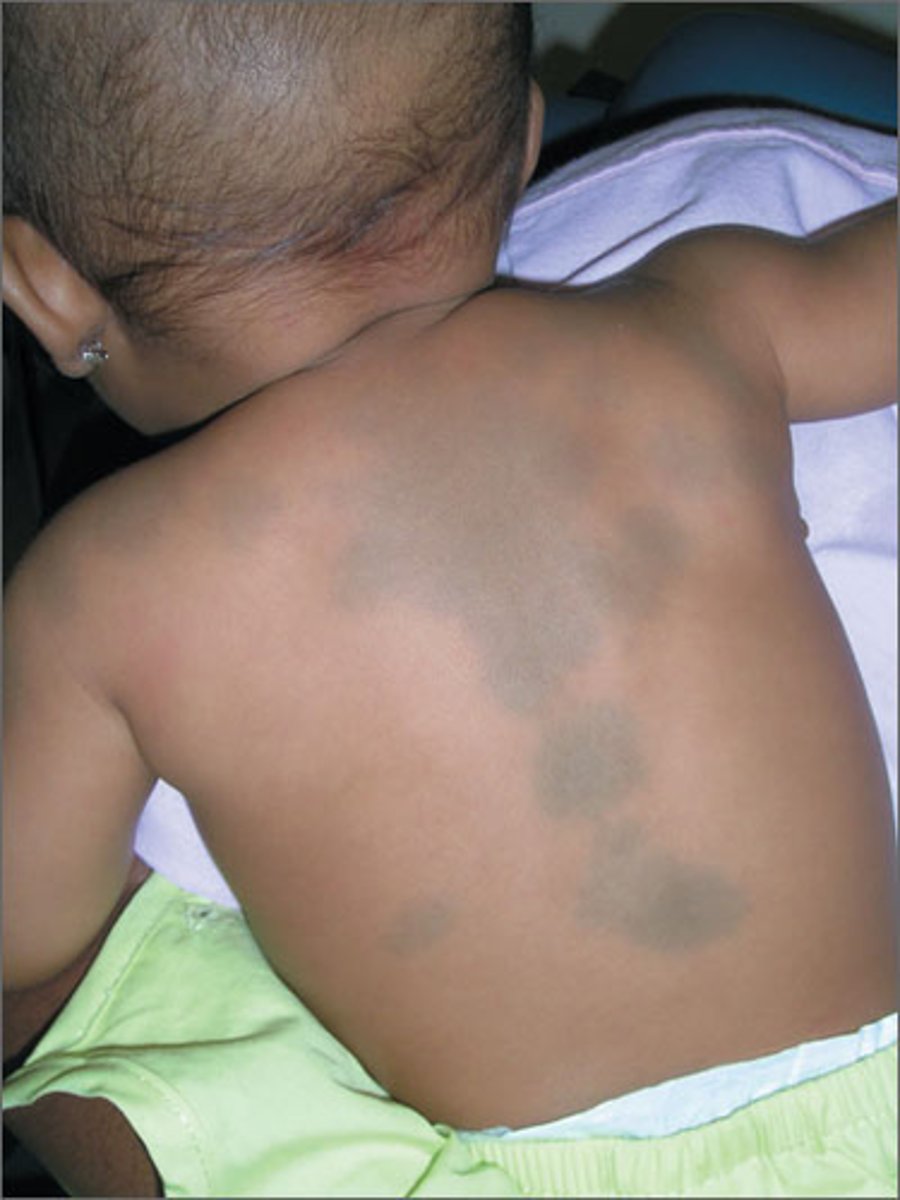
this picture indicates:
mongolian spots
hyperpigmented nevi common in dark-skinned infants
mongolian spots
this picture indicates:
9-18 months
when does the anterior fontanel close?
2 months
when does the posterior fontanel close?
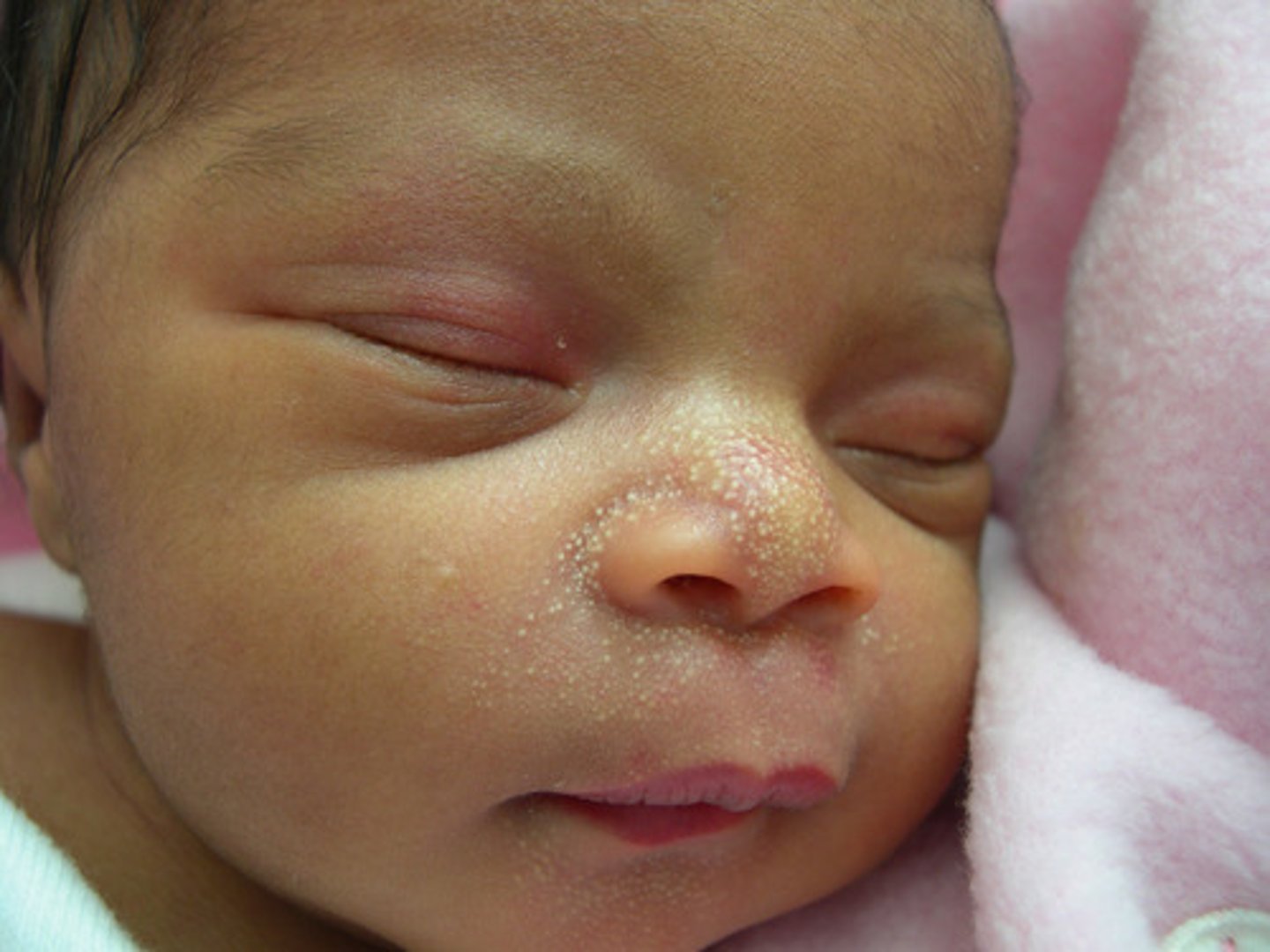
milia
small white papules on the face of an infant
milia
this picture indicates:

positional plagiocephaly
a flattened occiput in an infant may be due to _____
plagiocephaly
develops when an infant's soft skull becomes flattened in one area, due to repeated pressure on one part of the head
plagiocephaly
this picture indicates:
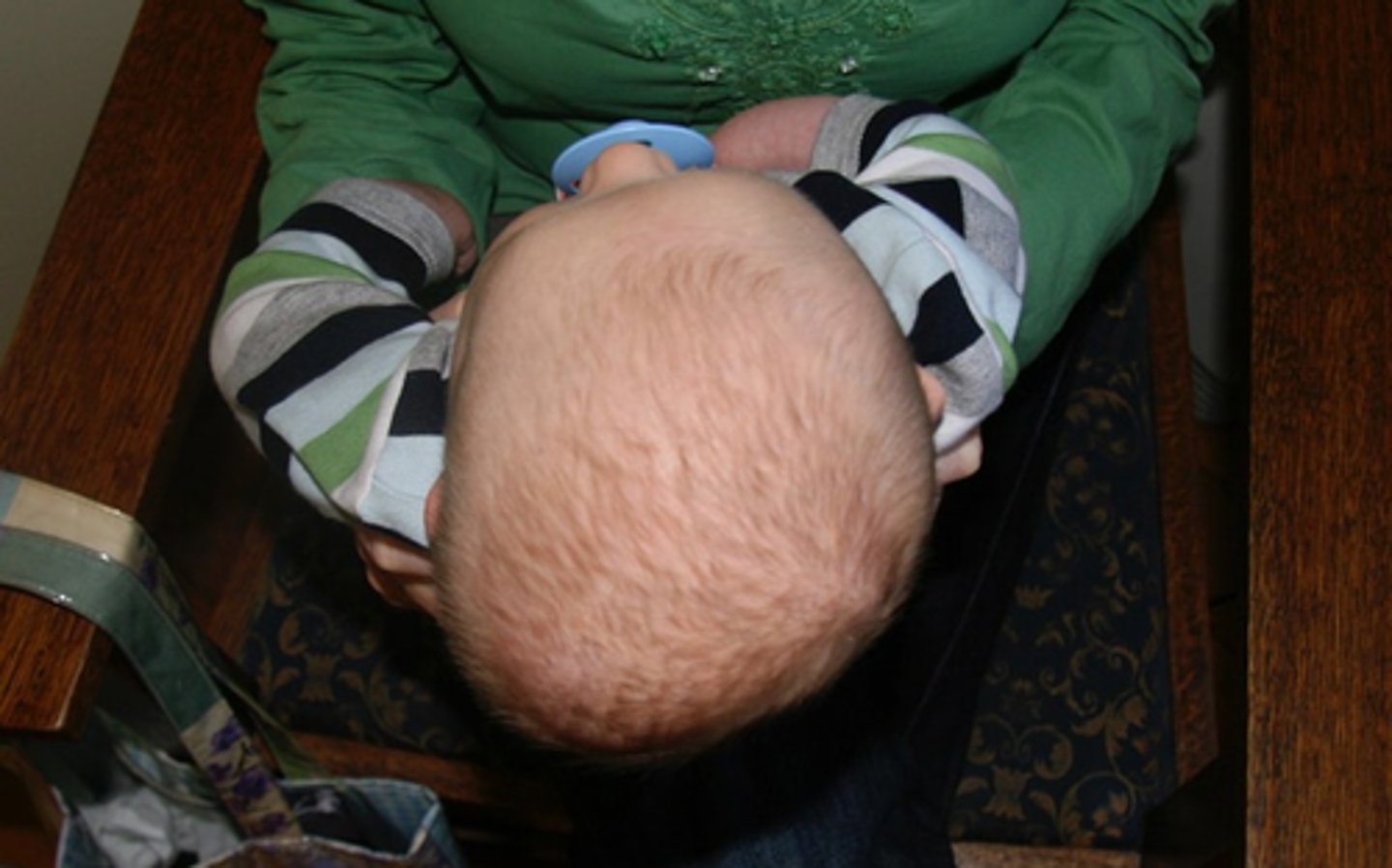
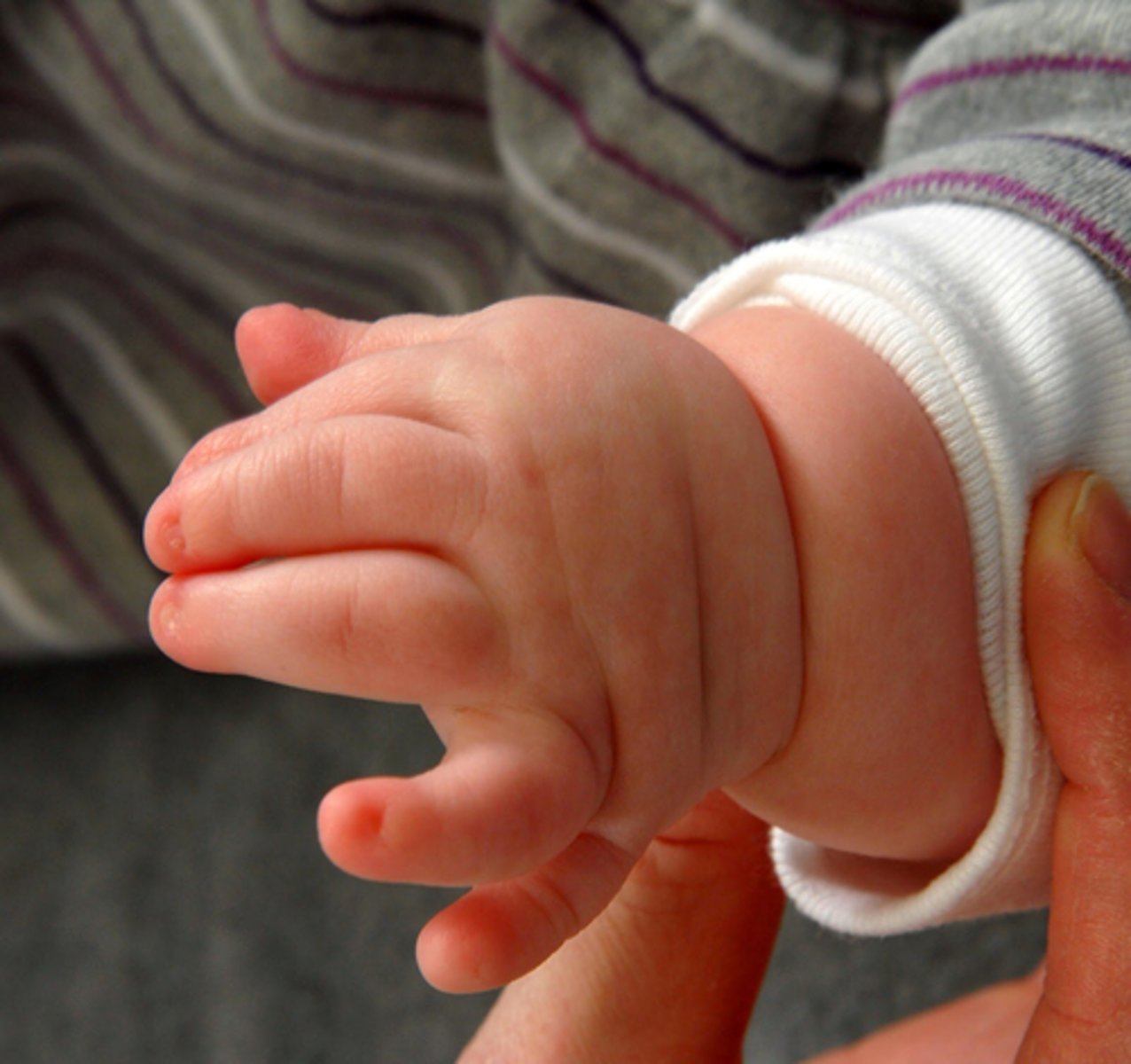
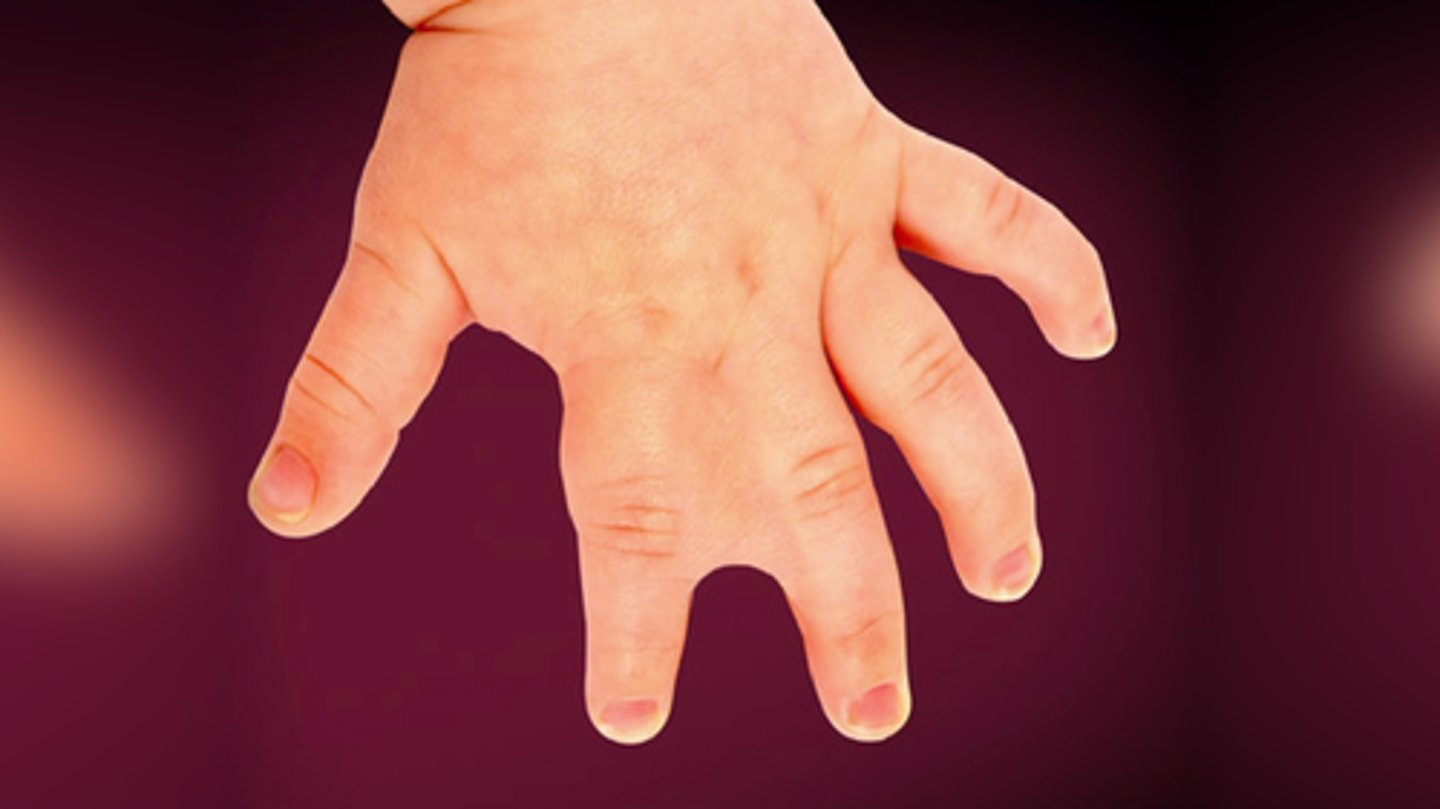
polydactyly
increased number of digits
polydactyly
this picture indicates:

syndactyly
webbed digits
syndactyly
this picture indicates:
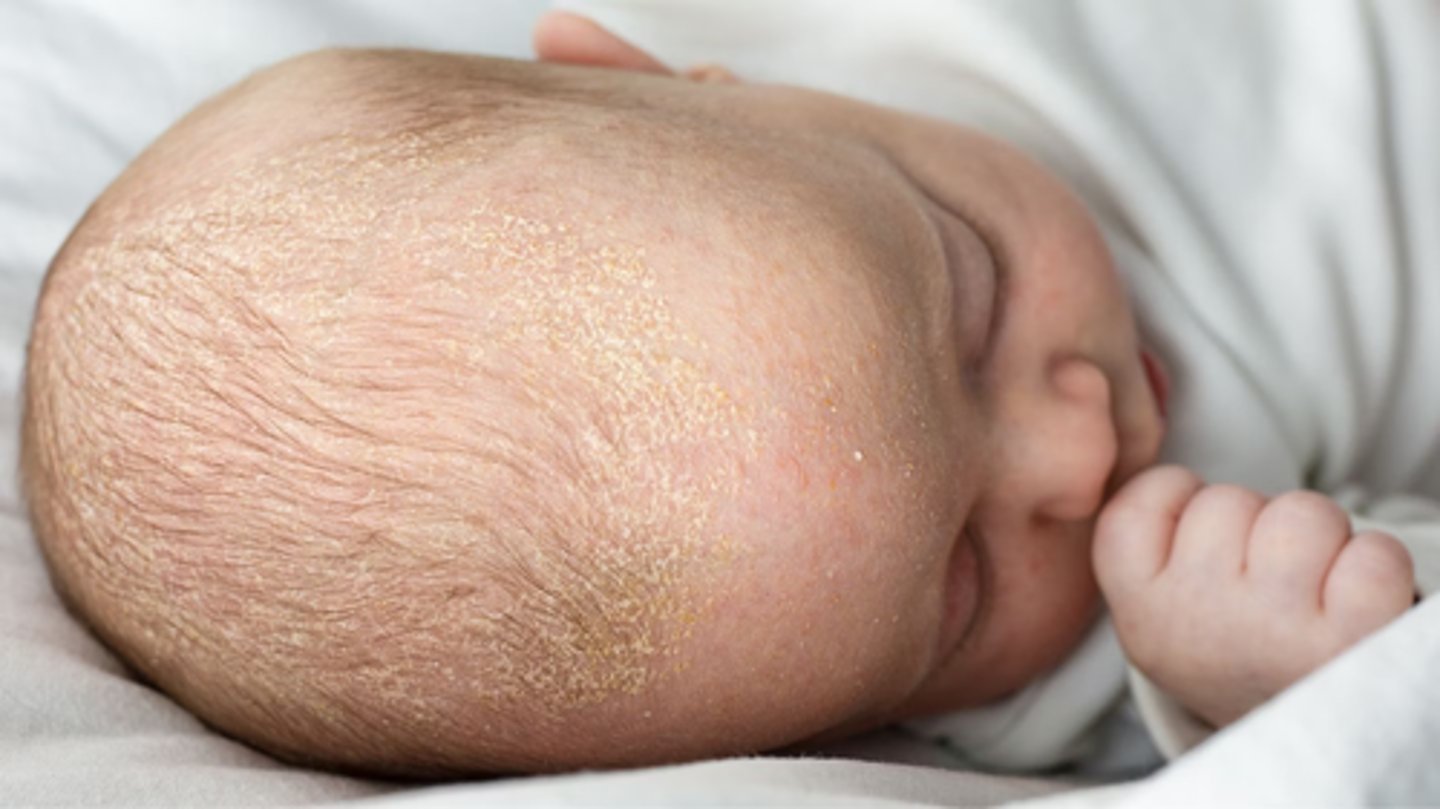
cradle cap
seborrheic dermatitis in infants
cradle cap
this picture indicates:
4-6 months
intermittent strabismus is normal in infants until _____
genetic syndromes
low set ears in infants may indicate _____
3-6 months
infants are obligate nose breathers until _____
3 months
in infants, salivation begins at _____
6 months
in infants, the tongue extrusion reflex lasts up to _____
5-6 months
infants have no teeth until _____
4 months
head control in infants is expected by _____
umbilical hernia
type of hernia in infants that usually goes away on it's own and doesn't require surgical intervention
30 months
toddlers should have 20 teeth by _____
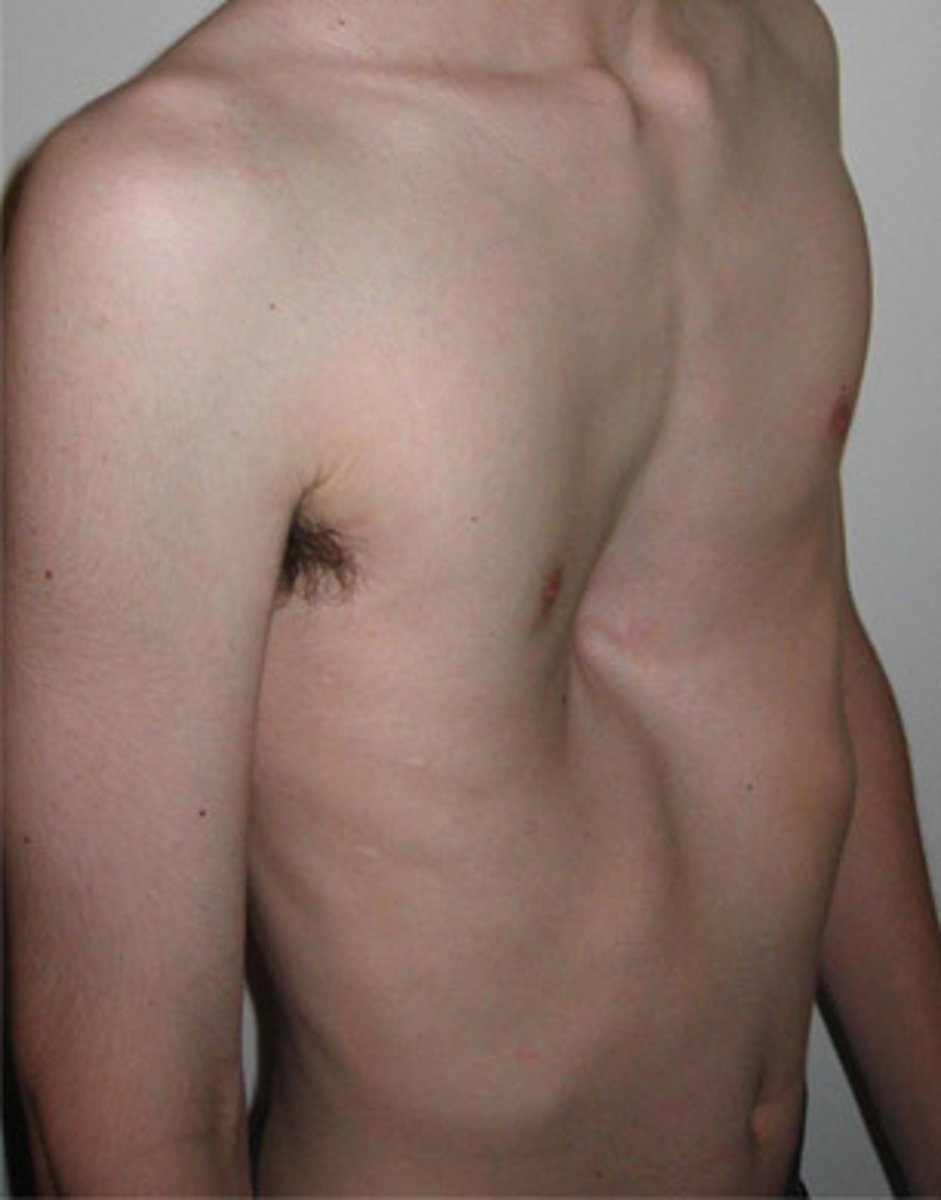
pectus excavatum
depressed sternum
pectus excavatum
this picture indicates:
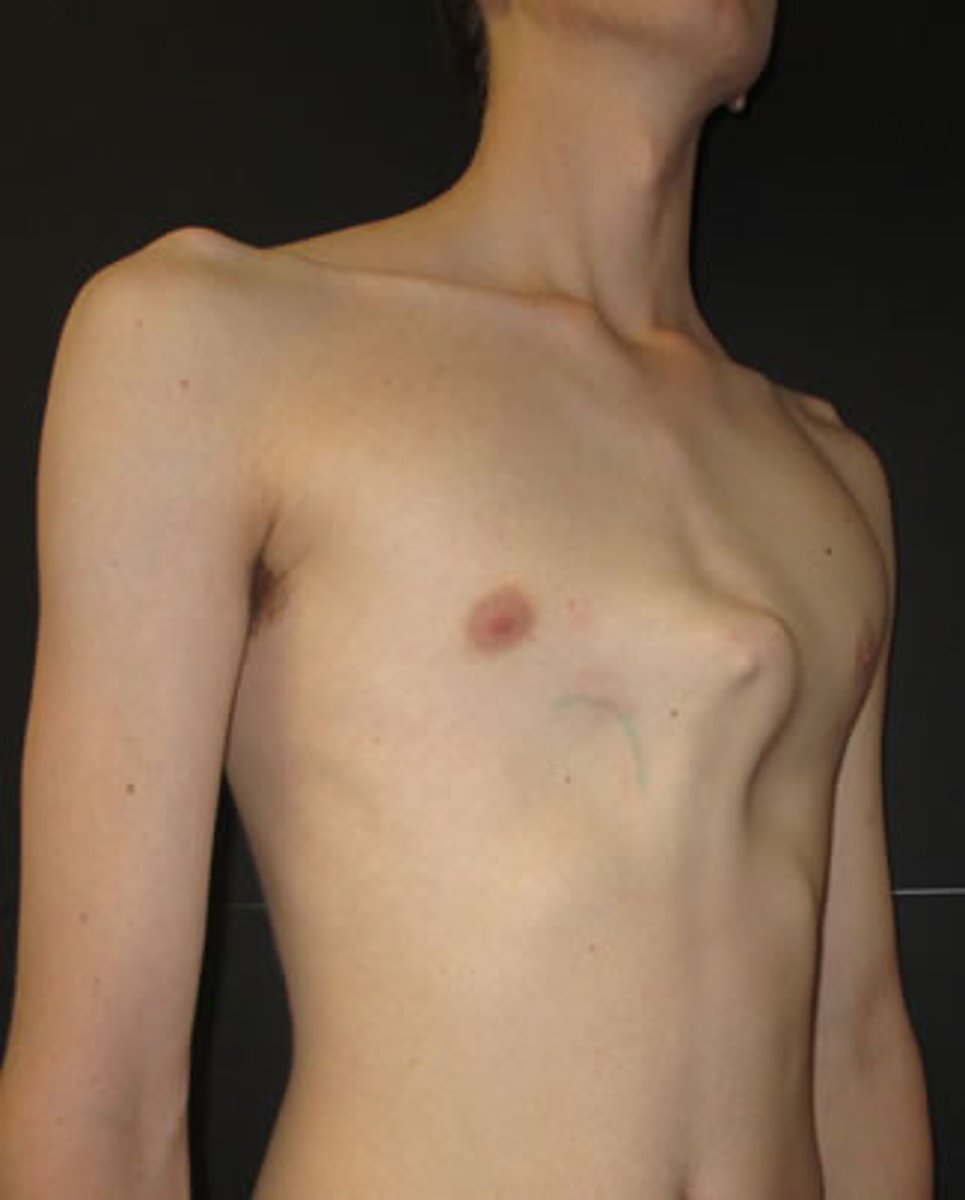
pectus carinatum
protuberant sternum
pectus carinatum
this picture indicates:
internal tibial torsion
pigeon toes
large
_____ tonsils are normal in toddlers
flat
_____ feet are normal in toddlers
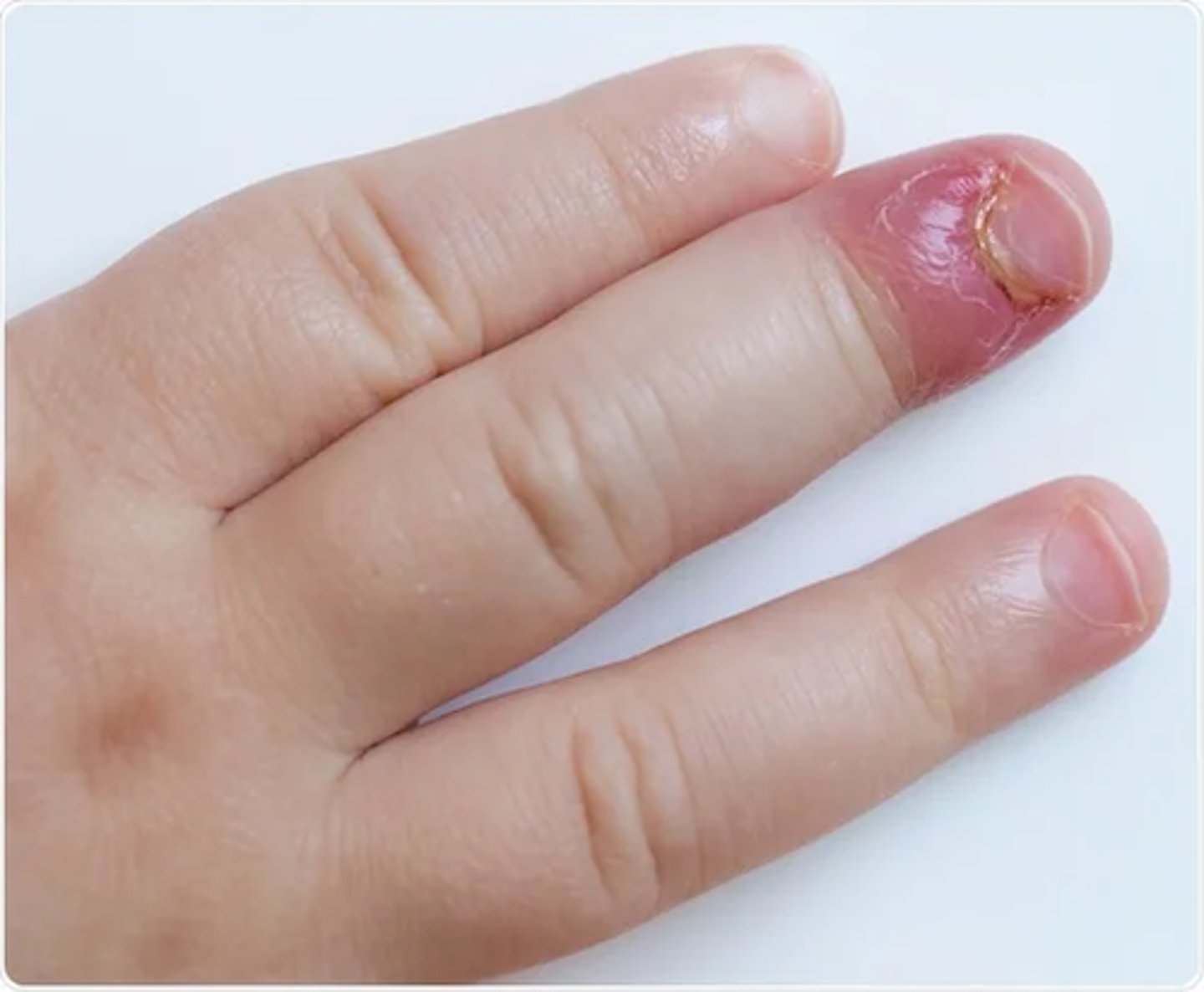
paronychia
inflammation of the nail fold
paronychia
this picture indicates:
chronic hypoxia
clubbing of nails indicates _____
clubbing of nails (chronic hypoxia)
this picture indicates:
koilonychia
spoon shaped nails
koilonychia (iron-deficiency anemia)
this picture indicates:
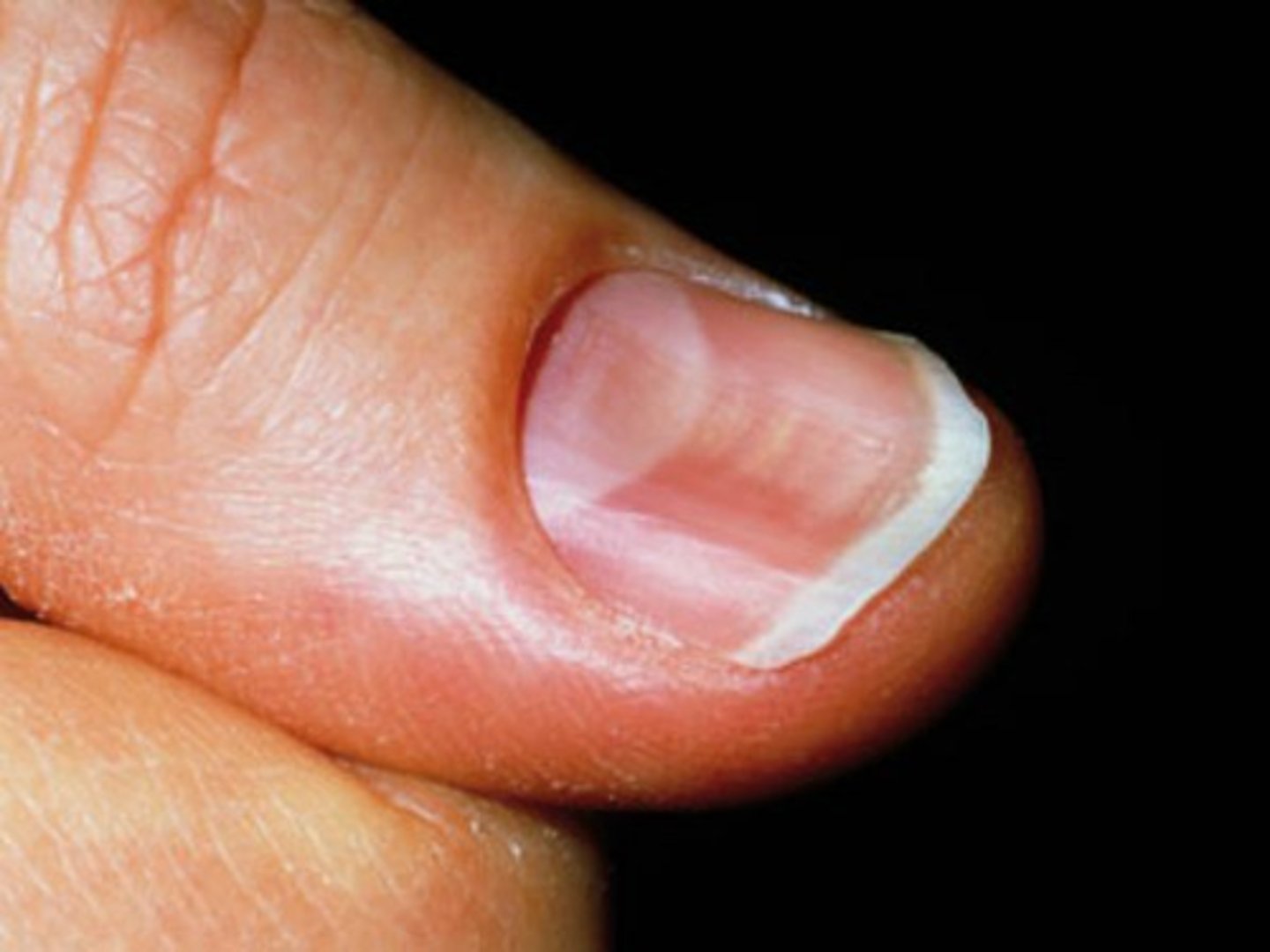
iron-deficiency anemia
koilonychia indicates _____
8 years
female breast development may begin as early as _____
tanner staging
sexual maturity rating scale for breasts, genitalia, and pubic hair
13
female breast development begins at age _____ in most girls
facial expressions (brow contracting, quivering chin)
the most common response to pain in infants
CRIES scale
pain scale used for newborns and infants
crying
requires O2 for an SpO2 > 95%
increased vital signs
expression
sleeplessness
categories of the CRIES scale:
Wong-Baker FACES scale
pain scale used for ages 3-8 on average
FLACC scale
pain scale used for children who can't verbalize the FACES pain scale (children younger than 3, those with developmental issues, those who are nonverbal)
face
legs
activity
cry
consolability
categories of the FLACC scale:
therapeutic hugging
relaxation
distraction
guided imagery
biofeedback
thought stopping, positive self-talk
cognitive-behavioral strategies for pain management:
massage, acupressure
cold therapy, ice
heat therapy
nonnutrive sucking with sucrose (sweet-ease)
biophysical interventions for pain management:
nonopioids
analgesics indicated for mild (0-3) to moderate (4-6) pain
ibuprofen
ketorolac (toradol)
acetaminophen
nonopioids for pain management:
ibuprofen
nonopioid that should not be given to children under 6 months of age due to gastrointestinal issues and problems that can occur with the kidneys
aspirin
nonopioid that should not be given to children due to the risk for Reye syndrome, which causes brain and liver swelling, neurological impairment, and death
opioids
analgesics indicated for severe pain (>7)
hydrocodone
morphine
opioids for pain management:
morphine
the gold standard for severe pain
meperidine (demerol)
opioid that should be avoided because it has been known to cause seizures and CNS toxicity
codeine and tramadol
opioids that should not be given to children younger than 12
diazepam (anxiety)
midazolam (amnesia)
benzodiazepines for pain management:
gabapentin (neuropathic pain)
anticonvulsants for pain management:
EMLA cream
vapocoolants
local anesthetics for pain management:
strained healthcare funding
shorter hospital stays
cost containment
acute care is not a good environment for children
reasons for early transitions of care from hospitals to communities:
teaching
communicating
care coordination
resource allocation
primary functions of the community health nurse for the pediatric population
protest phase
despair phase
detachment or denial phase
three phases of separation anxiety:
protest phase
phase of separation anxiety: crying, clinging to parents
protest phase
phase of separation anxiety: expressing agitation and aggression toward strangers
protest phase
phase of separation anxiety: rejecting others who attempt to offer comfort
despair phase
phase of separation anxiety: hopelessness
despair phase
phase of separation anxiety: withdrawal, decreased communication, quiet, depressed, apathetic, sad
despair phase
phase of separation anxiety: lack of interest
detachment or denial phase
phase of separation anxiety: long-term separations
detachment or denial phase
phase of separation anxiety: coping skills developed
detachment or denial phase
phase of separation anxiety: superficial relationships formed
detachment or denial phase
phase of separation anxiety: parents are ignored if they return
detachment or denial phase
phase of separation anxiety: delays may occur (developmental regression)
trust and bonding
a developmentally delayed infant may fail to develop sense of _____
autonomy
a developmentally delayed toddler may have difficulty developing _____
initiative
a developmentally delayed preschooler may have difficulty achieving a sense of _____
industry
a developmentally delayed school-age child may have difficulty achieving _____
self-identity relative to peers
a developmentally delayed adolescent may have difficulty forming a sense of _____
vulnerable child syndrome
describes a phenomenon in which a child is perceived as being at higher risk for medical, behavioral, or developmental problems than is warranted by the child's current health
vulnerable child syndrome
occurs when a parent continues to exhibit unwarranted concerns as a reaction to a serious event in the child's past
preterm birth
congenital anomaly
newborn jaundice
handicapping condition
an accident or illness that the child was not expected to recover from
crying or feeding problems in the first 5 years of life
risk factors for vulnerable child syndrome:
failure to thrive
a condition of inadequate growth in infants and children
developmental issues
a child with failure to thrive may develop _____ due to the poor nutritional intake
observe parent-child interactions
develop and maintain appropriate feeding schedule
weigh child daily and record strict I&O
educate parents on feeding techniques and amounts
provide consistent nursing care and support
nursing interventions for failure to thrive: