01 - Cryptography
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
cryptography
the science of encryption, making information unreadable to unauthorized parties.
sender
person sending the message
receiver
person receiving (recipient)
attacker
eavesdropper/hacker trying to access the message
passive attack
only getting the message
active attack
intercepts the communication
authentication
verifies the sender is who they claim to be
confidentiality
information only intended receiver can understand
integrity
ensures message wasn’t modified
non-repudiation/non-repudiable
prevents sender/receiver from denying what they did
caesar cipher (shift cipher)
shifts letters in the alphabet by a fixed number
plaintext
original message
ciphertext
encoded message
key (symmetric)
shared parameter used for both decryption & encryption
— shift number (e.g., 3)
symmetric-key encryption
same key for both sender & receiver
brute force (caesar cipher)
trying all 26 possible shifts until plaintext (message) makes sense
public key
shared openly for encryption [mailbox address]
private key
secret key for decryption [mailbox address]
public-key cryptosystem — Diffie-Hellman, 1975
system using 2 keys: public key (encrypt) and private key (decrypt)
RSA
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman, public-key encryption system (1977)
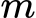
modulus
product of two large prime numbers
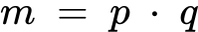
Euler’s Totient (φ)
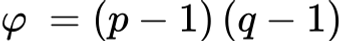
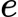
encryption/encoding exponent
number chosen such that
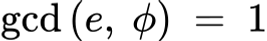
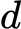
decryption/decoding exponent
number satisfying

coding (plaintext → ciphertext)
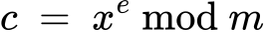
decoding (ciphertext → plaintext)
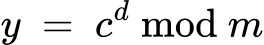
RSA public key
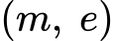
RSA private key
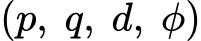
RSA security
based on difficulty of factoring large numbers