ECHO PATHOLOGY QUIZZES
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Which of the following is a classic finding of mitral stenosis?
Leaflet doming
The heart responds to an increased preload by an increase in:
Contractility
Which Mitral Valve leaflets are seen in SAX?
Anterior & Posterior
Blood flow through the lungs is increasingly harder when ___________is elevated?
Pressure
In the chamber that is ________ to the stenotic valve, the blood backs up, drives the pressure up, and creates a pressure overload pattern.
Proximal
Secondary findings in mitral stenosis can be:
Left atrial enlargement and signs of pulmonary hypertension
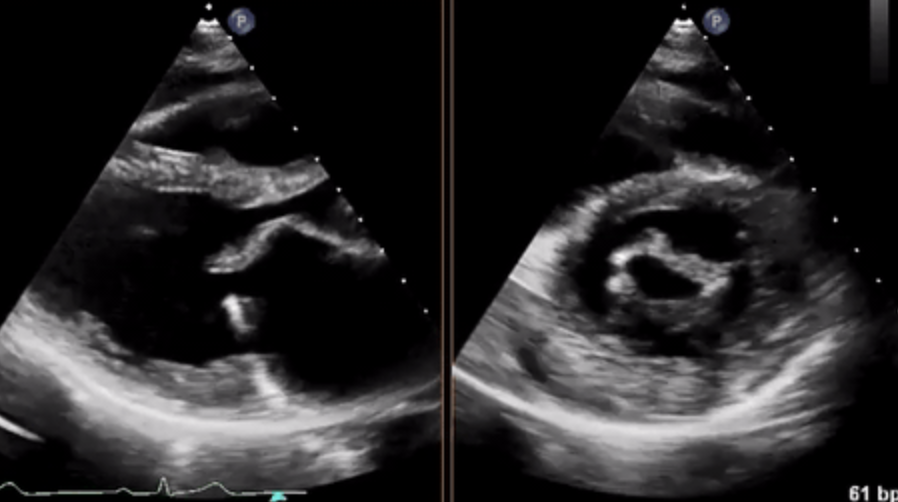
What pathology is seen on this video clip
mitral valve stenosis
Which Mitral Valve leaflets are seen in SAX?
Anterior & Posterior
The_________ assumes that the rate at which the gradient drops during diastole corresponds to the severity of mitral stenosis.
PHT method
The E-wave peak velocity _________ .
Represents the early diastolic LA-LV pressure gradient
In PLAX when do you measure the LVOT diameter?
Mid Systole
What is the most common cause of mitral stenosis?
Rheumatic heart disease
When is end diastole captured?
Left ventricle at largest dimension
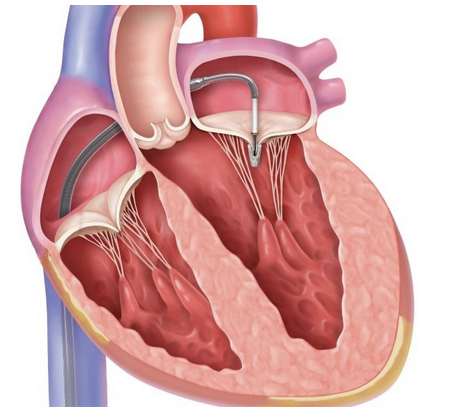
What procedure is this referring to?
mitral clip, mitraclip
When is end diastole captured?
Left ventricle at largest dimension
Mean pressure gradient averages the instantaneous gradient across the open valve and is acquired via planimetry of the entire Doppler waveform.
True
What is the most common Doppler method utilized to calculate the mitral valve area?
Pressure ½ time method
Identify the Doppler calculation used to determine mitral stenosis severity
Pressure half-time
In the PLAX, one can differentiate between the coronary sinus and descending aorta because the coronary sinus is seen within the _______; whereas the aorta is a separate structure posterior to the left atrium.
Myocardium
Complications of mitral stenosis include ____________.
Increased left atrial pressure
______________ of the valve leaflets is caused by a combination of the pressure pushing on the undersurface of the leaflets and commissural fusion.
Doming
In LAX when do you measure the AO Root, and the Sinotubular junction?
End Diastole
Estimation of the mitral valve area from Doppler is calculated by the:
Pressure half-time
Atrial fibrillation is most commonly associated with which valvular disease?
Rheumatic mitral stenosis
An absent “a” wave combined with mid-systolic closure of the pulmonic valve are seen in the presence of ______.
Pulmonary hypertension
Which of the following valves is least likely to be affected in patients with rheumatic heart disease?
Pulmonic
Identify the murmur associated with mitral stenosis
Low pitched, diastolic rumble with an opening snap
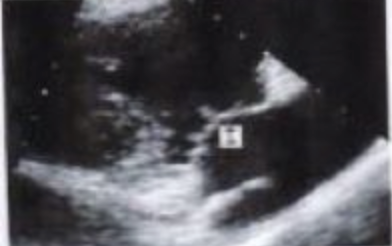
I?
TV
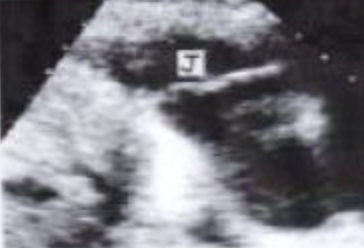
J?
PV
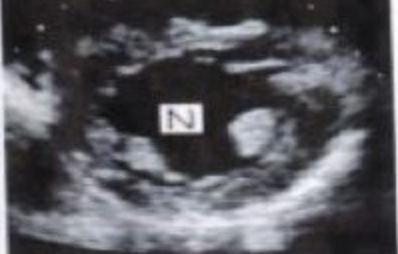
N?
SAX PM / MID
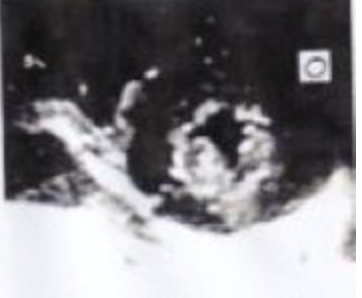
O?
LV APEX
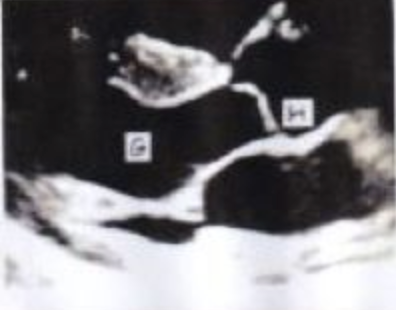
G?
LAX LV
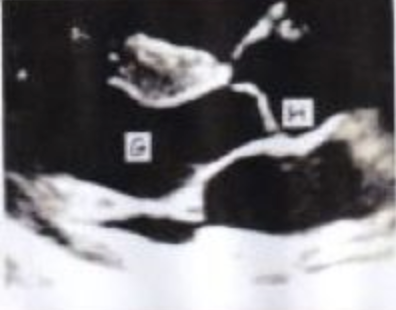
H?
AOV NCC
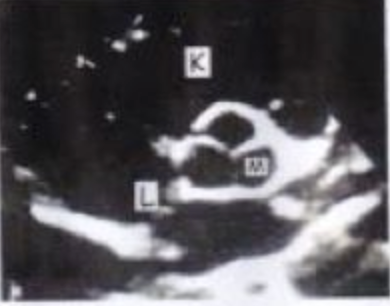
K?
SAX BASE RV
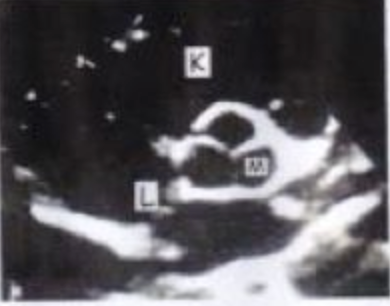
M?
AOV LCC
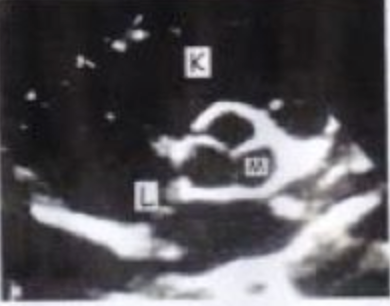
L?
IAS
Planimetry of the Doppler waveform calculates the mean pressure gradient.
True
When the heart has to compensate for increased afterload, the result is ___________ of the ventricular walls because the heart has to work harder to eject the blood.
Hypertrophy
Echo findings of mitral stenosis include ____________ .
LA spontaneous echo contrast
Identify a potential treatment option from mitral stenosis
All of these can be potential treatment options
________ is measured by planimetry in the short-axis view during the maximum opening in mid-diastole.
MVA
Left ventricular measurements should be obtained from the parasternal long axis view at the level of which of the following?
Tips of the mitral valve leaflets
________________ is a treatment option for mitral stenosis.
All of the above